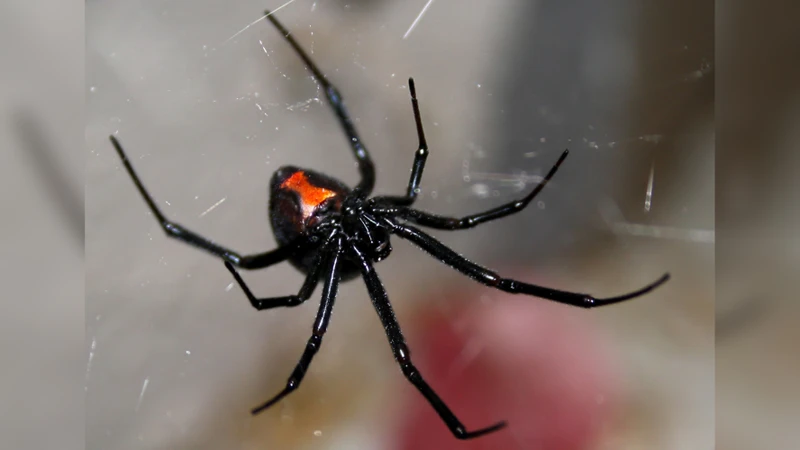
When it comes to survival in different habitats, one type of spider that often comes to mind is the black widow spider. Black widow spiders are fascinating creatures that are known for their venomous bite and striking appearance. However, there is much more to these spiders than just their looks and toxic bites. In this article, we will explore the different habitats that black widow spiders live in, their adaptations for survival, the threats they face, and more. So, grab your magnifying glass, put on your explorer hat, and let’s delve into the world of black widow spiders together.
What are Black Widow Spiders?
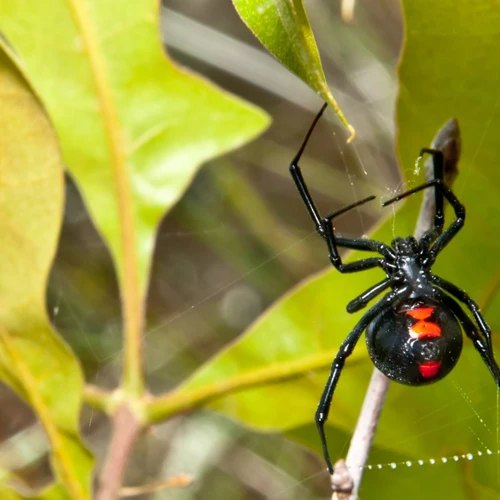

Black widow spiders are fascinating creatures that have garnered a great deal of attention from scientists and arachnid enthusiasts alike. These venomous spiders are known for their distinct appearance, with females having shiny black bodies and distinctive red hourglass markings. However, there is much more to black widow spiders than just their striking appearance. In this section, we will dive deeper into various aspects of black widow spiders such as their physical appearance, different types of black widow spiders, and their common characteristics. Understanding these features of black widow spiders is crucial to exploring how they adapt to different environments and survive in different habitats.
Physical appearance of black widow spiders
Black Widow Spiders are highly dangerous and venomous spiders that are indigenous to various parts of the world, mainly found in warm and tropical regions such as South Africa, South America, and America. The following table demonstrates the Physical appearance of the Black Widow Spider.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Color | Black or dark brown in color. The female black widow spider has a distinctive red hourglass shape on the underside of its abdomen, while the males possess different markings. |
| Size | On average, adult female black widow spiders are roughly 1.5 inches long, while adult males are smaller in size, reaching up to just half the size of the females. |
| Legs | Eight long legs that are thin and hairless. |
| Webs | These spiders build messy, tangled webs that are strong enough to trap small insects. They prefer to reside in dark, secluded areas, such as garages, woodpiles, or underneath rocks and crevices. |
Apart from the distinct hourglass shape on the female’s underside, the color and size of the spider can vary slightly based on the species and region in which they are found. One of the most prominent characteristics that differentiate the black widow spider from others is its unique webbing style and preference for residing in specific locations where they can trap prey effectively. The physical appearance of the black widow spider allows them to survive and thrive in their natural habitat, which is why they can be found in different parts of the world.
Types of black widow spiders
The black widow spider belongs to the genus Latrodectus, which consists of 32 recognized species worldwide. The most common species of black widow spider in North America is Latrodectus mactans, which is found throughout the United States.
