As we observe the animal kingdom, it never fails to amaze us with its incredible diversity and adaptability. From the tiniest insects to mammoth-sized whales, each species has evolved unique characteristics to survive in their respective environments. One such animal that has captured our attention is the wolf spider. These spiders are known for their hunting techniques, but what stands out is the role speed plays in it. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of wolf spiders and explore the crucial role speed plays in their ambush hunting tactics. So, fasten your seatbelts and let’s go on this thrilling journey.
What are wolf spiders?
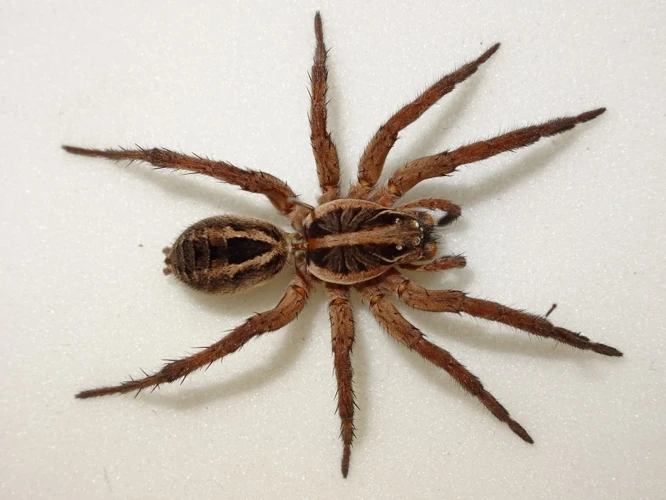

The world of spiders is diverse and fascinating, with each species possessing unique characteristics that set them apart from one another. One such species is the wolf spider, known for its impressive hunting tactics and remarkable physical abilities. These spiders are found all over the world, from the tropical rainforests to the frozen tundra. In this section, we will explore the physical characteristics of wolf spiders, as well as their lifestyle and habitat. We will also examine how they hunt, specifically their ambush hunting technique, and the role of speed in their hunting tactics. For more information on wolf spider hunting methods, take a look at our article on wolf spider ambush hunting techniques.
Physical Characteristics
Wolf spiders are arachnids that belong to the family Lycosidae. These spiders are known for their agility and speed, which are crucial factors for their hunting success. In this section, we will explore the physical characteristics of wolf spiders, which enable them to execute their ambush hunting tactics.
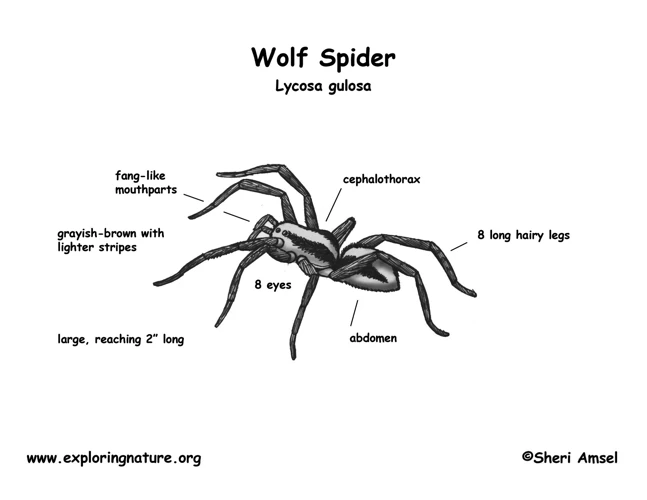
Body Shape and Size: Wolf spiders are generally robust and compact in shape, with a “hairy” appearance. Their body size ranges from small (about 0.04 inch or 1 millimeter) to large (1.38 inches or 35 millimeters). Wolf spiders have two main body parts – the cephalothorax (head and thorax joined together) and the abdomen.
| Body Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Cephalothorax | Large, muscular, dark, and hairy |
| Abdomen | Round, flattened, and covered with hair and setae |
| Eyes | Eight eyes arranged into three rows, with the front row having larger eyes |
| Legs | Strong and agile, with two claws at the end of each leg |
Coloration: Wolf spiders have a unique coloration pattern that varies across species and individuals. This variation is helpful for camouflage hunting in different environments, as some wolf spiders have a darker or lighter body color. Some species have stripes or spot patterns that help them blend in with their surroundings.
