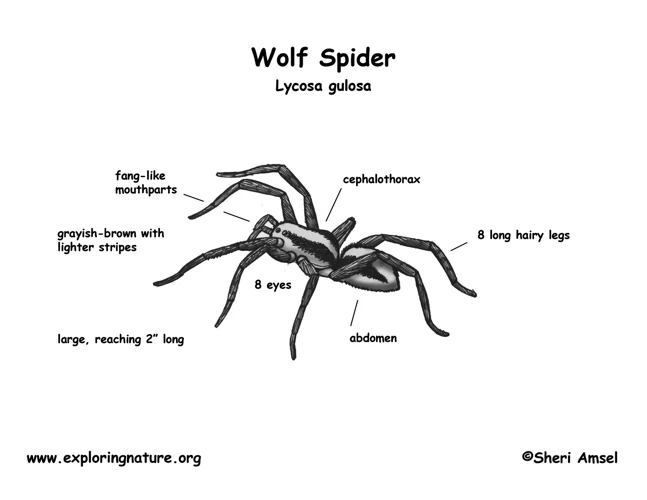
As we observe the world around us, we may come across a creature that sends shivers down our spine – the wolf spider. With its eight legs and swift movements, the wolf spider is a fascinating and sometimes intimidating arachnid. But have you ever wondered about the importance of the different parts of their body? In this article, we will dive deep into the intricacies of the cephalothorax and abdomen, exploring their functions and significance in the life of a wolf spider. So, grab your magnifying glass and prepare to discover the marvels of these tiny creatures.
Understanding Wolf Spider Anatomy
As we investigate the fascinating world of wolf spiders, we discover that their anatomy is truly remarkable. From their distinctive body structure to the way they hunt and mate, every aspect of these creatures has evolved to enable their survival in a vast range of environments. While many people are familiar with the appearance of wolf spiders, there is so much more to learn about their body and how it functions. In this section, we will delve deeper into the unique features of the wolf spider’s anatomy that make them such skilled and adaptable hunters. To learn more, check out our comprehensive guide to wolf spider anatomy.
The Cephalothorax
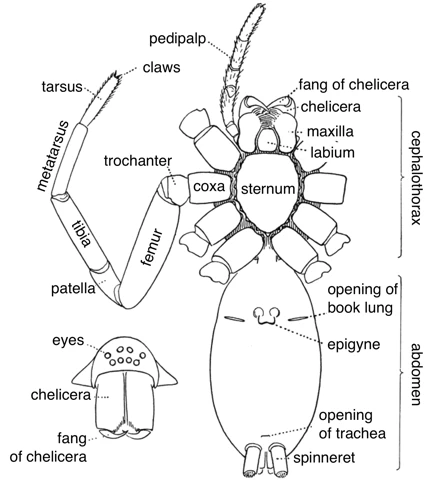
The cephalothorax is the head and thorax region of the wolf spider’s body, and it houses several crucial anatomical features. This region is covered by a hard exoskeleton made of chitin, which protects the internal organs from damage and external threats. One of the most notable features of the cephalothorax is the wolf spider’s eight eyes, which are arranged in three rows and have excellent vision in low light conditions. These eyes allow the spider to have a 360-degree view of its surroundings and detect prey and predators.
In addition to the eyes, the cephalothorax also contains the wolf spider’s fangs, which are highly specialized appendages used for feeding and defense. The fangs are connected to venom glands, which produce a potent venom that can paralyze or kill prey and deter predators. When hunting, the wolf spider uses its fangs to bite and subdue its victim, and then injects venom to immobilize it.
Another significant feature of the cephalothorax is the setae, which are small, hair-like structures that cover the spider’s body. Setae plays a crucial role in the spider’s sensory perception, allowing it to detect vibrations, temperature changes, and chemical signals in its environment.
Finally, the cephalothorax functions as a platform for the spider’s eight legs, providing attachment points for the muscles that control their movement. The legs are covered with bristles that help the spider to climb on different surfaces, and the two front legs are longer and thicker than the others, aiding in Capture prey.
