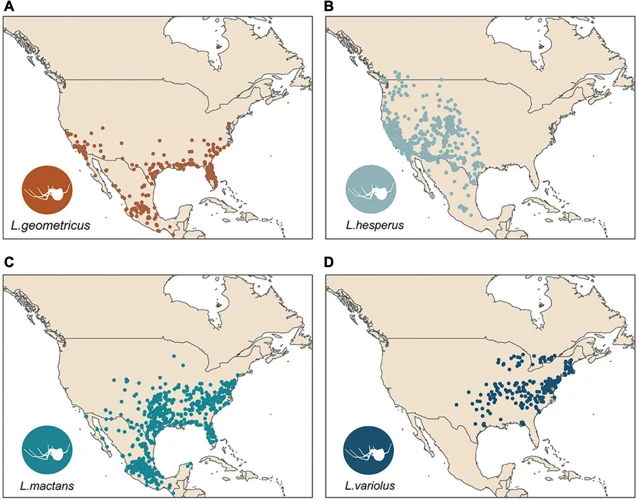
The Black Widow Spider is an enigmatic arachnid known for its venomous bite and unique web-building capabilities. While these spiders have been studied extensively, there is still much that is unknown about their habitat use. Scientists have developed the Habitat Suitability Index as a tool to assess the quality of habitats for various species, including Black Widows. This index takes into account a variety of habitat characteristics to determine how suitable a habitat is for a particular species. In this article, we will explore the Habitat Suitability Index and how it is used to assess Black Widow Spider habitat use.
What is Habitat Suitability Index?
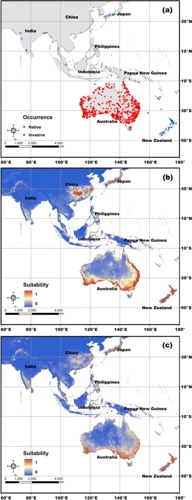
The Habitat Suitability Index (HSI) is a tool used to assess the suitability of an environment for a given species. Habitat suitability is crucial for the survival and reproduction of many species, including the black widow spider. Understanding the habitat requirements of black widow spiders and how to assess their habitat suitability via the HSI can provide insight into their distribution patterns and interactions with other species. For more information on the habitat of black widow spiders, check out this article on black widow spider habitat and its impact on urban and rural areas.
Habitat Requirements of Black Widow Spiders
Black Widow Spiders are commonly found in North America and are known for their infamous venomous bite. These spiders inhabit a variety of ecosystems including natural habitats such as forests, swamps, and deserts, as well as human-made environments like structures and gardens. They have specific habitat requirements that must be met for their survival and reproduction.
Some of the key habitat requirements of Black Widow Spiders include:
- Shelter: Black Widows require a secure shelter to avoid predators and harsh weather conditions. They can often be found in crevices, burrows, and other protected spots.
- Temperature: These spiders prefer warm temperatures ranging from 20 to 35°C. Higher temperatures increase their metabolic rate and activity level.
- Moisture: Black Widows require a moderate level of moisture for survival. Droughts can reduce their prey availability and decrease their survival rate.
- Prey Availability: Black Widow Spiders are carnivorous and feed on a variety of insects. Their habitats need to have an adequate supply of prey to ensure their survival.
- Vegetation: Despite being predators, Black Widows require vegetation for constructing webs and finding shelters. Dense vegetation also provides a suitable microclimate that offers shade and moisture.
Understanding these habitat requirements can assist in evaluating Black Widow Spiders’ habitat use via habitat suitability index. Additionally, consideration of abiotic and biotic factors influencing these requirements can provide insight into the spiders’ population ecology and can help inform management and conservation activities. For example, factors such as human activity and light pollution can negatively impact Black Widow Spider habitats. For more information on these and other factors affecting Black Widow Spider habitats, visit this resource.