Hairs: Wolf spiders have a dense covering of hairs all over their bodies. These hairs have different functions, such as sensory perception and insulation. The hairs on their legs also enable them to climb and cling to surfaces, which is helpful for their hunting tactics.
Wolf spiders have various physical characteristics that make them well-adapted ambush hunters. Their body shape, size, coloration, and hairy covering enable them to succeed in their environments. To learn more about wolf spiders’ hunting tactics, check out our article on Environmental Factors Affecting Wolf Spider Hunting.
Lifestyle and Habitat
Wolf spiders are commonly found throughout the world, in a variety of habitats ranging from deserts to mountains and forests. These solitary creatures are well adapted to their environments and are not known to be aggressive towards humans. Their active lifestyles and hunting behaviors make them an important part of the ecosystem.
Lifestyle:
Wolf spiders are nocturnal hunters, spending their days hiding in burrows or under rocks and debris. They are active hunters, as opposed to passive web-builders, relying on their excellent eyesight and sensory perception to locate their prey. Most wolf spider species are solitary and do not interact with others of their own kind, except for mating.
Habitat:
Wolf spiders are found in a wide range of habitats, from grasslands to deserts, and from forests to marshes. They are most commonly found in areas with lots of ground cover, such as leaf litter, rocks, or debris. Their burrows are made in soil, and they may line their burrows with silk for added stability. Some species of wolf spiders are also known to climb trees or shrubs in search of prey.
These spiders are well known for their hunting and camouflage abilities. They are able to blend in with their surroundings, using their coloring and body posture to avoid detection by both prey and predators. To learn more about wolf spider hunting techniques, visit our article on wolf spider camouflage hunting. Wolf spiders are also very efficient hunters. They are able to capture prey larger than themselves, and they consume a variety of insects and other arthropods. To learn more about their hunting efficiency, visit our article on wolf spider hunting efficiency.
How do wolf spiders hunt?

Have you ever wondered how wolf spiders hunt their prey? These skilled hunters have developed a unique ambush technique that relies heavily on their physical attributes and lightning-fast reflexes. Through a combination of patience, speed, and accuracy, they are able to take down prey much larger than themselves. Let’s explore the fascinating world of wolf spider hunting and the techniques they use to survive in the wild.
The Ambush Hunting Technique
The ambush hunting technique used by wolf spiders is a form of sit-and-wait predation. They do not actively chase and pursue their prey but instead remain motionless and hidden until suitable prey comes within reach. Once prey is in range, they use their exceptional speed to launch a lightning-fast attack.
Advantages
This hunting technique has several advantages. Firstly, it conserves energy as it minimizes the expenditure required to catch prey. Secondly, it allows them to capitalize on their speed as they only need to sprint for a short distance to capture their prey. Lastly, it increases their chances of success as they are not expending energy in capturing prey that may be too large or difficult to subdue.
Disadvantages
However, this technique also has its disadvantages. It requires excellent camouflage and patience, making it unsuitable in areas with limited cover. Additionally, it relies on the spider’s visual acuity, so it may not be successful in low light conditions.
To make up for these disadvantages, wolf spiders employ a range of adaptations to enhance their ambush hunting technique. These include their incredible speed, precise vision, and specialized leg and muscle structure. Wolf spiders also determine their prey size and type to gauge their chance of success before initiating an attack.
The Role of Speed in Ambush Hunting
For wolf spiders, speed is a critical factor in ambush hunting, allowing them to quickly capture their prey before it can escape. These spiders are able to move with lightning-fast speed, which is key to their success as ambush predators.
