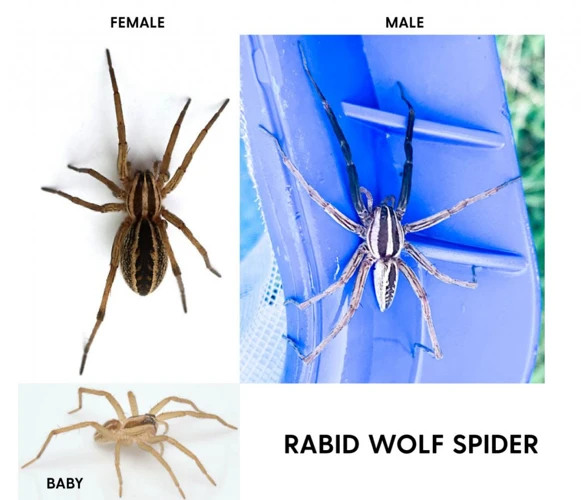
As we delve into the diverse and fascinating world of wolf spider species, we can’t help but be intrigued by those with bright, eye-catching coloration. With many species of wolf spiders boasting muted tones of brown, gray, and black, it begs the question: why do some species show off with bright colors? What advantages could such an obvious appearance offer them in the wild? In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of bright coloration, as well as the factors influencing it and provide examples of some of these stunningly colorful species. So, let’s embark on our journey to uncover the mysteries behind this intriguing characteristic of wolf spiders.
The Benefits of Bright Coloration

The bright coloration of some wolf spider species is not just visually stunning, it serves an important purpose in their survival. The evolution of this coloration has been influenced by several factors such as sexual dimorphism, geographic location, and genetic mutations. In this article, we will be discussing the benefits of this bright coloration, including how it aids in camouflage and warning off predators. Additionally, we will explore some of the factors that have influenced this coloration in wolf spiders and examine some examples of different brightly colored species. So, let’s dive deep into the fascinating world of wolf spider coloration and discover why it is crucial for their survival. To learn more about the camouflage benefits of wolf spider coloration, check out our article on wolf spider coloration and its role in camouflage.
Camouflage in Leaf Litter
Wolf spiders have evolved incredible camouflage skills to blend into their environment to avoid detection by both predator and prey. One form of this is bright coloration. Despite what one might think, the bright coloration actually provides excellent camouflage for wolf spiders. The camouflage works by breaking up the spider’s outline, blending with forest litter, and providing a false sense of depth making it difficult for predators to distinguish shape or location. Additionally, bright coloration may reflect ultraviolet light in a way that enhances the pattern of varied lighting in the ground cover, making it even more difficult to detect. The combination of bright coloration and clever use of natural light can ultimately leave predators at a loss as to where the wolf spider may be hiding.
Not only that, the unique ability of wolf spiders to successfully camouflage with bright coloration also creates a distinct advantage when hunting prey. Wolf spiders are hunters that pursue their prey and ambush them. The camouflage allows wolf spiders to get closer to their prey before pouncing. By using their bright coloration as a tool for camouflage, they become much more successful hunters. It’s also been observed that wolf spiders with brighter markings and stripes actually have higher success rates in hunting activity.
Bright colouration can also provide other advantages like warning off predators. This will be discussed in more detail in the next section. To learn more about other factors influencing wolf spider colouration, check out this article.
Warning off Predators
One advantage of bright coloration in wolf spider species is to warn off potential predators. Bright colors serve as a visual signal to predators that the spider may be dangerous or unpalatable. This phenomenon is known as aposematism. Wolf spiders that are brightly colored can be easier for predators to remember and avoid in the future.
Interestingly, some species of wolf spiders have evolved to mimic the colors and patterns of more venomous or dangerous species, benefiting from the fact that these species are avoided by predators. The mimicry allows for the non-toxic wolf spider to be left alone by potential predators who mistake it for a more dangerous creature.
In contrast, some wolf spider species have developed the opposite strategy – they use cryptic coloration to hide from predators and remain undetected. These spiders blend into their surroundings and appear invisible to predators, serving as a form of camouflage.
It is important to note that not all bright-colored wolf spiders are warning predators of their toxicity. Some species use their bright colors as a form of communication to attract mates or establish dominance, as discussed in the previous section on sexual dimorphism. The purpose of the coloration can vary depending on the environmental circumstances.
So, while bright coloration in wolf spiders may serve as a warning to predators, it could also have alternative purposes. To learn more about the unique color patterns and behaviors of wolf spiders, check out our article on wolf spider coloration communication. Or, explore the evolution of wolf spider coloration in our article on wolf spider color evolution.
