Introduction
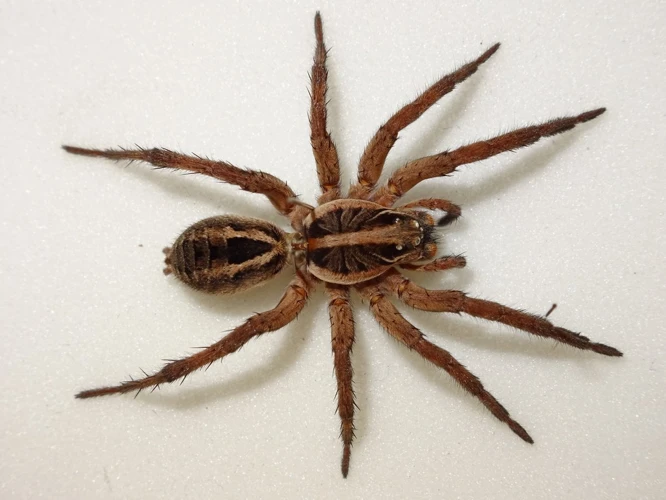

As we delve into the fascinating world of wolf spiders, it is important to understand their origins and evolution. These arachnids have evolved into an incredibly diverse group of species, with adaptations that allow them to thrive in various ecosystems. In this article, we will explore the anatomy, physiology, and evolutionary biology of wolf spiders, as well as their ecological significance. By further understanding these creatures, we can gain insights into their place in the food chain and the role they play in maintaining ecosystems. Let’s begin our journey into the world of wolf spider evolution.
Overview of wolf spiders
Wolf spiders are a diverse group of arachnids that belong to the family Lycosidae. There are around 2,300 known species of wolf spiders, which are found all over the world, with different habitats and lifestyles. These spiders are so named because of their hunting behavior, which mimics that of wolves.
Key characteristics of wolf spiders include:
- Wolf spiders have eight legs, two main body parts, and four pairs of eyes positioned on the front of their head.
- They are usually brown, gray, or black in color, with a hairy body and long legs.
- They can range in size from 0.04 to 1.18 inches (1 to 30 mm) in length and can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, deserts, and wetlands, among others.
- These spiders can be active both during the day and at night, depending on their species and habitat.
Behavioral and ecological characteristics of wolf spiders include:
- They are solitary hunters and do not spin webs to catch prey.
- Instead, they chase after their prey on foot, using their excellent eyesight and speed.
- Wolf spiders feed on a range of invertebrates and other small animals, including insects, other spiders, and even small vertebrates such as lizards.
- Female wolf spiders carry their eggs in a sac attached to their spinnerets, and sometimes also carry their young on their back.
Understanding the overall characteristics and natural history of wolf spiders is crucial to their study. Many researchers are interested in the diversity and distribution of this group of spiders, as well as their ecological significance. You can find more information about wolf spider species’ physical characteristics and diversity guide in this guide.
Importance of studying wolf spider evolution
Studying the evolution of wolf spiders is crucial in understanding the vast biodiversity of spider species and their ecological significance. Understanding the intricacies of the evolution of wolf spiders can shed light on how these predators have adapted to their environments over time, and how they have managed to survive and thrive despite the many challenges they face.
The significance of studying wolf spider evolution can be broken down into several points:
- Insights into physical characteristics: By exploring the evolutionary history of wolf spiders, we can gain insights into the physical characteristics that have allowed them to survive and evolve over millions of years. Studying the physical traits of different wolf spider species can help us determine the factors that have contributed to the immense diversity of wolf spiders we see today.
- Understanding distribution and diversity: Studying the evolution of wolf spiders can also help us understand why some species are distributed more widely than others, and why certain species have different physical characteristics that allow them to thrive in specific habitats. Exploring wolf spider distribution can also give us a better understanding of the ecological roles they play in different ecosystems. (source)
- Genetic factors in species diversity: Understanding the genetic factors that drive the diversification of wolf spiders can provide insights into the mechanisms of speciation and hybridization. By studying the genetic makeup of different wolf spider species, we can determine the relationships between species and identify potential hybrids. These insights can help us better understand the reproductive isolation mechanisms that prevent hybridization and the development of new species. (source)
- Ecological significance in food webs: Wolf spiders play an essential role in food webs and ecosystems, making them a crucial subject of study. By understanding the ecological significance of different wolf spider species, we can gain insights into their interactions with other species and the impacts they have on their environments. We can also study how they respond to environmental changes and how they are affected by human activities. (source)
- Conservation implications: Finally, studying the evolution of wolf spiders can have significant implications for their conservation and preservation. By understanding their evolutionary history and ecological significance, we can identify the threats to their survival and take action to protect them. Emerging technologies in molecular studies offer new possibilities for exploring wolf spider diversity and assessing their conservation status. (source)
As we can see, studying the evolution of wolf spiders can provide us with valuable insights into the biodiversity of spider species, their interactions with other species, and the factors that have driven their evolution over millions of years. By gaining a better understanding of their physiology, genetics, and ecological significance, we can develop more effective strategies for their conservation and protection.
