As we explore the complex world of arachnids, we often encounter the wolf spider, a fascinating creature known for its exceptional hunting skills. But what causes wolf spiders to be such successful predators? The answer lies in their venom. Wolf spider venom is a powerful tool that enables them to immobilize their prey quickly and efficiently. In this article, we’ll delve into the science behind wolf spider venom, its unique composition and types, and how it works in prey immobilization. We’ll also discuss recent research on wolf spider venom and its potential therapeutic benefits. So, let’s begin our journey into the intriguing world of wolf spider venom!
What is Wolf Spider Venom?

When we hear the word “venom,” we may picture snakes, scorpions, or spiders that inject deadly substances into their prey or enemies. Wolf spiders are no exception. These fascinating creatures that belong to the family Lycosidae inject venom to subdue their prey. But what exactly is wolf spider venom made of, and why is it so effective in immobilizing their prey? Let’s explore the composition and types of wolf spider venom in further detail. If you’re interested in learning more about how venom composition affects hunting preferences of venomous wolf spiders, check out this article.
Composition
Wolf spiders belong to the Lycosidae family of spiders and are known for their spectacular hunting techniques. These spiders are venomous, and their venom composition varies depending on different factors such as species, gender, and geographic location.
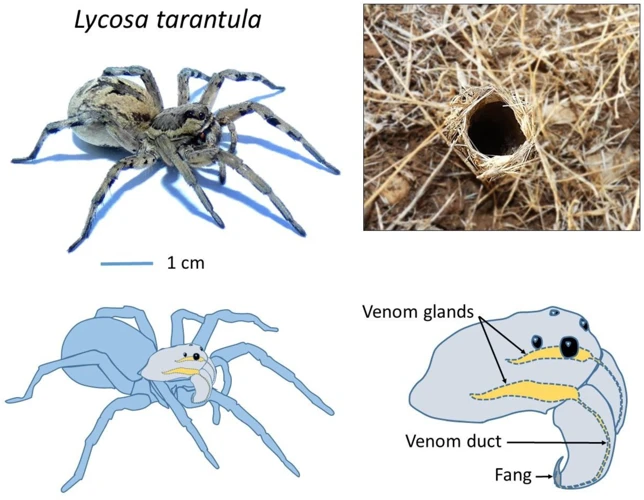
Wolf spider venom contains a complex mixture of small molecules, including neurotransmitters, enzymes, and other proteins. These molecules work together to target different organs of the prey and cause paralysis, leading to immobilization and ultimately death.
The major components of wolf spider venom include various types of enzymes such as proteases, nucleases, and lipases, which are capable of breaking down various macromolecules in the prey’s body. In addition to enzymes, the venom also contains other molecules such as histamines, which can cause inflammation, pain, and itching.
It is interesting to note that the size of the venom glands in wolf spiders is relatively large compared to their body size. This makes them efficient predators, as they can store and deliver a considerable amount of venom to their prey, contributing to their hunting success. You can read more about how venom size in wolf spiders affects their prey in this interesting article.
Another fascinating aspect of wolf spider venom is its composition’s variability among different species. A comparison of venomous wolf spiders’ venom is necessary to understand this variability, of which you can read more in our article here.
Wolf spider venom has an intricate composition that contributes to its hunting success. The venom’s variability among different wolf spider species makes it a fascinating area of study and offers insights into their hunting strategies. More research is necessary to explore the full therapeutic potential of wolf spider venom, but its unique composition is a promising area of research.
Types of Venom
Wolf spiders are known for their venom that contains a cocktail of diverse compounds. The composition of venom varies significantly from one species to another. Depending on the species, there are different types of venom that a wolf spider can produce. Let’s explore some of the most common venom types produced by wolf spiders.
| Venom Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Neurotoxins | These are the most common types of venom produced by wolf spiders. Neurotoxins affect the nervous system of prey causing paralysis, immobilization, and death. Some examples of neurotoxins include latrotoxin and atracotoxin. |
| Necrotic Venom | Necrotic venom is a type of venom that causes the death of cells and tissues. When injected into prey, this type of venom causes tissue damage, leading to skin necrosis and cell death. This type of venom contains enzymes that break down the tissues of prey. |
| Cytotoxic Venom | Cytotoxic venom is another type of venom that wolf spiders produce. This venom attacks the cells of prey, causing tissue damage and cell death. This type of venom contains enzymes that break down cell membranes. |
| Hemolytic Venom | Hemolytic venom is a type of venom that breaks down red blood cells. This type of venom causes anemia in prey, leading to weakness, dizziness, and death. |
Some wolf spiders can produce a combination of the above venom types. Depending on the species, the venom may contain one or more types of venom. However, research has shown that the most effective venom in prey immobilization is the neurotoxic venom.
Interestingly, research has shown that the venom composition in wolf spiders can vary depending on their hunting success. A study found out that venomous wolf spiders that had more hunting success had venom with a higher concentration of toxic compounds. This suggests that the venom composition in wolf spiders may change over time to match their hunting needs.
