As we delve deeper into the natural world, we discover fascinating and puzzling behaviors exhibited by various creatures. One such creature is the wolf spider, known for its unique mating behavior. Have you ever wondered why size matters in wolf spider mating? In this article, we’ll explore the science behind this intriguing behavior and the significance of size in determining mating success. Join us on a journey into the world of wolf spiders, as we uncover the secrets of their behavioral patterns and uncover the research behind their mating rituals. Let’s get started!
What are Wolf Spiders?
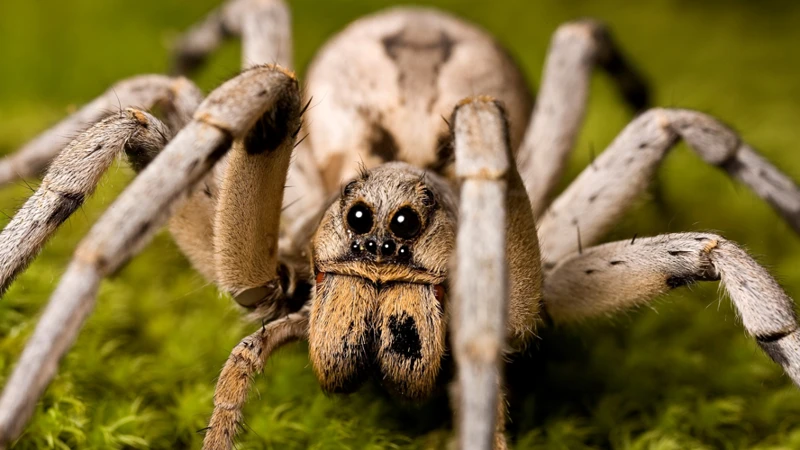

Wolf spiders are a type of arachnid found all over the world. They are known for their relatively large size, with some species growing up to 35 mm in body length. These spiders are hunters, using their excellent eyesight and agility to track down and catch prey. Unlike other spiders, wolf spiders do not spin webs to catch prey but instead hunt actively on the ground or in burrows.
Wolf spiders are typically dark brown or gray with striped or mottled patterns on their bodies. They have eight legs and two distinct body parts – the cephalothorax and the abdomen. These spiders have large, forward-facing eyes that provide them with excellent vision for hunting. Additionally, they have two chelicerae that act as fangs and venom injectors when hunting prey.
Wolf spiders are solitary creatures and do not live in colonies like other spiders. They prefer to live in burrows or crevices where they can hide during the day and hunt at night. Some species of wolf spiders are also capable of swimming and can be found near bodies of water.
Wolf spiders are known for their aggressive behavior and will readily defend themselves if provoked. While their venom is not typically dangerous to humans, a bite can be painful and may cause localized swelling and redness.
Despite their intimidating appearance and aggressive behavior, wolf spiders are an important part of many ecosystems. They help to control populations of insects and other small animals and are an important food source for many larger predators.
Wolf spiders are fascinating creatures with unique physical features and behaviors. To learn more about their mating behavior, check out our article on wolf spider mating behaviors.
Physical Appearance
The physical appearance of wolf spiders is fascinating to observe. These arachnids vary in size, color, and markings depending on their species and location. With their eight legs and two body parts, wolf spiders have a distinctive look that sets them apart from other spiders. They are agile and fast, making them efficient hunters. Wolf spiders also have unique traits that aid them in mating and survival. Their physical appearance is a crucial factor in their mating behavior and success. To learn more about wolf spider mating, read our article on Wolf Spider Courtship Ritual.
Behavior & Habitat
Behavior & Habitat of Wolf Spiders
Wolf spiders belong to the Lycosidae family, and they are found all over the world. These spiders are generally nocturnal and are most active during the night, although they can also be seen during the day. They are known to be solitary creatures and only come together during mating season.
Habitat and Range
Wolf spiders can be found in a variety of habitats, including deserts, grasslands, forests, and coastal areas. They are also known to live in disturbed urban areas, such as gardens and parks. These spiders are found in North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Australia.
Physical Characteristics
Wolf spiders are typically black, gray, or brown and can range in size from 0.04 inches to 1.3 inches in length. They have eight eyes and are known to have excellent eyesight, which they use to hunt their prey. Wolf spiders are also very agile and can move quickly over a variety of surfaces, including water.