Wolf Spider Origins
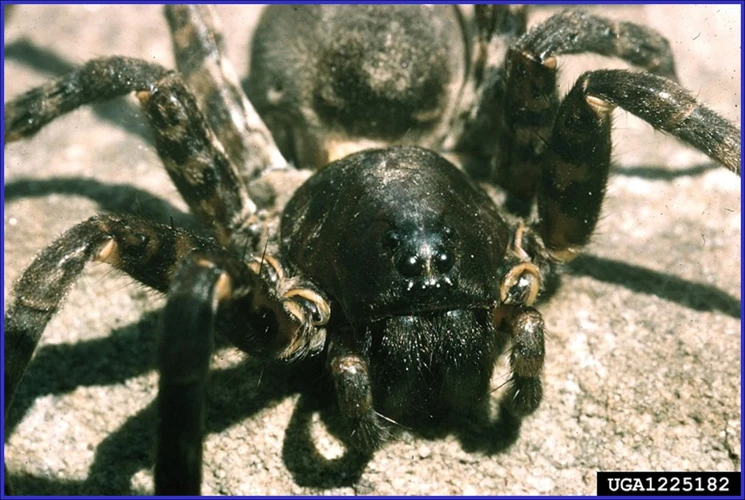

The origin of wolf spiders can be traced back to their ancestral relationships with other spider species and their early fossil records. These spiders belong to the Lycosidae family, one of the largest spider families known. It is believed that wolf spiders evolved from a common ancestor with other hunting spiders and developed unique features that allowed them to adapt to different environments. These features will be discussed later in this article under the section on Anatomy and Physiology. To learn more about physical characteristics and hybridization of wolf spiders check out our articles on wolf spider species physical characteristics and wolf spider hybrids, species diversity, and reproductive isolation respectively.
Ancestral relationships with other spider species
Wolf spiders belong to the family Lycosidae, which includes over 2000 species. They are closely related to other spider families, including Pisauridae (nursery web spiders) and Oxyopidae (lynx spiders). Despite their similarities, each family has distinct characteristics that make them unique. For instance, Lycosids are known for their distinctive eye arrangement, with four small eyes in a row and two larger eyes above. This arrangement allows them to have exceptional vision, which is important for hunting. In contrast, Pisaurids have eight eyes arranged in two rows, and Oxyopids have relatively large frontal eyes adapted for acute vision in dim light.
Despite these differences, genetic analyses have revealed surprising ancestral relationships between wolf spiders and other spider families. For example, a study conducted in 2017 found that wolf spiders are more closely related to jumping spiders (family Salticidae) than previously thought. This study was based on a molecular analysis of 14 genes from 181 spider species, providing strong evidence of the evolutionary relationships between spider families. The results showed that Lycosids and Salticids diverged from a common ancestor about 220 million years ago.
Other studies have also shed light on the evolutionary relationships between spider families. For example, a study conducted in 2019 used morphological and molecular data to explore the phylogenetic relationships between the families within the superfamily Lycosoidea. This study found that wolf spiders (Lycosidae) and nursery web spiders (Pisauridae) are sister groups, which means they share a common ancestor. This finding challenges previous assumptions about the relationships between spider families and highlights the need for more detailed research.
The ancestral relationships between wolf spiders and other spider families are complex and fascinating. Ongoing research is helping to uncover new insights into the evolutionary history of these amazing creatures, and we can look forward to learning more about their genetic and morphological adaptations in the future.
Early fossil records of wolf spiders
Scientists have relied heavily on the study of fossils to understand the evolution of wolf spiders. The earliest fossil records of wolf spiders date back to the Mesozoic Era, around 120 million years ago. These fossils are crucial in tracing the early origins and evolutionary history of these unique spiders.
One of the most notable features of early wolf spider fossils is their similarity to modern-day wolf spiders. These ancient fossils share many distinctive features with their present counterparts, including their stout body shape, elongated legs, and impressive hunting abilities. This suggests that wolf spiders have undergone minimal morphological change over millions of years of evolution.
Table: Early Fossil Records of Wolf Spiders
| Fossil | Age (million years ago) | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lycosiphytum | 120 | Brazil | Fossilized trackways of wolf spiders |
| Acantholycosa lignitifera | 30 | Germany | Fossilized wolf spider preserved in lignite |
| Lycosites | 23 | Dominican Republic | Fossilized wolf spider preserved in amber |
| Lycosa exquisita | 18 | Burma | Fossilized wolf spider with ornate markings on the carapace |
Some of the most significant discoveries in recent years have come from fossils preserved in amber, which capture the details of these spiders with unprecedented clarity. One such discovery includes the fossil of a wolf spider with ornate markings on its carapace, which is dated to around 18 million years ago and was found in Burma. These fossils offer valuable insight into the evolutionary adaptations of wolf spiders and how these adaptations have allowed them to survive and thrive over millions of years.