The cephalothorax is a critical part of the wolf spider’s body as it houses vital features such as the eyes, fangs, setae, and legs. These structures contribute to the spider’s survival and success in hunting prey and avoiding predators. To learn more about the body structure of wolf spiders, check out our informative page on body structure of wolf spiders.
The Abdomen
The abdomen is the second major part of the Wolf spider’s body, located below the cephalothorax. It has a soft and flexible exoskeleton, unlike the cephalothorax. The abdomen is the site of most of the spider’s important internal organs, including the heart, reproductive organs, and silk glands.
Here are some key points about the importance of the abdomen in Wolf spiders:
- Reproduction and Offspring Protection: Female wolf spiders use their abdomen to carry their eggs and young spiderlings on their backs. They spin a special silk container, which they attach to their abdomen, called an egg sac. The abdomen provides a safe and warm space for the eggs to develop and for the spiderlings to grow. Male Wolf spiders also use their abdomen to transfer sperm to female spiders during mating, which is an important reproductive function.
- Silk Production and Web Weaving: The abdomen of a Wolf spider also contains specialized glands for the production of silk. These glands secrete different types of silk that are used for different purposes, such as building egg sacs or webs for hunting. Wolf spiders do not build webs to catch prey like some other spiders, but they may spin silk as a shelter or to help them climb or jump.
Wolf spiders can vary in size and color, depending on the species and their geographic location. For example, in the United States, some wolf spiders can be brown or gray, while others can have bright and bold patterns. Wolf spiders are sexually dimorphic, with males being smaller and less brightly colored than females.
If you want to learn more about the differences between male and female Wolf spiders, check out our article on Male vs Female Wolf Spiders. Also, if you are interested in learning more about the Wolf spider’s exoskeleton, check out our article on Wolf Spider Exoskeleton.
Importance of Cephalothorax in Wolf Spiders

The cephalothorax, which encompasses the head and thorax, is a crucial part of the anatomy of a wolf spider. This part of their body plays a significant role in their survival and day-to-day living. Without the cephalothorax, these spiders would face significant challenges in hunting, mating, and defending themselves against potential predators. Explore the intricate details of this body part with us as we uncover why it is vital to the wolf spider’s existence.
Protection and Camouflage
The cephalothorax of a wolf spider serves many important functions, including protection and camouflage. The carapace, or hard outer shell of the cephalothorax, provides physical defense against predators and other threats. Additionally, the pattern and coloration of the carapace can help the spider blend in with its surroundings and avoid detection.
However, not all wolf spiders have the same coloration and pattern on their cephalothorax. Some may have more muted tones while others may have bright colors. According to research, the coloration of the cephalothorax is likely influenced by the environment in which the wolf spider lives. For example, wolf spiders living on dark soil may have darker coloration, while those living on light-colored sand may have lighter hues.
Wolf spiders may add bits of debris to their carapace as a form of camouflage. This behavior is known as debris-carrying, and it can help wolf spiders go undetected by predators. A wolf spider may pick up bits of twigs, leaves, or grass and stick them to its carapace, creating a makeshift camouflage that helps it blend in with its surroundings.
| Function of Cephalothorax in Wolf Spiders | Details |
|---|---|
| Protection | The carapace provides physical defense against predators and other threats |
| Camouflage | The pattern and coloration of the carapace can help the spider blend in with its surroundings, and some wolf spiders add bits of debris to their carapace to improve camouflage |
The cephalothorax plays a crucial role in the protection and camouflage of wolf spiders. The carapace serves as a physical defense, while the coloration and pattern can help the spider blend into its environment. Additionally, some wolf spiders add bits of debris to their carapace as a form of camouflage. These adaptations allow wolf spiders to defend themselves against predators and stay hidden from danger.
