Introduction
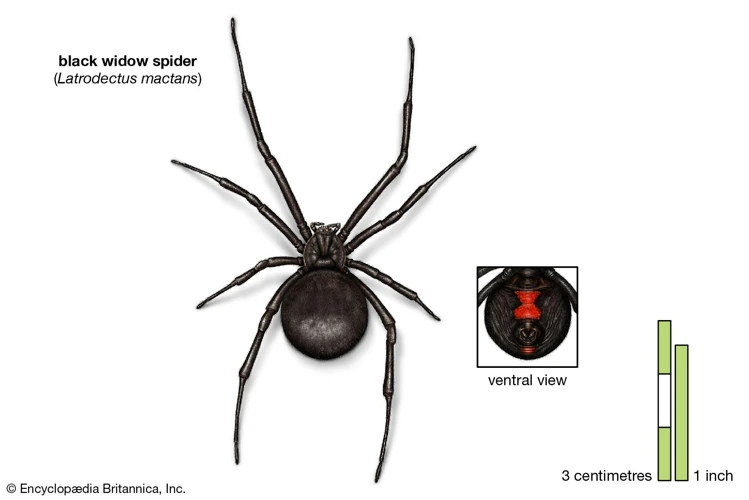

Understanding the complexities of black widow venom is a crucial step in preventing and treating spider bites. The potency of their venom has earned the black widow spider a reputation as one of the most venomous spiders in the world. In this article, we will take a closer look at the components of black widow venom that make it so dangerous and discuss their effects on humans. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to identify a black widow spider bite and seek the appropriate treatment. So, sit tight and get ready to delve into the fascinating world of black widow venom.
What is a black widow spider?
Black widow spider is a highly venomous arachnid that belongs to the Latrodectus genus. These spiders are primarily found in temperate regions, including the United States, Canada, Southern Europe, and Asia. They are identifiable by their shiny black body with a distinctive red hourglass marking on the abdomen. Females are known to be larger and more venomous than males, measuring up to 1.5 inches in body length as compared to males, who are about half their size.
| Common name | Black widow spider |
|---|---|
| Scientific name | Latrodectus spp. |
| Physical characteristics | The female is larger than the male, has a shiny black body, and a distinctive red hourglass marking on the abdomen. |
| Distribution | Primarily found in temperate regions such as the United States, Canada, Southern Europe, and Asia. |
| Venom | Extremely venomous and contains a complex mixture of neurotoxins, affecting the nervous system of the prey, including humans. |
The black widow spider’s venom is extremely potent, and because of this, it poses a significant risk to humans and other animals. Their venom is composed of a complex mixture of neurotoxins that targets the nervous system of its prey, including humans. To learn more about the components of black widow venom, read on to the next section. If you’re interested in understanding the risk associated with black widow spider bites, follow the link to Black Widow Venom Risk.
Why are black widows venomous?
Black widows are venomous spiders known for their potent venom that can cause severe symptoms in humans. But, why are black widows venomous? To answer this question, let’s take a closer look at the composition of their venom.
Black widow venom contains a complex mixture of toxins, which are primarily used to subdue their prey and defend against predators. The venom is produced in glands located in the spider’s cephalothorax and delivered through their chelicerae, which are modified fangs used for feeding and defense.
The venom of black widow spiders consists of several types of toxins, including α-latrotoxin, latrodectin, and latrotoxins. Each of these toxins has a specific function and target in the victim’s body. For example, α-latrotoxin is responsible for inducing the release of neurotransmitters, while latrodectin can disrupt cell membranes. Other toxins in black widow venom can affect various body systems, including the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
Table: Major components of black widow venom
| Toxin name | Function |
| ———————-| ——– |
| α-latrotoxin | Induces massive neurotransmitter release |
| Latrodectin | Disrupts cell membranes |
| Latrotoxins | Damages nerve terminals |
| Neurotransmitter | Regulators Modulate the release of neurotransmitters |
The potency of black widow venom can vary based on geographic location, with regional differences in toxin composition and concentration. Some studies also suggest that female black widows are generally more venomous than males.
If you want to know more about the effects of black widow venom, our article on the effects of black widow venom goes into further detail on the symptoms and impacts on the body.
Black widows are venomous due to the complex mixture of toxins in their venom, which are primarily used for defense and subduing prey. The venom contains several types of toxins that can affect different body systems and have varying degrees of potency.
The key components of black widow venom

The venom of a black widow spider is a complex mixture of chemicals that can have serious effects on the human body. The venom contains a variety of compounds that can affect different systems within the body, each with its own unique properties. Understanding the components of black widow venom will help us better understand the spider’s effects on the human body. In this section, we will take a closer look at the various compounds that make up black widow venom and their effects on the body. Let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of black widow venom!