Anatomy and Physiology
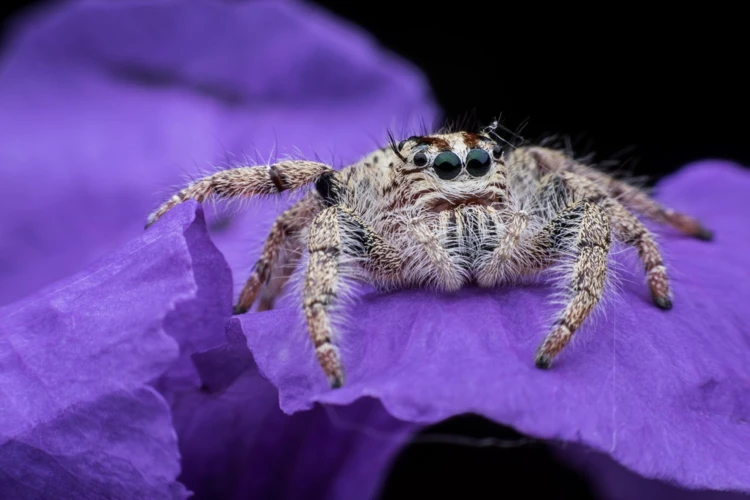

As we delve deeper into the evolution of wolf spiders, it’s important to take a closer look at their anatomy and physiology. These distinctive arachnids have unique features and adaptations that have allowed them to thrive and survive for millions of years. From their impressive hunting techniques to their physiological changes over time, the anatomy and physiology of wolf spiders offer valuable insights into their evolutionary history and ecological diversity. In this section, we’ll explore the fascinating world of wolf spider physiology and the factors that have contributed to their success as a species.
Distinctive features of wolf spiders
Wolf spiders are a diverse group of arachnids that have a number of distinctive features that set them apart from other spider species. Let’s take a closer look at some of these unique characteristics:
| Feature | Description |
| Eyes | Wolf spiders have large, forward-facing eyes that provide them with excellent depth perception and the ability to detect movement from a distance. |
| Hunting style | Unlike other spiders that spin webs to catch their prey, wolf spiders are active hunters that chase down their victims on foot. They use their speed and agility to catch a wide variety of insects and other small creatures. |
| Size | Wolf spiders come in a range of sizes, but many species are relatively large and can grow up to several inches in length. This makes them one of the largest families of spiders in the world. |
| Coloration | Wolf spiders are typically brown or gray, with some species featuring distinctive markings or patterns on their bodies. This coloration helps them blend in with their surroundings and avoid predators. |
| Mating behavior | Male wolf spiders are known for their unique mating behavior, which involves using specialized pedipalps to transfer sperm to the female. This behavior has evolved as a way to ensure that the male’s genes are passed on to future generations. |
| Legs | Wolf spiders have long, powerful legs that enable them to run and jump with incredible speed and precision. Their legs are covered in tiny hairs and bristles that help them grip onto surfaces and move quickly. |
These distinctive features have enabled wolf spiders to adapt to a wide range of habitats and ecological niches over the course of their evolution. From their hunting style and size to their unique mating behavior and coloration, these arachnids are truly one of a kind in the world of spiders.
Adaptations for hunting and survival
Wolf spiders have evolved several distinctive adaptations for hunting and survival that have enabled their success in the natural world.
Vision: They have excellent vision, thanks to their big eyes located at the front of their cephalothorax, or “head”. Wolf spiders use their vision to spot prey, navigate their surroundings, and avoid predators.
Silk: Unlike many other spider species, wolf spiders do not construct webs to catch prey. Instead, they use silk in other ways. Adult females often create silk-lined burrows in the ground, which they use for shelter, molting, and raising their young. Spiderlings may also create small silken “draglines” to help them float or travel through the air.
Senses: Wolf spiders rely on sensory receptors on their legs to detect sound and vibrations. They can pick up on the movement and location of potential prey or predators from quite a distance away through tiny hairs and trichobothria.
Speed: Wolf spiders are incredibly fast and agile predators. They are able to chase after and capture their prey on the ground or in the air with their powerful, muscular legs. Their long, spiny legs allow them to grip onto their prey for extended periods of time, while also providing balance and stability as they move throughout their environment.
Camouflage: Many species of wolf spider have evolved to have coloration or markings that blend in with their surroundings, making them difficult to spot by both predators and prey alike. They may also have tufts of hair or spines that mimic nearby plant material or soil.
These adaptations make wolf spiders not only incredibly effective hunters, but also resilient survivors in a variety of environments, from forests and deserts to grasslands and wetlands.