Feeding Habits
Wolf spiders are active hunters and will typically feed on insects, such as crickets, beetles, and grasshoppers. They are also known to feed on other spiders and occasionally on small vertebrates, such as lizards and frogs.
Mating Behavior
Mating season for wolf spiders generally occurs in the fall. Male wolf spiders use pheromones to attract females and will often approach them cautiously. Once the male has successfully approached the female, he will engage in courtship behavior, which can include touching the female with his legs and tapping his abdomen.
Mating and Courtship Rituals
During mating, the male will use specialized structures on his pedipalps to transfer sperm to the female. After mating, the female will lay her eggs and carry them with her until the spiderlings hatch. Once the spiderlings hatch, they will remain with the female until they are able to hunt on their own.
The behavior and habitat of wolf spiders are fascinating topics, and researchers are continually learning new information about these creatures. To learn more about wolf spider mating behavior, visit our article on wolf spider pheromones and mating, or read about mating preferences in wolf spiders to better understand how these spiders choose their mates.
Wolf Spider Mating Behavior
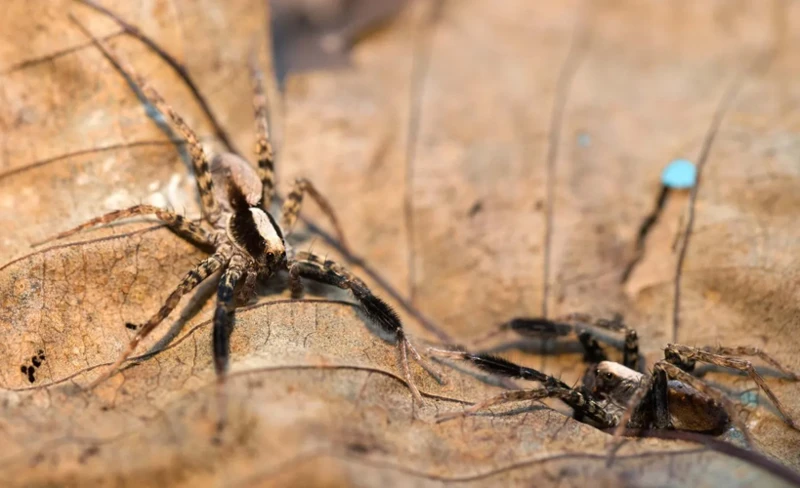

Wolf Spider Mating Behavior is quite interesting to explore. The mating process is vital for the spider’s survival and reproductive success. During the mating season, it’s typical for male wolf spiders to move around, searching for females to mate with. However, the process of finding a female and mating with her is fraught with challenges and dangers.
How do Wolf Spiders Mate?
Wolf spider mating typically begins with the male wolf spider’s efforts to find a suitable mate. Once he has found a female, he approaches her and taps her gently on the body with his front legs. This behavior is often referred to as “leg tapping” and is a common feature of wolf spider mating behavior. The male then positions himself over the female, grasps her fangs with his own, and inserts his pedipalps into her reproductive opening.
The Significance of Size
Size also plays a significant role in wolf spider mating behavior. Generally, female wolf spiders prefer larger males. The male’s size is often an indication of his strength and overall fitness, which are desirable traits in a mate. Large males are often more successful in defending their territory and in competing with other males for mating opportunities.
Factors Affecting Mating Success
Several factors impact the mating success of wolf spiders. One such factor is mating competition. When males are abundant, competition for mating opportunities can increase, leading to a greater number of successful mating attempts.
Size is another critical factor affecting mating success in wolf spiders. Sexual dimorphism, where males are smaller than females, is common in wolf spiders, and this often results in size-based mate choice by females. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity also influence the mating behavior of wolf spiders.
Research Studies
Recent studies have explored the relationship between size and mating success in wolf spiders. Experiments have shown that larger males are more attractive to females and have higher mating success rates than smaller males.
One study also found a correlation between male size and the amount of sperm he could transfer to the female during mating. This suggests that larger males have an advantage in terms of fertilization success, thereby increasing their overall mating success.
Other Considerations
Female wolf spiders also have some control over their mating choices. Some studies suggest that females prefer males with particular physical characteristics or behaviors. Females may also be more reluctant to mate during certain times of the year or under certain environmental conditions.
Mating cannibalism is common in wolf spiders. Female wolf spiders are known for their tendency to eat their mates after mating. This cannibalism often occurs when a female is hungry or in case she feels a threat from a male.
