As we explore the wonders of the natural world, it becomes apparent that each species has its unique features and attributes. One such remarkable species is the wolf spider, known for its agility and hunting prowess. Interestingly, there are significant variations between male and female wolf spiders in terms of body structures and behavior. In this article, we will delve into the intriguing comparison of body structures between male and female wolf spiders, exploring the somatic differences, reproductive system differences, and behavioral differences. So, let’s dive in and discover the fascinating world of wolf spiders.
Somatic Differences
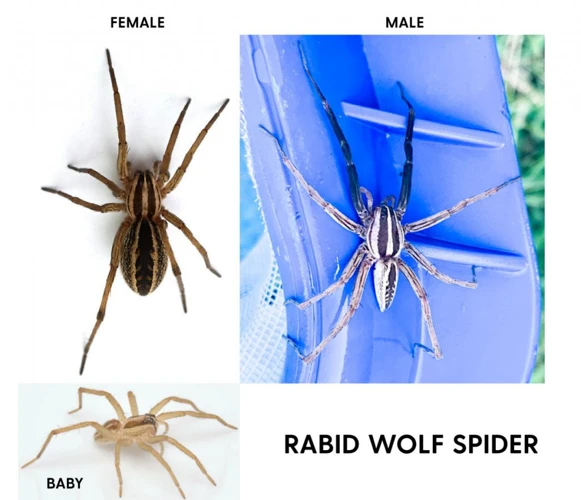
When it comes to understanding the differences between male and female wolf spiders, one of the most evident factors is their somatic or physical structure. These differences can be observed in several aspects, such as the size and shape of their abdomen, length and thickness of their legs, and body coloration. To fully comprehend the significance of these physical distinctions and their role in the lives of wolf spiders, it’s essential to take a closer look at their anatomy. To gain a thorough understanding of wolf spider anatomy, check out our anatomy guide for an in-depth analysis of their body structure and intricate bodily systems.
Abdomen Size and Shape
When it comes to comparing the body structures between male and female wolf spiders, the differences in abdomen size and shape are quite noticeable.
Abdomen size: In general, female wolf spiders tend to have larger abdomens than males. This is mainly because the female carries the eggs inside her abdomen until they hatch. The size of the abdomen can vary depending on the number of eggs being carried by the female. Male wolf spiders generally have smaller abdomens because they do not carry any eggs.
Abdomen Shape: The shape of the abdomen in male and female wolf spiders is different as well. In females, the abdomen is generally more rounded and bulbous in shape, while in males it is slightly flattened. This difference in shape is mainly due to the fact that females need a large enough space to carry their eggs while males do not have such a need.
To simplify these differences, we can use the following table:
| Abdomen Size | Abdomen Shape | |
|---|---|---|
| Male Wolf Spider | Smaller | Flatter |
| Female Wolf Spider | Larger | Rounded and bulbous |
Understanding the differences in abdomen size and shape is important in distinguishing between male and female wolf spiders. Additionally, the exoskeleton and the importance of the cephalothorax and abdomen in wolf spiders can also play a role in species identification.
Leg Length and Thickness
Male and female wolf spiders have differences in their leg length and thickness. The first pair of legs are often longer and thicker in males, while in females, all legs are generally the same size. This difference in leg size is due to the mating ritual of wolf spiders.
Male Wolf Spiders:
Male wolf spiders use their long and thick legs to hold onto females during mating. These legs also provide the necessary leverage to keep the female from escaping. Their legs also contain spines and claws, which aid in gripping the female during mating.
Female Wolf Spiders:
Females, on the other hand, have shorter and thinner legs to provide greater mobility while searching for food and caring for their young. Interestingly, female wolf spiders can lose legs during mating due to the male’s gripping behavior, but they are able to regenerate them during molting.
It is important to note that leg length and thickness are directly related to the spider’s exoskeleton, which plays a crucial role in the wolf spider’s ability to function and survive. The exoskeleton protects the spider’s internal organs and provides strength and support. To learn more about the importance of the cephalothorax and abdomen in wolf spiders, read our article on the importance of the cephalothorax and abdomen in wolf spiders.
