Introduction

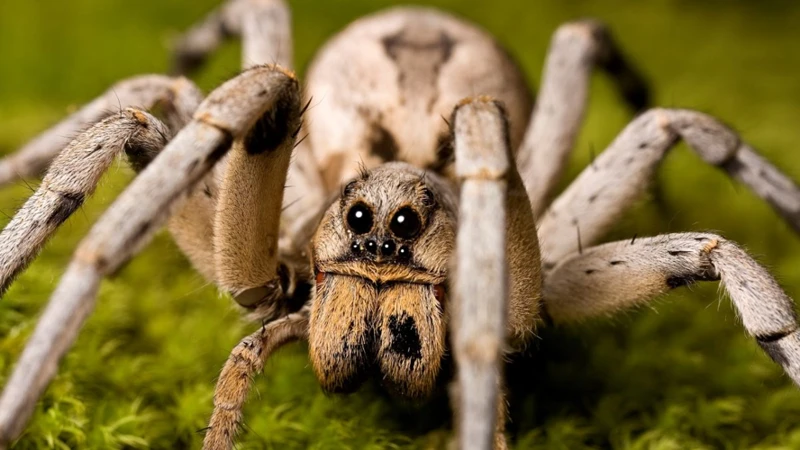
The world of spiders is full of fascinating creatures with unique hunting strategies. One such spider is the wolf spider, known for its agile and speedy hunting techniques. These spiders play an important role in maintaining natural ecosystems and are of great interest to researchers studying their behavior. In this article, we will delve into the role of vision in the active hunting tactics of wolf spiders, examining their body structure, hunting techniques, and the environmental and ecological factors that influence their behavior.
What are wolf spiders?
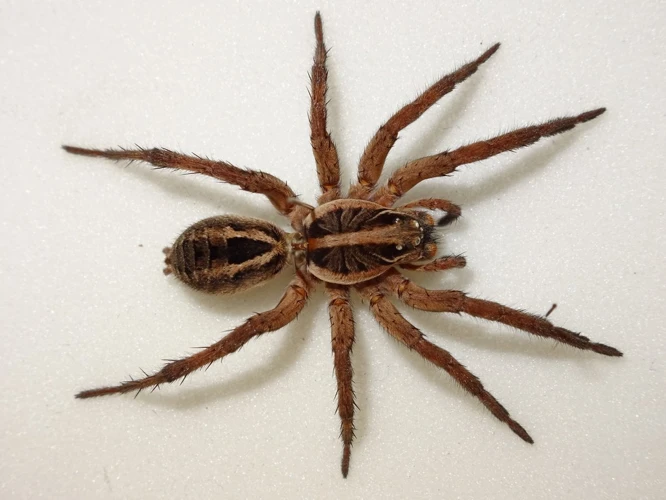
Wolf spiders are members of the Lycosidae family, which is one of the most diverse in the spider order. They are found in various habitats ranging from deserts to forests and can be identified by their characteristic coloration and morphology. Wolf spiders have a stout, hairy body with long legs and eight eyes arranged in three rows. They belong to the arachnid class, which also includes ticks, mites, and scorpions.
There are over 2,300 species of wolf spiders around the world, and they vary in size from a few millimeters to more than 10 centimeters in leg span. These spiders have strong, curved fangs that are used for biting and injecting venom into their prey. In general, wolf spiders are opportunistic predators that hunt for a wide range of prey, including insects, other spiders, and even small vertebrates.
One of the unique features of wolf spiders is their ability to hunt actively, which means they do not rely solely on web-building tactics to capture prey. Instead, they use their powerful legs and keen eyesight to chase down their victims. Wolf spiders are also known for their unique vibration behavior, where they use their legs to communicate with each other and to lure prey.
Wolf spiders are a diverse and fascinating group of arachnids with unique hunting tactics and adaptations. To learn more about their hunting behavior, see our article on Wolf Spider Hunting Tactics. To delve deeper into the ecological impact of wolf spiders, read our article on Wolf Spider Environment Impact.
Why are wolf spiders important?
Wolf spiders are a crucial part of the ecosystem and play a vital role in controlling the populations of insects and other invertebrates. Their long, spindly legs and keen eyesight make them excellent hunters, and they are known to consume a wide variety of prey items, ranging from mosquitoes and flies to grasshoppers and even small vertebrates like lizards and frogs.
One of the most fascinating aspects of wolf spiders is their unique method of capturing prey. Unlike many other spiders, which spin webs to ensnare their victims, wolf spiders rely on their sheer agility and quick reflexes to catch their meals. They are incredibly fast and are capable of sprinting short distances to chase down their prey. Additionally, they have been known to use ambush tactics, waiting patiently for their prey to come to them before pouncing suddenly and snatching it up in their jaws.
But perhaps the most interesting thing about wolf spiders is the way in which they use vibrations to locate their prey. The spiders are equipped with special sensory organs on their legs that allow them to detect vibrations in the ground. When they sense prey nearby, they will often drum their legs on the ground, causing the surface to vibrate and alerting them to the location of their meal.
In addition to their importance in controlling pest populations, wolf spiders are also fascinating subjects for scientific study. Researchers are interested in studying their hunting behaviors and sensory abilities in order to better understand the ways in which animals interact with their environments. By gaining a greater understanding of wolf spider behavior, scientists hope to gain new insights into the workings of the natural world and develop new strategies for managing insect populations.