Some of the reasons why speed is so important in this hunting technique are highlighted in the table below:
| Predator’s Perspective | Prey’s Perspective |
|---|---|
| Surprise Attack: The element of surprise is critical to the success of an ambush hunter like the wolf spider. By moving quickly and quietly, the spider is able to get close to its prey undetected, and quickly spring into action before the prey can react. | Evading Attack: Prey species have evolved a range of strategies to evade predators, such as quick bursts of speed, camouflage, and mimicry. By moving at high speeds, the wolf spider is able to overcome these strategies and catch its prey before it can escape. |
| Accuracy: Moving quickly allows the wolf spider to accurately target its prey, ensuring that it can make a successful capture. This is particularly important for small prey, which can be difficult to catch with slower movements. | Survival: From the prey’s perspective, surviving an attack from a predator like the wolf spider requires quick reflexes and the ability to move quickly. Slower prey is at a huge disadvantage, allowing the wolf spider to easily catch and kill its intended target. |
| Energy Efficiency: Moving quickly and accurately minimizes the amount of energy expended in the hunting process. This is important for the wolf spider, as it needs to conserve precious energy resources to survive in the wild. | Energy Use: For the prey, moving quickly requires a significant amount of energy, which can be a disadvantage if the prey is not as energy-efficient as the wolf spider. |
As can be seen from the table, speed is a critical component of the wolf spider’s ambush hunting techniques, giving it a significant advantage over its prey. By moving quickly and accurately, the wolf spider can survive and thrive in the wild, using the element of surprise and superior hunting skills to capture its prey.
Factors Affecting Speed
Speed is a crucial factor for wolf spiders during ambush hunting, but it can be affected by various factors. Some of the main factors affecting a wolf spider’s speed during ambush hunting include:
- Movement of Prey: Wolf spiders’ speed is heavily influenced by the movement patterns of their prey. When an approaching prey moves in a predictable path, the wolf spider can easily predict its trajectory and adjust its approach angle accordingly, resulting in a greater chance of successful ambush. Conversely, prey with erratic movement patterns or sudden changes in direction can pose a challenge for wolf spiders to catch, making their movements less precise and slower.
- Environmental Factors: The environment in which the spider is hunting can also influence its speed. For instance, surfaces with low traction, such as sand or mud, can reduce the spider’s running speed, while smooth surfaces like leaves or twigs are conducive to fast movements.
- Body Condition: The wolf spider’s body condition also plays a vital role in determining its speed during ambush hunting. Injured or sick spiders may not be able to run as fast as healthy spiders, reducing their chances of successfully hunting their prey.
- Time of Day: Wolf spiders are more active at night, when they have evolved to hunt, and may be more successful ambush predators during those hours.
Many factors can affect a wolf spider’s speed during ambush hunting and hunting success. Conserving energy and maintaining good health through proper nutrition and rest are essential for sustained speed and optimal performance during hunting.
Prey Size and Type
The size and type of the prey can greatly affect the speed at which wolf spiders hunt. As shown in the table below, larger prey such as crickets and grasshoppers require much higher speeds to be caught, while smaller prey such as ants and flies can be caught at lower speeds. This is because larger prey typically have higher escape speeds and are able to detect predators from farther away.
| Prey Type | Average Size | Escape Speed (cm/s) | Required Speed (cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crickets | 2-3 cm | 40-50 | 70-80 |
| Grasshoppers | 3-4 cm | 50-60 | 90-100 |
| Beetles | 1-2 cm | 20-30 | 40-50 |
| Flies | 0.2-0.5 cm | 10-20 | 20-30 |
| Ants | 0.2-0.3 cm | 5-10 | 10-15 |
The speed required to catch different types of prey is also affected by the wolf spiders’ body size. As wolf spiders increase in size, their required speed to catch prey also increases. This is because larger spiders have a greater distance to cover to reach their prey, and require more momentum to capture it. Smaller spiders can catch smaller prey at lower speeds because their body size is better suited to handle the force needed to capture these prey.
Wolf spiders are highly adapted to hunt different types of prey using their unique ambush hunting technique. The ability to adjust their speed based on the size and type of prey is a crucial component of their hunting strategy.
Adaptations for Speed and Accuracy
The wolf spider’s ambush hunting technique requires it to be quick and precise in its movements, and in order to do so, it has developed a range of adaptations that help with speed and accuracy. These adaptations are crucial to the wolf spider’s survival in the wild, and they have evolved over time to perfectly suit the spider’s hunting needs. Let’s delve into some of the fascinating adaptations that make the wolf spider such a formidable hunter.