Physiological changes over time
As wolf spiders evolved over time, they underwent several physiological changes that allowed them to thrive and adapt in various environments. Here are some of the key changes that have taken place:
| Physiological Changes | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased size | As wolf spiders adapted to different prey and environments, some species grew larger in size. For example, the Hobo spider (Tegenaria agrestis) can reach up to 18 millimeters in length. |
| Better vision | Wolf spiders have keen eyesight and can detect movement up to a few feet away. Their eyes have also evolved to detect polarized light, which helps them navigate and hunt. |
| Increase in venom potency | Wolf spider venom varies in potency depending on the species, but recent studies have shown that some species have increased venom toxicity over time. This adaptation may be in response to changes in prey availability and increased competition. |
| Improved camouflage | Some wolf spiders have adapted to blend in with their environment, allowing them to better evade predators and hunt prey. For example, the Desert Wolf Spider (Tigrosa georgicola) has a sand-colored body and brown spots that help it blend in with its surroundings. |
| Changes in reproductive behavior | As wolf spiders evolved, their reproductive behavior also changed. Some species have developed elaborate courtship displays, while others have evolved to reproduce asexually, allowing them to expand their range and colonize new habitats. |
These physiological changes have allowed wolf spiders to successfully adapt and survive in a range of environments and ecological niches. As research into wolf spider evolution continues, we may discover even more adaptations and changes that have taken place over millions of years.
Evolutionary Biology of Wolf Spiders
As we dive deeper into the world of wolf spiders, it’s important to understand the evolutionary biology behind their existence. Through genetic analyses and speciation, these arachnids have undergone significant changes to adapt and thrive in various environments. Let’s explore the fascinating journey of wolf spider evolution and the factors that contribute to their ecological diversity.
Genetic analyses of wolf spider species
Wolves are considered to be one of the most diverse spider families due, in part, to their remarkable ability to adapt to various environments. Their evolutionary history is a fascinating subject of study, and one of the most useful tools researchers have for understanding this history is genetic analysis.
Studies of wolf spider DNA have enabled researchers to analyze evolutionary relationships within the family, and to determine which species are most closely related. One study, for example, found that H. graminicola is the sister group to a clade comprising H. puncturata and H. paganettii. These genetic analyses have also provided insight into the patterns and processes underlying wolf spider diversification.
To better understand the genetic makeup of different wolf spider species, researchers have analyzed the DNA sequence of various genes. In one study, researchers analyzed the sequence of the mitochondrial gene cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) and found that it was useful in differentiating between wolf spider species. A table outlining the differences in COI sequences among several wolf spider species is shown below:
| Species | COI Sequence |
|---|---|
| Lycosa tarentula | AAGGTGTATTCTAATTTTGATCATTTTTATCATTTGTGAGCACAGTATATTCTATTCGGTAACTGCTGGGCACTTATTAGGAGATGACCAAATTTATAATGTTATTATTAACAGCTCATGCCTTTATTATAATTTTCTTTATAGTAATACCAATCATAATTGGGGGATTTGGAAACTGGCTAGTTCCTTTAATAATTGGTGCCCCCGATATAGCCTTTCCCCCGTATAAATAATATAAGTTTCTGACTCCTACCTCCCTCTTTTAACTTCTACTTGTTGAGAAGTTGTTGAACTGGTGCAGGTAAAATGGAGCCGTTGACTGGATTTAACAATTTTTTCTTTACATCTAGCAGGTGTATCTTCTATTCTTGGGAGCCATTAACTTTATTACTACTATTATCAATTTTATTACTACTATTTTTAATATACGGTATTTGGAATACTATAGTACCAGTGATCTGATACAGCCTTTTTGTTTGAGCAGTATTAGTTACAGCTGTACTTCTACTCCTGTCTCTCCCAGTTTTAGCTGGTGGTATCACTATACTTTTAACTGATCGAAATCTAAATACCACATTCTTTGACCCAGCAGGAGGAGGTGATCCTATTTTATTTCAACATCTTTT |
| Tigrosa helluo | AAGGTGTAATCATTGCTTGATCATTTTCTATTTGGTGAGCACAGTA IA TTCTATTCTGTAACTGCTGGACAATTACTAGGAGATGACCAAATTTATAATGTTATTATTACTAGCTCATGCCTTTATTATAATTTTCCTTAACTAGTAATACCAATCGTATTGGGGGATTTGGAAACTGGCTAGTTCCTTTAATAATTGGTGCCCCCGATATAGCCTTTCCCCCGAATAAATAATATAAGTTTCTGACTGCTACCTCCCCCTCTTTTAACTTCTGTTGAGAAGTTGTTGGATCGGCGCAGGTAAAATGGAGCCGTTGACTGTGTTTACAATTTTTTCTTTACATCTAGCAGGTGTATCTTCTATTTTAGGAGCCATTAACTTTATTACTATTATCAATTTTATTACCTATTATTTTTAATATAAAATATTTGAGGATAAATAACTTAACTCACAGTTGTATTAATACATTTAACTGATCGAAACCTAAATACCACATTCTTTGACCCAGCAGGAGGAGGAGATCCTATTTTATTTCAACATTTATTT |
| Hogna carolinensis | AAGGTGTAATCATTGCTTGATCATTTTCTATTTGGTGAGCACAGTATATTCTATTCTGTAATTGCTGGACAATTTTTAGGAGACGACCAAATTTATAATGTTATTATTACTAGCTCATGCCTTTATTATAATtttccttAACTAGGAATACCAATCGTATTGGGGGATTTGGAAACTGGCTAGTTCCTTTAATAATTGGTGCCCCCGATATAGCCTTTCCCCCGAATAAATAATATAAGTTTCTGACTGCTACCTCCCCCTCTTTTAACTTCTGTTGAGAAGTTGTTGAACTGGGGCAGGTAAAATGGAGCCGTTGACTGTGTTTACAATTTTTTCTTTACATCTAGCAGGTGTATCTTCTATTTTAGGAGCCATTAACTTTATTACTATTATCAATTTTATTACCTATTATTTTTAATATAAAATATTTGAGGATAAATAACTTAACTCACAGTTGTATTAATACATTTAACTGATCGAAACCTAAATACCACATTCTTTGACCCAGCAGGAGGAGGAGATCCTATTTTATTTCAACATTTATTT |
As can be seen from the table, the COI sequences for each species are quite distinct, and can be used as a reliable marker to differentiate between species. These findings highlight the importance of genetic analyses in understanding the evolutionary biology of wolf spiders, and may pave the way for future research in this area.
