As we venture through the vast kingdom of spiders, we encounter a fascinating species of wolf spiders. These unique creatures have intricate and intriguing mating habits that have puzzled scientists for decades. How do these spiders choose their mates? What cues do they use? How does the courtship dance work, and what is the copulation process like? Join us on this journey to explore the world of wolf spiders and unravel the secrets of their mating behavior. Through a detailed breakdown of their biology, behavior, and other crucial factors, we aim to explain the enigma behind how wolf spiders choose their mates. Welcome to a world of spider romance!
Understanding Wolf Spiders

It’s fascinating to explore the unique world of wolf spiders and their complex mating behaviors. Understanding the biology and behavior of these arachnids is crucial to gain insight into their mating cycles and how male wolf spiders choose their mates. From chemical signals to visual cues and environmental factors, there are many elements to consider. Let’s delve deeper into this curious world of spider mating and explore how these creatures select their partners. To learn more about wolf spider courtship rituals, jump to the corresponding section in this article.
Biology and Behavior
One fascinating aspect of wolf spiders is their biology and behavior, which influence their mating rituals. Wolf spiders belong to the family Lycosidae, which contains over 2000 species. They are ground-dwelling spiders that vary in size from small (e.g., less than 1 cm) to relatively large (e.g., up to 3 cm). Wolf spiders have eight legs, two main body parts, and sharp fangs that they use to capture prey.
Wolf Spider Behavior:
- Wolf spiders are typically solitary creatures, except during the mating season;
- They hunt at night with their good eyesight;
- They don’t build webs to catch prey. Instead, they chase them down, relying on their speed and agility to catch their prey.
With regards to mating, male wolf spiders tend to be more active in finding a mate. Females wait patiently in their burrows until they detect the right signals from a male. It’s thought that male wolf spiders have to be strategic in their approach to finding a mate, as they risk being eaten by females during the mating process (a behavior known as mating cannibalism). They may use a wide range of strategies to detect receptive females, such as sensory cues.
It’s also important to note that female wolf spiders have a biological clock that regulates their reproductive cycles. They can only mate and reproduce when they are receptive. The timing of this cycle is influenced by factors such as temperature and food availability.
Understanding the basic biology and behavior of wolf spiders is crucial for understanding their unique mating rituals. Factors such as size, mating preferences, and environmental conditions can all influence how wolf spiders seek and select mates. To learn more about wolf spider mating behaviors, check out wolf spider mating behaviors.
Mating Cycles
During mating cycles, male and female wolf spiders engage in a complex mating ritual that involves chemical and visual cues. The reproductive cycle of wolf spiders varies depending on species and environmental factors. Mating seasons generally occur in the late summer and fall when wolf spiders are most active. Females are receptive to mating during specific times of their reproductive cycle, which is determined by the release of hormones.
Once males detect a female’s pheromones, they begin their search for a mate. Male wolf spiders may engage in mating cannibalism, where they risk being eaten by the female during copulation. Larger males have a better chance of avoiding being eaten, but small males may resort to sneaky mating tactics. Since wolf spiders come in various sizes, the strategies for mating vary. The size of the male compared to the female, and the survival strategy employed by the male, are instrumental to a successful mating.
However, finding a mate is just the beginning of the courtship dance, which involves intricate visual and tactile cues. Male wolf spiders approach females with caution, tapping their legs as they judge whether the female is receptive. The male will then weave a dance to attract and seduce the female. This dance is complicated and can last hours, but it is essential before copulation can occur.
Factors that can affect wolf spider mating include mating competition, environmental factors, and predator avoidance. Male wolf spiders have to compete for female attention and fight off rival suitors for the chance to mate. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can also impact the reproductive cycle and behavior of wolf spiders. Lastly, predators such as birds and other larger spiders can capture wolf spiders while they are searching for mates.
The mating cycles of wolf spiders are complex and involve intricate behavioral patterns. The combination of chemical signals, visual cues, and tactile stimulation are all essential in the mating process. Environmental factors and other variables can also impact wolf spider mating behavior, making it an interesting area for research. For more information on wolf spider mating and pheromones, visit wolf spider pheromones and mating.
How Do Male Wolf Spiders Find a Mate?