Alpha-latrotoxin
Alpha-latrotoxin is one of the key components of black widow venom. It is a high-molecular weight protein that triggers the release of neurotransmitters from nerve terminals. This toxin can cause fatal neurotoxic effects, especially in children and elderly people.
Research shows that alpha-latrotoxin has a unique mechanism of action that involves a protein in nerve cells called neurexin. The toxin binds to neurexin and sets off a cascade of events that leads to the release of neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, norepinephrine, and dopamine. This causes uncontrolled muscle spasms, contractions, and other neurological symptoms that can be life-threatening.
Some of the symptoms of alpha-latrotoxin poisoning include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Anxiety and agitation
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Headaches and dizziness
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Muscle weakness, twitching, and spasms
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sweating and salivation
- Tremors and convulsions
Alpha-latrotoxin can also cause respiratory failure, cardiovascular collapse, and death in severe cases. It is essential to seek immediate medical attention if you suspect that you have been bitten by a black widow spider.
Interesting fact: Did you know that alpha-latrotoxin has been studied for its potential use in medical research? It has been shown to be effective in stimulating the release of neurotransmitters in cultured cells and can be used as a tool to study neuronal physiology.
If you want to learn more about how black widow venom affects the nervous system, check out our article on black widow venom and the nervous system.
Latrodectus lactis factor
Latrodectus lactis factor is a protein found in the venom of black widow spiders that has been shown to have a wide range of effects on the human body. This protein is a potent neurotoxin that specifically targets calcium channels in nerve cells, causing disruptions in nerve signaling throughout the body.
Effects of Latrodectus lactis factor
Studies have shown that Latrodectus lactis factor can cause muscle spasms and pain, as well as affect the respiratory system and cardiovascular system. When injected into the body, it can lead to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure, as well as cause breathing difficulties through ongoing interference with neurotransmitters. This can lead to wheezing and difficulty in swallowing, which can develop into pneumonia and secondary infections in some cases. Other studies showed that it is capable of causing nausea, sweating, muscle cramps, and abdominal pain. The symptoms may become worse if the bite occurs in elderly or immunocompromised patients.
Latrodectus lactis factor can also interact with various ion channels in the body, leading to altered sensory perception. The venom can cause painful muscle contractions and spasms, which can eventually lead to muscle rigidity and paralysis. It may also cause disruptions in the release of neurotransmitters, leading to further impairments in neurological function. The effects of the venom are felt immediately, and can last for several days.
Impact of geographical variations
The potency and composition of black widow venom can vary geographically and it is indicated that there is a link between milder symptoms and the species found in the Northern United States, compared to those in the Southern US and other regions where symptoms tend to be severe. However, it can vary considerably even within the same regions. According to some sources, the venom of the black widow spider may contain as many as 40 different toxic proteins, which is likely one of the reasons for the wide range of effects it can have on the human body. More details about other types of black widow venom can be found in our article /black-widow-venom-types/.
It is important to mention that Latrodectus lactis factor is not the only component of black widow venom that can cause harmful effects on the human body. A detailed overview of other key components of black widow venom can be found in our article: /chemistry-black-widow-venom/. Depending on the severity of symptoms, it is also important to understand the short-term and long-term effects of black widow venom that can be found in /black-widow-venom-long-term-effects/. If bitten by a black widow spider, it is recommended to seek medical attention immediately and antivenom therapy can be very helpful in alleviating symptoms and preventing further damage, more information can be found in /antivenom-black-widow-bites/.
Latroinsectotoxin
Latroinsectotoxin is a type of protein found in black widow venom. This toxin is responsible for attacking the insect’s nervous system, which in turn causes paralysis and death. Although latroinsectotoxin is mainly intended for their prey, it can also affect humans if they are bitten by a black widow.
The way in which latroinsectotoxin works is quite interesting. It starts by binding with the neurotransmitter receptors in the insect’s nervous system, which then causes the ion channels to open in the nerve cells. The influx of calcium ions, in turn, triggers the release of neurotransmitters and results in uncontrolled muscle contractions, paralysis, and ultimately death.
In humans, the effect of latroinsectotoxin is a bit different. When the spider bites, the venom enters the body and targets the cells of the nervous system. The binding of latroinsectotoxin with the receptors in the human nervous system causes a release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that controls muscle contractions. As a result, the victim may experience muscle spasms and cramps, especially in the abdomen.
Latroinsectotoxin is just one of the four key components found in black widow venom, each with its own unique properties and functions. By studying these components, scientists have been able to understand just how potent black widow venom is, and how it affects both its prey and humans.
It is important to note that the effects of black widow venom on humans, including latroinsectotoxin, can be serious and may even be life-threatening in some cases. If you are bitten by a black widow, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. To learn more about the other components of black widow venom, you can read our articles on black widow venom and the respiratory system and regional variation of black widow venom potency.