Speciation and diversification
One of the most fascinating aspects of wolf spiders is their incredible speciation and diversification over time. This process is the mechanism that allows for the creation of new species from existing ones and has resulted in the vast array of unique and diverse wolf spider species we see today.
Speciation: Speciation occurs when a population of a species becomes isolated from the main group and evolves in response to different environmental pressures, leading to the development of distinct characteristics. This can happen through a variety of mechanisms, such as geographic isolation, genetic drift, or natural selection. In the case of wolf spiders, speciation has resulted in more than 2,000 species worldwide, each with its own unique adaptations and abilities.
Diversification: Diversification, on the other hand, refers to the evolutionary process by which a single lineage gives rise to multiple, distinct lineages through speciation. This is particularly relevant in the case of wolf spiders, where a single ancestral species has given rise to an incredible variety of different species, each with its own unique traits and behaviors.
To better understand the speciation and diversification of wolf spiders, scientists have conducted a range of studies, including genetic analyses, phylogenetic studies, and morphological analyses. These studies have allowed scientists to identify key factors that have contributed to the incredible diversity of wolf spiders, such as geographic isolation, environmental factors, and reproductive barriers.
To further illustrate the diversity of the wolf spider species, we have created a table showing some of the unique characteristics and adaptations of several different wolf spider species:
| Species | Distinguishing Characteristics | Adaptations |
|---|---|---|
| Lycosa tarantula | Large size, banded legs | Powerful venom, fast running speed |
| Trochosa ruricola | Small size, metallic green coloration | Excellent camouflage, agile hunting ability |
| Sosippus californicus | Red markings on legs, elongated body | Ability to jump long distances, fast reflexes |
As we can see from the table, each species of wolf spider has its own unique features and abilities, highlighting the incredible diversity that has been developed over time through the process of speciation and diversification.
Factors contributing to ecological diversity
Ecological diversity among wolf spider species can be attributed to a variety of factors, ranging from environmental pressures to genetic mutations. The following table outlines some of the key factors that have contributed to the remarkable diversity of wolf spiders:
| Factor | Description |
| Geographical Isolation | Isolated populations of wolf spiders have evolved to adapt to their specific environmental conditions, leading to the development of distinct characteristics and behaviors |
| Climate Variability | The changing climate over time has shaped the evolution of wolf spiders by selecting for traits that allow them to survive and reproduce in different temperature and moisture conditions |
| Prey Availability | The abundance and types of prey available in a given environment has influenced the development of wolf spiders’ hunting strategies and morphology |
| Competition | The presence of other predators and competitors in an ecosystem has driven the evolution of wolf spiders to become more efficient and specialized hunters |
| Genetic Drift | Random mutations in a population’s genetic makeup can lead to the development of new traits and characteristics that contribute to ecological diversity among wolf spider species |
These various factors have worked in tandem to create the vast array of wolf spider species that exist today, each adapted to their specific ecological niches. By understanding the origins and evolutionary processes of wolf spiders, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and diversity of the natural world.
Ecological Significance of Wolf Spiders
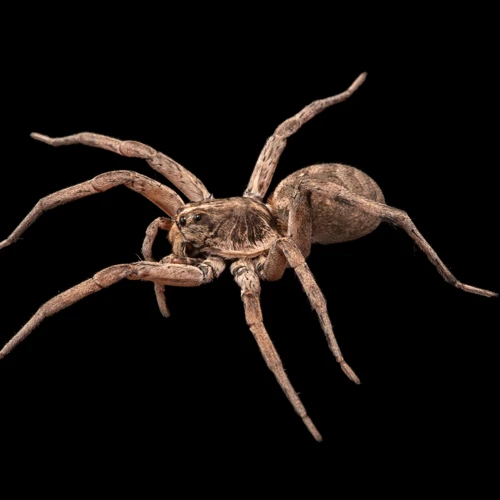

As with any species, wolf spiders play a crucial ecological role in their respective ecosystems. These predatory arachnids are both the hunters and the hunted, interweaving themselves into the food webs of various habitats. Understanding the ecological significance of wolf spiders involves examining their relationships with other organisms, as well as how they are affected by environmental changes. Let’s delve further into the world of wolf spiders and explore their ecological importance.
