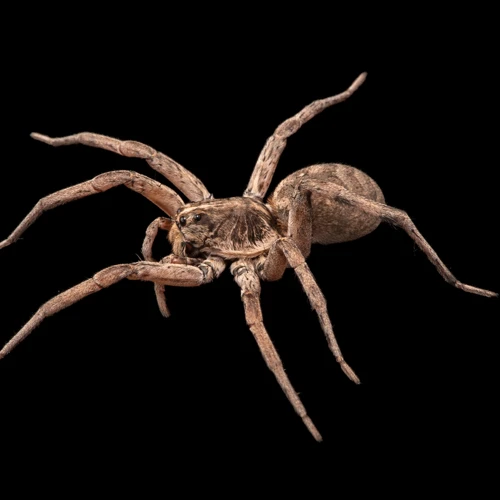
The Basics: Anatomy of Wolf Spiders
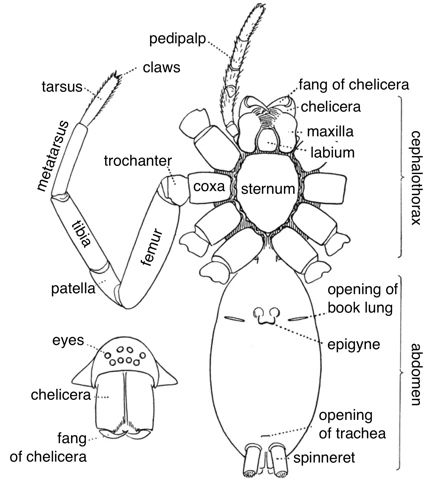
Wolf spiders are fascinating creatures that have been the subject of numerous scientific studies. Understanding the anatomy of these spiders is crucial when it comes to their behavior, habitat, and ultimately, their survival. In this section of the article, we will delve into the intricate details of wolf spider anatomy and physiology, exploring everything from their size and appearance, to their habitat and behavior. By the end of this section, you will have a deeper understanding of the body structure and importance of the cephalothorax and abdomen for the wolf spider. For an in-depth guide on the anatomy of wolf spiders, check out our comprehensive guide.
1. Size and Appearance
The size and appearance of wolf spiders can vary greatly depending on the species and gender. These creatures are generally larger compared to other spider species and are known for their impressive hunting abilities.
Female Wolf Spiders
Female wolf spiders can grow up to an inch in length, while some species can reach up to two inches including their legs. They have a stocky and robust body with a larger abdomen and a smaller cephalothorax. Wolf spiders have eight legs, with the hind legs being the longest, designed primarily for jumping. Along with their legs, female wolf spiders have excellent eyesight and usually have six to eight eyes arranged in three rows.
Male Wolf Spiders
Male wolf spiders, on the other hand, are generally smaller in size compared to female wolf spiders and have a significantly smaller abdomen. They are also more slender and spindly in appearance with longer legs, which makes them faster than their female counterparts. Although they are smaller, male wolf spiders also possess impressive hunting and mating ability.
To get a better understanding of the body structure of wolf spiders, the cephalothorax and the abdomen are the two main parts of their body that play significant roles in their hunting, survival, and reproduction. The cephalothorax is where the eyes, mouth, and legs of the spider are found. It is the most distinctive and essential part of the wolf spider’s anatomy, and it controls most of the spider’s activities. The abdomen, on the other hand, stores the spider’s silk glands, reproductive organs, and digestive organs. Without these parts, their lives might be drastically affected.
Wolf spiders’ unique body structure does not just play essential roles to their species, but also for their environment and predators. For example, their large size and intimidating appearance can discourage potential predators. By studying their body structure, scientists have also been able to learn more about how they survive and thrive, leading to significant scientific discoveries.
Wolf spiders’ size and appearance are fascinating topics to explore. By understanding their anatomy, we can better understand how these creatures successfully hunt, survive and reproduce in their environments. To learn more about the exoskeleton of these fascinating creatures, see our article on body structure in wolf spiders.
2. Habitat and Behavior
Wolf spiders are found all over the world living in different habitats. The remarkable species hunt and live on the ground level, where they make burrows, or they can climb trees, live near and in the water. Wolf spiders are commonly found in gardens, forests, fields, and even in deserts. They are versatile creatures that can adapt to different environmental conditions. These creatures are solitary hunters and lead an independent lifestyle.