The differences in leg length and thickness between male and female wolf spiders reflect their unique mating behaviors and the adaptability required for survival in the wild. To learn more about the body structure of wolf spiders, check out our article on body structure of wolf spiders and the importance of their exoskeleton.
Body Coloration
One of the most noticeable differences between male and female wolf spiders lies in the color of their exoskeletons. Males are typically more brightly colored than females, which helps them in the mating process. The underside of a male’s abdomen is often embellished with vivid red, orange, or yellow spots, while the female’s abdomen tends to be less colorful, with muted patterns of gray, brown, or black.
The reason for these differences is rooted in sexual selection. Male wolf spiders attract mates by displaying their bright colors and patterns during intricate courtship dances. Females are attracted to males with particularly bold or striking visuals, as they are seen as a sign of a healthier, more capable partner. In contrast, female wolf spiders are not as brightly colored because they do not need to attract mates, but rather to blend in with their environment in order to avoid predators.
Interestingly, the coloration of wolf spiders can also vary depending on the time of year and temperature. In the colder months, wolf spiders tend to have darker coloring to absorb more heat, while in the warmer months, they may be lighter in color to reflect heat and avoid overheating.
It is also worth noting that wolf spiders can change their color based on their surroundings, a process known as background adaptation. They can tweak their coloration to match their surroundings, which helps them to remain camouflaged and avoid detection by predators. This makes it difficult to pin down concrete color differences between male and female wolf spiders, as their coloration can change depending on their environment.
While male wolf spiders are typically more brightly colored than females due to sexual selection, the coloration of both male and female wolf spiders varies depending on the time of year and their surroundings. To learn more about wolf spider exoskeleton and how it affects these creatures, see our article on wolf spider exoskeleton.
Reproductive System Differences

The reproductive system of male and female wolf spiders showcases intriguing differences in their anatomy and behavior. Understanding these differences can provide insight into the breeding habits and social structure of these arachnids. In this section, we will explore the unique features and functions of their reproductive systems, which play crucial roles in their survival and proliferation.
Male Palps and Sperm Transfer
Male wolf spiders have specialized structures called “palps” that are used for reproduction. These palps are located at the front of the pedipalps, which are the second pair of appendages located near the mouth. The structure of male and female palps differs significantly, which is an important factor in distinguishing between male and female wolf spiders.
Morphology of Male Palps:
Male palps are relatively large and complex structures that consist of several different parts. The main body of the palp, or the “bulb,” is connected to a long, coiled tube called the “embolus.” The embolus is where sperm is housed before it is transferred to the female spider during mating. The tip of the embolus is also important because it has specialized structures that help anchor the palp in place during copulation.
Sperm Transfer:
During mating, the male spider will use his palp to transfer sperm to the female’s genital opening, which is located on the underside of her abdomen. Male wolf spiders have evolved a unique method of sperm transfer that involves inserting one palp at a time into the female’s epigynum, or genital opening. This method allows the male to ensure that both palps are used to transfer a sufficient amount of sperm during mating.
Male Competition:
Male wolf spiders will often compete with each other for mating rights. This can involve aggressive behavior, including fighting and courtship displays. In some cases, males will also attempt to mate with virgin females more than once to ensure that their sperm fertilizes the eggs.
Male wolf spiders have specialized structures called “palps” that are specifically designed for mating and sperm transfer. These structures are vital for reproduction, as they allow the male spider to ensure that his sperm is transferred to the female spider during mating. Additionally, male wolf spiders may compete with each other for mating rights, which can involve fighting and courtship displays.
Female Epigynum and Egg-Laying
Female wolf spiders have a unique reproductive system that allows them to lay eggs directly onto their silk webs. This process begins with the female spider creating a silk sac to lay her eggs in, which she attaches to her spinnerets located at the rear of her abdomen.
The structure that allows the female wolf spider to lay eggs is known as the epigynum, a genital plate located on the underside of the spider’s abdomen. The shape and size of the epigynum varies among different species of wolf spiders, and can be used to distinguish between them.