Neurotransmitter regulators
Neurotransmitter regulators are a group of compounds found in black widow spider venom that target the central nervous system of their prey, causing involuntary muscle movements and paralysis. These are small molecules that are able to penetrate the cell membranes and interfere with the signaling process between nerve cells. This leads to a disruption of normal neurological function, resulting in a range of symptoms and possible long-term effects.
One of the neurotransmitter regulators found in black widow venom is acetylcholine. This molecule is responsible for transmitting nerve impulses across the synapses, which are the gaps between nerve cells. Normally, acetylcholine is broken down and recycled quickly after it has transmitted a signal. However, black widow venom contains a compound that prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine, causing it to build up and overload the nerve cells. This results in the involuntary muscle contractions and spasms characteristic of black widow spider bites.
Another neurotransmitter regulator found in black widow venom is gamma-aminobutyric acid, or GABA. This molecule acts as an inhibitory transmitter, meaning it reduces the activity of nerve cells. Black widow venom contains a compound that blocks the action of GABA, leading to hyperactivity and excitability of the nerve cells. This in turn can cause muscle rigidity, tremors, and seizures.
There is also evidence that black widow venom may contain compounds that target other neurotransmitter systems, such as glutamate and dopamine. Glutamate is an important neurotransmitter that plays a role in learning and memory, but excessive activity can lead to nerve cell damage. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in reward and pleasure, but abnormal levels can cause a range of psychological and neurological disorders.
Black widow venom contains a diverse array of compounds that target the central nervous system, including neurotransmitter regulators such as acetylcholine and GABA, as well as compounds that affect other neurological pathways. The effects of these compounds can range from mild muscle spasms to severe neurological damage, depending on the amount of venom injected and the individual’s sensitivity. If you want to learn more about black widow venom and its effects on cardiovascular system, you can read our article on black widow venom and the cardiovascular system.
How black widow venom affects humans

The effects of black widow venom on the human body can be quite serious and potentially life-threatening. Once injected, it quickly targets the nervous system, disrupting normal neurotransmitter functions. The venom contains several key components that have different effects on the body. These effects range from immediate symptoms to long-term damage. Let’s dive into the specifics of how black widow venom affects humans.
Immediate symptoms
Black widow venom is one of the most potent venoms found in spiders, and its effects on humans can be devastating. Black widow bites often cause immediate symptoms, which can vary depending on the individual and the amount of venom injected. Here are some of the most common symptoms associated with a black widow bite:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Pain and swelling at the bite site | Black widow venom is a neurotoxin that attacks the nervous system, causing intense pain and swelling at the site of the bite. Depending on the severity of the bite, this can be a minor annoyance or a major issue that requires medical attention. |
| Muscle cramps and spasms | One of the hallmark symptoms of a black widow bite is muscle pain and spasms. This is because the venom works by stimulating the nerves that control muscles, causing them to contract and spasm uncontrollably. These spasms can be extremely painful and can last for several hours or even days. |
| Nausea and vomiting | Black widow venom can also affect the digestive system, causing nausea and vomiting in some individuals. This is because the venom can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive tract, leading to discomfort and even vomiting. |
| Headache and dizziness | Black widow venom can also affect the nervous system in other ways, causing symptoms such as headaches and dizziness. These symptoms are often the result of the venom affecting the blood vessels in the brain and can be quite severe in some cases. |
| In severe cases, unconsciousness and seizures | In rare cases, a black widow bite can lead to unconsciousness and seizures. This usually only occurs in individuals who are extremely sensitive to the venom or who have a preexisting condition that makes them more susceptible to the effects of the venom. |
It is important to note that not everyone will experience all of these symptoms, and the severity of the symptoms can vary depending on the person and the amount of venom injected. If you experience any of these symptoms after a black widow bite, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. In the next section, we will discuss the long-term effects of black widow venom on the human body.
Long-term effects
Long-term effects of black widow spider bites can cause a range of symptoms that can last for weeks or even months after the initial bite. These symptoms can vary from person to person and depend on several factors such as age, overall health, and the amount of venom injected.
One of the most common long-term effects of black widow spider bites is muscle pain and cramping. Research shows that black widow venom targets the nervous system, which can cause muscles to become tense and painful. This muscle pain and cramping can affect entire muscle groups, and become severe enough to interfere with normal activities.
In some cases, black widow spider bites can also cause cardiovascular symptoms. This can include changes in blood pressure, irregular heartbeats, and even heart attacks in rare cases. These symptoms are more likely to occur in older adults and people with pre-existing heart conditions.