Habitat and behavior are closely related, particularly when it comes to wolf spiders. Being active hunters, wolf spiders need to move around to find prey, which includes insects, other small spiders, and even small vertebrates like lizards and frogs. They have well-developed eyes and good eyesight, which help them spot and capture prey effectively. Wolf spiders are nocturnal creatures, so they are mainly active at night when their prey is also active.
Here is a table to summarize the information about habitat and behavior:
| Habitat | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Ground burrows | Live and hunt on the ground |
| Trees, forests, gardens, fields, deserts | Can adapt to various environments and hunt |
| No specific social behavior | Solitary hunters |
| Nocturnal creatures | Mainly active at night |
| Well-developed eyes and good eyesight | Effective hunters of insects, small spiders, and even small vertebrates like lizards and frogs |
The body structure of wolf spiders also plays a vital role in their behavior, allowing them to move quickly and quietly, enhancing their abilities as hunters. Wolf spiders have eight legs, and their bodies are divided into two sections: cephalothorax and abdomen. The cephalothorax is the front part of the body, and it is where the legs and eyes are located. The abdomen is the back part of the body, and it contains the respiratory and digestive systems. These two parts of the wolf spider’s body work together to ensure they can move around and hunt efficiently.
Finally, Male and female wolf spiders are also known to have varied behaviors, sexual dimorphism, and differences in morphology. Males and females show differences in respect of the size of their bodies, which affects behavior and their hunting abilities. Understanding these differences is essential in understanding the full range of behaviors available in wolf spiders.
3. Anatomy and Physiology
Wolf spiders belong to the family Lycosidae and are one of the most fascinating arachnids to study. Understanding their anatomy and physiology is crucial to exploring their behavior and survival strategies. Wolf spiders are equipped with strong bodies that allow them to be proficient hunters.
Anatomy of Wolf Spiders
Wolf spiders have two main body parts, the cephalothorax, and the abdomen. The cephalothorax is the combined head and thorax region and it supports the legs, eyes, and mouthparts. The abdomen is the largest part of the spider’s body and is responsible for digestion, respiration, and reproduction.
Physiology of Wolf Spiders
Wolf spiders are active hunters and rely on their good eyesight to track and catch their prey. They have four pairs of eyes, with the main pair being the largest and situated centrally on the front of the cephalothorax. This pair of eyes has excellent resolution and helps the spider to detect movement and identify prey.
Wolf spiders also have specialized mouthparts that are designed for biting and injecting venom into their prey. Their venom is not considered harmful to humans, but it can cause discomfort and swelling.
Wolf spiders have excellent sensory hairs on their legs and body that help them navigate their surroundings and detect vibrations. They use their sense of touch, along with vision, to locate their prey and avoid predators.
Another notable feature of wolf spiders is their ability to jump. They use their powerful legs to pounce on their prey or quickly evade danger.
To summarize, the anatomy and physiology of wolf spiders are perfectly adapted to their predatory lifestyle. Understanding the importance of the cephalothorax and abdomen in their body structure and their hunting techniques equips us better to appreciate and study these fascinating creatures.
| Anatomy | Physiology |
|---|---|
| Cephalothorax | Good eyesight to track and catch prey |
| Abdomen | Specialized mouthparts for venom injection |
| Excellent sensory hairs on legs and body | |
| Ability to jump with powerful legs |
For more information on the importance of the cephalothorax and abdomen in wolf spiders, check out our previous article on this topic.
The Exoskeleton: Defense and Adaptation

As we delve deeper into the world of wolf spiders, one cannot ignore the remarkable protective abilities offered by their exoskeleton. The exoskeleton is an external shell that covers the spider’s body, serving as both armor and support. It is an essential structure that enables the wolf spider to survive in its natural habitat while providing a multitude of benefits. In this section, we will explore the defense and adaptation mechanism of the wolf spider exoskeleton in detail. So, let’s put on our magnifying glasses and take a closer look, shall we?
1. What is an exoskeleton?
Anatomy Basics: The Exoskeleton
To understand the intricate exoskeleton of wolf spiders, we must first explore what an exoskeleton is and why it is essential for survival. An exoskeleton is a rigid external covering found in some animals, providing support, protection, and muscle attachment. It is composed of chitin, a complex carbohydrate, and protein combination, and offers a range of functions, from defense to sensory perception.