Male wolf spiders rely on a unique set of skills and instincts in order to find a mate. These spiders utilize a combination of chemical signals, visual cues, and other behavioral patterns to locate and court a female wolf spider. The process of mate selection is a fascinating one, with many factors at play. Let’s explore some of the methods and strategies that male wolf spiders use in their search for a mate. But before we dive in, it is important to understand some basic information about wolf spiders. If you want to learn more about wolf spider mating, check out this article on mating systems of wolf spiders.
Chemical Signals
Chemical signals play a crucial role in wolf spider mating behavior. Male wolf spiders release pheromones that attract females to their location. These pheromones are species-specific, which means that only female wolf spiders of the same species can detect and respond to them. These pheromones are a type of chemical language that wolf spiders use to communicate with one another.
Table: Chemical Signals in Wolf Spider Mating
| Type of Chemical Signal | Description |
|---|---|
| Pheromones | Male wolf spiders release pheromones to attract females for mating. |
| Semiochemicals | Chemicals that affect the behavior of other wolf spiders. They can be involved in male-male competition or anti-predator defense. |
| Courtship Chemicals | Specific chemicals that male and female wolf spiders use to signal their willingness to mate. |
Female wolf spiders are highly attuned to these chemical cues and can detect them from a distance. When a male wolf spider releases pheromones, nearby females will pick up the scent and follow it to its source. This is why males will often leave a trail of pheromones as they search for a mate. Once a female has located the male, she will use additional chemical cues to determine if he is a suitable mate.
It is important to note that chemical signals are not the only way that wolf spiders find mates. They also use visual cues and other factors to identify potential partners. However, pheromones are a key component of wolf spider mating behavior and play a critical role in bringing males and females together.
If you want to know more about wolf spider mating behavior, you can click on these links to read about their size and mating preferences, mating cannibalism, reproductive cycles, and environmental factors that can impact their mating behavior.
Visual Cues
Male wolf spiders also rely on visual cues to identify potential female mates. These cues include size, color, and pattern. Studies have shown that male wolf spiders are more attracted to larger females, as they are likely to produce more offspring.[1]
Many species of wolf spiders exhibit sexually dichromatic coloration, meaning that males and females have different color patterns. This makes it easier for males to identify females during their search for a mate.[2] In some species, males have even evolved complex eyes and visual processing centers to better detect and track females.[3]
In addition to size and color, male wolf spiders also use the movement patterns of females to identify potential mates. Female wolf spiders typically move in specific ways to signal their receptivity to mating. For example, they may raise their front legs or move side-to-side in a particular motion.[4]
It is important to note, however, that visual cues are not the only factor that male wolf spiders use to find a mate. Chemical signals, discussed earlier in this article, also play a significant role. The interplay between visual and chemical cues is complex and varies between species.[5]
Research has shown that wolf spiders have a surprising level of complexity in their mating behavior, with individual differences in mating preferences and strategies. The study of wolf spider mating behavior continues to be an active area of research in the fields of evolutionary biology and behavioral ecology.
| Visual Cues Used By Male Wolf Spiders |
|---|
| Size |
| Color |
| Pattern |
| Movement Patterns |
Sources:
[1]https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S000334720400385X?via%3Dihub
[2]https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00265-008-0638-3
[3]https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4409999/
[4]https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/full/10.1098/rspb.2011.2001
[5]https://www.researchgate.net/publication/249623575_Visual_and_olfactory_cues_used_by_male_wolf_spiders_in_mating_decision-making
Other Factors
While chemical signals and visual cues are critical in the mate-finding process, there are other factors that influence how male Wolf Spiders choose their mates. These include tactile and acoustic signals, as well as the quality and quantity of prey.
Tactile Signals: Male Wolf Spiders use their legs to “tap” on vegetation. Wolf spiders have sensitive sensory hairs on their legs that help them detect prey. Tapping not only attracts females but also helps male spiders locate them. Once the male wolf spider detects a female’s location through the vibration of her tap on the ground, he often responds with his own tap. The female may then tap in response, leading to an intimate dance between the two.
Acoustic Signals: Unlike other spiders, wolf spiders do not produce webs to attract and catch prey, so they use vibrations instead. They produce courtship songs by rubbing their abdomen against their legs, creating a unique noise that attracts females. The frequency of the sound differs between species, which helps to prevent inter-species breeding.