Wolf spiders have a diverse venom composition that varies depending on the species. They produce various types of venom, including neurotoxic, necrotic, cytotoxic, and hemolytic venom. However, neurotoxic venom is the most effective type of venom in prey immobilization.
How Does it Work?

Have you ever wondered how wolf spider venom works? The answer lies in the complex composition of the venom, which is made up of a variety of molecules that each play a role in immobilizing the spider’s prey. This process is both fascinating and perplexing, and has been the subject of numerous research studies. Research has shown that wolf spiders have a high hunting success rate due, in part, to the effectiveness of their venomous bites. So what is it about wolf spider venom that makes it so potent? Let’s take a closer look. If you want to learn more about venomous wolf spiders’ hunting success, check out this article.
Toxicity and Enzymatic Activity
Wolf spider venom has been shown to possess both high toxicity and notable enzymatic activity. The toxicity of the venom varies depending on the species of spider and the size and characteristics of the prey. The enzymatic activity of the venom is primarily due to the presence of various enzymes like protease, hyaluronidase, and lipase.
| Enzyme | Function |
|---|---|
| Protease | Breaks down proteins and plays a role in the digestion of prey |
| Hyaluronidase | Degrades hyaluronic acid, a major component of connective tissue, facilitating the spread of venom through tissues and into the bloodstream |
| Lipase | Degrades lipids and aids in the digestion of lipids in prey, assisting in their immobilization |
The venom of wolf spiders has a strong effect on the nervous system of prey, causing various symptoms such as paralysis, tremors, and convulsions. The venom also affects the cardiovascular system, leading to decreased heart rate and blood pressure, which further contributes to the immobilization of prey.
It is important to note that while wolf spider bites are not typically life-threatening to humans, they can cause pain, swelling, and other localized symptoms. In rare cases, individuals may experience more severe reactions, such as anaphylactic shock, which requires immediate medical attention.
The high toxicity and enzymatic activity of wolf spider venom allow these spiders to effectively prey on a wide variety of species and immobilize their prey quickly and effectively. Further research into the specific mechanisms of wolf spider venom could provide insights into its potential therapeutic applications.
Effectiveness in Prey Immobilization
It is well-known that wolf spiders are efficient predators, and their venom plays a key role in immobilizing prey. Wolf spider venom attacks the nervous system of their victim, paralyzing the muscles and rendering them helpless. But just how effective is wolf spider venom at immobilizing their prey? Let’s take a look at some research studies.
A study conducted by the University of California, Berkeley found that the venom of the wolf spider, Lycosa singoriensis, contains several components that work together to induce paralysis in their prey. The study found that the venom is effective at immobilizing insects, with paralysis typically occurring within 1-3 minutes. The researchers noted that the venom was more effective at paralyzing larger prey compared to smaller prey.
Another study published in the Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins including Tropical Diseases found that the venom of wolf spiders contains several neurotoxins that aid in prey immobilization. The study found that the venom of the wolf spider Lycosa godeffroyi was more potent than that of the closely related species Hogna carolinensis. The researchers also found that the venom was able to immobilize a variety of prey, including crickets and flies.
To better understand the effectiveness of wolf spider venom, the table below provides a comparison of the venom of different species of spiders:
| Spider Species | LD50 (mg/kg) | Time to paralysis (minutes) | Target prey |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wolf spider (Lycosa godeffroyi) | 0.35 | 1-5 | Insects, small vertebrates |
| Black widow | 0.33 | 15-60 | Insects, vertebrates |
| Funnel web spider | 0.15 | 10-20 | Insects, vertebrates |
| Tarantula | 2.0 | 5-10 | Insects, small vertebrates |
From the table, it is clear that the venom of the wolf spider is highly effective at immobilizing prey, with a lower LD50 value and a shorter time to paralysis than several other spider species. The wolf spider’s venom is particularly effective against insects and small vertebrates.
The wolf spider’s venom is a potent tool in their hunting arsenal. Its effectiveness in prey immobilization is due to the presence of potent neurotoxins that attack the nervous system of their prey, paralyzing their muscles and rendering them helpless. The wolf spider is an amazing predator that relies heavily on its venom to capture and immobilize its prey.
Research on Wolf Spider Venom
As scientists continue to explore the world of venomous creatures, wolf spiders have caught their attention for their potent venom and potential therapeutic applications. Researchers have conducted numerous studies to better understand the components and effects of wolf spider venom on both prey and humans. In this section, we’ll dive into some of the latest research findings on wolf spider venom, including its therapeutic potential and comparisons to other spider venoms. Let’s explore the fascinating world of wolf spider venom research.
Therapeutic Potential
Wolf spider venom has demonstrated a range of potential therapeutic applications. Here are a few areas where wolf spider venom may be used in the future:
Pain Relief: Certain components of wolf spider venom have been found to possess analgesic properties that can help alleviate pain. Research has found that some of the toxins found in wolf spider venom effectively block pain signals in the nervous system, making it a promising candidate for pain relief medication in the future.