Vision and Perception
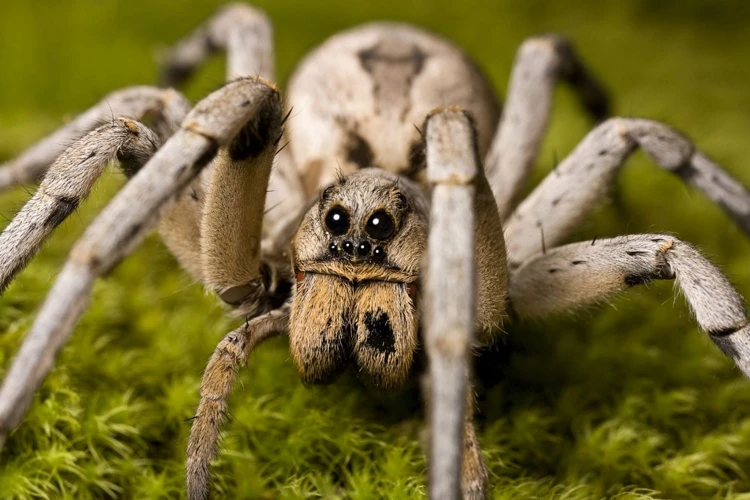
Wolf spiders have a highly developed visual system that is specialized for detecting prey and predators. Their eyes are made up of eight simple eyes that are arranged in three rows, with the middle row containing the largest eyes.
Acute vision: The large central eyes provide the wolf spider with acute vision and a wide field of view, allowing them to perceive even small movements of their prey and predators. These eyes are adapted to low light conditions, making it easier for the spiders to hunt during nighttime.
Depth perception: The two smaller eyes at the front of the head enable wolf spiders to have good depth perception, which is essential for their ambush hunting technique.
Color vision: Although wolf spiders are not known for having color vision, they have a greater sensitivity to contrast. This means they are able to differentiate between dark and light areas more easily, which is particularly useful in low light conditions.
In addition to their eyes, wolf spiders also have specialized hairs on their legs called trichobothria. These hairs are extremely sensitive to movement and vibrations in the air, allowing the spiders to detect the presence of potential prey even when they cannot see it.
The combination of acute vision and sensitivity to vibrations allows wolf spiders to detect and locate prey with great accuracy. This, in turn, enables them to make quick and accurate attacks, subduing their prey within seconds.
Leg Anatomy and Muscle Structure
The leg anatomy and muscle structure of wolf spiders play a crucial role in their ambush hunting tactics. The unique structure of their legs allows them to move with incredible speed and remain precise as they pursue their prey.
Leg Anatomy: Wolf spiders have eight legs that are divided into three main parts – coxa, femur, and tibia. The coxa is the base of the leg, and it is attached to the cephalothorax. The femur is the largest part of the leg and is responsible for most of the spider’s movement. The tibia is the narrow part of the leg that connects to the tarsus, which contains the spider’s claws.
Muscle Structure: Wolf spiders have specialized muscles in their legs that allow them to move with incredible speed and precision. These muscles are arranged in a unique manner that allows the spider to generate a lot of force with each movement. The muscles are also arranged in such a way that they can contract and relax quickly, giving the spider an advantage in capturing its prey.
To better understand how the leg anatomy and muscle structure of wolf spiders works, let’s take a look at a comparison table of the leg structure between humans and wolf spiders:
| Humans | Wolf Spiders | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of legs | 2 | 8 |
| Main leg parts | Thigh, calf, and foot | Coxa, femur, and tibia |
| Leg muscle arrangement | Parallel to the bone | Perpendicular to the bone |
| Muscle force generation | Dependent on the muscle cross-sectional area | Dependent on muscle arrangement in a fan-like structure |
As you can see from the table above, the leg anatomy and muscle structure of wolf spiders is incredibly different from that of humans. This difference allows wolf spiders to move with incredible speed and precision, making them formidable hunters in their environment.