Habitat Suitability Index
The Habitat Suitability Index, or HSI, is a method used to evaluate the suitability of a specific habitat for a particular species. In the case of black widow spiders, the HSI can provide valuable insight into their preferences for habitat characteristics, allowing for more targeted conservation efforts. The HSI is based on a set of criteria that are important for the species in question, with each criterion assigned a suitability rating based on how well it meets the species’ needs.
Some of the factors that are commonly considered when developing an HSI for black widow spiders include:
- Temperature
- Moisture
- Vegetation
- Prey availability
- Human impacts
Each factor is given a rating based on how well it meets the needs of the species, with higher ratings indicating greater suitability. The ratings are then weighted according to their importance to the species, with more important factors given a higher weight.
The resulting weighted scores are then combined to produce an overall index of habitat suitability. The HSI can be used to compare different habitats or to evaluate the suitability of a single habitat over time, allowing for the monitoring of changes in habitat quality.
Understanding the HSI can be a valuable tool for conservationists and land managers who are working to protect black widow spider populations. By evaluating the suitability of different habitats, they can identify areas that are most important for the species and prioritize conservation efforts accordingly. For more information on the types of habitats that black widow spiders prefer, and how they interact with their environment, check out our article on urban and rural habitats for black widows.
Steps to Assess Black Widow Spiders Habitat Suitability

When assessing the habitat suitability for black widow spiders, there are several important steps to follow. These steps involve identifying and rating specific habitat characteristics, calculating weighted scores, and interpreting the results. It is crucial to consider the various factors that affect black widow spider habitat suitability, such as temperature, moisture, vegetation, prey availability, and human impact. In order to get a more comprehensive understanding of these factors and their impact on black widow habitats, you can check out our article on abiotic factors affecting black widow habitat or our article on human impact on black widow spider habitats. Now, let’s dive into the steps for assessing black widow spider habitat suitability.
1. Identify Habitat Characteristics
To accurately assess the habitat suitability of Black Widow spiders, the first step is to identify the habitat characteristics that are relevant to their survival. These characteristics are vital in determining the suitability of the habitat for the spiders’ breeding, feeding, and sheltering requirements. Here are some of the essential habitat characteristics you need to identify:
1. Vegetation: Vegetation is one of the essential factors that affect the Black Widow spider’s habitat. They prefer habitats with dense vegetation to provide them with hiding places. The presence of prey insects and other arthropods in the vegetation also attracts them. It is necessary to identify the type and density of vegetation in the habitat to assess the habitat suitability for Black Widow spiders.
2. Moisture: Black Widow spiders prefer habitats with moderate humidity levels. High humidity levels are beneficial for spiders’ survival as they require moisture to survive. On the other hand, dryer environments make it harder for spiders to feed and reproduce, leading to a lower habitat suitability. It’s crucial to assess the moisture level in the habitat.
3. Temperature: Temperature is a crucial factor in determining Black Widow spider’s habitat suitability. Spiders require a warm and dry environment for their survival. They are active during the warmest part of the day and look for cooler places for shelter and hiding. Assessing the temperature requirements of Black Widow spiders is necessary to determine the habitat suitability.
4. Prey availability: Prey availability is another critical factor in the habitat suitability of Black Widow spiders. These spiders require a stable source of prey to survive. The presence of insects and other arthropods in the habitat is vital to the spider’s survival. As such, it’s necessary to assess the prey availability in the habitat to determine its suitability.
5. Soil Factors: The type and quality of the soil in a habitat is another crucial factor to consider when assessing the suitability of a habitat for Black Widow spiders. The soil characteristics can affect the abundance and diversity of prey, which in turn impacts the spiders’ survival. Soil factors such as texture, moisture content, and nutrient availability should be evaluated to determine habitat suitability.
After identifying all the relevant habitat characteristics, the next step is to assign suitability ratings to each characteristic, calculate their weighted scores, and interpret the results. For more information on assessing Black Widow spiders’ habitat suitability, check out this article on black widow spiders’ shelter.