Prey Quality and Quantity: A male wolf spider’s diet determines his body size, and size influences the outcome of male-male contests for females. Larger males win in these contests, and they also produce more offspring. The male also needs to provide the female with food, which he offers during the courtship. So, if a male can provide more food to the female, the chances of mating increase.
The table below summarizes the key factors that affect how male Wolf Spiders choose their mates.
| Factors | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Tactile Signals | Male Wolf Spiders use their legs to “tap” on vegetation to locate and attract females. |
| Acoustic Signals | Male Wolf Spiders use vibrations to produce courtship songs that attract females. |
| Prey Quality and Quantity | A male wolf spider’s diet determines his body size, which influences his chances of winning contests for mates. Providing enough food for the female increases the chances of mating. |
Thus, while chemical signals and visual cues are essential in mate-finding, it is the combination of all these factors that ultimately determines mating success for male Wolf Spiders.
The Courtship Dance of Wolf Spiders
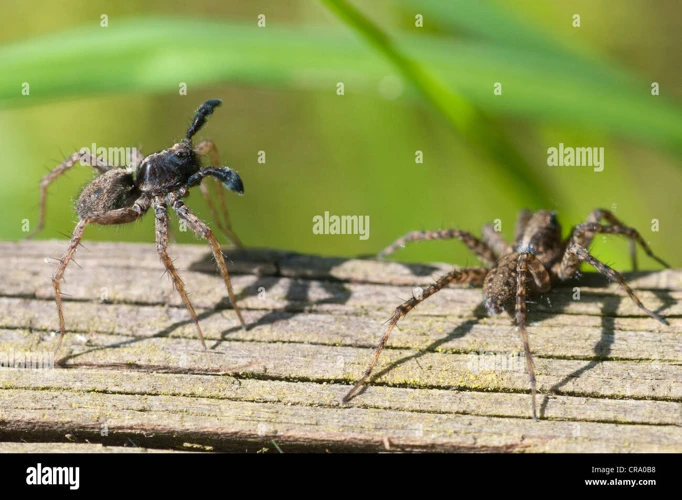

As mysterious as it is fascinating, the courtship dance of the wolf spiders can be nothing but impressive to observe. Male wolf spiders use a unique approach to communicate with females and determine if they are ready to mate. Through various cues and signals, the male spider must decipher whether or not he’s welcome to approach the female. Let’s take a closer look at the courtship dance of the wolf spiders and how it helps them ensure a successful mating process.
Dance Interpretation
The courtship dance of wolf spiders is a complex process that involves a lot of movements and interactions between the male and female. This dance is crucial for the male spider to attract and convince the female to mate with him. Let’s take a closer look at the different components of this dance and their interpretation.
One of the first movements in the dance is the male approaching the female. The male spider may take a circuitous route, moving in a zigzag or circular motion, before finally approaching the female. This movement is thought to be an attempt to avoid detection by predators and other males.
Once the male approaches the female, he raises his front legs in a display known as the “leg-waving display”. The male will wave his legs up and down while facing the female and may also vibrate his body. This display is thought to be a way of communicating his presence and intentions to the female.
If the female is receptive to the male, she may respond by also waving her front legs. This is known as the “female reciprocation display”. The female may also raise her abdomen and rotate it in a circular motion.
The male then moves closer to the female and touches her with his pedipalps, the two appendages near his mouth. He will also use his pedipalps to transfer sperm to the female during copulation. If the female is still receptive, she will allow the male to mate with her.
It’s important to note that not all females will respond to the male’s advances. In some cases, the female may attack and kill the male, making it important for the male to choose his partner wisely.
The dance between male and female wolf spiders is a complex and important part of their mating behavior. Through a combination of leg-waving displays, female reciprocation displays, and touching with the pedipalps, the male is able to communicate his intentions and convince the female to mate with him.