Psychological effects have also been documented in some individuals bitten by black widow spiders. Anxiety, panic attacks, and depression have all been reported and may persist for several weeks after the bite.
| Long-Term Effects of Black Widow Spider Bites | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Muscle Pain and Cramping | Can affect entire muscle groups and interfere with normal activities |
| Cardiovascular Symptoms | Changes in blood pressure, irregular heartbeats, and even heart attacks (in rare cases) |
| Psychological Effects | Anxiety, panic attacks, and depression may persist for several weeks after the bite |
It’s important to note that not everyone who is bitten by a black widow spider will experience long-term effects. However, if you do experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention to ensure proper treatment and care.
What to do if you’re bitten by a black widow spider?
Being bitten by a black widow spider can be a scary and potentially dangerous experience. If you find yourself in this situation, it’s important to stay calm and seek medical attention immediately. Here are the key steps to take if you are bitten by a black widow spider:
Step 1: Wash the bite area
The first thing you should do is wash the bite area thoroughly with soap and water. This will help remove any dirt or bacteria on the skin that could cause an infection.
Step 2: Apply a cold compress
You can also apply a cold compress to the bite area to help reduce swelling and pain. Wrap some ice in a towel or use a cold pack and apply it to the bite area for about 10 minutes at a time, several times a day.
Step 3: Monitor your symptoms
It’s important to monitor your symptoms closely after a black widow spider bite. If you experience any of the severe symptoms mentioned earlier, such as difficulty breathing or muscle spasms, seek medical attention immediately.
Step 4: Seek medical attention
If you are experiencing severe symptoms or are unsure of the severity of your symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. Your healthcare provider may give you pain medication or anti-venom to help manage your symptoms.
Step 5: Prevent future bites
To prevent future bites, take steps to minimize your exposure to black widow spiders. Clear away clutter and debris from your outdoor living spaces, wear protective clothing when working outside, and take care when reaching into dark or confined spaces where spiders may reside.
Remember, while a black widow spider bite can be scary, prompt and appropriate medical attention can help manage your symptoms and ensure a full recovery.
Conclusion
After thoroughly examining the components of black widow venom and its effects on humans, it’s clear that this venomous spider is not to be taken lightly. The potent mixture of alpha-latrotoxin, latrodectus lactis factor, latroinsectotoxin, and neurotransmitter regulators can lead to a variety of immediate and long-term symptoms that can be life-threatening if left untreated.
That being said, it’s important to remember that black widow spiders are not aggressive and will only bite in self-defense. Therefore, the best way to avoid being bitten by a black widow is to avoid contact with them altogether. If you suspect that you have a black widow infestation, it’s best to contact a pest control professional to handle the situation.
In the event that you are bitten by a black widow spider, seek medical attention immediately. It’s crucial to receive appropriate treatment as soon as possible to minimize the effects of the venom on your body. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in the outcome of the bite.
Finally, it’s important to note that while black widow venom is undoubtedly dangerous, it also has potential as a treatment for certain medical conditions. Researchers are currently investigating the use of alpha-latrotoxin in pain management and neuronal regeneration, among other applications. By understanding the components of black widow venom, scientists can better harness its therapeutic potential while also taking measures to protect the public from its harmful effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can black widow venom be fatal?
Yes, black widow spider bites can be fatal, especially in young children and elderly people. However, with proper medical attention, fatalities are rare.
2. How long does it take for symptoms to appear after a black widow spider bite?
Symptoms may appear within minutes to hours after the bite. However, in some cases, it may take up to 24 hours for symptoms to appear.
3. Is black widow venom used for medical purposes?
Yes, black widow venom contains compounds that can be used to treat conditions such as high blood pressure and erectile dysfunction.
4. Can you die from a black widow spider bite?
While deaths are rare, a black widow spider bite can be fatal, especially if left untreated. Seek medical attention immediately if you suspect you have been bitten.
5. How common are black widow spiders?
Black widow spiders are found throughout the world, but they are most commonly found in warmer regions such as the southern United States, Mexico, and South America.
6. Are all black widow spider bites venomous?
Yes, all black widow spider bites are venomous.
7. How can I prevent black widow spider bites?
To prevent black widow spider bites, avoid contact with these spiders and their webs. Shake out clothing and shoes before wearing them, and keep outdoor areas clean and clutter-free.
8. Can black widow spiders be kept as pets?
While some people do keep black widow spiders as pets, it is not recommended due to their venomous nature and potentially dangerous bites.
9. How do black widow spiders catch their prey?
Black widow spiders catch their prey by trapping them in their webs. They will then inject them with venom and spin them in a cocoon-like structure before eating them.
10. Can black widow spiders survive in cold temperatures?
Black widow spiders are not adapted to survive in very cold temperatures and are often found in warmer regions. However, some species have been known to survive in cooler climates such as Canada and Alaska.