Table: Functions of Exoskeleton in Animals
| Function | Examples |
|---|---|
| Protection | Crustaceans, insects, spiders |
| Support | Crustaceans, insects, spiders |
| Prevention of Water Loss | Arachnids |
| Sensory Reception | Spiders |
The exoskeleton allows animals to adjust to their environment. For example, insects, crustaceans, and some spiders have an exoskeleton that protects them from physical injury and environmental hazards. In arachnids such as wolf spiders, it serves as a barrier to prevent water loss, while for others, it protects against predators.
In some animals, such as spiders, the exoskeleton has evolved to provide unique sensory functions. For example, the exoskeleton is essential for detecting vibrations in the environment used for communication, locating prey and detecting danger. In wolf spiders, the exoskeleton plays an essential role in their modes of hunting and defensive behavior.
The exoskeleton is a multifaceted feature that has evolved to address different needs in animals. In wolf spiders, the exoskeleton has taken on specific adaptations that help them survive and thrive in their habitats. These adaptations are essential for future research as we continue to explore and learn about these fascinating creatures.
2. Protective Qualities of an Exoskeleton
The exoskeleton of wolf spiders is an incredibly complex and multifunctional feature that plays a critical role in their survival. One of the most significant benefits of having an exoskeleton is its protective qualities, which allow wolf spiders to fend off predators and survive in harsh environments.
Table: Protective Qualities of Wolf Spider Exoskeleton
| Protective Quality | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Physical Barrier | The exoskeleton provides a solid, impenetrable barrier against predators and other environmental factors such as extreme temperatures or harsh weather conditions. |
| Shock Absorption | The exoskeleton also acts as a shock absorber, helping to reduce the impact of any blows or falls that a wolf spider may experience. |
| Armor | The exoskeleton can be thickened or reinforced in certain areas to create an armor-like appearance that provides even greater protection against predators. |
| Chemical Protection | Some wolf spiders have compounds in their exoskeleton that deter predators, such as toxic substances that cause a negative reaction upon ingestion. |
The physical barrier offered by the exoskeleton is the most basic and straightforward form of protection. The exoskeleton is composed of a hard, chitinous material that forms a rigid shield around the spider, preventing predators from injuring or devouring it.
In addition to its physical barrier function, the exoskeleton also acts as a shock absorber. This is particularly important for wolf spiders that live in rocky or mountainous environments, where falls from heights could be fatal. The exoskeleton helps to reduce the impact of such falls and prevents the spider from sustaining serious injury.
Some wolf spiders take their protective measures even further by thickening or reinforcing their exoskeleton in certain areas to create armor-like plates. This provides a higher level of protection against predators such as birds or small mammals that may try to strike at specific areas of the spider’s body.
Another unique feature of the wolf spider exoskeleton is its ability to offer chemical protection. Certain species of wolf spiders produce toxic compounds that are incorporated into the exoskeleton, making them unpalatable or even deadly to predators. These substances are often used as a last resort when the physical protection provided by the exoskeleton is not enough.
The protective qualities of the wolf spider exoskeleton are a testament to the incredible adaptability and resilience of these creatures. Their exoskeleton is a vital component of their survival in the wild, enabling them to thrive in some of the harshest environments on Earth.
3. Sensory Functions of the Exoskeleton
The exoskeleton of Wolf spiders is not only a protective layer, but it also serves as a part of their sensory system. In this section, we’ll explore the various sensory functions of the exoskeleton that aid in the spider’s daily life.
Function | Description
— | —
Tactile Sensation | The exoskeleton acts as an external receptor for touch and vibrations. It is filled with numerous sensory hairs called setae, sensitivity pits, and modified setae. These specialized hairs help the spider detect the slightest of movement in its surroundings.
Gustatory Sensation | The exoskeleton of Wolf spiders also bears chemosensory cues that detect taste. They have chemoreceptors arranged specifically on their mouthparts for detecting chemicals in their environment. They use this sense to determine the quality of their food. Some chemoreceptors on their legs can help them recognize specific types of surfaces, which they can use to navigate in the dark.