Role in food webs and ecosystems
When it comes to the role that wolf spiders play in food webs and ecosystems, they are often considered to be important predators. In fact, wolf spiders are known to consume a wide range of prey, including insects, other spiders, and even small vertebrates. This makes them a critical part of many different ecosystems, especially in areas where they are abundant.
One important aspect of their role in food webs is that they help to control the populations of other arthropod species. For example, if there is an outbreak of a certain type of insect in a particular ecosystem, wolf spiders may prey on that insect and reduce its population. This, in turn, can prevent the insect from causing significant damage to crops or other important plants.
In addition to their direct impact on other arthropods, wolf spiders also play an important indirect role in food webs. For example, they are preyed upon by a variety of other species, including birds, lizards, and other predators. This means that their presence in an ecosystem can contribute to the overall health and diversity of that ecosystem, helping to maintain a balance between different species.
To illustrate the importance of wolf spiders in food webs and ecosystems, we can take a look at the table below, which lists some of the species that they commonly prey upon and some of the species that commonly prey upon them.
| Predators | Prey | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Birds | Robins, sparrows, finches | Insects | Crickets, grasshoppers, beetles, flies |
| Lizards | Green anoles, skinks | Other Spiders | Jumping spiders, orb weavers, cellar spiders |
| Other Predators | Mantids, assassin bugs, robber flies | Small Vertebrates | Frogs, lizards, mice |
As you can see, wolf spiders are an important part of the diets of many different predators, while also consuming a diverse range of prey themselves. This level of interconnectedness highlights the critical role that wolf spiders play in maintaining the health and balance of many different ecosystems.
The role of wolf spiders in food webs and ecosystems is multifaceted and complex. They are important predators, controlling the populations of other arthropods, while also serving as prey for a variety of other species. This highlights the need for continued research into the ecological significance of wolf spiders, as well as the importance of their conservation and preservation.
Relationships with other species
Wolf spiders have various relationships with other species in their ecosystem, ranging from prey-predator interactions to symbiotic relationships. One of the most notable prey-predator relationships the wolf spider has is with birds. Many species of birds, such as robins and blue jays, rely on wolf spiders as a significant food source. Indeed, wolf spiders make up a large share of the diets of many bird species, particularly during the breeding season when the demand for food is high.
On the other hand, wolf spiders also form symbiotic relationships with other species such as burrowing owls. These owls use abandoned spider burrows as their nest sites, which provides a safe and secure nesting place for the owls and helps the spiders as well, as the owl maintains the burrow structure.
Another unique relationship is with certain frog species, where they may feed on wolf spiders and, in return, the frog provides them protection from certain predators. Wolf spiders can also impact plant growth and plant-insect interactions, both positively and negatively.
For instance, studies have shown that wolf spiders reduce herbivory damage of various plant species by consuming herbivorous insects. But, in contrast, some spider species can adversely affect plant-pollinator interactions, reducing pollination rates by preying on pollinators.
Wolf spiders have a wide range of relationships with other species in their ecosystem, and these relationships can have both positive and negative effects on the other species involved. The interactions of wolf spiders with their prey, predators, and other organisms in their ecosystem have significant consequences that contribute to the overall health and stability of the ecosystem.
Here is a summary table of the relationships of wolf spiders with other species:
| Species | Relationship | Impact |
|————-|——————–|—————————————————|
| Birds | Prey-predator | Significant food source |
| Burrowing Owls | Symbiotic | Provides nesting spots |
| Frogs | Predator-Prey | May provide protection against other predators |
| Plants | Herbivore/Pollinator | Reduces herbivory damage |
| Pollinators | Predator | Reduces pollination rates |
Impacts of environmental changes
The impact of environmental changes on wolf spiders is a crucial aspect of understanding their adaptation and survival. Wolf spiders are highly adaptable to environments with a range of temperature, moisture, and habitat complexities. However, the altering environmental conditions caused by natural disasters or human activities can greatly affect the wolf spiders’ growth, development, behavior, and reproduction.
| Environmental Change | Impact on Wolf Spiders |
|---|---|
| Drought and Heatwaves | Reduced Survival: Wolf spiders are likely to experience dehydration and heat stress during long periods of drought and heatwaves. Such stress can cause physiological damage, reduce reproductive success, and lead to population decline. Changes in Behavior: Wolf spiders may change their activity patterns and alter their range to find cooler and moister microhabitats. |
| Flooding and Heavy Rains | Flood Mortality: Wolf spiders can drown during flooding events, especially if they are located in burrows or webs that are submerged underwater. Displacement: Wolf spiders living in low-lying areas or near waterbodies are likely to be displaced during flood events. This can cause a disturbance in their territory and migration patterns. |
| Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation | Loss of Genetic Diversity: Habitat destruction and fragmentation can lead to a loss of gene flow and genetic diversity, which can reduce the wolf spiders’ adaptability and resilience to changing environments. Altered Behavior: Wolf spiders may modify their behaviors to cope with fragmented habitats, such as changing their movement patterns, hunting strategies, and mating behaviors. |
| Climate Change | Range Shifts: Wolf spiders are expected to shift their ranges towards cooler and moister regions as the global temperature rises, which can lead to competition with other species. Alterations in Life Cycles: Climate change can cause shifts in phenology, such as earlier emergence or delayed molting, which can affect the synchronization of wolf spiders’ life cycles with their prey and predators. |
To minimize the potentially adverse impacts of environmental changes on wolf spiders, it is essential to develop sound conservation and management strategies that aim to preserve and restore their habitats and protect ecological integrity. This can be done by implementing measures such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, managing water resources, restoring degraded habitats, and promoting connectivity among different ecosystems.