2. Assign Suitability Ratings
After identifying the required habitat characteristics, the next step is to assign suitability ratings to each characteristic. This rating should be based on the specific requirements of black widow spiders, as well as their behavior within the habitat. A rating of 1 to 10 is commonly used, with 1 indicating unsuitable habitat and 10 indicating perfect habitat. Creating a table to easily visualize the suitability ratings for each characteristic can be helpful.
For example, the following table shows how suitability ratings can be assigned for black widow spiders’ habitat characteristics:
| Habitat Characteristic | Suitability Rating |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 8 |
| Moisture | 6 |
| Vegetation | 3 |
| Prey Availability | 9 |
| Human Impacts | 2 |
In this example, the overall suitability rating for this specific habitat would be:
Overall Suitability Rating = (Temperature x 0.4) + (Moisture x 0.3) + (Vegetation x 0.1) + (Prey Availability x 0.2) – (Human Impacts x 0.2)
Overall Suitability Rating = (8 x 0.4) + (6 x 0.3) + (3 x 0.1) + (9 x 0.2) – (2 x 0.2) = 5.5
As seen in this example, the rating for each characteristic is multiplied by a specific weight, which is usually based on the relative importance of that factor for a specific organism.
It’s important to note that these ratings are subjective and may vary depending on the researcher’s interpretation of the habitat as well as the specific study area. It’s crucial to use an objective method for assigning ratings to minimize any potential biases. Additionally, these ratings may be adjusted based on the results obtained from field sampling or other research methods.
To understand more about how the habitat suitability index is used to assess black widow spiders’ habitat use, continue reading the next section.[1]
3. Calculate Weighted Scores
After assigning suitability ratings to each habitat characteristic, the next step is to calculate the weighted scores. The weighted scores are obtained by multiplying the suitability ratings with the corresponding weights assigned to each habitat characteristic. The weights represent the relative importance of each habitat characteristic to the overall suitability of a habitat for black widow spiders.
The formula for calculating the weighted score for each habitat characteristic is:
Weighted score = Suitability rating x Weight
Once the weighted scores for each habitat characteristic have been calculated, they can be summed up to obtain the overall habitat suitability index (HSI). The HSI represents the overall suitability of a habitat for black widow spiders and ranges from 0 to 1, with 1 indicating the most suitable habitat.
To calculate the HSI:
1. Add up the weighted scores for each habitat characteristic.
2. Divide the sum by the total possible weight (the sum of all weights assigned to each habitat characteristic).
The resulting number is the HSI for that habitat.
For example, if a habitat has suitability ratings of 0.6 for temperature, 0.8 for moisture, 0.7 for vegetation, and 0.5 for prey availability, and weights of 0.3, 0.4, 0.2, and 0.1 for each characteristic, respectively, the weighted scores and HSI can be calculated as follows:
– Temperature weighted score = 0.6 x 0.3 = 0.18
– Moisture weighted score = 0.8 x 0.4 = 0.32
– Vegetation weighted score = 0.7 x 0.2 = 0.14
– Prey availability weighted score = 0.5 x 0.1 = 0.05
The sum of the weighted scores is 0.18 + 0.32 + 0.14 + 0.05 = 0.69. The total possible weight is 0.3 + 0.4 + 0.2 + 0.1 = 1. The HSI for this habitat is 0.69/1 = 0.69.
It’s important to note that the accuracy of the HSI depends on the suitability ratings and weights assigned to each habitat characteristic. These values should be based on accurate and comprehensive data about black widow spider habitats.
To learn more about black widow spider habitats, check out our article on black widow habitats. Additionally, it’s crucial to understand the potential threats to black widow spider habitats, which are discussed in our article about habitats black widow threat. Finally, assessing soil factors that affect habitat suitability for black widow spiders is important, which is covered in our article on evaluating soil factors and black widow spiders habitat.
4. Interpret Results
After calculating the weighted scores for each habitat characteristic, the next step is to interpret the results. This involves comparing the overall suitability index of the habitat to determine if it is suitable or unsuitable for black widow spiders.