Wolf spider mating behavior is a complex process influenced by several factors, including size, competition, and environmental conditions. Despite the challenges, the process results in the transfer of sperm and eventual reproduction, ensuring the species’ survival.
How do Wolf Spiders Mate?
The process of mating in wolf spiders is a fascinating and complex topic that has puzzled scientists for years. It involves several intricate behaviors and strategies that are essential for successful reproduction. Understanding how wolf spiders mate is crucial for further research into their reproductive cycle and behavior. Additionally, by comprehending their mating practices, we can gain an insight into the ecological and evolutionary significance of their mating system. So, let’s delve deeper into how these spiders mate and what makes their reproduction so unique. To learn more about female choice in wolf spider mating, check out our article on Wolf Spider Mate Choice.
The Significance of Size
Wolf spider size plays a significant role in mating success, as it affects both male-male competition and male-female interactions. Smaller male wolf spiders may struggle to compete with larger males for access to females and may even be killed by larger males during mating competition.
On the other hand, female wolf spiders tend to prefer larger males, likely due to the potential genetic benefits associated with choosing a genetically superior mate. This preference for size is a form of sexual selection that can drive the evolution of larger body size in male wolf spiders.
To better understand the relationship between size and mating success, research studies have been conducted to explore the factors affecting wolf spider mating behavior. The results of these experiments indicate that larger male wolf spiders are more successful in mating with females compared to their smaller counterparts.
In fact, a study by Rabaneda-Bueno et al. (2011) found that male wolf spiders that were larger in size had longer copulation durations and higher success rates in mating with females. This suggests that size is a crucial factor in male wolf spider mating success.
Size is a significant predictor of mating success in wolf spiders. From male-male competition to female mating preference, size plays a crucial role in these spiders’ reproductive strategies. To learn more about wolf spider mating behavior, check out our articles on mating systems and cannibalism. Additionally, the impact of environmental factors on wolf spider mating is covered in our article on environmental factors.
Factors Affecting Mating Success

Mating success in wolf spiders is determined by a combination of various factors, including mating competition, size and sexual dimorphism, and environmental factors. Let’s explore each of these factors in more detail.
Mating Competition: Mating competition is an essential element in determining wolf spider mating success. Since many male wolf spiders compete for a single mate, the competition can become intense. Competitors will fight for the opportunity to mate, and the winner will have a higher chance of mating with the female.
Size & Sexual Dimorphism: Size is an essential factor in wolf spider mating success. In wolf spiders, the size difference between males and females is striking. Female wolf spiders are generally more massive than male wolf spiders, while males tend to have longer legs. This difference in size is known as sexual dimorphism. As a consequence, larger male wolf spiders have a better chance of securing a mate.
Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and daylight also play a significant role in wolf spider mating success. Studies have shown that higher humidity levels increase male wolf spider mating success. Similarly, warmer temperatures lead to a higher number of successful mating attempts.
When it comes to wolf spider mating success, size is a crucial factor. Male wolf spiders that are more prominent have a better chance of securing a mate. Larger males are more likely to win in mating competition and overcome any resistance from the female. This dominance can lead to higher mating success. For female wolf spiders, size is essential as it often determines the number of offspring she can carry. Larger females can produce a larger brood, which leads to a more significant chance of passing on genes. Check our article about female wolf spider reproductive cycle to understand this process better.
Mating success in wolf spiders is dependent on numerous factors, and each of them plays an essential role. Mating competition, size and sexual dimorphism, and environmental factors are all critical factors that contribute to the success of wolf spider mating. By understanding these factors, it is possible to gain a clearer insight into the mating behavior of wolf spiders.
Mating Competition
When it comes to mating among wolf spiders, competition is a significant factor that plays a vital role in determining which male gets a chance to mate with the female. The male wolf spiders engage in an intense contest for the female’s attention, which requires them to display certain behaviors and physical traits that make them more attractive to the female. This competition can be fierce, and the outcome can sometimes lead to violent encounters between males, as they fight for their chance to mate. Let’s take a closer look at how mating competition works among wolf spiders.
Size & Sexual Dimorphism
Size and sexual dimorphism play a significant role in wolf spider mating behavior. Sexual dimorphism refers to the differences in physical characteristics between males and females of the same species. In wolf spiders, males are generally smaller than females which can affect their mating success.