During the mating process, the male wolf spider uses his pedipalps, or specialized appendages near the front of his body, to transfer sperm to the female’s epigynum. Fertilization occurs internally, and the female stores the sperm until she is ready to lay her eggs.
Once the eggs are fertilized, the female wolf spider attaches the silk sac containing her eggs to a secure location, such as a crevice or plant stem. She then covers the sac with additional layers of silk to protect it from predators and the elements.
The number of eggs laid by female wolf spiders can vary greatly, depending on the species and environmental conditions. Some species may lay only a few dozen eggs, while others may lay hundreds.
In general, female wolf spiders provide little to no parental care after the eggs are laid. The spiderlings, or baby spiders, hatch from the eggs and are fully independent from birth. They disperse from the silk sac and begin hunting for food on their own.
The female wolf spider’s unique reproductive system and egg-laying behavior play a crucial role in the survival and reproduction of their species.
| Female Epigynum and Egg-Laying |
|---|
| The epigynum is a genital plate located on the underside of the spider’s abdomen |
| The shape and size of the epigynum varies among different species of wolf spiders |
| During mating, the male spider transfers sperm to the female’s epigynum using his pedipalps |
| Female wolf spiders lay their eggs directly onto silk webs, attaching them with a silk sac |
| The number of eggs laid can vary greatly, with some species laying only a few dozen while others may lay hundreds |
| Females provide little to no parental care after the eggs are laid, with spiderlings being fully independent from birth |
Behavioral Differences
When it comes to behavioral differences, male and female wolf spiders exhibit interesting contrasts that are vital for their survival. These behaviors can range from mating rituals to parental care, and are influenced by a wide range of factors including environmental conditions and innate physiological characteristics. Understanding these differences is crucial for gaining insight into the social and ecological dynamics of wolf spider populations. Let’s take a closer look at some of these behaviors.
Mating Rituals
When it comes to mating, male and female wolf spiders have completely different rituals. Here are some notable differences:
- Males are typically more active during courtship: Male wolf spiders are known for their energetic and sometimes even aggressive courting behaviors. They will often approach a female while waving their legs and tapping their pedipalps on the ground. The male may also approach the female from behind and bite her to initiate mating.
- Females initiate copulation: Despite the seemingly dominant behavior of male wolf spiders during courtship, females are the ones who ultimately decide when and with whom they will mate. Once a female has decided to mate with a particular male, she will signal her readiness by lifting her abdomen and opening her epigynum, which is the opening to her reproductive system.
- Mating can be dangerous for males: After mating, female wolf spiders may sometimes eat the male. This behavior is believed to be a way for the female to gain extra nutrition to support the eggs she will lay. In some species, males have evolved various strategies to avoid being eaten after mating, such as quickly scurrying away or even breaking off their own pedipalps inside the female to prevent her from being able to eat them.
The mating rituals of male and female wolf spiders are fascinating to observe and highlight the unique evolutionary strategies that each sex has developed for reproduction.
Parental Care
When it comes to parental care, male and female wolf spiders have very different approaches. After mating, the male typically leaves to seek out a new mate while the female wolf spider assumes responsibility for caring for her offspring. Here are a few ways in which the parenting styles of male and female wolf spiders differ:
- Female Wolf Spider Parenting: Female wolf spiders are known for their exceptional maternal care. After laying her eggs, the female wolf spider will carry her egg sac with her wherever she goes. She will carefully guard her eggs from predators and even rotate the sac to ensure that all eggs receive equal warmth and protection. Once the spiderlings hatch, the female will continue to care for them by carrying them on her back until they are large enough to fend for themselves.
- Male Wolf Spider Parenting: In contrast, male wolf spiders do not provide any parental care. After mating, the male will typically leave to find another mate or to focus on his own survival. There have been rare cases where male wolf spiders have been observed guarding egg sacs, but this behavior is not typical.
The differences in parental care between male and female wolf spiders highlight the unique reproductive strategies of each gender. While females prioritize the survival and development of their offspring, males prioritize their ability to reproduce with multiple partners.
