Introduction
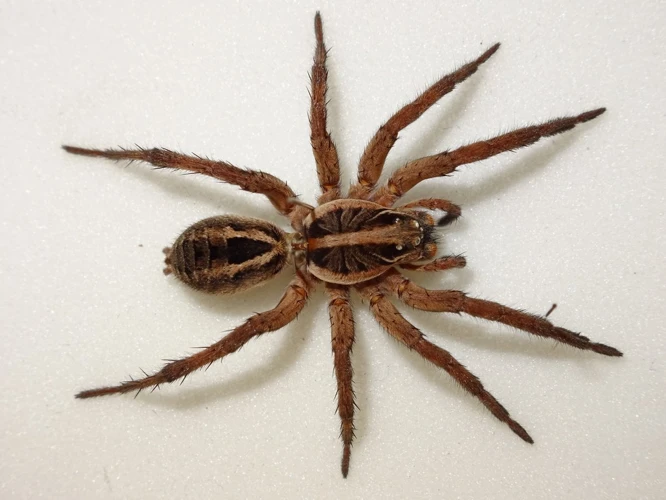

As we delve into the fascinating world of wolf spiders and their classification based on body structure, it’s important to first understand the significance of this topic. Wolf spiders are a diverse group of arachnids that inhabit nearly every corner of the globe. They vary greatly in size, shape, and behavior, which can make it difficult to identify and classify them accurately. However, by examining their external and internal body features, as well as their behavioral characteristics and ecological significance, we can gain a deeper understanding of their taxonomy and role in the ecosystem. Let’s explore the importance of body structure on wolf spider classification step-by-step.
Overview of Wolf Spiders
Wolf spiders belong to the family Lycosidae and are known for their hunting skills and unique physical features. These spiders are found all over the world, with over 2000 species known to exist. Wolf spiders are named after their hunting behavior, as they actively stalk and capture their prey, instead of relying on webs to catch food.
Physical Features
One of the most distinct features of wolf spiders is their eye arrangement. They have two large eyes in the front, with four smaller eyes on top of their head. Their body structure is also unique, with stocky legs that enable them to move quickly. Some species of wolf spiders can grow up to 1.5 inches in length, making them one of the largest spider species.
Hunting Behavior
Wolf spiders actively hunt for their food and do not rely on webs for catching prey. They use their strong legs to chase and capture their prey, which can range from insects to small animals. Their hunting behavior has been studied extensively, with many researchers observing their predatory tactics in the wild. One such observation can be found in the article “Amazing Hunting of Wolf Spiders”, where you can read that Wolf spiders are efficient hunters because they are able to move quickly and stealthily, making them a formidable predator.
Ecological Significance
Wolf spiders play an important role in the food chain and are considered beneficial to ecosystems. As predators, they help control the population of insects and other small animals. They are also preyed upon by larger animals such as birds and other arachnids. Their unique physical features and hunting behavior make them an interesting species to study. If you want to learn more about wolf spider anatomy, check out the article “Wolf Spider Anatomy”.
Wolf spiders are fascinating creatures with unique physical features and hunting behaviors. Their role in the ecosystem and predatory tactics make them an important species to study and protect.
The Importance of Body Structure in Classification
The Importance of Body Structure in Classification
When it comes to classifying wolf spiders, body structure plays a crucial role. In fact, it is one of the primary factors that scientists use to distinguish between different species of wolf spiders. From leg structure to eye arrangement to abdomen shape, the physical features of a wolf spider provide valuable insight into its classification.
To further understand the significance of body structure in classification, let us take a closer look at some of the key characteristics that scientists use to categorize wolf spiders.
| Body Feature | Role in Classification |
|---|---|
| Leg structure | Distinguishes between different groups and subfamilies of wolf spiders |
| Eye arrangement | Used to identify individual species |
| Abdomen shape | Often used in combination with other features to determine a wolf spider’s species or genus |
| Presence of certain internal organs | Provides insight into a wolf spider’s reproductive and respiratory systems, which can aid in classification |
As we can see from the above table, body structure plays a critical role in the classification of wolf spiders. By analyzing different physical features, scientists are able to distinguish between different species and assign them to their appropriate groups and subfamilies.
To learn more about the physical features of wolf spiders and how they are used in classification, visit our article on wolf spider physical features. Additionally, for a size comparison between wolf spiders and other spider species, go to our article on wolf spider size comparison with other spider species.