Temperature Sensation | Wolf spiders are cold-blooded creatures. Their exoskeleton serves as a thermoreceptor, allowing them to detect changes in temperature in their environment. It also helps them regulate their internal body temperature by adjusting their position in relation to the sun and other sources of heat. Their body hairs and setae can help insulate their exoskeleton, keeping them warm in colder weather.
Pheromone Detection | Wolf spiders use pheromones to communicate with each other. The exoskeleton contains specialized chemoreceptors that are sensitive to these pheromones. This allows the spider to recognize the presence of other spiders and identify potential mates.
The exoskeleton of Wolf spiders serves a variety of sensory functions, including tactile, chemosensory, thermoreceptive, and pheromone detection. These specialized structures help the spider navigate and survive in its environment.
4. Growth and Limitations of the Exoskeleton
Growth and Limitations of the Exoskeleton
The exoskeleton of a wolf spider provides essential protection but also poses certain limitations. One of the primary functions of an exoskeleton is to provide support for the body, and the rigidity of the exoskeleton limits the growth of the spider. As the spider grows, it needs to shed the exoskeleton to develop a new one that is larger in size. This shedding process is called molting, and it allows the spider to grow and develop.
The growth of a wolf spider’s exoskeleton is regulated by hormones that trigger molting. During molting, the old exoskeleton is shed, and the new one is formed underneath. The new exoskeleton is initially soft and vulnerable, but it hardens over time through a process called sclerotization. The spider then expands its body to its full size before the new exoskeleton hardens completely.
However, the molting process is not without risks. The spider’s body is exposed and vulnerable during this time, making it more susceptible to predators and environmental hazards. If the new exoskeleton does not form properly or harden correctly, it can lead to deformities or death.
Despite its limitations, the exoskeleton of the wolf spider is essential for its survival. The rigid structure provides protection from potential predators, while the molting process allows the spider to continue to grow and develop.
The Intricate Details of Wolf Spider Exoskeleton
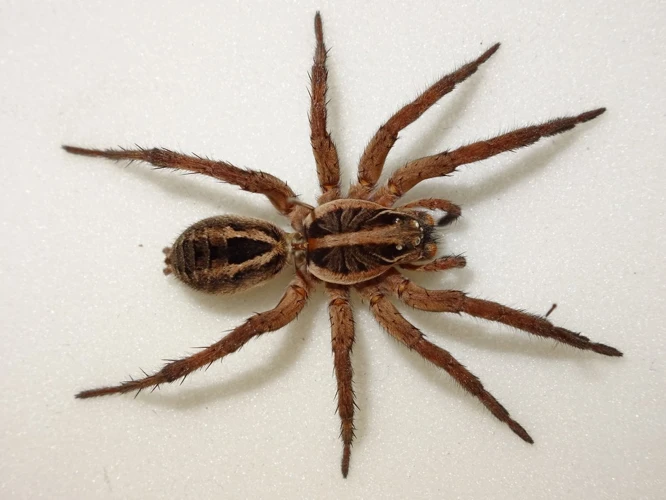

As we delve further into the anatomy of wolf spiders, one of the most intriguing and complex features to explore is their exoskeleton. This outer layer not only provides protection and support for the spider, but also plays a vital role in their sensory functions and adaptability. The intricate details of the wolf spider exoskeleton are a fascinating subject of study and reveal unique characteristics about this enigmatic arachnid species. From their microscopic features to their structural functions and camouflage abilities, let us embark on a journey to uncover the mysteries of the wolf spider’s exoskeleton.
1. Microscopic Features
As we explore the exoskeleton of Wolf Spiders, we cannot miss the intricate microscopic features that make them unique among other spiders. The exoskeleton of wolf spiders is covered in fine hairs called setae, which serve various purposes including sensory, camouflage, and thermoregulation. These setae are arranged in patterns that differ among species and between males and females.
The exoskeleton itself consists of multiple layers with distinct compositions and structures. The outermost layer is the epicuticle, which serves as a protective barrier against external factors such as desiccation and pathogens. The epicuticle is primarily composed of lipids and proteins, and its thickness varies among different body parts and individuals.