Cancer Treatment: Researchers have discovered that certain compounds found in wolf spider venom may have the ability to selectively kill cancer cells while leaving healthy cells unaffected. One particular compound that has shown promise is the Lycosin-I peptide, which has demonstrated anti-tumor properties in multiple studies.
Anti-Microbial: Studies have shown that certain components of wolf spider venom are effective against a variety of microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi. In particular, the peptide Lycotoxin has been found to have strong anti-fungal properties, which could prove valuable in the development of new anti-fungal drugs.
Neurological Disorders: Some of the compounds found in wolf spider venom have been found to have neuroprotective properties, which could be beneficial in treating a range of neurological disorders. Researchers are currently examining the potential efficacy of these compounds for treating conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s disease.
The therapeutic potential of wolf spider venom is vast, and further studies are likely to uncover even more potential applications for this complex and fascinating substance.
Comparison with Other Spiders
When it comes to spiders, venom is a common denominator, but that’s where the similarities end. There are over 45,000 species of spiders in the world, each with unique venom properties. Wolf spiders stand out amongst their arachnid peers due to their venom’s composition and effectiveness in prey immobilization.
Comparing the venom of wolf spiders to that of other spiders is like comparing apples to oranges. For example, the venom of the funnel-web spider is notorious for its lethality to humans, causing muscular spasms and respiratory dysfunction. On the other hand, the venom of the black widow spider is predominantly neurotoxic, triggering painful muscle contractions and spasms.
When compared to the venom of their hunting spider brethren, wolf spider venom causes moderate to mild neurotoxic effects on prey. The venom (depending on the species) can contain a mélange of peptides, enzymes, and proteins, which produce a wide spectrum of effects, from paralysis to cell death.
The funnel-web spider’s venom, for instance, contains a compound known as delta-atracotoxin, which targets specific ion channels in the nervous system. This toxin is incredibly lethal to humans and other mammals. In contrast, wolf spiders’ venom contains compounds that act on different mechanisms to gradually immobilize their prey.
When compared to other spiders’ venom, the wolf spider’s venom is less lethal to humans but more effective in prey immobilization. Its diverse composition allows it to induce multiple symptoms in prey, from paralysis to cell death, which makes it a formidable weapon in the wolf spider’s arsenal.
Conclusion
After analyzing the science behind wolf spider venom and its effectiveness in prey immobilization, we can conclude that this spider species possesses a potent and complex venom that overwhelms its prey’s nervous system, rendering them immobile and unable to escape.
Additionally, wolf spider venom’s therapeutic potential is still being explored, with some studies indicating that its compounds may have medicinal properties that could be used in the development of new drugs. It is also interesting to note that different types of wolf spider venom have varying levels of toxicity and enzymatic activity, with some species producing lethal venom that could be dangerous to humans.
Furthermore, in comparison to other spider species, wolf spiders appear to have a unique venom composition that sets them apart. Their venom’s impact primarily depends on the species they belong to and their hunting techniques.
In conclusion, the study of wolf spider venom provides an insight into the complex and fascinating world of spider biology. Understanding the science behind venom can help with developing new treatments for various medical conditions. However, caution should be taken when dealing with wolf spiders, as their venom can be harmful to humans and should be treated with respect.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes wolf spiders unique from other spiders?
Wolf spiders are unique from other spiders due to their hunting style and ability to run down their prey. They also have excellent vision and are able to detect motion from up to two feet away.
Is wolf spider venom dangerous to humans?
While wolf spider venom is not deadly to humans, it can cause mild symptoms such as pain, swelling, and itching at the site of the bite.
How does wolf spider venom immobilize its prey?
Wolf spider venom contains a mixture of toxins that work together to immobilize their prey. These toxins can affect the nervous system and muscle function of the prey, ultimately paralyzing it.
Can wolf spiders be kept as pets?
Yes, wolf spiders can be kept as pets. However, it is important to note that they are not as docile as some other spider species and can bite when provoked.
Do all wolf spiders have venom?
Yes, all wolf spiders have venom. However, not all species of wolf spiders have venom that is strong enough to immobilize their prey.
What is the range of a wolf spider?
Wolf spiders can be found worldwide, with some species found in almost every continent except for Antarctica.
How long can a wolf spider live?
Most species of wolf spiders live for about one year. However, some species can live up to several years with proper care.
Can wolf spiders climb walls?
Yes, wolf spiders have the ability to climb walls and other surfaces with their strong legs and claws.
What is the difference between male and female wolf spiders?
Male wolf spiders are typically smaller than females and have more distinct markings on their bodies. Females are also known to carry their egg sacs with them on their abdomen.
How do wolf spiders reproduce?
Male wolf spiders perform a courtship dance to attract females. After mating, the female will lay her eggs and carry them with her until they hatch.