Interpreting Results:
- If the overall suitability index is below 0.5, the habitat is considered unsuitable for black widow spiders.
- If the overall suitability index is between 0.5 and 0.7, the habitat is considered marginally suitable for black widow spiders.
- If the overall suitability index is above 0.7, the habitat is considered suitable for black widow spiders.
It is important to note that the suitability index is based on the weighted scores assigned to each habitat characteristic. Habitat characteristics with high weightings have a greater influence on the overall suitability index than those with lower weightings.
Example: If the vegetation characteristic has a high weighting and is rated as highly suitable, while the prey availability characteristic has a low weighting and is rated as marginally suitable, the overall suitability index will be influenced more by the vegetation rating than the prey availability rating.
Interpreting the results of the habitat suitability index can help in making decisions regarding management and conservation of black widow spider habitats. If the habitat is found to be unsuitable, management measures can be taken to improve the habitat conditions. Conversely, if the habitat is found to be suitable, it can be prioritized for conservation efforts to maintain and protect it.
Factors Affecting Habitat Suitability
When it comes to assessing the habitat suitability of black widow spiders, several factors have a significant impact. Understanding these factors and how they affect the spider’s habitat preference is crucial for obtaining accurate results with Habitat Suitability Index (HSI). In this section, we’ll delve deeper into the various factors influencing the habitat suitability of black widows. We’ll examine factors such as temperature, moisture, vegetation, prey availability, and human impacts, highlighting their importance in assessing the habitat suitability of the black widow spider. So, let’s take a closer look at how these factors play a crucial role in the spider’s chosen habitat.
1. Temperature
The temperature is a crucial factor affecting the habitat suitability of black widow spiders. As arachnids are cold-blooded creatures, their metabolism depends on external temperatures, making them highly sensitive to changes in temperature. Understanding the relationship between temperature and the habitat suitability index is essential for assessing black widow spider habitats accurately.
Here are some specific ways temperature can affect habitat suitability:
- Minimum and Maximum Temperature Ranges: Black widow spiders have a set range of temperatures in which they can survive. High temperatures can desiccate spider eggs or cause heat stress; low temperatures can slow their metabolism and lead to death. Knowledge of the minimum and maximum temperature ranges is necessary to assess habitat suitability.
- Seasonal Variations: Seasonal variations in temperature can significantly affect black widow spider populations. Extremes of temperature with low and high humidity can cause mortality rates to rise. Additionally, understanding the weighting of seasons is crucial when calculating habitat suitability indexes to reflect the seasonal changes in temperature.
- Microclimates: Microclimates, like crevices or shaded areas, can create isolated pockets of suitable temperatures that can support black widow spiders. These pockets of microclimate can help maintain spider communities in areas that are otherwise unsuitable.
Understanding the temperature requirements of black widow spiders and how it interacts with the habitat suitability index is crucial. Failing to consider the temperature-related variables will lead to inaccurate assessments of habitat suitability, and consequently, ineffective management strategies.
2. Moisture
Moisture is a critical factor affecting the habitat suitability for black widow spiders. These spiders prefer environments with moderate to high levels of humidity. In areas with low levels of moisture, black widow spiders may struggle to find adequate water sources and may struggle to survive. On the other hand, excessively wet environments may also negatively impact the spiders. Flooded areas can damage the spider’s web and lead to a reduction in prey availability.
Factors impacting moisture
The availability of moisture is influenced by various environmental factors such as rainfall, humidity, soils, and topography. In areas with low rainfall, black widow spiders may struggle to find enough water, making these areas unsuitable habitats for them. Habitats with well-draining soils can lead to drier conditions that may not support these spiders.
Impact of moisture on prey availability
Prey availability is also impacted by moisture levels in a habitat. Black widow spiders feed on insects, and insects require moisture to survive and thrive. In areas with low moisture, insect population may be lower, making it difficult for the spiders to find prey. In excessively wet habitats, insects may also be less abundant, as flooding can drown insect populations.