Body Structure and Taxonomy
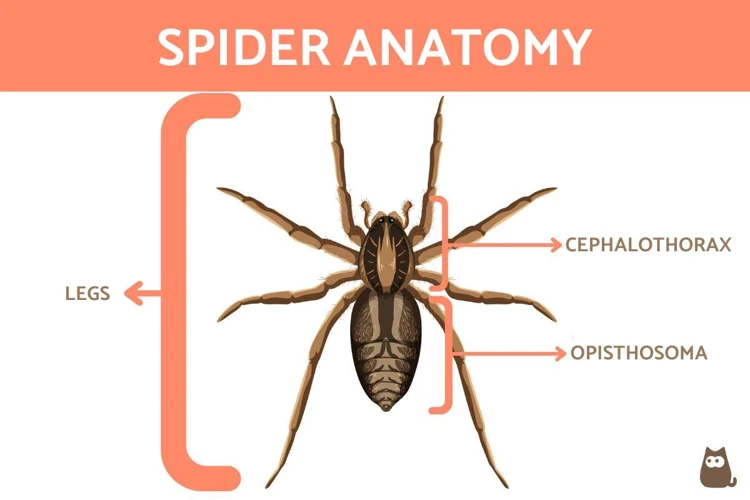
As we delve into the world of wolf spiders, one cannot ignore the crucial role that body structure plays in their classification. The way these eight-legged creatures are built provides valuable insight into their taxonomic hierarchy and evolutionary history. Let’s explore the intricate anatomy of wolf spiders and discover how it has helped in their classification.
Anatomy of Wolf Spiders
Wolf spiders, like other spiders, have two main body parts – the cephalothorax and the abdomen. The cephalothorax, also known as the prosoma, is the front part of the spider’s body and houses the head and thorax. The abdomen, or opisthosoma, is the rear part of the body. Here are some key features of wolf spider anatomy:
- Eyes: Wolf spiders have eight eyes arranged in three rows. The bottom row has four small eyes, the middle row has two large eyes, and the top row has two medium-sized eyes. This arrangement gives wolf spiders excellent vision, particularly in dim light.
- Chelicerae and fangs: Like all spiders, wolf spiders have chelicerae – appendages near the mouth used for grasping and biting prey. At the tips of the chelicerae are the fangs, which inject venom into prey. Wolf spider fangs are relatively large and can cause painful bites in humans, though they are not usually dangerous.
- Legs: Wolf spiders have eight legs, each with seven segments. The legs are covered in sensory hairs that help the spider detect vibrations and chemical signals in the environment. The first pair of legs is typically longer and thicker than the others and is used for capturing and holding prey.
- Pedipalps: The pedipalps are a pair of appendages between the chelicerae and the first pair of legs. In male wolf spiders, the pedipalps are enlarged and used for mating.
- Spinnerets: Wolf spiders have three pairs of spinnerets located at the back end of the abdomen. These produce silk, which the spider uses to build shelters, wrap prey, and create egg sacs.
- Book lungs: Like many spiders, wolf spiders have book lungs – respiratory structures consisting of alternating layers of air-filled chambers and blood vessels. The book lungs are located on the underside of the abdomen.
- Muscles: Wolf spiders have powerful muscles that allow them to run, jump, and subdue prey. The muscles are anchored to an interior exoskeleton, which provides support and protection.
- Internal organs: The internal organs of wolf spiders are located in the cephalothorax and abdomen. These include the digestive system, reproductive system, nervous system, and respiratory/circulatory system.
The anatomy of wolf spiders is adapted for efficient hunting and survival in a wide range of environments. Their sharp vision, powerful muscles, and venomous bites make them formidable predators in the animal kingdom.
Classification of Wolf Spiders Based on Body Structure
Wolf spiders belong to the family Lycosidae, which is further divided into several genera based on the body structure of these fascinating creatures. The classification of these spiders is based on several factors such as the arrangement of the eyes, shape of the abdomen, and leg structure. Here are some of the key characteristics that are used to classify wolf spiders.
- Leg structure: The arrangement of the legs is important in classifying wolf spiders. The first pair of legs is the longest and strongest, while the other three pairs are shorter and smoother. The length and thickness of the legs also vary depending on the species and gender of the wolf spider.