Table: Summary of Wolf Spider Courtship Dance
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Approach | Male approaches female in a zigzag or circular motion to avoid detection |
| Leg-waving display | Male waves his front legs up and down while facing the female to communicate his presence and intentions |
| Female reciprocation display | Female waves her front legs and rotates her abdomen in response to the male’s display, indicating receptivity |
| Pedipalp touching | Male touches female with his pedipalps to transfer sperm during copulation |
Cues to Female Receptivity
When it comes to female wolf spiders, they have a very specific set of cues that communicate their receptivity to males. These cues can help males to determine whether or not it is worth pursuing a particular female. Some of the most important cues to female receptivity include:
| Hair | Coloration | Posture |
|---|---|---|
| Female wolf spiders have specialized hairs on their body that can provide important signals to males. For example, hair on the front legs can be used for tactile communication during courtship. | Female wolf spiders may also have different coloration when they are receptive. For example, some species may have brighter or more vivid markings on their body when they are ready to mate. | Finally, posture is also an important cue to female receptivity. Females may adopt a specific stance or pose to signal their willingness to mate, such as arching their back or raising their abdomen. |
These cues help males to better understand the behavior and intentions of potential mates. By paying attention to these subtle signals, male wolf spiders can increase their chances of successfully mating and producing offspring.
The Copulation Process of Wolf Spiders
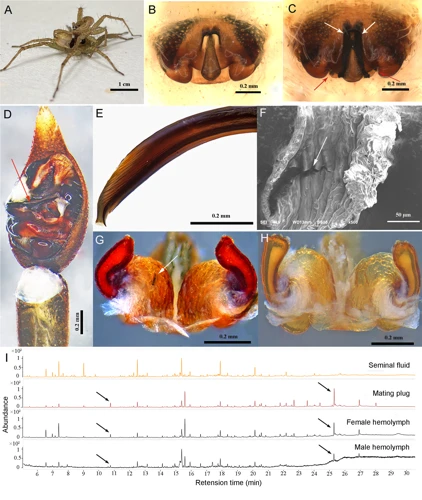
As we delve deeper into the world of wolf spiders and their mating rituals, we come to a crucial step in the process: the copulation process. This is where the male spider finally succeeds in mating with the female, leading to the creation of the next generation of wolf spiders. But how exactly does this process play out? Let’s find out.
Mating Behavior
During copulation, the male wolf spider approaches the female carefully to avoid being mistaken for prey. Once he reaches her, he initiates physical contact by tapping her with his forelegs. If she is receptive, the male spider climbs on top of her back and the two spiders align their genital openings for insemination. This process can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours depending on the species and individual pair.
During copulation, the male transfers sperm to the female through specialized openings on his pedipalps, which are modified appendages near his mouth. These pedipalps function as both sensory and copulatory organs, and males often display them prominently during courtship displays.
The female wolf spider may mate with multiple males during a single reproductive season, and her reproductive tract is able to store sperm from multiple partners. This allows for a high degree of genetic diversity within a single litter of spiderlings.
However, mating behavior can also be aggressive in wolf spiders. Some species engage in mate guarding, where males will actively prevent females from mating with other males. This can lead to intense competition between males and physical fights, which can result in injury or death.
Wolf spider mating behavior is complex and varied, with different species exhibiting different strategies for finding and securing mates. It is fascinating to explore the diversity of strategies used by these fascinating creatures in their quest to reproduce and pass on their genes to future generations.
| Mating Behavior | Description |
|---|---|
| Copulation | The male approaches the female, taps her with his forelegs, climbs on her back, and aligns genital openings for insemination. |
| Sperm Transfer | The male transfers sperm to the female through specialized openings on his pedipalps. |
| Mating with Multiple Males | The female may mate with multiple males during a single reproductive season and store the sperm from various partners in her reproductive tract. |
| Mate Guarding | Male spiders may prevent females from mating with other males, leading to intense competition and physical fights. |
Post-coital Behavior
After the mating process, the male wolf spider must carefully disengage from the female’s fangs to avoid being mistaken for prey and devoured. Once this is accomplished, the male will typically flee the area quickly to avoid being attacked.
Post-coital behavior in wolf spiders varies depending on the species, but it generally follows the same pattern across the board. After the male has retreated from the female, she will take steps to guard her egg sac and ensure the safety of her offspring.