The next layer is the procuticle, which provides the exoskeleton with its strength and flexibility. The procuticle is subdivided into two layers, the outer exocuticle and the inner endocuticle. The exocuticle contains chitin, a polysaccharide that forms a network of fibers and provides the exoskeleton with its hardness. The endocuticle, on the other hand, consists of chitin and proteins, giving the exoskeleton its flexibility.
Finally, the basal membrane separates the exoskeleton from the underlying epidermis which produces and secretes the different layers of the exoskeleton. The basal membrane also serves as a site for muscle attachment and is involved in the shedding process, where the old exoskeleton is molted to make way for a new one.
All these microscopic features come together to provide wolf spiders with remarkable adaptations and unique advantages in their natural environment. By understanding the composition and structure of these features, we can gain insights into the function and behavior of wolf spiders and their ecological role.
To summarize, here is a table outlining the different layers of the exoskeleton and their compositions:
| Layer | Composition | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Epicuticle | Lipids and proteins | Protective barrier against external factors |
| Exocuticle | Chitin and protein fibers | Provides hardness to the exoskeleton |
| Endocuticle | Chitin and proteins | Provides flexibility to the exoskeleton |
| Basal membrane | Protein | Serves as a site for muscle attachment and involved in the shedding process |
The dynamics of these layers and the setae that cover them offers a fascinating area for future exploration and discovery.
2. Structural Functions
The exoskeleton of wolf spiders serves many important structural functions beyond defense and protection. This complex outer covering plays a crucial role in supporting their bodies and facilitating movement. Here are some of the key structural functions of the wolf spider exoskeleton:
- Support: Wolf spiders use their stiff exoskeleton to provide support to their entire body, allowing them to move around with agility and speed. This outer covering greatly enhances their stability and balance, which is crucial for predators who need to move quickly to catch their prey. The exoskeleton acts as a “lightweight armor” that helps to distribute the weight of the spider evenly, reducing strain on its internal structure.
- Muscle Attachment: Another crucial function of the wolf spider exoskeleton is to provide attachment points for muscles. Wolf spiders have powerful muscles that enable them to move quickly and accurately. The exoskeleton acts as a platform for the muscles to attach to, giving them a strong anchor point to work from. This enables them to exert maximum power and control over their movement.
- Protection: While defensive properties of the exoskeleton are well-known, it also serves the function of protecting softer, more delicate structures and organs within the spider’s body. The exoskeleton acts like a shell, creating barriers between the external environment and the spider itself. This protection is vital to the well-being and survival of the spider.
- Sensory Perception: The exoskeleton also plays a role in how wolf spiders perceive their environment. While they are known for their keen vision, they also have small, sensitive hairs on their body that help them feel vibrations and other tactile stimuli. These hairs are embedded within the exoskeleton and act as receptors that send information to the spider’s brain.
The wolf spider’s exoskeleton serves some crucial structural functions beyond defense and protection. It provides support, attachment points for muscles, protection for delicate structures, and even aids in sensory perception. This complex outer covering is essential to the survival and success of this fascinating predator.
3. Camouflage and Adaptability
Wolf spiders are known for their remarkable camouflage abilities. They can blend into their environment so seamlessly that they become almost invisible to their prey or predators. This camouflage is achieved through the colors and patterns on their exoskeleton, which can mimic the appearance of the surrounding flora or rocks.
Additionally, their exoskeleton also provides them with adaptability to changing environments. They can shed their exoskeletons as they grow, allowing them to adapt to both the changing seasons and their own growth. As they shed their old exoskeleton, they reveal a new, softer exoskeleton that will harden over time. This new exoskeleton is not only protective, but it also allows for a new coloration and pattern to emerge, providing even better camouflage.
Wolf spiders have the ability to adjust their body position and posture to match their environment. For example, they may flatten themselves against the ground or against a rock to better blend into their surroundings. This adaptability makes them even more difficult to spot and capture, ensuring their survival in the wild.
Wolf spiders have also been observed to modify their behavior to better suit their environment. In areas where there is less cover for them to hide, they may become more active during the night or move to areas with more hiding spots. This behavior modification is a testament to their intelligence and adaptability in the face of changing environments.
The camouflage and adaptability of wolf spider exoskeletons are fascinating and crucial aspects of their survival. Their exoskeletons are not simply protective, but they also allow for adaptability to their ever-changing environment. From shedding their exoskeletons to changing their behavior, these spiders are masters of camouflage and survival.