Latrodectus mactans: This is the most widespread black widow spider species in North America. They are distributed across the entire continent and can be found in a wide range of habitats.
Latrodectus hesperus: This species is commonly known as the western black widow spider and is found throughout the western United States. They are often found in dry habitats such as deserts, but can also be found in forests and other habitats.
Latrodectus variolus: Also known as the northern black widow spider, this species is found in the eastern and central United States. They are typically found in wooded areas and forests.
Latrodectus bishopi: This species is known as the red widow spider. They are found in the southeastern United States and are typically found in sandy or rocky habitats.
Latrodectus geometricus: This species is commonly known as the brown widow spider and is found in many parts of the world. They have become increasingly common in the southern United States in recent years.
It’s interesting to note that despite being toxic and deadly, black widow spiders play an important role in ecosystems. They are apex predators, meaning they are at the top of the food chain in their habitats. They help control insect populations and serve as a food source for certain predators.
If you want to learn more about the distribution and range factors affecting black widow spiders, check out the relevant anchor “factors affecting black widow spider distribution“.
Where Do Black Widow Spiders Live?
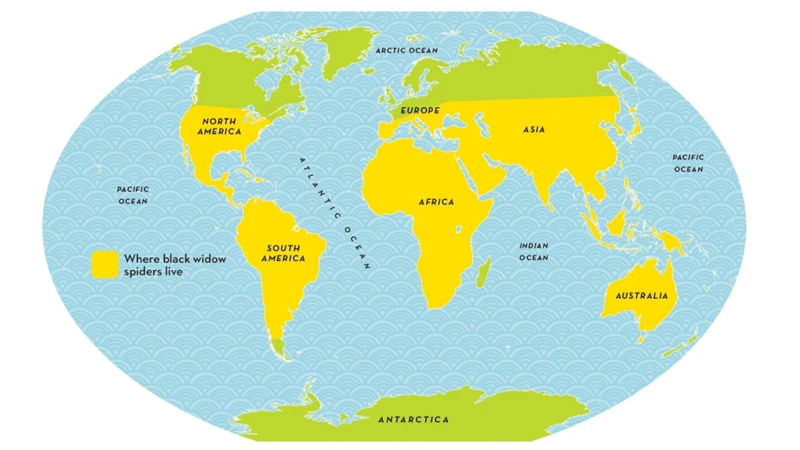
The black widow spider is a fascinating creature that has captured the attention of many people around the world. Understanding where these spiders live and their habitat requirements is crucial to understand how they survive. While these spiders are found in many different parts of the world, their distribution can be affected by various factors, including climate and competition with other species. In this section, we will take a closer look at the specific habitats where black widow spiders are commonly found.
Habitats of black widow spiders
Black widow spiders are known for their preference for warm and dry climates, which is why they are commonly found in different habitats across the world. According to research, black widow spiders thrive in areas with temperatures ranging from 70 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit. These spiders can be found living in a variety of habitats, including forests, deserts, wetlands, and even residential areas.
Forests: Black widow spiders are often found in forests where there is an abundance of vegetation, such as fallen logs and tree stumps. Research shows that the spiders prefer to build their webs in areas that offer a good vantage point from which they can hunt prey. Black widow spiders are also known to build their webs in close proximity to other spider species.
Deserts: Although black widow spiders thrive in hot and dry conditions, they are not limited to desert environments. However, deserts provide a suitable environment for them to live in due to the hot and dry conditions, desert shrubs, and the sandy soil that makes it easy for them to burrow. Black widow spiders found in deserts have adapted to the harsh conditions by remaining active during the cool evening hours, building their webs at the base of shrubs, and avoiding direct sunlight during the day.
Wetlands: Black widow spiders can also be found in wetlands, such as swamps, marshes, and bogs. In these areas, they typically build their webs near the water’s edge or in low-lying areas where they are protected from the wind. Black widow spiders found in wetland habitats tend to be larger in size and have darker coloration than those found in other habitats.
| Habitats | Features |
|---|---|
| Forests | Abundance of vegetation such as fallen logs and tree stumps; webs built in areas with a good vantage point; close proximity to other spider species |
| Deserts | Hot and dry conditions; sandy soil that makes it easy to burrow; active during cool evening hours; building webs at the base of shrubs; avoiding direct sunlight |
| Wetlands | Build webs near the water’s edge or in low-lying areas; protected from the wind; larger in size; darker coloration |
Black widow spiders are found all over the world and can survive in different habitats as long as they have access to shelter, food, and water. These spiders play an important role in the ecosystem by controlling pest populations and serving as a food source for other animals (source). However, they also pose a risk to humans due to their venomous bites. In fact, most black widow bites occur in areas where the spiders are most commonly found (source).