- Eye arrangement: The placement and number of eyes on the cephalothorax (head) vary greatly and is an important factor in the classification of wolf spiders. Some species have two eyes on the top, while others have six or eight eyes arranged in different patterns. The size of the eyes also varies from one species to another.
- Abdomen shape and coloration: The shape and color of the abdomen are also important factors in the classification of wolf spiders. The abdomen can be cylindrical or flattened, and it can vary in color from brown to gray or black.
- Reproductive organs: Another factor in the classification of wolf spiders is the shape and structure of their reproductive organs. Male wolf spiders have specialized structures on their palps that are used to transfer sperm to the female during mating.
- Habitat: Different wolf spider species can be found in a variety of habitats across the world. Some species prefer dry, sandy habitats, while others can be found in wetland areas, forests, or even in caves.
- Size: Wolf spiders range in size from small to large, with some species growing up to 35 mm in length.
Understanding the various body structures and characteristics of wolf spiders is crucial in proper classification. Proper identification of these fascinating creatures can help researchers better understand their behaviors, ecological roles, and interactions with other species in the environment.
External Body Features
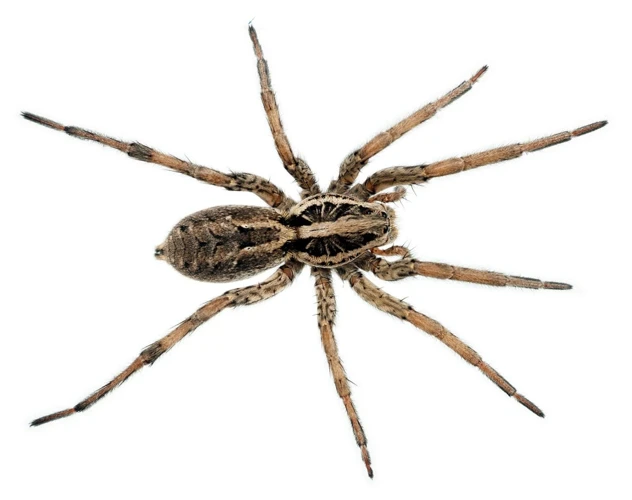

As we delve deeper into the anatomy of wolf spiders, we cannot overlook the significance of their external body features. These features provide valuable insights into the behaviors and adaptations of these fascinating creatures. From their unique leg structure to their keen vision and colorful abdomens, every aspect of their anatomy has a purpose. In this section, we’ll explore some of these distinctive external body features and what they reveal about wolf spiders. So, let’s take a closer look!
Leg Structure and Function
Wolf spiders are known for their exceptional hunting abilities, which are largely attributed to their unique body structure. One of the most notable features of wolf spiders is their legs, which play a crucial role in their movement and hunting patterns.
Leg Structure:
Wolf spiders have eight long and strong legs, which are attached to their cephalothorax. Each leg is composed of seven segments, including the coxa, trochanter, femur, patella, tibia, metatarsus, and tarsus. At the end of each leg, there are two small claws that help the spider grip onto surfaces.
Function:
The structure of wolf spider legs allows them to move with incredible speed and agility. Unlike other spiders that use their webs to capture prey, wolf spiders rely on their legs to chase and catch their prey on foot. They use a unique combination of fast running, jumping, and pouncing movements to quickly subdue their prey.
The legs of wolf spiders also play a critical role in their communication and social structure. During courtship, male wolf spiders perform a unique “leg drumming” behavior to attract females. This involves tapping their legs on the ground to create a rhythmic vibration that can be felt by nearby spiders.
The leg structure and function of wolf spiders is a key factor in their classification and ecological significance. Their unique hunting abilities and social behaviors are made possible by their adept use of their powerful legs.
Eye Arrangement and Vision
Wolf spiders are known for their acute sense of vision that helps them hunt and navigate their environment. Their eight eyes are arranged in three rows: a straight row of four small eyes in the front, two larger eyes directly behind them, and two medium-sized eyes on either side of the head.
The forward-facing eyes (also known as the anterior median eyes or AME) have the highest visual acuity and resolution among all the eyes. They are responsible for stereoscopic vision, depth perception, and the detection of prey movement. The lateral eyes (also known as the anterior lateral eyes or ALE) are sensitive to the intensity and polarization of light, which helps in orientation and hunting at low-light conditions.