Experiments and Discoveries

As we continue to delve deeper into the world of wolf spiders, researchers have conducted numerous experiments and made groundbreaking discoveries. These findings have shed light on various aspects of these fascinating creatures and their delicate exoskeletons. From the tools used in these experiments to the scientific implications of the findings, let’s take a closer look at the exciting world of wolf spider exploration.
1. Research Methods and Tools
When it comes to exploring the intricate exoskeleton of wolf spiders, the research methods and tools used are crucial in obtaining accurate and detailed information.
Research Methods
Researchers typically use a combination of field and lab studies to gather information about wolf spiders. Field studies involve observing these spiders in their natural habitats, while lab studies enable researchers to conduct experiments in a controlled environment. These experiments may involve manipulating different variables to study their effects on the spider and its exoskeleton.
Tools Used for Research
A wide range of tools is used in wolf spider research, including:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Microscopes | Used to examine the intricate details of the wolf spider exoskeleton on a microscopic level. |
| Forceps | Used to handle the delicate and often fragile spider specimens without causing damage. |
| Digital Cameras | Used to document the appearance and structure of the wolf spider exoskeleton for later analysis and comparison to other specimens. |
| Chemical Solutions | Used to preserve the spider specimens for long-term study and analysis. |
| Measurement Tools | Used to accurately measure the dimensions of the wolf spider exoskeleton, enabling researchers to compare and contrast different specimens. |
The research methods and tools used in studying the exoskeleton of wolf spiders are essential for gaining a deep understanding of this fascinating and complex aspect of these creatures. Only through continued research and exploration can we fully appreciate the beauty and intricacy of the exoskeleton and the role it plays in the lives of these often-misunderstood arachnids.
2. Scientific Findings and Implications
Scientists have conducted numerous experiments and studies to understand the intricate exoskeleton of wolf spiders. Through their research, they have discovered fascinating findings and implications that shed light on the adaptability and survival strategies of these arachnids.
One of the significant scientific findings is the exoskeleton’s microstructure. Wolf spiders have an exoskeleton with a “scaffold structure,” consisting of interconnected and overlapping plates. These plates provide the exoskeleton with extreme flexibility and resistance to damage. Additionally, scientists have discovered that wolf spider exoskeleton contains chitin, a protein that helps arthropods’ exoskeleton maintain its shape.
Another essential scientific finding is the wolf spiders’ sensory capabilities through their exoskeleton. The exoskeleton of wolf spiders contains sensory hairs that help detect vibrations and movements in their environment, making them well-equipped hunters. The exoskeleton also plays a crucial role in wolf spiders’ mating behavior, providing sensory cues and signals to potential mates.
The implications of these scientific findings are far-reaching, revealing that wolf spiders have a highly complex and sophisticated exoskeleton with versatile functions. This knowledge can be applied to various fields, such as biomimicry and material engineering, where researchers can explore and develop new technologies inspired by wolf spider exoskeleton structures and functions.
Biomimicry, the imitation of nature’s design to solve human problems, can significantly benefit from wolf spider exoskeleton research. For instance, engineers can develop versatile and robust materials for applications like aerospace engineering, construction, and transportation. The exoskeleton’s sensitivity and adaptability can inspire new sensors and robotics technologies, enabling machines to navigate dynamic and unpredictable environments.
Scientific research on wolf spider exoskeleton has revealed intriguing findings and implications that have broad applications. By studying and learning from these natural systems, we can develop new technologies, solutions, and approaches that benefit society while respecting the environment.
| Scientific Findings | Implications |
|---|---|
| Wolf spider exoskeleton has a scaffold structure with overlapping plates. | Inspiration for building versatile and damage-resistant materials for various engineering applications. |
| Exoskeleton has chitin, a protein that helps maintain shape and flexibility. | Development of new biomaterials and applications in areas such as medicine and construction. |
| Exoskeleton contains sensory hairs that detect vibrations and movements. | Inspiration for developing new technologies with superior sensors and robotics features. |
| The exoskeleton plays a crucial role in wolf spider mating behavior. | Contributes to our knowledge of animal mating strategies and the evolution of exoskeletons. |
The Future of Exploration and Conservation
As we delve deeper into the intricate exoskeleton of wolf spiders, we must consider the future of our exploration and conservation efforts in order to preserve these fascinating creatures for future generations. The future of exploration and conservation poses several challenges and opportunities, as we uncover the secrets of these spiders and their crucial role in maintaining our ecosystem. Let us take a closer look at the various aspects that will shape the future of wolf spider research and conservation.