Current and Future Research
As our understanding of wolf spiders and their evolution continues to grow, there are many exciting avenues for future research to explore. From molecular studies to ecological investigations, these upcoming efforts will shed further light on the fascinating world of wolf spiders. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at some of the most promising areas for advancement in wolf spider research, providing insights into what we may learn in the coming years.
Advancements in molecular studies
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in molecular studies related to wolf spiders. These studies have provided a deeper understanding of the genetics and evolutionary history of different species, as well as their unique adaptations and ecological roles. Here are some notable examples of these advancements:
| Advancement | Description |
|---|---|
| Genome sequencing | Genetic analyses have advanced significantly with the help of genome sequencing techniques. By mapping the entire DNA sequence of different wolf spider species, researchers have been able to study their evolutionary history and identify the genes and genetic mutations responsible for their unique physical and behavioral characteristics. |
| Gene expression analysis | Advanced techniques for studying gene expression have allowed researchers to identify the specific genes and molecular pathways that control different aspects of wolf spider biology. This has provided insight into how these spiders have adapted to different ecological niches, as well as how they interact with their environments. |
| Phylogenetic analysis | Comparative studies of the DNA sequences of different wolf spider species have allowed researchers to develop more accurate models of their evolutionary history. These models have revealed important information about how these spiders have diversified over time and adapted to different ecological roles. |
| Proteomic analysis | Proteomic techniques have allowed researchers to analyze the proteins produced by different wolf spider species. This has provided detailed information about their biochemical processes and physiological adaptations, as well as their interactions with other species and the surrounding environment. |
These advancements in molecular studies have greatly enhanced our understanding of wolf spider biology and evolution. They have provided insight into the unique adaptations and ecological diversity of these spiders, as well as the factors that have influenced their evolution over time. As new molecular techniques continue to be developed and refined, we can expect even greater insights into the fascinating world of wolf spider biology.
Areas for future research and discovery
As researchers continue to delve deeper into the world of wolf spiders, there are several areas of future research and discovery that show promise. These range from genetics to ecology, and each hold great potential for uncovering new information about these fascinating creatures. Some of the most promising areas of future study include:
| Genetic analysis of wolf spider populations: With advancements in DNA sequencing technology, researchers can now study the genetic makeup of wolf spider populations in greater detail than ever before. This opens up new avenues of research into the evolutionary biology of these spiders, including the identification of key genes that contribute to traits like hunting ability and habitat preference. |
| Investigation of physiological responses to environmental stressors: As climate change and other environmental stressors continue to impact ecosystems around the world, it’s important to understand how wolf spiders and other species are adapting. Future research may focus on studying the physiological responses of wolf spiders to stressors like increased temperatures, changes in humidity, and exposure to pollutants. |
| Exploration of wolf spider behavior and communication: While much is known about the physical characteristics and hunting behavior of wolf spiders, little is understood about their communication strategies. Future research may focus on investigating how these spiders use vibrations, pheromones, and other signals to communicate with each other, as well as how they respond to other species in their environment. |
| Development of new methodologies for studying wolf spider ecology: As technology continues to evolve, there is increasing potential for developing new tools and methodologies for studying wolf spider ecology in more detail. This may include the use of drones or other remote sensing technologies to study spider populations over larger areas, or the development of new software tools for analyzing large datasets of spider observations. |
| Investigation of the impacts of wolf spider populations on ecosystems: While wolf spiders are known to play important roles in food webs and ecosystems, the precise nature of their impact is not fully understood. Future research may focus on studying the ecological effects of wolf spider populations, including their interactions with other species and their contribution to ecosystem services like pest control. |
The future of wolf spider research looks bright, with many exciting opportunities for new discoveries and insights into the biology and ecology of these fascinating creatures. Through continued effort and innovation, researchers will be able to expand our understanding of wolf spiders and other species, helping to inform conservation and management efforts for many years to come.
Conclusion
As we come to the end of our exploration into the fascinating world of wolf spider evolution, it is clear that these creatures have undergone tremendous adaptations and diversification over time. From their ancestral origins to their current ecological diversity, wolf spiders have played an important role in shaping the ecosystems in which they reside. In this section, we will summarize our findings and discuss the implications for conservation and preservation. Let’s delve deeper into the significance of these findings and what they mean for the future of wolf spider research.