Powerful Jaws and Venom
The powerful jaws and potent venom of wolf spiders make them among the most fearsome arachnids in the animal kingdom. The cephalothorax houses the spider’s jaws, which are capable of delivering a powerful bite that can subdue their prey in an instant.
An interesting fact is that wolf spider’s venom is not harmful to humans, so there’s no need to fear them. But for their prey, it’s a different story. Their venom is a crucial tool for their survival, as it paralyzes their prey and makes it easier for them to consume. It also helps to break down the prey’s internal organs, enabling the spider to extract the nutrients it needs.
The venom of wolf spiders is a complex cocktail of different molecules, including toxins that affect the nervous system and enzymes that break down the prey’s tissue. Interestingly, the composition of this venom can vary depending on the spider’s diet and environment.
Let’s take a look at some of the key components of wolf spider venom:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Neurotoxins | Disrupt the nervous system of the prey, leading to paralysis and death. |
| Enzymes | Break down the prey’s tissue, making it easier for the spider to feed. |
| Structural proteins | Help to maintain the shape and function of the venom gland. |
| Metal ions | Play a role in the chemical reactions that occur within the venom gland. |
The powerful jaws and venom of wolf spiders are essential adaptations that enable them to survive in their environment. They use these tools to hunt and feed, and to protect themselves from predators. While they may seem scary to humans, these amazing creatures are a vital part of their ecosystem and serve an important role in controlling insect populations.
Importance of Abdomen in Wolf Spiders
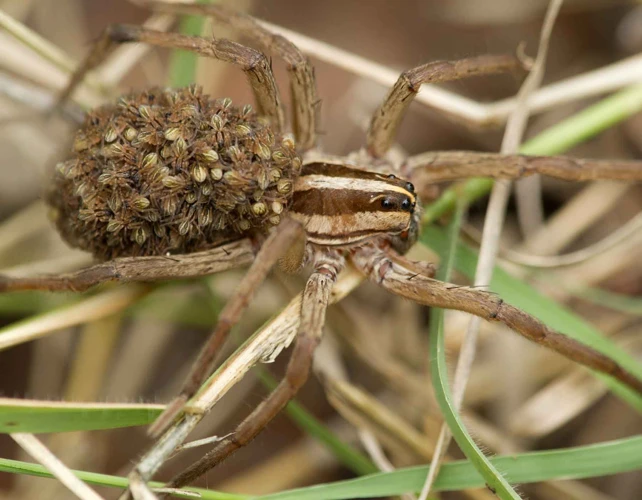

When it comes to the anatomy of wolf spiders, the importance of the abdomen cannot be ignored. The abdomen plays a crucial role in the life of a wolf spider, contributing to functions ranging from reproduction and silk production to prey capture and digestion. In this section, we will explore the significance of the abdomen in the life of a wolf spider, examining the various ways it contributes to the survival and well-being of these fascinating arachnids. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of wolf spider anatomy and behavior to understand the importance of the abdomen.
Reproduction and Offspring Protection
Wolf spiders are known for their unique way of reproducing and strongly protecting their offspring. The abdomen in wolf spiders is an essential part of their reproductive system and plays a vital role in the early stage of their offspring’s life.
Reproduction: Wolf spiders reproduce sexually, and females lay eggs that develop inside the abdomen. The abdomen of a female wolf spider is much larger than that of a male due to its role in reproduction. The female’s gonads are situated in the abdomen. When a female wolf spider is ready to lay her eggs, she spins a dense white silk sac that contains hundreds of eggs.
Offspring Protection: After laying eggs, the female wolf spider carries the egg sac around with her. She attaches the sac to her spinnerets, located at the end of her abdomen, and carries them with her everywhere she goes. This process is called “carrying the egg sac,” and it protects the eggs from predators and harsh environmental conditions.
Once the spiderlings hatch, they will complete their development inside the sac before venturing out. The spiderlings then climb to their mother’s back, and she carries them until they are strong enough to disperse on their own. Wolf spider mothers have been known to fiercely protect their young from predators, even sacrificing themselves if necessary.