The arrangement of the eyes is consistent within a species and can be used for identification purposes. Researchers have found that the size and shape of the AME vary within and among species, which suggests that they might have an adaptive function. For instance, some species that inhabit higher altitudes or darker environments have relatively larger AME to increase their sensitivity to light and movement.
Wolf spiders are well-equipped for their nocturnal lifestyle, and their eyes reflect this. Their visual system can adjust to different light conditions rapidly, allowing them to hunt even in dimly lit environments. The arrangement of their eyes also allows them to scan their surroundings constantly, keeping an eye out for potential prey or predators.
The arrangement and function of the eyes in wolf spiders are crucial in their survival and adaptation to their environment. Their unique eye arrangement also allows for easy identification, which can benefit researchers in studying the different species of this fascinating arachnid.
Abdomen Shape and Coloration
The abdomen shape and coloration of wolf spiders is an important factor in their classification. Wolf spiders have an elongated abdomen that is typically wider at the posterior end. The shape of the abdomen can vary between species, with some having a more rounded shape and others having a more flattened shape. This variation is important in distinguishing between different species of wolf spiders.
Additionally, the coloration of the abdomen is highly variable and can be used to identify different species. Some wolf spiders have brightly colored abdomens with intricate patterns, while others have more subdued coloration. The coloration of the abdomen can also vary depending on factors like age and gender. For example, male wolf spiders may have more vivid coloration than females.
One example of a wolf spider with distinctive abdomen coloration is the Carolina wolf spider (Hogna carolinensis). This species has a contrasting dark brown and cream coloration on its abdomen, with a distinctive stripe pattern. Other wolf spider species may have similar patterns or unique markings on their abdomens.
The shape and coloration of the abdomen can provide important clues to the identity of different wolf spider species. By studying these features, researchers can gain a better understanding of the diversity and evolution of wolf spiders.
Internal Body Features
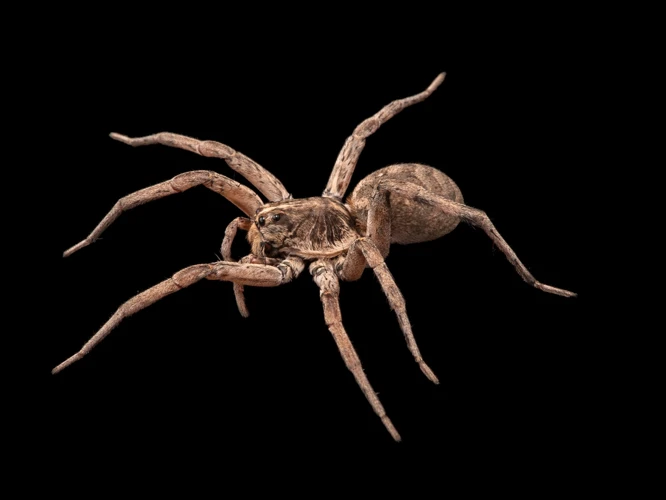

As we delve deeper into the world of wolf spiders, it’s crucial to uncover the intricate details of their internal body features. These structures serve essential functions such as reproduction, respiration, and circulation, shaping the unique characteristics of each species. Let’s explore the fascinating internal anatomy of these arachnids and discover how it contributes to their classification and behavior.
Reproductive Organs and Mating Behavior
Wolf spiders have an interesting mating behaviour that is closely linked to their unique reproductive organs. These spiders have well-developed reproductive systems that ensure successful reproduction.
The male wolf spider possesses two palp organs that are used for reproduction. The palps are the male reproductive organs, and they are located near the spider’s mouth. The palps are used to transfer the sperm to the female during mating. The female, on the other hand, has a single genital opening located at the base of the abdomen.
During mating, the male wolf spider approaches the female and taps her abdomen with his front legs. This courtship ritual is followed by the male inserting his palp into the female’s genital opening, thereby transferring the sperm. The female stores the sperm in a sac and releases it when she is ready to fertilize her eggs.
Table:
| Spider’s Gender | Reproductive Organ | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Palp Organs | Near the mouth | Transfer of sperm during mating |
| Female | Genital Opening | Base of the abdomen | Receive and store sperm for fertilization of eggs |
Interestingly, male wolf spiders may attempt to mate with other males, mistaking them for females, in a behavior known as homosexual copulation. This behavior is not uncommon in the animal kingdom and is thought to be a result of the male’s inability to distinguish between sexes.