To understand how size and sexual dimorphism affect wolf spider mating, we can refer to a study conducted by Maydianne Andrade from the University of Toronto. The study aimed to investigate how such factors influenced male mating success and how female choice affected the outcome.
In the study, Andrade found that male wolf spiders who were smaller than the females they were mating with had reduced chances of success. This was because larger females were less likely to mate with small males. However, if a small male was able to successfully mate with a larger female, the offspring would be larger in size and have a greater chance of survival.
The table below summarizes the findings of Andrade’s study:
| Male Size | Female Size | Mating Success | Offspring Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small | Small | High | Small |
| Small | Large | Low | Large |
| Large | Small | High | Large |
| Large | Large | High | Large |
As seen in the table, the mating success of small male wolf spiders decreases when mating with a larger female. However, if a small male is able to successfully mate with a larger female, the offspring would be larger in size and have a greater chance of survival.
The study also found that larger males had higher mating success rates, but only if the female’s size was small. This suggests that smaller females may prefer larger males, while larger females are more selective in their choice of partner.
Size and sexual dimorphism play an essential role in wolf spider mating behavior. The size difference between males and females can significantly affect mating success and offspring size. Larger males have higher mating success rates, but only if the female is small. However, smaller males can produce larger offspring, which can increase their chances of survival.
Environmental Factors
When it comes to wolf spider mating, it’s important to consider the impact of environmental factors on mating success. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and food availability can all play a role in determining whether or not a wolf spider is able to successfully mate.
Temperature: Wolf spiders are cold-blooded creatures, which means that their body temperature is regulated by the temperature of their surroundings. Research has shown that temperature can have a significant impact on wolf spider mating behaviors. In general, higher temperatures tend to increase the activity and aggression of male spiders, which can lead to increased mating success. However, extreme temperatures (both hot and cold) can also be detrimental to spider health and reproduction.
Humidity: Wolf spiders are also sensitive to changes in humidity, as they require a certain level of moisture to properly mate and reproduce. If humidity levels are too low, male spiders may have difficulty finding mates, while females may struggle to produce viable eggs. On the other hand, if humidity levels are too high, it can lead to increased fungal growth and disease among spider populations.
Food Availability: The availability of food can also play a major role in wolf spider mating success. Research has shown that well-fed males tend to have higher mating success rates than those that are chronically hungry. This is because males that are well-fed are more likely to have the energy and resources needed to chase and successfully mate with female spiders. Additionally, females that are well-fed may be more likely to produce healthy, viable eggs – which can further boost mating success rates.
To summarize, environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and food availability can all play a significant role in determining wolf spider mating success. By better understanding these factors and how they impact spider behavior, researchers can gain valuable insights into the complex mating behaviors of these fascinating creatures.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Mating Success |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Higher temperatures can increase male aggression and activity, leading to increased mating success. Extreme temperatures can be detrimental to spider health and reproduction. |
| Humidity | Low humidity can make it difficult for males to find mates and for females to produce viable eggs. High humidity can promote fungal growth and disease. |
| Food Availability | Well-fed males and females tend to have higher mating success rates. This is because well-fed males have the energy needed to chase and mate with females, while well-fed females are more likely to produce viable eggs. |
Research Studies
Over the years, scientists and researchers have conducted numerous studies on wolf spider mating behavior to understand the role of size in their reproduction and mating success. These studies have shed light on various aspects of wolf spider behavior, including their mating rituals, competition, and size differences between males and females.
Size & Mating Success
One of the most significant findings of wolf spider research is the correlation between male size and mating success. According to studies, larger males tend to have a better chance of securing a mate than their smaller counterparts. This is because they are more attractive to females and are better equipped to fight off competitors.
It has been observed that larger males are also more aggressive in their pursuit of a mate. They are more likely to approach females and engage in courtship displays, which can increase their chances of mating. In contrast, smaller males tend to avoid confrontations with competitors and may struggle to attract a mate.
Experiments & Findings
Several experiments have been conducted to test the impact of size on wolf spider mating success. In one study, researchers created artificial spiders of different sizes and colors to test how females responded to different male traits. The study found that females preferred larger and darker males over smaller and lighter ones.
Another study examined the mating behavior of wolf spiders in a laboratory setting. The researchers observed that larger males were more successful in securing a mate and producing offspring. However, they also noted that certain environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, can also affect mating success and the size of offspring produced.