It is worth noting that not all female wolf spiders carry the egg sac. Some species of wolf spiders bury the sac in a protected area. In such cases, the abdomen of the female wolf spider still plays a vital role in the development and safety of her offspring.
The abdomen of wolf spiders is a significant part of their reproductive system and plays an essential role in protecting their offspring. The unique strategy of carrying the egg sacs also showcases the spider’s advanced behavior and care for their young.
Silk Production and Web Weaving
One of the most fascinating attributes of wolf spiders is their ability to produce silk and weave webs. Although they do not use their silk for web creation like some other spider species, they use it for a variety of purposes that are essential to their survival and reproduction. Here are some of the incredible ways in which wolf spiders utilize their silk:
- Cocooning: Wolf spiders use their silk to wrap eggs in a tough, protective cocoon. The cocoon not only protects eggs from predators, but also regulates temperature and humidity levels to ensure proper development of spiderlings.
- Hunting: Some wolf spider species use their silk to construct silk-lined burrows where they lie in wait for prey to pass by. The silk acts as a trip wire, alerting the spider to the presence of food, and also prevents prey from escaping.
- Mating: During mating season, male wolf spiders produce silk to create a “safety line” while courting females. This prevents the male from accidentally falling off and also allows them to retreat quickly if necessary.
- Dispersal: After hatchling, spiderlings use silk to create a balloon-like structure, called a “ballooning,” which enables them to disperse and colonize new territories. They release a single strand of silk that catches the wind and carries them away.
- Capturing Prey: Wolf spiders often use their silk to create egg sacs in which the prey is entangled and eaten alive.
Silk production and web weaving are integral aspects of a wolf spider’s life cycle, from protecting eggs to capturing prey and dispersing offspring. The versatile use of the silk is one of the many adaptations that have allowed wolf spiders to thrive as a species.
Adaptations and Behavior
As we delve deeper into the fascinating world of wolf spiders, it becomes apparent that their unique adaptations and behavior play a crucial role in their survival. From hunting techniques to courtship rituals, these arachnids have evolved to thrive in a variety of environments. Let’s explore some of the fascinating adaptations and behaviors that make wolf spiders stand out in the animal kingdom.
Hunting and Feeding
Wolf spiders are carnivorous creatures that use their strong and agile bodies to hunt and capture their prey. They have a keen sense of touch and smell, as well as excellent eyesight, which allows them to detect prey movement from long distances.
Hunting Techniques:
- One of the main hunting techniques used by wolf spiders is ambush hunting. They wait patiently and quietly in a concealed location, such as under a rock or in a burrow, and pounce on their unsuspecting prey when it comes within range.
- Wolf spiders also utilize active hunting where they stalk their prey using their superior eyesight and speed. They often use their camouflage to blend in with their surroundings, waiting for the perfect moment to launch an attack.
- In addition to using their speed and agility, wolf spiders also have an impressive ability to jump, allowing them to catch prey that is out of their reach. They use their strong hind legs to propel themselves towards their prey with incredible force and accuracy.
Feeding Habits:
- Once the wolf spider catches its prey, it will inject it with a paralyzing venom using its powerful chelicerae, or jaws. The venom not only paralyzes the prey, but also begins to break down its internal organs, making it easier for the spider to digest.
- Wolf spiders feed on a wide variety of insects, including grasshoppers, crickets, and even other spiders. They are also known to eat small reptiles and amphibians, but this is less common.
- While wolf spiders have a voracious appetite and can consume prey that is much larger than themselves, they do not eat often. They will typically only feed once every few days, or even weeks, depending on the availability of prey.
Wolf spiders are skilled hunters that employ a variety of techniques to catch and consume their prey. Their impressive speed, agility, and jumping ability allow them to capture a wide range of insects, while their powerful jaws and venom help them break down and digest their meals with ease.