The reproductive organs of wolf spiders play a critical role in their mating behavior and eventual reproduction. The unique genital structures and mating behaviors of these spiders shed light on the intricate and fascinating world of spider behavior and biology.
Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
Wolf spiders have a unique respiratory and circulatory system that allows them to survive in a variety of habitats. They do not have lungs, instead, they have book lungs. These are modified respiratory organs that are made up of many thin sheets of tissue, folded like the pages of a book. The book lungs are located in the abdomen, between the heart and the digestive system.
Respiratory System
The book lungs allow wolf spiders to breathe air. They work by diffusing oxygen from the air into the blood vessels that run through the sheets of tissue. Carbon dioxide is removed from the blood in the same way and is exhaled out through the openings of the lung slits. Through this mechanism, the spider is able to efficiently exchange gases with its surroundings.
Circulatory System
Wolf spiders have an open circulatory system, which means that their blood doesn’t always stay inside blood vessels. Instead, the spider has a tubular heart that pumps blood into the body cavity. From there, the blood flows through spaces called sinuses and bathes the organs and tissues with nutrients and oxygen.
The blood in wolf spiders is colored blue-green due to the presence of hemocyanin, a copper-based protein that carries oxygen. This protein functions similarly to the iron-based hemoglobin in vertebrates, which gives red color to their blood.
The respiratory and circulatory system of wolf spiders is essential for their survival as it allows them to breathe and transport oxygen efficiently through their body. Any disturbance to these systems can lead to an adverse impact on their overall health and functioning.
Behavioral Characteristics
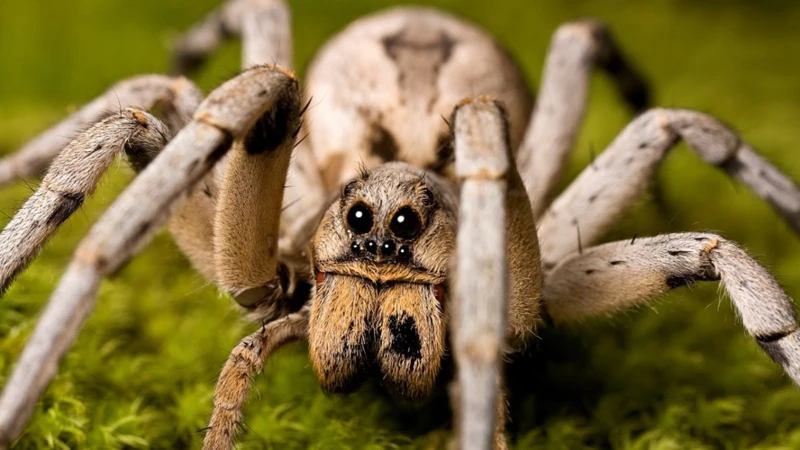

As we delve deeper into the classification of wolf spiders, the focus shifts towards their behavioral characteristics – a key aspect that plays a pivotal role in understanding their unique body structure and ecological significance. From their movement patterns to communication skills, wolf spiders exhibit a range of interesting behaviors that make them stand out in the world of arachnids. Let’s take a closer look at some of the fascinating behavioral traits of these spiders and how they help in their survival.
Movement and Hunting Patterns
Wolf spiders are known for their unique hunting techniques, which rely heavily on their agile movement and excellent eyesight. They are equipped with strong legs that allow them to move quickly and efficiently, making them adept hunters both on the ground and in the air. Here are some key points about their movement and hunting patterns:
- Active hunters: Wolf spiders are active hunters that search for prey both during the day and at night. They do not build webs to catch their prey, but instead rely on their speed and agility to catch it on the ground or in the air.
- Ambush tactics: While wolf spiders are typically active hunters, some species use ambush tactics as well. They will hide in burrows or other concealed areas and wait for prey to come within striking distance.
- Quick movements: Wolf spiders are known for their quick movements. They can run up to 2 feet per second, which is incredibly fast for a spider of their size.
- Hunting range: Depending on the species, wolf spiders may range in their hunting grounds from only a few inches to several feet.
- Jumping abilities: Many species of wolf spiders are capable of jumping several times their own body length, which can give them an advantage when hunting prey.
- Stealthy approach: Wolf spiders are known to approach their prey stealthily, often stalking it for several minutes before attacking.
- Predators and prey: Just like any other species, wolf spiders face a variety of predators and prey. The larger species are known to feed on other spiders and even small vertebrates, while smaller species may feed on insects, ants, and other small prey.