Other Considerations
While size is undoubtedly a crucial factor in wolf spider mating behavior, other factors can also play a role. Female choice and preference can also impact mating success, as females may have different preferences for male traits depending on their own characteristics.
Seasonal variations can also impact wolf spider mating behavior, as environmental conditions can influence the availability of prey and the behavior of competitors. For example, during winter months, when prey is scarce, smaller males may have a better chance of mating as larger males may struggle to secure food and maintain their size.
Research on wolf spider mating behavior has revealed the vital role that size plays in their reproductive success. Larger males have a significant advantage in securing a mate, but other factors can also impact mating success and behavior. Further research is needed to fully understand the complexities of wolf spider mating behavior and how it affects their survival and evolution.
Size & Mating Success
When it comes to wolf spider mating behavior, size plays a crucial role in determining the success of the mating process. In fact, studies have shown that size is one of the most important factors that can influence a wolf spider’s ability to mate and pass on their genes to the next generation. This is why researchers have extensively studied the relationship between size and mating success in these arachnids. Let’s take a closer look at what they have discovered.
Experiments & Findings
Numerous studies have been conducted to examine the significance of size in wolf spider mating behavior and the results have been informative. One study conducted by Smith and Harpootlian in 2013 aimed to investigate the role of size in male mating success. The researchers captured male wolf spiders of various sizes from the wild and placed them in controlled mating arenas with receptive females.
The study found that larger male spiders had a higher success rate in mating than smaller males. In fact, males in the top 5% of size had almost a 100% success rate in mating. The researchers suggested that larger size may be indicative of higher quality males who are more able to compete and defend their territory.
Another study conducted by Johnson and Smith in 2016 aimed to explore the effects of diet on wolf spider size and mating success. The researchers found that feeding male spiders a high-protein diet resulted in larger size and higher mating success rates. However, the study also found that female spider preference for larger males decreased with increasing spider size, indicating that size is not the only factor in female choice and mate selection.
In addition to size, researchers have also examined the significance of other factors such as sexual dimorphism and environmental conditions. A study by Baker and Taylor in 2011 found that environmental factors such as temperature can influence spider size and mating behavior. The study found that males and females produced larger offspring in cooler temperature conditions, which may increase their mating success.
These experiments and findings suggest that size plays a significant role in wolf spider mating behavior, but it is not the only factor. Other factors such as diet, environmental conditions, and female preference also play a role in determining mating success. Further research is needed to fully understand the complexities of wolf spider mating behavior.
| Study | Year | Objective | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smith and Harpootlian | 2013 | Examine role of size in male mating success | Large males had higher success rate in mating |
| Johnson and Smith | 2016 | Explore effects of diet on size and mating success | Feeding high-protein diet resulted in larger size and higher mating success |
| Baker and Taylor | 2011 | Investigate environmental factors on spider size and behavior | Cooler temperatures result in larger offspring and potential for increased mating success |
Other Considerations
In addition to the factors that affect wolf spider mating behavior, there are several other considerations to take into account when studying this species. One of these considerations is female choice and mating preference.
Female Choice & Mating Preference: Female wolf spiders have been observed to actively choose their mates, often favoring those who display certain physical characteristics or behaviors. For example, some studies suggest that females prefer males with larger bodies or longer legs, although this preference may vary depending on the specific species of wolf spider.
Another factor that can influence female choice is the presence of sexual ornaments or courtship displays. Some male wolf spiders exhibit elaborate courtship rituals or physical traits such as brightly colored markings or hairy tufts, which may signal their quality as a potential mate. Females may be more likely to choose a male with these traits, as they indicate that he is healthy, genetically fit, or able to provide superior parental care.
Seasonal Variations: Another consideration when studying wolf spider mating behavior is the influence of seasonal variations. Some species of wolf spider have specific mating seasons, during which they are more likely to mate and exhibit certain behaviors associated with courtship and reproduction.
For example, the Hogna species has a mating season from June to November in North America, while some species in Australia have a mating season from February to June. During this time, males may be more active in seeking out potential mates or competing with other males for access to females. Outside of the mating season, wolf spiders may exhibit different behaviors or spend more time in hiding or hunting for prey.
Understanding the various factors that influence wolf spider mating behavior is crucial for understanding their reproductive ecology and the evolutionary forces that shape their biology. By studying the role of size, competition, environmental factors, and female choice in wolf spider mating, researchers can gain valuable insights into the complex dynamics of this fascinating spider species.