Mating and Courtship
Wolf spiders go through a complex mating and courtship process, which often involves the use of pheromones and vibratory signals. Here are some points that illustrate how wolf spiders mate and court their partners:
- Male Recognition: Male wolf spiders use their acute vision to locate female spiders from a distance. Once the male spider identifies a potential mate, he quickly approaches her.
- Visual Display: The male spider begins to wave his front legs in a rhythmic pattern to signal his interest in the female spider. This visual display also helps in attracting female spiders.
- Vibratory Signals: Some wolf spiders use vibratory signals to communicate with their potential partners. The male spider will tap the ground with his palps, transmitting vibrations that the female picks up through specialized receptors on her legs.
- Chemical Signals: Male wolf spiders also release pheromones that act as signals to attract females. The scent of pheromones can linger for a long time, making it easier for males to attract females from a distance.
- The Chase: After attracting the female spider, the male will begin to chase her, often engaging in a game of cat and mouse. The chase is an essential part of courtship, as it serves to demonstrate the male’s strength and agility.
- Mating: When the male catches up to the female, he gently taps her with his palps. The female will then respond by either accepting or rejecting the male. If she accepts, the male will then mate with her.
Wolf spider mating and courtship can be a fascinating yet perplexing process to observe. The use of visual, vibratory and chemical signals by male spiders to attract females demonstrates the importance of these senses in wolf spider behavior.
Conclusion
Our exploration of the anatomy and importance of cephalothorax and abdomen in wolf spiders has revealed fascinating insights into the world of these creatures. Despite their small size, wolf spiders are incredibly skilled hunters and rely on their unique body structures to survive and thrive in their environments.
Overall, wolf spiders are impressive creatures that continue to fascinate researchers and enthusiasts alike. By understanding the importance of their cephalothorax and abdomen, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate adaptations and behaviors that allow them to succeed in their habitats. From their powerful jaws and venom to their silk production and web weaving, every aspect of their anatomy serves a critical purpose.
As we continue to study and learn more about wolf spiders, we may uncover even greater secrets and adaptations that allow these tiny predators to continue thriving in diverse environments. Whether you’re a biologist or simply a lover of nature, it’s clear that these creatures have plenty to teach us about the beauty and complexity of the natural world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the cephalothorax in a wolf spider’s body?
The cephalothorax is the head and thorax structure of the wolf spider’s body and serves various purposes such as protection, camouflage, and housing vital organs such as the brain, heart, and respiratory system.
How is the cephalothorax vital in a wolf spider’s hunting technique?
The cephalothorax houses the powerful jaws of the wolf spider, which enables it to execute quick and effective attacks on prey. It also facilitates the venom injection process.
Can the cephalothorax protect the wolf spider from predators?
Yes, the cephalothorax serves as a protective shield against predators by covering the wolf spider’s vital organs.
What is the abdomen’s function in a wolf spider’s body?
The abdomen is responsible for various functions such as digestion, reproduction, silk production, and web weaving.
How does the abdomen contribute to a wolf spider’s offspring protection?
The female wolf spider carries its egg sack in the abdomen, protecting and nurturing the offspring until they are strong enough to fend for themselves.
Can the abdomen be used as a form of self-defense?
Yes, some species of wolf spiders have stinging hairs on their abdomens that can be utilized for self-defense.
Is silk production unique to the abdomen of a wolf spider?
Yes, silk production is solely performed in specialized structures located in the wolf spider’s abdomen.
What is the significance of silk production in a wolf spider?
Wolf spiders use silk for numerous purposes such as creating egg sacs, lining their burrows, and catching prey.
How do wolf spiders hunt and feed?
Wolf spiders are active hunters that use their keen senses and powerful jaws to track and kill prey. They mainly feed on insects and other small invertebrates.
What is the courtship process like for a wolf spider?
During courtship, the male wolf spider performs a complex ritual that involves creating vibrations, visual cues, and pheromones to attract the female. The female then decides whether or not to mate with the male.