Assessing moisture for habitat suitability index
When assessing the habitat suitability index of an area for black widow spiders, it is essential to consider moisture levels. Factors such as annual precipitation, humidity levels, and soil types should be evaluated to determine whether the habitat is suitable. Favourable habitats for black widow spiders would have moderate to high moisture levels but will not be subject to flooding.
Management practices for moisture
To enhance and manage black widow spider habitat suitability, it is essential to strike a balance between dry and wet conditions in the environment. Wet areas can be maintained to an optimal moisture level, while dry areas can be moistened by small-scale interventions, such as creating small drinking sources. Land use practices that limit soil erosion can increase water retention, thus supporting the growth of vegetation and the survival of these spiders.
3. Vegetation
The vegetation surrounding the habitat of black widow spiders plays a crucial role in determining their suitability. The type and density of vegetation in and around the preferred habitat can either encourage or discourage the presence of Black widow spiders.
Factors Affecting Vegetation
Vegetation is influenced by several environmental factors such as soil quality, sunlight, and water availability. The moisture levels in the soil and the amount of rainfall during rainy seasons are among the most important factors. Black widow spiders favor areas with dry soils and low moisture content. Areas with more dense vegetation may not be suitable for spiders as they can lead to higher humidity levels.
Vegetation Density
Vegetation density or the degree of plant growth is another important factor affecting black widow spider habitat suitability. Vegetation density can affect the availability of shelter and breeding sites for spiders. The preferred habitat of black widow spiders contains open areas with low vegetation cover such as shrubs, bushes, or tall grasses. Overgrown vegetation can also limit the mobility of spiders since it may prevent them from moving quickly and efficiently.
Plant Species
In addition to density, plant species also play a role in determining black widow spider habitat suitability. Black widow spiders prefer plants with large leaves and branches, such as shrubs, which provide both shelter and hunting locations. Plant diversity can also affect the suitability of a habitat, as the more diverse the plant species, the more diverse the prey species. This can be helpful in providing suitable conditions to support the spider food web.
Impact of Human Activity
Anthropogenic activities have a significant impact on the vegetation composition in different habitats. Land conversion and urbanization have led to a reduction in natural habitats. The negative consequences of these activities include the destruction of vegetation cover and changes in climate conditions, which can alter the suitability of habitats for black widow spiders. In some cases, the introduction of non-native species can also have an impact on the suitability of the habitat.
Vegetation plays a vital role in determining the suitability of the habitat for black widow spiders. The type and density of vegetation, plant species, and the impact of human activities are all crucial factors to consider when assessing the suitability of a habitat for black widow spiders.
4. Prey Availability
One of the crucial factors that affect the habitat suitability index of black widow spiders is the availability of prey. These spiders are carnivorous and primarily feed on insects such as beetles, grasshoppers, and other spiders. Without an adequate supply of prey, black widow spiders may not survive and thrive in a particular habitat.
Factors Affecting Prey Availability
There are several factors that affect the prey availability in a habitat, including:
- Climate: The availability of prey is highly dependent on the climate of a particular region. Insects tend to be more abundant in warmer and humid environments, making such habitats suitable for black widow spiders.
- Vegetation: Vegetation plays a critical role in providing shelter and food for prey species. The presence of forests, shrubs, and grassland in a habitat can have a positive impact on the availability of prey for black widow spiders.
- Habitat fragmentation: Fragmentation of habitats due to human activities can lead to a decline in the abundance of prey populations. This can have a negative impact on the habitat suitability index of black widow spiders.
- Prey population: The population of prey species in a habitat can fluctuate due to natural and human factors. For instance, the use of insecticides can affect the abundance of prey species in a habitat, which can ultimately impact the habitat suitability of black widow spiders.
Impact of Prey Availability on Habitat Suitability
The availability of prey has a direct impact on the habitat suitability index of black widow spiders. In habitats where prey is abundant, black widow spiders are more likely to survive and reproduce, leading to a higher habitat suitability index. On the other hand, in habitats where prey is scarce, the black widow spider population may decline, negatively impacting the habitat suitability index.