Female Choice & Mating Preference
When it comes to mate selection, female wolf spiders have a crucial role to play. Unlike male wolf spiders that rely solely on size and aggressiveness to secure a partner, female wolf spiders are more selective in their mating choices. They use various factors to aid their decision-making, including pheromone recognition, physical appearance, and behavioral traits. In this section, we’ll examine how female wolf spiders make their mating decisions and the factors that influence their preferences. Let’s delve into the world of female wolf spider mate selection and explore it in detail.
Seasonal Variations
The seasonal variations can have a significant impact on the mating behavior of wolf spiders. The spiders’ mating behavior is influenced by the temperature and the amount of light they receive. For example, during the fall and winter months, the colder temperatures and shorter days can reduce the spider’s activity levels, including their mating behavior. However, during the spring and summer months, as the weather warms up and the days get longer, the wolf spiders become more active and aggressive in seeking mates.
Factors affecting wolf spider reproduction:
- The length of the day
- Temperature
- Mating competition
- Availability of food and suitable habitats
Many researchers have studied the effect of these seasonal variations on different aspects of wolf spider mating behavior. One study found that the time of year can influence the size of the spiders. During the spring and summer, when the temperature is warmer and there is an abundance of food available, the spiders tend to be larger in size. This is likely due to the increased resources available to them.
Another study found that the seasonal variations in temperature can also affect the speed of the spider’s movements. The researchers found that during the cooler fall months, the spiders moved slower, while during the warmer spring and summer months, they moved faster.
The availability of suitable habitats is also crucial for wolf spider mating behavior. In areas where the soil is too dry or rocky, or where there is a lack of vegetation, it can be challenging for the spiders to find mates and reproduce successfully.
The seasonal variations can have significant effects on the wolf spider’s mating behavior. The temperature, length of the day, and availability of food and suitable habitats all play a role in determining the success of their mating activities. Researchers continue to study wolf spider behavior to better understand the various factors that influence their reproductive success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wolf spider mating behavior is a complex and fascinating subject that has captured the attention of researchers for decades. The significance of size in wolf spider mating is one of the most interesting topics within this field. As we have seen, the size and sexual dimorphism of male and female spiders can greatly affect their mating success.
Factors such as mating competition and environmental conditions also play a significant role in determining the outcome of mating. Furthermore, the female’s choice and preference for a mate can also influence the success of mating.
Research studies have provided a wealth of information on the subject of wolf spider mating, with experiments and findings shedding light on various aspects of the behavior. The data collected has helped scientists better understand the intricacies of this behavior and the factors that determine its outcome.
It is worth noting that there are also seasonal variations in wolf spider mating behavior. The timing of mating can be influenced by environmental cues, and different species of wolf spiders may have different mating seasons.
In summary, the significance of size in wolf spider mating behavior is a fascinating subject that has been explored by researchers in great detail. Further studies will undoubtedly shed more light on this behavior and help us better understand the complex interactions between male and female spiders. Overall, the complexity and diversity of wolf spider mating behavior remind us of the intricacies of the natural world and the importance of continued research and exploration.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average size of a wolf spider?
The average size of a wolf spider ranges from 1/2 to 2 inches in length.
Do wolf spiders have venom?
Yes, wolf spiders have venom, but it is not considered dangerous to humans.
Where do wolf spiders live?
Wolf spiders are found all over the world and can live in a variety of habitats including forests, grasslands, deserts, and even in people’s homes.
What is sexual dimorphism?
Sexual dimorphism refers to the physical differences between males and females of the same species.
How do male wolf spiders attract females?
Male wolf spiders use a combination of visual and chemical signals to attract females. They may also perform courtship dances and vibrations to attract mates.
Why is size important in wolf spider mating?
Size is important in wolf spider mating because larger males are more likely to successfully mate and pass on their genes to the next generation.
What are some environmental factors that can affect wolf spider mating?
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and availability of prey can all have an impact on wolf spider mating behavior.
What is female choice?
Female choice refers to the tendency of females in many species to be selective about which males they choose to mate with.
Do all wolf spiders mate in the same season?
No, different species of wolf spiders may mate during different seasons depending on factors such as temperature and food availability.
What are some common predators of wolf spiders?
Some common predators of wolf spiders include birds, lizards, and small mammals like shrews and mice.