Distribution of black widow spiders
Black widow spiders are found in many parts of the world and different species of black widow spiders have different distributions. They are commonly found in warm and temperate regions. In the United States, they are commonly found in the southern and western parts of the country. However, they can also be found in other parts of the country such as the northeast and the Midwest.
Table:
| Location | Species of Black Widow Spiders Found |
|---|---|
| North America | Lactrodectus mactans, Lactrodectus variolus, Lactrodectus geometricus |
| South America | Lactrodectus hesperus, Lactrodectus bishopi, Lactrodectus cinctus |
| Africa | Lactrodectus geometricus, Lactrodectus indistinctus, Lactrodectus karrooensis |
| Middle East/Asia | Lactrodectus tredecimguttatus, Lactrodectus pallidus, Lactrodectus dahli |
| Australia | Lactrodectus hasseltii, Lactrodectus katipo, Lactrodectus hesperus |
The distribution of black widow spiders can be affected by a number of factors such as climate and habitat. Some species are more adaptable and can live in a variety of habitats, while others are more specialized. The black widow spiders found in North America, for example, are adapted to live in a variety of habitats, including deserts, forests, and wetlands.
Understanding the distribution of black widow spiders is important for researchers studying these creatures as well as individuals who want to avoid them. Despite their venomous nature, black widow spiders play an important role in their respective ecosystems and are fascinating creatures to study. To learn more about the range of factors that influence black widow distribution, please see our article on factors that influence black widow range. To learn more about the different species of black widow spiders found throughout the world, please see our article on types of black widow spiders found.
How Do Black Widow Spiders Survive in Different Habitats?
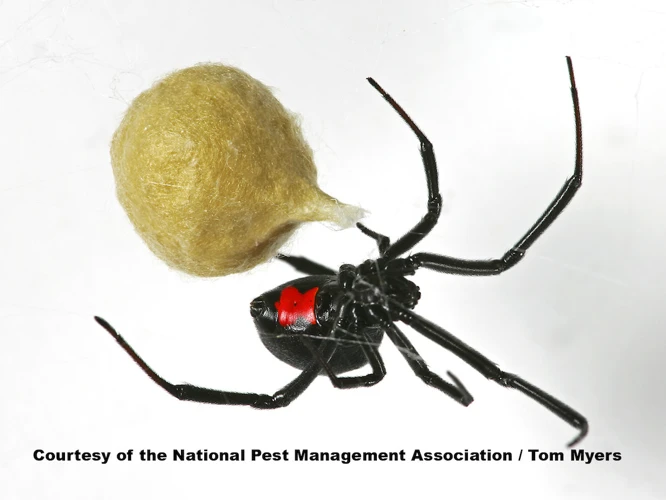

When it comes to survival, black widow spiders are known to be highly adaptable to different habitats. These venomous spiders have developed a variety of adaptations to help them thrive in various environments, from deserts to forests to wetlands. Let’s examine how black widow spiders have managed to survive and thrive in different habitats around the world. To learn more about the distribution of black widow spiders globally, check out our previous article on black widow spiders around the world.
Adaptations to survive in deserts
Black widow spiders are known for their amazing ability to adapt to different environments, including deserts. To survive in the harsh desert climate, black widow spiders have developed some unique adaptations and behaviors.
Temperature Regulation: One of the biggest challenges for black widows in the desert is maintaining a consistent body temperature. They do this by avoiding the hot sun during the day and coming out to hunt when it gets cooler at night.
Burrowing: Black widow spiders in the desert often burrow in the sand to stay cool during the day and protected from predators. They create a burrow in the sand using silk to line the walls and hide inside during the day.
Conserving Water: Desert environments can be very dry and water is scarce. Black widow spiders have adapted to this by being very efficient with their use of water. They can go weeks without drinking water by getting moisture from the prey they eat.
Camouflage: To avoid being seen by predators, black widow spiders in the desert use their natural coloring to blend in with the sand and rocks. They have a black body with red hourglass-shaped marking on their abdomen, which may not be very noticeable against the desert background.
Feeding behavior: Black widow spiders in the desert have adapted their feeding behavior to take advantage of the abundance of insects that are active at night. They are known to eat insects that are attracted to lights at night, and they also scavenge for food in the early morning.