Summary of findings
After years of research on the evolution of wolf spider species, several key findings have emerged. These findings highlight the remarkable adaptability and diversity of wolf spiders, as well as their critical role in various ecosystems. Here is a summary of some of the most significant research on wolf spider evolution.
|Findings|Explanation|
|————————|———————–|
| Diverse ancestry | Wolf spiders have a complex ancestral history, with close relationships to several other spider species. They have existed for over 200 million years, evolving to fill varied ecological niches. |
| Distinctive features | With their eight eyes, powerful jaws, and agile hunting abilities, wolf spiders have a unique set of features that allow them to hunt and survive in diverse habitats. |
| Genetic diversity | Molecular and genetic studies have shown that wolf spiders exhibit significant genetic diversity across different species. This suggests that there are multiple, distinct evolutionary pathways for these species. |
| Adaptive radiation | Wolf spiders have undergone rapid adaptive radiation, with numerous speciation events leading to the evolution of many different species with unique traits and behaviors. |
| Ecological significance | Wolf spiders play critical roles as predators in many ecosystems, impacting the populations of their prey and facilitating processes like decomposition. They are also influenced by environmental changes, including habitat loss and climate change.
These findings underscore the ecological and evolutionary importance of wolf spiders, as well as the need for continued research to understand these fascinating creatures further. By exploring the genetic, physiological, and ecological factors that shape wolf spider evolution, we can gain critical insights into the broader processes that drive biodiversity and ecological complexity.
Implications for conservation and preservation
The evolution of wolf spider species has implications for conservation and preservation efforts, as understanding their ecological significance can help guide management and protection strategies. Wolf spiders play a crucial role in food webs and ecosystems, as they are both predators and prey, and their diversity and abundance can reflect the health of an ecosystem.
One important consideration for conservation is the impact of habitat loss and fragmentation on wolf spider populations. As human development and land use change continue to alter natural habitats, it is important to assess the effects on these species. Research has shown that some wolf spider populations are negatively impacted by habitat fragmentation, leading to reduced genetic diversity and potential declines in population size. Conservation efforts should consider preserving and connecting intact areas of natural habitats to maintain viable populations.
Another factor to consider is the impact of climate change on wolf spider species. As temperatures and precipitation patterns shift, it may affect the distribution and abundance of these spiders, as well as their prey and competitors. This could have ripple effects throughout the food web and ecosystem, potentially leading to cascading impacts on other species. Thus, conservation efforts should take into account the potential impacts of climate change on wolf spider populations and their ecosystems.
Conservation and preservation efforts that take into account the ecological significance of wolf spiders can help maintain healthy and diverse ecosystems for future generations. By highlighting the importance of these spiders in food webs and ecosystems, we can work towards a better understanding of their role in maintaining ecological balance.
| Conservation Impacts | Ways to Address Them |
|---|---|
| Habitat loss and fragmentation | – Preserve and connect intact natural habitats – Implement land-use plans that balance human needs with ecosystem health |
| Climate change | – Assess potential impacts on wolf spider populations and ecosystems – Implement measures to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions |
As we continue to learn more about the evolution and ecological significance of wolf spider species, it is important to use this knowledge to inform conservation and preservation efforts. By taking a proactive and holistic approach to managing these spiders and their ecosystems, we can help ensure their survival for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are wolf spiders?
Wolf spiders belong to the Lycosidae family of spiders and are known for their hunting abilities. They are usually brown or gray in color and have eight eyes arranged in three rows.
Why is studying the evolution of wolf spiders important?
Studying the evolution of wolf spiders can provide insight into the broader history of arachnids while contributing to our understanding of species diversification and adaptation over time.
What is the ancestral relationship between wolf spiders and other spider species?
Wolf spiders share a common ancestor with the nursery web spiders and the fishing spiders, which belong to the Pisauridae family.
What do early fossil records of wolf spiders tell us about their evolution?
Early fossil records suggest that wolf spiders have existed for at least 125 million years and have undergone minimal morphological changes over time. This indicates that wolf spiders are well-suited for their environments and have been for millions of years.
What are some distinctive features of wolf spiders?
Wolf spiders are known for their keen vision, agility, and speed. They also have long hairy legs and unique sensory hairs on their bodies, which help with navigation and hunting.
What are some adaptations that wolf spiders have for hunting and survival?
Wolf spiders have developed keen venomous fangs that can paralyze their prey, which often includes small insects, spiders, and even other wolf spiders. They are also able to camouflage themselves and are skilled at hiding from predators.
What genetic analyses have been done on wolf spider species?
Recent genetic studies have shown that there is significant variation in wolf spider genes even within the same species, indicating that these spiders are evolving rapidly.
What factors have contributed to the ecological diversity of wolf spiders?
Wolf spiders thrive in a variety of environments, ranging from deserts to forests. Their ability to adapt to different climates and prey sources has resulted in the development of numerous species with various ecological niches.
What roles do wolf spiders play in food webs and ecosystems?
Wolf spiders are important predators and can help control populations of other insects and spiders. They can also serve as prey for larger predators, such as birds and small mammals.
What future areas of research are there for wolf spider evolution?
Future research could explore the mechanism behind the rapid evolution of wolf spiders, investigate the environmental factors that contribute to species diversification, and uncover new species that have yet to be discovered.