Conclusion
After comparing the body structures and behaviors of male and female wolf spiders, it is apparent that there are some noticeable differences between the sexes. From their abdomen size and shape to their mating rituals, male and female wolf spiders have evolved in distinct ways to ensure successful reproduction and survival.
Somatic differences are one of the most striking distinctions between male and female wolf spiders. Females tend to have larger and rounder abdomens compared to males, as they carry eggs and young within their bodies. Additionally, females are typically larger overall than males, with longer and thicker legs for better maneuverability and hunting.
Another key somatic difference is the body coloration, with male wolf spiders often having more intricate and vibrant color patterns to attract female mates, while female wolf spiders are typically less colorful to blend in with their surroundings and avoid predators.
Reproductive system differences play a crucial role in the survival and evolution of wolf spiders. Male wolf spiders use their palps to transfer sperm to the female during mating, while females have an epigynum for receiving and storing male sperm until they are ready to lay their fertilized eggs.
Furthermore, female wolf spiders have a unique ability to control the number of eggs they lay based on environmental factors such as the availability of food and shelter. This adaptability allows them to optimize their reproductive success and ensure the survival of their offspring.
Behavioral differences between male and female wolf spiders also contribute to their distinct ways of life. Mating rituals, for example, often involve complex courtship displays from males to attract females. Additionally, females are typically the ones to provide parental care, with some species keeping their young on their backs until they are old enough to fend for themselves.
In conclusion, the comparison of body structures and behaviors between male and female wolf spiders reveals a fascinating insight into the intricacies of reproduction and survival in the animal kingdom. As with many species, the evolution of distinct and complementary characteristics between the sexes is a testament to the amazing adaptability and resilience of life on earth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some of the major differences in body structures between male and female wolf spiders?
Female wolf spiders are generally larger than males, and they have more robust abdomens and shorter legs than males. Males, on the other hand, have longer and thinner legs that they use for courtship and combat, as well as distinctive reproductive structures.
What is the purpose of the abdomen in female wolf spiders?
The abdomen in female wolf spiders serves as a location for storing eggs until they are ready to be laid. It is also used to store fat reserves that help to sustain the spider during periods of low food availability.
What factors contribute to leg length and thickness in wolf spiders?
Leg length and thickness in wolf spiders are influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and availability of prey. Spiders that are raised in conditions that promote growth tend to have longer and thicker legs than those raised in less favorable conditions.
Do male and female wolf spiders differ in their coloration?
Yes, there are differences in coloration between male and female wolf spiders. Males tend to be lighter in color and have distinctive marking on their bodies, while females are typically darker and have less prominent marking.
What is the function of male palps in wolf spiders?
Male palps in wolf spiders are used to transfer sperm to the female during mating. They are unique to male spiders and allow for the transfer of genetic material from the male to the female.
How do female wolf spiders lay eggs?
Female wolf spiders lay their eggs by depositing them into a silk sac that is attached to the underside of their abdomen. The eggs are then carried around by the female until they hatch.
What are some common mating rituals in wolf spiders?
Male wolf spiders engage in a variety of courtship behaviors to attract females, including presenting a gift of food or performing a distinctive dance. Females may also use chemical signals to indicate their receptiveness to mating.
Do wolf spiders exhibit any form of parental care?
Yes, female wolf spiders are known to exhibit some form of parental care. After laying their eggs, females will carry their egg sacs around with them, protecting them from predators and environmental hazards until the eggs hatch.
Are there any behavioral differences between male and female wolf spiders?
Yes, there are some differences in behavior between male and female wolf spiders. For example, males are more likely to engage in aggressive behaviors towards other males, while females are typically more focused on caring for their young.
What can we learn from studying the differences between male and female wolf spiders?
Studying the differences between male and female wolf spiders can help us to better understand the complexities of sexual dimorphism in the animal kingdom. It can also provide insights into the evolution of reproductive strategies and the benefits and costs of exhibiting sexually dimorphic traits.