One post-coital behavior that is common in wolf spiders is that the female will spin a web around the egg sac to protect it. This web serves as a barrier to prevent predators from getting too close to the eggs. During this time, the female will also stop feeding and focus solely on protecting her offspring.
It is important to remember that wolf spiders are solitary creatures and do not engage in any sort of co-parenting behavior. Once the eggs have hatched, the young spiders will scatter and go their separate ways, fending for themselves.
In some species, the female may live for several months after mating while guarding her egg sac. During this time, she will not feed and will remain immobile for extended periods. This behavior is known as “mommy guarding” and it is thought to increase the survival rates of the offspring.
Post-coital behavior in wolf spiders is largely focused on the survival and protection of the next generation. The female will take steps to ensure that her eggs hatch successfully and that her offspring are protected from predators until they are old enough to fend for themselves.
Factors That Affect Wolf Spider Mating Behavior
The complex mating behavior of wolf spiders is influenced by a variety of factors. Understanding these factors can help shed light on the fascinating world of these arachnids. From mating competition to environmental factors and predator avoidance, there are many variables at play that can affect how wolf spiders choose their mates. In this section, we will examine some of the key factors that impact wolf spider mating behavior and what role they play in shaping the spider’s courtship and copulation process.
Mating Competition
Male wolf spiders face fierce competition when it comes to mating. As such, they have to employ a wide range of tactics to ensure they have the best chance of mating with a female. Here are some factors that come into play during mating competition amongst wolf spiders:
- Size: Male wolf spiders that are larger in size than their competitors have a better chance of mating with a female.
- Strength: Male wolf spiders will quite often engage in physical combat to fight for the right to mate with a female. The stronger spider will usually emerge victorious.
- Fitness: Female wolf spiders are attracted to male spiders that exhibit good health and vitality. As such, male spiders that are fit and healthy have a better chance of mating.
- Location: Male spiders that are located in close proximity to female spiders have a better chance of mating than those located in distant areas.
- Mating Plugs: During copulation, male wolf spiders will often deposit a mating plug inside the female, which prevents other males from mating with her. This helps to ensure they are the only male to mate with the female.
In addition to these factors, male wolf spiders also engage in a variety of other behaviors to boost their chances of mating. For example, they will perform courtship dances to attract female spiders and display their fitness. They also emit chemical signals that can attract a female, help to establish territoriality, and deter other males from approaching.
The mating competition amongst wolf spiders is intense and males must use various strategies to ensure they have the best chance of mating. Size, strength, fitness, location, and mating plugs all play an important role in helping males to succeed in the competition.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a crucial role in wolf spider mating behavior. As with any animal species, the environment in which they live can greatly impact how they behave and reproduce. There are several environmental factors that can affect wolf spider mating behaviors.
One of the most important factors is temperature. Wolf spiders are cold-blooded and require a specific range of temperatures for optimal mating behavior. According to a study published in the Journal of Insect Behavior, male wolf spiders show a preference for temperatures around 25°C (77°F) for mating. Temperatures outside of this range can negatively affect mating behavior in both males and females.
Another important environmental factor is habitat. Wolf spiders inhabit a wide range of ecosystems, and mating behavior can differ depending on the specific environment in which they live. For example, some studies have shown that wolf spiders living in arid habitats are more promiscuous than those living in forested areas. This could be due to differences in resource availability and predator density between these habitats.
Availability of prey is also important for wolf spider mating behavior. Female wolf spiders require a sufficient food supply to produce viable offspring. A study published in the Journal of Arachnology found that female wolf spiders fed a diet of crickets produced more viable offspring than those fed a diet of mealworms.
The presence of predators can also impact wolf spider mating behavior. In the presence of predators, male wolf spiders may alter their behavior to avoid being detected by potential predators. Additionally, the risk of predation may cause females to be more selective in their choice of mating partners. In a study published in the journal Ethology, researchers found that female wolf spiders were less likely to mate when exposed to the scent of a predatory ant species.
| Environmental Factors | Impact on Wolf Spider Mating Behavior |
|---|---|
| Temperature | The optimal temperature range for mating is around 25°C (77°F). Temperatures outside of this range can negatively affect mating behavior. |
| Habitat | Mating behavior can differ depending on the specific environment in which wolf spiders live. Habitat can impact predator density and resource availability, which can affect mating behavior. |
| Prey availability | Female wolf spiders require a sufficient food supply to produce viable offspring. Different prey types can impact offspring viability. |
| Predators | The presence of predators can cause male and female wolf spiders to alter their behavior or be more selective in their choice of mating partners. |
Wolf spider mating behavior is heavily influenced by environmental factors. Temperature, habitat, prey availability, and predation risk all play a role in how wolf spiders choose their mates. Understanding these factors can provide valuable insights into how wolf spider populations may be impacted by environmental disturbances or other changes in their ecosystem.