1. Challenges and Opportunities
The study of wolf spiders and their intricate exoskeleton presents both challenges and opportunities for researchers and enthusiasts alike. Here are some of the challenges and opportunities associated with this fascinating exploration:
Challenges:
- Accessibility: Wolf spiders are often found in remote locations, which can make research and observation difficult.
- Complexity: The exoskeleton of wolf spiders is incredibly complex, and understanding its features and functions requires advanced technological tools and methods.
- Cost: Advanced research tools and methods require significant funding, which can be a barrier for many researchers and institutions.
- Limited research: Despite the potential benefits of studying wolf spiders, there has been limited research on their exoskeleton and its functions.
- Environmental impact: Conducting research in remote locations can have an environmental impact, and it is important to minimize this impact as much as possible.
Opportunities:
- Advancing scientific knowledge: Studying the intricate exoskeleton of wolf spiders can help us better understand the functions and adaptations of exoskeletons in general, which can have significant implications for fields such as biomimicry.
- Medicine: Discoveries made through the study of wolf spider exoskeleton could have implications for medicine, particularly in the development of new materials for prosthetics or protective gear for those in dangerous professions.
- Technology: Understanding the functions and properties of the wolf spider exoskeleton could lead to the development of new materials and technologies for a wide range of applications, from aerospace to sports equipment.
- Conservation: Studying wolf spider exoskeletons can also help us better understand these important creatures, which in turn can inform conservation efforts to protect their habitats and populations.
- Inspiration: The intricate and fascinating exoskeleton of the wolf spider can inspire artists, designers, and writers, providing a unique lens through which to explore themes such as resilience, adaptability, and transformation.
Navigating the challenges associated with studying wolf spiders and their exoskeleton requires tenacity, resources, and creativity. However, the potential benefits of this exploration are numerous, making it an area of significant interest for many researchers and enthusiasts.
2. Benefits of Studying Wolf Spiders
Studying wolf spiders can provide numerous benefits, both for scientific research and for conservation efforts. Here are some of the key benefits of studying these fascinating arachnids:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Understanding biodiversity | Wolf spiders are incredibly diverse, with over 2,300 known species. By studying wolf spiders, researchers can gain a better understanding of the overall diversity of life on Earth. |
| Analysis of habitats | Wolf spiders are found in a wide range of habitats, from deserts to forests to wetlands. By studying the distribution and abundance of wolf spiders in different habitats, researchers can gain insights into the ecosystems they inhabit. |
| Insights into predator-prey dynamics | As predators themselves, wolf spiders play an important role in controlling the populations of smaller insects and other arthropods. By studying the hunting and feeding behavior of wolf spiders, researchers can gain insights into the dynamics of predator-prey relationships in ecosystems. |
| Medical applications | Wolf spiders produce a variety of bioactive molecules, some of which have the potential to be used for medical purposes. For example, some wolf spider venoms have been found to have antimicrobial properties, which could be useful in the development of new antibiotics. Studying the venom and other bioactive molecules produced by wolf spiders could lead to the development of new drugs and other medical treatments. |
| Conservation efforts | Many species of wolf spiders are threatened by habitat loss and other human activities. Studying these spiders can help conservationists better understand their ecology and how to protect them. It can also help identify key habitats that are critical for the survival of different species of wolf spiders. |
As you can see, studying wolf spiders can provide a wealth of information and benefits. By learning more about these fascinating creatures, we can gain insights into the natural world and develop new ways to protect and preserve it.
3. The Need for Preservation and Respect
It’s crucial to recognize the importance of preserving and respecting the habitats of wolf spiders. These creatures play a vital role in the ecosystem, and their presence contributes to the balance of nature.
Here are some key points that highlight the need for preservation and respect:
- Environmental Balance: Wolf spiders are essential in keeping pest populations under control, such as mosquitoes and flies. By consuming these pests, they help to maintain environmental balance, which is crucial for the well-being of other species in the ecosystem.