Factors Influencing Coloration

When it comes to the bright colors of wolf spiders, there is no single factor that determines their vibrant hues. Instead, a combination of factors interact to create the striking patterns and shades that we observe in various species. By understanding these factors, we can gain insight into how and why some wolf spiders have evolved to exhibit such colorful appearances. Let’s explore some of the most influential factors that dictate wolf spider coloration in further detail. If you’re interested in the patterns and stripes often found in wolf spider coloration, check out this article on stripes and patterns in wolf spider coloration. Alternatively, if you’re curious about the relationship between wolf spider color and venom potency, read more on this article about wolf spider color and venom. Additionally, if you’re curious about how to identify wolf spiders by color, you can learn more on identifying wolf spiders by color.
Sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism refers to the physical differences between male and female wolf spiders. In some species, brightly colored males are more commonly found, while in others females exhibit more vibrant coloration. The differences in coloration between males and females can be used for sexual selection and mating purposes.
Examples of sexual dimorphism in wolf spiders:
- In the species Hogna helluo, males have bright orange spots on their legs, while females have muted brown tones.
- Male Schizocosa ocreata have striking iridescent green chelicerae, while females have brownish chelicerae with a less noticeable sheen.
- Some species of Rabidosa have females with bright green or yellow abdomens, while males typically have less vibrant markings.
The differences in coloration between males and females can also be used to avoid competition and reduce aggression between the sexes. In some cases, males may exhibit brighter coloration to attract females, while females may have more subdued colors to avoid drawing the attention of males.
Sexual dimorphism plays an important role in the evolution of coloration in wolf spiders, and understanding these differences can provide valuable insights into the biology and behavior of these fascinating creatures.
Geographic location and local environment
The geographic location and local environment can have a significant impact on the coloration of wolf spider species. This is because spiders that live in different environments need to adapt to those surroundings in order to survive. Here are some factors related to geographic location and local environment that affect wolf spider coloration:
- Soil composition: The color of the soil can have an effect on the coloration of wolf spiders that live in the area. For example, if the soil is red in color, the wolf spider may develop red hues to blend in with its environment.
- Vegetation: The type of vegetation can also influence wolf spider coloration. If the spider lives near green plants, it may have green or yellow tones in order to blend in.
- Temperature: Wolf spiders that live in warmer environments may develop brighter hues to reflect heat, while those in cool environments may be darker to absorb heat.
- Humidity: The humidity of the area can also impact wolf spider coloration. In humid areas, wolf spiders may be darker to resist mold growth, while in arid areas, they may be lighter to reflect the sun’s rays.
The coloration of wolf spiders is influenced by a variety of factors, including their geographic location and local environment. By adapting to their surroundings, they are better able to survive and thrive in their natural habitats.
Genetic mutations
It has been observed that some wolf spider species’ bright coloration can be attributed to genetic mutations. These mutations can result in unique color patterns that are not seen in other members of the same species. These deviations are often considered a result of genetic drift, which refers to the random fluctuations in the frequency of alleles in a population.
Here are some factors related to genetic mutations that can impact wolf spider coloration:
- The random appearance of novel color patterns can result from changes in a single gene or multiple genes.
- Point mutations, in which a single nucleotide in the DNA sequence is altered, can result in new color patterns.
- Chromosomal rearrangements, such as inversions and translocations, can also lead to new color patterns.
- New color patterns generated by genetic mutations may have selective advantages, such as improved camouflage or predator deterrence, leading to their proliferation in a population.
- However, not all genetic mutations are advantageous, and some may result in unfavorable color patterns that decrease an individual’s survival ability, leading to their elimination from the population.
Genetic mutations play a significant role in the development of wolf spider coloration, contributing to the diversity of these arachnids. The unpredictability of these mutations makes it difficult to predict how coloration may evolve in the future.
Examples of Brightly Colored Species

When it comes to wolf spiders, bright coloration is not a common trait among the species. However, there are some cases where certain wolf spider species have evolved to exhibit vibrant hues, making them stand out from their surroundings. One such example is the Australian Peacock spider (Maratus spp.) which is known for its mesmerizing colorful display during courtship rituals.
Another example of a wolf spider with bright colors is the Habronattus americanus which inhabits regions of North America. The male of this species is usually brightly colored, featuring shades of blue, red, and green, while the female is generally more muted in color. This difference in coloration is believed to signal the male’s quality as a potential mate and distinguish him from other males competing for the same female.
The wolf spider species Schizocosa malitiosa is also known for its bright color patterns that include bold stripes and vivid hues such as orange, yellow, and red. This species of wolf spider can be found in the eastern regions of North America.
Finally, the wolf spider species Lycosa erythrognatha indigenous to the deserts of Israel and Jordan exhibits a dramatic coloration of deep red to orange that allows it to blend in perfectly with its surroundings while also adding an extra level of protection.
These examples of brightly colored wolf spider species demonstrate the diverse range of reasons for wolf spiders to exhibit such coloration. From signaling to potential mates to confusing potential predators or blending in with surroundings, bright coloration can play a significant role in the success of these fascinating arachnids.
Coloration and Spiderling Development
A crucial aspect of wolf spider coloration is its role in the development of spiderlings. In many species, the mother spider carries her spiderlings on her back for several weeks after hatching. During this time, the spiderlings rely on their mother for protection and nourishment.