Predator Avoidance
Wolf spiders face various predators during their mating period, including birds, rodents, and other spiders. To avoid becoming prey, male wolf spiders have developed a few tactics.
1. Camouflage: Male wolf spiders have adapted to blend in with their surroundings. They use their brown or grayish colors to hide from predators that may be lurking nearby. These spiders also move slowly and stealthily, making it difficult for predators to detect them.
2. Vigilance: Once male wolf spiders have detected a potential mate, they become fiercely vigilant of their surroundings. They are constantly on the lookout for predators that may come their way. Male wolf spiders are equipped with multiple eyes, which they use to scan their surroundings for any potential danger.
3. Fast movements: If a male wolf spider senses danger, it quickly moves away from the area. They can run at incredibly fast speeds, which gives them an advantage when outrunning predators.
Wolf spiders have evolved another powerful predator avoidance mechanism – they use their sensitivity to vibrations to detect movement and danger around them. Using their specialized sense of hearing, they are able to detect sounds from predators and prey alike and quickly respond to them, avoiding danger altogether.
It’s fascinating to see how wolf spiders have adapted to survive in their environment and avoid becoming prey. These strategies help them to continue their mating cycles and ensure the continuation of the species.
Conclusion
After exploring the fascinating world of wolf spider mating behavior, we can conclude that these arachnids have developed complex mechanisms to find mates and reproduce successfully.
Through a combination of physical and chemical cues, male wolf spiders can locate receptive females and initiate their courtship dance. This dance, with its intricate movements and postures, plays a crucial role in female assessment of male quality and fitness as a mate.
Furthermore, the mating process itself is quite unique, as male wolf spiders must insert their pedipalps into the female’s genital opening to transfer sperm. This process can be risky, as the male may sometimes become prey to the larger, cannibalistic female.
Various factors, such as mating competition, environmental conditions, and predator avoidance, can also influence wolf spider mating behavior and success. However, given their adaptability and resilience, these creatures have managed to thrive across diverse habitats worldwide.
Overall, the study of wolf spider mating is a testament to the wonders and complexities of nature, providing insight into the evolutionary strategies and challenges presented by reproductive behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the scientific name for wolf spiders?
The scientific name for wolf spiders is Lycosidae.
How does the courtship dance of wolf spiders differ from other spiders?
The courtship dance of wolf spiders is unique because it involves both males and females dancing in sync with one another.
What do male wolf spiders use to sense female pheromones?
Male wolf spiders have special structures called tarsal organs on their legs that help them detect the pheromones of female spiders.
Do all wolf spider species have the same mating behavior?
No, different species of wolf spiders have unique mating behaviors that are shaped by their environments and behaviors.
What is the role of female wolf spiders in the mating process?
Female wolf spiders play an active role in the mating process, signaling to males when they are receptive to mating.
How can environmental factors affect wolf spider mating behavior?
Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, can impact wolf spider mating behavior by influencing male and female activity levels and changing communication cues.
How long do wolf spiders typically mate for?
Wolf spider mating typically lasts between two to four hours, with females controlling the duration of copulation.
Can male wolf spiders sometimes be harmed or killed during mating?
Yes, male wolf spiders are sometimes killed or eaten by females after copulation. This is known as sexual cannibalism.
Do wolf spiders have any predators that can disrupt their mating behavior?
Yes, predators such as birds and larger spiders can disrupt wolf spider mating behavior by attacking individuals during courtship rituals or copulation.
What is the importance of studying wolf spider mating behavior?
Studying wolf spider mating behavior provides insights into the complex reproductive strategies of arthropods and can have implications for understanding evolution and biodiversity.