- Threatened Species: Unfortunately, many species of wolf spiders are currently endangered because of human activities such as habitat destruction and fragmentation. It’s imperative that we take steps to protect these species and their habitats to prevent further damage to the environment.
- Biodiversity: Wolf spiders are part of the vast array of biodiversity found in the world. Without preserving these species, we risk losing them forever, leading to a decline in overall biodiversity.
- Education and Awareness: By researching and studying wolf spiders, we can learn more about these unique creatures and raise awareness about the importance of preserving their habitats. This can lead to a better understanding of how we can protect and preserve other species in the ecosystem as well.
- Ethical Considerations: The ethical implications of harming or neglecting wolf spider habitats shouldn’t be overlooked. As humans, we have a responsibility to protect and respect nature, and preserving wolf spider habitats is a part of that responsibility.
- Future Generations: Lastly, preserving wolf spider habitats is also crucial for the benefit of future generations. By ensuring that these species thrive, we can provide future generations with a healthier environment to live in.
There are many reasons why preserving and respecting wolf spider habitats is crucial. It’s essential that we take action now to protect these creatures and their environments to ensure a healthy future for ourselves and for the world around us.
Conclusion
After delving into the anatomy, physiology, and exoskeleton of wolf spiders, it’s clear that these creatures are truly fascinating and worthy of admiration. Their unique features and adaptations have allowed them to thrive in a variety of habitats and environments.
However, our exploration and curiosity should not come at the expense of their well-being and conservation. It’s important to remember that wolf spiders play important roles in their ecosystems as both predators and prey. As such, efforts should be made to preserve their habitats and respect their place in the natural world.
Additionally, further research and experimentation in the study of wolf spiders could lead to exciting new discoveries and advancements in science and technology. Knowledge gained from understanding the intricacies of their exoskeletons could have wide-ranging applications in fields such as engineering and materials science.
In conclusion, studying wolf spiders and their exoskeletons is a worthwhile endeavor both for scientific inquiry and for promoting conservation efforts. By appreciating and learning from these fascinating creatures, we can foster a greater understanding and appreciation for the natural world as a whole. It’s up to us to ensure their continued existence and to act as responsible stewards of the earth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do wolf spiders look like?
Wolf spiders are typically hairy and have a large, stocky body. They range in color from gray to brown, and most have patterns or markings on their bodies that help camouflage them in their environment.
What is the habitat of wolf spiders?
Wolf spiders can be found in a variety of habitats, including grasslands, forests, deserts, and wetlands. They prefer to live in areas with ample prey and hiding places, such as under rocks or in leaf litter.
What is the purpose of an exoskeleton?
An exoskeleton serves as a protective outer layer for an organism’s body. It helps prevent physical damage from predators or the environment, and also supports the body’s internal structure.
How does a wolf spider’s exoskeleton protect it?
A wolf spider’s exoskeleton helps protect it from predators and environmental hazards by providing a hard, durable outer layer that shields the spider’s internal organs.
What sensory functions does a wolf spider’s exoskeleton have?
A wolf spider’s exoskeleton is covered in sensory receptors that can detect changes in light, temperature, pressure, and humidity. This allows the spider to navigate its environment and identify potential prey or predators.
Can a wolf spider’s exoskeleton grow with the spider?
While a wolf spider’s exoskeleton does not grow, the spider will periodically shed its outer layer and create a new, larger exoskeleton as it grows and matures.
What are some of the microscopic features of a wolf spider’s exoskeleton?
Wolf spider exoskeletons are covered in small, hairlike structures called setae, which help the spider sense its environment and detect prey. They also have chitinous plates and ribs that help reinforce the structure of the exoskeleton.
How does a wolf spider’s exoskeleton help with camouflage?
A wolf spider’s exoskeleton can change color based on its environment, allowing it to blend in with its surroundings and avoid detection by predators or prey.
What research methods are used to study wolf spiders?
Researchers may use field observations, laboratory experiments, or genetic analysis to study wolf spider behavior, physiology, and ecology.
Why is it important to preserve wolf spider habitats?
Preserving wolf spider habitats is important for maintaining the larger ecosystems in which they live, as well as for gaining a better understanding of the interactions between species and their environment. Additionally, many wolf spider species have valuable ecological roles as predators and prey.