Understanding the movement and hunting patterns of wolf spiders is crucial for classification and for understanding their place in the ecosystem. These patterns have evolved over time to most effectively hunt for prey and avoid being preyed upon themselves. By studying the unique characteristics of wolf spider movement and hunting, researchers can gain valuable insight into the larger evolutionary patterns that shape the animal kingdom.
Communication and Social Structure
Wolf spiders, like many other species of spiders, are typically solitary and do not exhibit complex social behaviors. However, they do engage in certain forms of communication and have a basic social structure that revolves around mating and caring for their young.
Communication: Wolf spiders communicate primarily through tactile, chemical, and visual cues. They use vibrations or drumming sounds to communicate with potential mates and rival males during courtship and territorial disputes. Chemical signals also play a significant role in communication, as males leave scent marks to attract females and discourage other males from entering their territory. Visual cues, such as posturing and coloring, are used to signal aggression, submission, or mating interest.
Social Structure: Wolf spiders have a relatively simple social structure that consists of solitary individuals coming together for mating and raising their young. Female wolf spiders are typically larger than males and often display aggressive behaviors during courtship. Once a male has successfully mated with a female, he will typically move on to find another mate. Females, on the other hand, are responsible for caring for their young. They will lay their eggs in a protective silk sac and carry it with them until the spiderlings hatch. Female wolf spiders will often display strong protective behaviors towards their young, which may include aggressive posturing towards threats or even carrying the spiderlings on their backs until they are ready to disperse.
While wolf spiders do not have complex social structures, they do engage in certain forms of communication and have a basic reproductive and caring structure for their young. This reinforces the importance of considering not only body structure but also behavioral and ecological characteristics when classifying different species of spiders.
| Communication | Social Structure |
|---|---|
| Tactile cues | Solitary individuals coming together for reproduction and raising young |
| Chemical signals | Female wolf spiders responsible for caring for their young |
| Visual cues | Female wolf spiders display protective behaviors towards their young |
Ecological Significance
The role of wolf spiders in their respective ecosystems is of great ecological significance. These hunters play a crucial part in maintaining the balance of various food chains and are important predator-control agents. Their impact on the ecosystem is worth studying, as understanding their role could lead to a better understanding of the ecosystem as a whole. Let’s delve into the details of how wolf spiders contribute to the ecological balance and how their absence, though small in size, could disrupt the natural order of things.
Role in the Food Chain
Wolf spiders play an essential role in the food chain and are part of the larger ecosystem. They are predators, feeding on a variety of insects and other small creatures. Their diet includes flies, crickets, grasshoppers, beetles, and other spiders. As ambush hunters, they depend on their excellent eyesight and powerful jaws to catch their prey.
At the same time, wolf spiders serve as prey for many other animals. They are eaten by birds, lizards, frogs, and other spider-hunting predators. They create a link in the food chain, connecting different levels of predators and prey.
Wolf spiders also contribute to biological control in ecosystems. By hunting on insects and other small animals, they regulate the population of these creatures. In this way, they help to prevent overpopulation of certain insects that could otherwise become pests.
Wolf spiders are food sources for many endangered species. In some ecosystems, they are crucial to the survival of certain predators, which rely on them for food. For example, the endangered San Joaquin kit fox, found in California, feeds on wolf spiders as part of its diet.
Wolf spiders play a vital role in the food chain and in maintaining ecological balance. They are predators, prey, and regulator of insect populations, making them an essential part of many ecosystems.
Impact on Ecosystems
Wolf spiders are a vital part of the ecosystem, with their presence having a significant impact on the balance of the food chain and the ecosystem as a whole. Their role in controlling insect populations is essential in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. Let’s take a closer look at the ecological significance of wolf spiders.
Role in Insect Control: Wolf spiders are known for being skilled hunters, and they play a crucial role in controlling the population of insects. They are natural predators of insects such as beetles, ants, and caterpillars. A single wolf spider can consume a large number of insects, thus reducing the number of pests that would otherwise damage crops and plants. By controlling insect populations, wolf spiders help maintain the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
Prey for Other Animals: Wolf spiders, like most other creatures, serve as food for other animals. Birds, lizards, and rodents, among other creatures, consider wolf spiders as a crucial part of their diet. Without wolf spiders, the population of these animals might decline, resulting in a catastrophic chain reaction that would ultimately harm the ecosystem.