Black widow spiders have developed a range of adaptations that allow them to survive in the harsh desert environment. These adaptations include temperature regulation, burrowing, conserving water, camouflage, and specific feeding behaviors.
Adaptations to survive in forests
One of the habitats where black widow spiders thrive is in forests. These areas provide the perfect mix of resources that support their survival. The black widow spiders in forests have made unique adaptations to meet the demands of their environment. Here are some of the adaptations they have made to survive:
- Web building: Black widow spiders in forests build their webs strategically. They spin webs that are strong and sticky, which help them catch prey more efficiently. These webs are usually woven near the ground level of the forest where they can capture prey easily.
- Camouflage: Black widow spiders in forests use camouflage to blend in with their surroundings. Their dark coloration helps them hide from predators that may be on the hunt for their next meal. They have also been known to adjust their body posture to resemble a dead leaf or twig to avoid detection.
- Predator detection: In forests, black widow spiders have developed a keen sense of predator detection. They are sensitive to vibrations and movements that occur around their webs. When they sense danger, they will hide in a nearby crevice or drop to the ground to avoid becoming prey.
- Feeding: Black widow spiders in forests have adapted to feed on prey that is abundant in their surroundings. They consume insects and other arthropods, such as moths, beetles, and grasshoppers. To ensure they have a ready supply of food, they often set their webs near a source of water or vegetation, where insects are more likely to be found.
- Mating: In forests, black widow spiders have adapted their mating behavior to ensure successful reproduction. Males are careful not to be mistaken for prey by females and will make contact with her web to test whether the female is receptive to mating. After mating, the male will usually leave the web to avoid being consumed by the female.
Black widow spiders in forests have evolved unique adaptations to help them survive in their habitat. From web-building to camouflage, their adaptations make them a formidable predator in the forest ecosystem.
Adaptations to survive in wetlands
Black widow spiders are known for being adaptable to various habitats, including wetlands. In order to survive in such diverse environments, these spiders have developed a range of unique adaptations. Some of these adaptations include:
| Adaptations to survive in wetlands: |
|---|
| 1. Water Resistance: Black widows have thick, water-resistant exoskeletons that prevent them from getting bogged down in wet, marshy areas. This adaptation also helps them avoid drowning in areas with standing water. |
| 2. Prey Adaptation: Black widows living in wetland areas often have to adapt to catching prey that is adapted to living in marshy environments. These spiders have strong, sticky webs that they use to catch a variety of prey, including insects, small amphibians, and even fish. |
| 3. Nesting Adaptation: Black widows living in wetlands typically make their nests in elevated locations, such as on reeds or grasses. This adaptation helps to keep their eggs and young safe from floods and other water-related dangers. |
| 4. Temperature Regulation: Wetlands can be cold and damp, which can be a challenge for cold-blooded creatures like black widows. To combat this, these spiders have adapted to regulate their body temperature by basking in the sun or seeking out warm, sheltered areas. |
These are just a few examples of the many adaptations that black widow spiders have developed to survive in wetland habitats. Despite the challenges posed by these environments, these spiders have proven to be highly adaptable and successful in a range of different ecosystems.
What Threats Do Black Widow Spiders Face in Different Habitats?
As with any living organism, black widow spiders face a number of obstacles and threats in their various habitats that they must overcome in order to survive. From predation to competition for resources, these arachnids have developed unique adaptations to withstand the challenges of diverse environments. Understanding the threats that black widows face is essential to gaining insight into their evolution and resilience in the wild. Let’s explore some of the dangers that black widow spiders encounter in different habitats.
Predators of black widow spiders
Black widow spiders are small but dangerous creatures that have developed various defensive mechanisms over time to protect themselves from predators. However, even with these adaptations, these spiders still face threats from a number of predators. Below is a list of some of the most common predators of black widow spiders:
- Birds: Birds such as hawks, falcons, and owls are known to feed on black widow spiders. They are often attracted to the spiders’ webs and will swoop down to catch them.
- Rodents: Small rodents such as mice and rats are also known to hunt black widow spiders. They are able to sneak up on the spiders and kill them with their sharp teeth.
- Other spiders: Some species of spiders, such as the mud dauber wasp, will prey on black widow spiders. They will often paralyze the spider with their venom before laying their eggs on them.
- Insects: Insects such as praying mantises, ants, and beetles have also been known to feed on black widow spiders. These insects are attracted to the spiders’ webs and will feed on them when they get caught.