The leg anatomy and muscle structure of wolf spiders are essential factors in their ambush hunting tactics that require speed and agility. These unique adaptations allow them to move with lightning-fast speed through their environment and capture prey with precision and accuracy, making them one of the most unique and fascinating creatures in the animal kingdom.
Neurological Specializations
Wolf spiders possess an intricate neurological system that is specialized for efficient and skillful hunting. Their unique neuroanatomy allows them to process sensory information and react quickly to changes in their environment. Some of the most important neurological specializations observed in wolf spiders include:
- Large Brain to Body Ratio: Studies have shown that wolf spiders have larger brain to body ratios compared to other spiders of similar size. This indicates that they have a more developed nervous system, which could explain their advanced hunting tactics.
- Advanced Visual Processing: Wolf spiders have unique vision systems that allow them to process visual information quickly and accurately. They have excellent depth perception, which helps them to judge distances accurately and make precise movements to capture prey.
- Rapid Reaction Times: The neurological specializations in wolf spiders enable them to react quickly to prey movements or other environmental changes. They can react to visual stimuli in as little as 40 milliseconds, which is much faster than other spiders.
- Specialized Ganglia: Wolf spiders have specialized nerve ganglia that are dedicated to processing and integrating sensory information. These ganglia are found in various parts of their body, including the legs, eyes, and pedipalps, and play a crucial role in coordinating their hunting movements.
The neurological specializations observed in wolf spiders provide them with a significant advantage when it comes to ambush hunting. Their ability to process sensory information quickly and react with speed and precision allows them to capture prey efficiently and effectively.
Conclusion
After exploring the hunting techniques of wolf spiders, it’s clear that speed plays a crucial role in their ambush tactics. Their ability to swiftly catch moving prey has allowed them to thrive in various habitats and ecosystems. This impressive speed is not only due to their anatomical adaptations but also their exceptional vision and neurological abilities.
It’s fascinating to learn how wolf spiders are capable of adjusting their speed based on their prey size and type, as well as environmental factors. Their leg anatomy and muscle structure also give them the advantage of agility, allowing them to make quick turns and adjust their direction mid-sprint. These adaptations have helped them become successful hunters and apex predators in their ecosystems.
Furthermore, studying the role of speed in wolf spider hunting techniques can provide insights into the evolutionary history of this species. Researchers may uncover how they have evolved to hunt efficiently in their environment over time.
In conclusion, the role of speed in wolf spiders’ ambush hunting tactics cannot be underestimated. Their anatomical, neurological, and sensory adaptations allow them to be agile and swift hunters. The study of these fascinating creatures expands our knowledge of the complexity of animal behavior and the importance of speed in predator-prey relationships.
Frequently Asked Questions
How fast can wolf spiders run?
Wolf spiders can run at speeds of up to 2 feet per second.
What is the average lifespan of a wolf spider?
The lifespan of a wolf spider varies depending on the species, but most live for around 1-2 years.
Do wolf spiders bite humans?
Yes, wolf spiders are capable of biting humans if they feel threatened. However, their venom is not considered dangerous to humans.
What is the ambush hunting technique?
The ambush hunting technique is when a predator, such as a wolf spider, waits quietly for their prey to come within striking distance before attacking.
What is burst speed?
Burst speed is the maximum speed a predator, such as a wolf spider, can reach in short bursts of energy to catch their prey.
What is the role of speed in wolf spider hunting?
Speed is crucial for wolf spiders during their ambush hunting technique as it allows them to quickly catch their prey before it has a chance to escape.
What factors affect a wolf spider’s speed?
The size and type of the prey, the terrain, and ambient temperature are all factors that can affect a wolf spider’s speed.
How do wolf spiders perceive their prey?
Wolf spiders have excellent vision and use it to detect movement and locate prey.
What adaptations do wolf spiders have for speed and accuracy?
Wolf spiders have specialized vision, leg anatomy and muscle structure, and neurological adaptations that allow them to move quickly and with precision.
Are wolf spiders beneficial to the environment?
Yes, wolf spiders are beneficial to the environment as they prey on a variety of insects and pests, helping to regulate their populations.