Indicators of Environmental Health: Wolf spiders serve as indicators of general environmental health, with their presence being an indication of a healthy and balanced ecosystem. They tend to be more abundant in areas with advanced vegetation cover, which is a sign of very healthy and fertile soil. A decline in the population of wolf spiders may suggest that the environmental health of an area is degrading.
Conclusion: Wolf spiders play a vital role in the ecosystem, and their presence is fundamental in maintaining the balance of the food chain. They help control insect populations, serve as food for other animals, and serve as indicators of environmental health. Their conservation is essential for the health and stability of the ecosystem.
| Importance | Impact |
|---|---|
| Role in Insect Control | Help in controlling insect populations |
| Prey for Other Animals | Considered as a crucial part of the diet of some birds, lizards, and rodents |
| Indicators of Environmental Health | Their presence signifies a healthy and balanced ecosystem. Their decline suggests a degrading environment. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the body structure of wolf spiders plays a crucial role in their classification, taxonomy, and ecological significance. Their unique anatomical features, external body structures, internal body systems, and behavioral characteristics help differentiate them from other spider species and determine their role in the food chain and impact on ecosystems.
The importance of body structure in classification cannot be overemphasized since it helps us understand the physical characteristics, evolutionary history, and ecological interactions of wolf spiders. By closely examining their legs, eyes, abdomen, reproductive organs, respiratory and circulatory systems, movement and hunting patterns, communication, and social structure, we can classify them into different species, subfamilies, and families based on their morphological and genetic traits. This information is critical for conservation and management efforts, taxonomic revisions, and scientific research.
Moreover, wolf spiders have unique ecological significance since they are top predators in many ecosystems and play a crucial role in controlling pest populations, maintaining food webs, and serving as indicators of environmental change. Their hunting behavior, territoriality, courtship displays, and parental care also provide insights into the complexity of arthropod behaviors and evolution.
In summary, understanding the body structure of wolf spiders is important not only for differentiating them from other spider species but also for appreciating their ecological significance and complexity of their behavior. Further research into their morphology, genetics, physiology, and behavior will undoubtedly reveal new insights into these fascinating creatures and their role in shaping ecological processes. As such, it is important to continue to study and appreciate these unique and important members of our planet’s biodiversity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What distinguishes wolf spiders from other spiders?
One distinguishing feature of wolf spiders is their eye arrangement, which is a key characteristic used in classification. They also have powerful legs that enable them to hunt down prey on the ground.
What is the role of body structure in wolf spider classification?
Body structure is essential in the classification of wolf spiders because it provides information about their evolutionary history, behavior, and ecology.
How do wolf spider legs differ from other spiders?
Wolf spider legs are covered in dense hairs and are powerful and agile, allowing them to run down prey on the ground. They have three claws on each foot that help them climb and cling to surfaces.
What is the significance of wolf spider eye arrangement?
The eye arrangement of wolf spiders is unique among spiders and is used as a key feature in classification. They have eight eyes arranged in three rows, with two large eyes in the front row that give them excellent vision.
What is the shape and coloration of wolf spider abdomens?
Wolf spider abdomens come in a range of colors from brown to gray to black, and some have distinctive markings such as stripes or spots. The shape of the abdomen is generally round, oval, or pear-shaped.
What is the mating behavior of wolf spiders?
Male wolf spiders perform elaborate courtship displays to attract females and avoid being mistaken for prey. They use their legs to drum on the ground and produce vibrations that can be heard by females.
What is the respiratory system of wolf spiders?
Wolf spiders have a book lung, which is a specialized organ used for gas exchange. The book lung consists of thin sheets of tissue arranged like the pages in a book, which allows for efficient diffusion of gases.
What is the social structure of wolf spiders?
Most wolf spiders are solitary and do not form social groups. However, some species exhibit maternal care, with the female guarding her eggs and young until they are ready to disperse.
What is the ecological significance of wolf spiders?
Wolf spiders play an essential role in the food chain as predators of insects and other small invertebrates. They also help to regulate insect populations and contribute to the overall health of ecosystems.
What is the impact of wolf spiders on ecosystems?
Wolf spiders are an important indicator of ecosystem health and can be used to monitor changes in biodiversity and habitat quality. They can also be affected by habitat fragmentation and other human activities, which can have negative impacts on their populations.