- Humans: While not a natural predator, humans can pose a threat to black widow spiders. Many people fear black widows and will go to great lengths to kill them if they find them in or around their homes.
Despite the threats posed by these predators, black widow spiders have survived for millions of years thanks to their unique adaptations and ability to thrive in a variety of habitats.
Competition for resources
Competition for resources among black widow spiders can be intense. These spiders compete for resources such as food, shelter, and breeding opportunities, which can be limited in some habitats.
One of the primary sources of competition is food. Black widows are carnivorous and feed predominantly on insects. However, in areas with high spider densities, resources can become scarce. In such situations, black widow spiders resort to cannibalism, with the larger females often preying on smaller males after mating. This phenomenon is known as “sexual cannibalism” and is a common occurrence among black widow spiders.
Another source of competition for black widows is shelter. They prefer areas with dense vegetation or debris, where they can spin webs to catch prey and mate. However, these locations may be limited in some habitats, forcing spiders to compete for the limited available space.
To further elaborate on the competition for resources among black widow spiders, the following table summarizes some of the key factors:
| Resource | Factors contributing to competition |
|---|---|
| Food | High spider densities: more spiders competing for the same food sources Diet overlap: potential competition with other carnivorous species for the same prey items Seasonal variations: fluctuations in insect populations can create food shortages |
| Shelter | Competition for space: dense vegetation or debris required for web-building can be limited in some habitats Displacement: larger individuals can displace smaller spiders from prime locations Habitat loss: human activities such as deforestation can reduce available shelter |
| Breeding opportunities | Sexual cannibalism: males risk being eaten by females during mating Male-male competition: males may compete for access to females Population density: high densities can limit mating opportunities |
Competition for resources is a significant challenge for black widow spiders in many habitats. This competition can impact their survival and reproductive success, and the strategies they use to cope with these challenges are an essential part of their survival in different habitats.
Conclusion
After exploring the survival of black widow spiders in different habitats, it’s clear that these spiders have unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in a variety of environments. Their distinct physical appearance and behavior, including the famous red hourglass mark on their abdomen, serve as warning signs to predators and humans alike.
Although black widow spiders are often associated with deserts, they also have a strong presence in forests and wetlands. In these different habitats, black widow spiders use their adaptations to effectively hunt prey and protect themselves against predators. For example, in deserts, they have the ability to store moisture and curl their legs to reduce water loss. In forests, they use their webs to capture prey and protect themselves from predators. In wetlands, they find protection in the unique vegetation and water sources.
Despite their adaptations, black widow spiders still face threats in their different habitats. Predators such as birds, lizards, and other spiders prey on black widow spiders. Competition for resources also plays a role in the survival of black widow spiders. In forests, they compete with other spiders for prey, while in wetlands, they compete with a variety of insects.
In conclusion, black widow spiders have unique adaptations that allow them to survive in different habitats. However, they still face threats from predators and competition for resources. It’s important to understand and respect these spiders and their habitats. Avoiding unnecessary interactions and taking precautions can ensure the survival of both black widow spiders and humans.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the scientific name of Black Widow Spiders?
The scientific name of Black Widow Spiders is Latrodectus.
How does one identify a Black Widow Spider?
Black Widow Spiders are identified by their shiny black bodies with a red or orange hourglass-shaped marking on their abdomen.
What do Black Widow Spiders eat?
Black Widow Spiders feed on insects, spiders and other small invertebrates.
Are Black Widow Spiders venomous?
Yes, Black Widow Spiders are venomous and their bites can be dangerous to humans. If bitten, seek medical attention immediately.
What is the lifespan of Black Widow Spiders?
The lifespan of Black Widow Spiders is approximately 1-3 years.
Can Black Widow Spiders be kept as pets?
Black Widow Spiders are not recommended as pets due to their venomous nature.
What is the habitat of Black Widow Spiders?
Black Widow Spiders can be found in a variety of habitats including forests, deserts, and wetlands.
What are the predators of Black Widow Spiders?
The main predators of Black Widow Spiders are birds, reptiles, and larger spiders.
Can Black Widow Spiders survive in cold climates?
Black Widow Spiders cannot survive in extremely cold climates and are typically not found in areas with prolonged winter weather.
What is the mating behavior of Black Widow Spiders?
During mating, the male Black Widow Spider will approach the female and perform a courtship ritual before mating. The female may eat the male after mating.