Studies have shown that the coloration of the mother spider plays an important role in the development of spiderlings. Brightly colored females are often preferred by male spiders as mates, as they are seen as healthier and better able to provide for offspring. This preference has led to evolutionary pressure on female spiders to develop brighter coloration.
In addition to mate choice, the coloration of the mother spider can also affect the survival and growth of spiderlings. For example, a study conducted on the wolf spider Pardosa milvina found that spiderlings raised by mothers with brighter coloration had a lower mortality rate and grew faster than spiderlings raised by mothers with duller coloration. This suggests that bright coloration may be an indicator of maternal quality and ability to provide for offspring.
Interestingly, studies have also shown that spiderlings themselves may develop brighter coloration as they mature. In some species, young spiderlings are initially pale and gradually develop brighter coloration as they age. This could be due to a number of factors, including changes in diet and exposure to sunlight.
The relationship between wolf spider coloration and spiderling development is a complex and fascinating subject that is still being explored by researchers.
Evolving Trends in Wolf Spider Coloration
The coloration of wolf spiders has been a topic of great interest among scientists and researchers over the years. One of the most intriguing aspects of their coloration is the way it has evolved over time, with different trends emerging as spiders adapt to changing environments.
Earth Tones to Bright Hues
In the past, most wolf spiders were characterized by earth tones and dull, muted colors that helped them blend in with their surroundings. However, with changing environmental conditions, certain species have transitioned to brighter, more vibrant hues that may serve both as camouflage and as a warning to predators.
Shift in Sexual Dimorphism
Another trend that has emerged in recent years is a shift in sexual dimorphism. Historically, male and female wolf spiders had similar coloration, making it difficult to tell them apart. However, as males developed brighter coloration, females evolved to have more muted tones, allowing them to remain camouflaged while their male counterparts use their vivid hues to attract mates.
Adapting to Climate Change
As global temperatures continue to rise, many wolf spiders are adapting by changing their coloration. In warmer climates, brighter hues have become more prevalent, as they help spiders to regulate their body temperature and avoid overheating.
Human Influence
Human influence has also played a role in the evolution of wolf spider coloration. With the expansion of cities and towns, certain species have begun to adapt to urban environments by developing lighter, more vibrant colors that blend in with concrete and steel.
The evolving trends in wolf spider coloration demonstrate the adaptability of these fascinating creatures. As they continue to face changing environmental conditions, they will undoubtedly develop new and innovative ways to survive and thrive in their ever-changing world.
Conclusion
After delving into the world of wolf spider coloration, it’s clear that there are a multitude of factors that can influence the development of bright hues in these arachnids. While some species may use their colors for camouflage in their leaf litter habitats, others may be warning off predators or even using coloration as a form of sexual dimorphism.
It’s important to note that while we have discussed several possible explanations for why certain species of wolf spiders have bright coloration, there is still much to be learned about these fascinating creatures. Future research will undoubtedly shed more light on the subject; and new discoveries may overturn some of the current beliefs.
What we do know is that wolf spider coloration is a topic of interest to both researchers and casual observers alike. With their dynamic hues and aggressive hunting behavior, they remain one of the most intriguing spider species to study.
Whether you’re a fan of these spiders or not, one thing is certain – the world of arachnids is full of surprises. From their hunting habits to their intricate webs and unique physical features, there’s always something new to discover and learn. So the next time you see a brightly colored wolf spider scurrying across the ground, take a moment to appreciate the complexity and beauty of these incredible creatures.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do wolf spiders have bright coloration?
Wolf spiders use bright coloration for camouflage and warning predators.
2. Do all wolf spider species have bright coloration?
No, not all species of wolf spiders have bright coloration.
3. What is the purpose of wolf spider coloration?
The purpose of wolf spider coloration is to camouflage in leaf litter and to warn off predators.
4. Are wolf spiders poisonous?
Yes, wolf spiders are venomous, but rarely dangerous to humans.
5. What is sexual dimorphism in wolf spiders?
Sexual dimorphism is the difference in appearance between males and females of the same species.
6. How does geography and environment affect wolf spider coloration?
Geography and environment can influence wolf spider coloration through adaptation to local environments and evolutionary pressures.
7. Can wolf spider coloration change due to genetic mutations?
Yes, wolf spider coloration can change due to genetic mutations that result in different pigmentation patterns.
8. What are some examples of brightly colored wolf spider species?
Examples of brightly colored wolf spider species include the regal wolf spider and the ornate wolf spider.
9. Does wolf spider coloration affect spiderling development?
Yes, wolf spider coloration can affect spiderling development through influences on behavior and survival.
10. Are there any evolving trends in wolf spider coloration?
Yes, evolving trends in wolf spider coloration can involve changes in pigmentation patterns, camouflage strategies, and predator warning signals.