When assessing the habitat suitability index of black widow spiders, it is essential to consider not only the presence of suitable prey species, but also the abundance and stability of their populations.
5. Human Impacts
Human impacts are one of the major factors affecting the habitat suitability for black widow spiders. As humans continue to urbanize and alter the natural landscape, the habitat of these spiders are being disturbed and degraded. Some of the key human impacts on black widow spider habitats are discussed below:
| Human Impacts | Effects on Black Widow Spider Habitats |
|---|---|
| Urbanization | Urbanization leads to destruction of natural habitats to make way for buildings, roads, and other infrastructure. This reduces the availability of suitable habitat for black widow spiders. |
| Agriculture | Intensive agriculture practices such as the use of pesticides and herbicides can have adverse effects on black widow spider habitats. These chemicals can kill the prey species of black widow spiders and make the environment unsuitable for their survival. |
| Deforestation | Deforestation leads to a loss of vegetation cover, which is essential for black widow spider survival. The loss of trees and plants also results in a decrease in prey availability for the spiders. |
| Pollution | Pollution of water and air can have a direct impact on black widow spider habitats. A polluted environment can reduce the prey availability and make the habitat unsuitable for their survival. |
| Climate Change | Climate change is a major threat to black widow spiders and their habitats. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can alter the vegetation cover and prey availability, making the habitat unsuitable for the spiders. |
The above table highlights the various human impacts on black widow spider habitats. It is important to understand these impacts and take necessary measures to conserve their habitats to ensure their survival.
Conclusion
In conclusion, assessing the habitat suitability index is a crucial step in understanding the habitat use of black widow spiders. By identifying habitat characteristics and assigning suitability ratings, weighted scores can be calculated, providing insight into the suitability of the habitat for these spiders. It is important to consider factors such as temperature, moisture, vegetation, prey availability, and human impacts when assessing habitat suitability.
Using the habitat suitability index can not only provide valuable information for research purposes, but also aid in management and conservation efforts. By understanding the specific habitat requirements of black widow spiders, steps can be taken to preserve and protect their habitat. Additionally, by considering the factors that affect habitat suitability, proper management and conservation strategies can be developed to ensure the persistence of these important species.
Overall, assessing the habitat suitability index is an effective tool for studying black widow spider habitat use and for developing conservation and management strategies. It is essential to continue research efforts to ensure the preservation of these important species and their habitats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Habitat Suitability Index?
The Habitat Suitability Index (HSI) is a tool used for assessing the suitability of a habitat for a specific species.
What are the habitat requirements of Black Widow Spiders?
Black widow spiders require warm, dry environments with low vegetation and an abundance of prey.
How is the Habitat Suitability Index calculated?
The Habitat Suitability Index is calculated by assigning suitability ratings to habitat characteristics and then calculating weighted scores based on the importance of each characteristic.
What are the steps to assess Black Widow Spiders habitat suitability?
The steps to assess Black Widow Spiders habitat suitability include identifying habitat characteristics, assigning suitability ratings, calculating weighted scores, and interpreting the results.
What factors affect habitat suitability?
Factors that affect habitat suitability include temperature, moisture, vegetation, prey availability, and human impacts.
How does temperature affect Black Widow Spider habitat suitability?
Black Widow Spiders prefer warm environments and are most active at temperatures between 70-90°F.
What is the role of moisture in Black Widow Spider habitat suitability?
Black Widow Spiders require low moisture environments and thrive in dry conditions.
What types of vegetation are preferred for Black Widow Spider habitat?
Black Widow Spiders prefer low vegetation such as grasses and shrubs.
What impact do human activities have on Black Widow Spider habitat suitability?
Human activities such as urbanization and agriculture can reduce suitable habitat for Black Widow Spiders.
Why is assessing habitat suitability important for Black Widow Spider conservation?
Assessing habitat suitability can help identify areas where conservation efforts should be focused and aid in the management of Black Widow Spider populations.