In conclusion, wolf spiders are an essential part of the ecosystem, and their unique hunting tactics and sensory abilities make them a fascinating subject of study. By continuing to investigate the habits and behaviors of these remarkable creatures, researchers can gain new insights into the workings of the natural world and develop innovative solutions to some of the challenges facing our planet today.
Learn more about how wolf spiders vibrations help them to catch their prey.
What is their hunting behavior?
Wolf spiders are efficient hunters with a diverse range of hunting strategies. They are highly adaptive and can modify their approach to suit different environments and prey. Here are some of the most common hunting behaviors of wolf spiders, presented in a table for easy reference:
| Hunting Behavior | Description |
|---|---|
| Chase-and-pounce strategy | Wolf spiders often pursue their prey on foot, using their speed and agility to catch insects, other spiders, and small arthropods. |
| Ambush tactics | Some wolf spiders prefer to wait in hiding places and attack prey that comes too close. They may use natural features like rocks and foliage to conceal themselves. |
| Web building and burrowing | While not all wolf spiders build webs or burrows, some species use these structures to trap and ambush their prey. They may construct simple or complex webs depending on the species and environment. |
It is worth noting that wolf spiders are opportunistic hunters and will exploit a variety of food sources. They are not restricted to a specific diet and will eat any small animal they can overpower and subdue. This includes insects, other spiders, and even small vertebrates like lizards. By utilizing these different hunting strategies, wolf spiders are able to maximize their hunting success and increase their chances of survival in the wild.
To learn more about spider hunting tactics, visit our article on Spider Hunting Tactics.
Body Structure
When it comes to the formidable hunters known as wolf spiders, their physical appearance plays a crucial role in their success on the hunt. From their distinctive size and coloration to their unique adaptations such as sensory hairs and eye placement, the body structure of wolf spiders is a marvel of natural design. By understanding the intricacies of their anatomy, one gains a greater appreciation for these impressive creatures and their active hunting tactics. Let’s take a closer look at what makes their body structure so remarkable.
Size and coloration
Body Structure of Wolf Spiders:
Wolf spiders are a fascinating group of arachnids that are found all over the world. While they vary in size, with some species being as small as a fingernail, and others being as large as a human hand, they share some common traits in their body structure.
- Size: The size of wolf spiders can range from 0.4 cm to 4.5 cm in length, depending on the species. Females are generally larger than males.
- Coloration: Wolf spiders come in a variety of colors, depending on the species and environment they live in. Common colors include shades of brown, black, and gray, often with patterns or markings that help them blend in with their surroundings. Their bodies are covered in dense hair, which gives them a fuzzy appearance.
It is thought that the coloration of wolf spiders serves multiple purposes. Firstly, it helps them camouflage themselves in their environment, making them less visible to predators and prey. Additionally, some species may use their coloration to attract mates.
Despite their sometimes-intimidating size, wolf spiders are generally not aggressive towards humans, and will only bite if threatened. Their bites are typically not dangerous, but can be painful and cause swelling.
Eye placement and function
Wolf spiders have eight eyes arranged in three rows on their face. The placement and function of these eyes play a crucial role in the spider’s hunting tactics.
Eye placement: The first row has four small eyes, the second row has two large eyes, and the third row has two medium-sized eyes. The eyes are positioned in such a way that the spider has a nearly 360-degree field of view, providing excellent spatial awareness.
Eye function: The two large eyes in the second row are responsible for acute vision, and the smaller eyes in the first and third rows provide peripheral vision. The acute vision is achieved due to the large size of the eyes and their unique arrangement of retinas. Each has a special reflective layer called a tapetum lucidum that enhances light sensitivity in low-light conditions. This adaptation allows wolf spiders to hunt effectively during the night.
The placement and function of the eyes also contribute to the spider’s ability to judge distances accurately and track moving objects. This is crucial for wolf spiders in executing their hunting tactics. In addition to their advanced vision, they also possess other adaptations like sensory hairs, which help them detect air movements and even hear sounds.
To summarize, the placement and function of the eyes in wolf spiders are remarkable adaptations that allow for excellent spatial awareness, acute vision, and accurately judging distances. These adaptations, along with other sensory adaptations like sensory hairs, enable wolf spiders to be efficient predators in their habitat.
Sensory hairs and other adaptations
Wolf spiders have a number of unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in their environment. One of these adaptations is their sensory hairs, also known as trichobothria. These hairs are extremely sensitive and can detect changes in air currents, allowing the spider to locate prey and avoid potential predators.
In addition to sensory hairs, wolf spiders also have adaptations such as strong hooks on their legs that allow them to grip onto surfaces with ease, and a flexible exoskeleton which allows for greater mobility during hunting.
These adaptations allow wolf spiders to be highly effective hunters in a variety of environments, from grasslands to forests. They are able to move quickly and with agility, and can navigate through complex terrain with ease.
Here is a table summarizing some of the key adaptations of wolf spiders:
| Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensory hairs (trichobothria) | Highly sensitive hairs that detect changes in air currents to locate prey and avoid predators. |
| Strong leg hooks | Allow wolf spiders to grip onto surfaces and move quickly and with agility. |
| Flexible exoskeleton | Allows for greater mobility and flexibility during hunting. |
These adaptations are critical for the survival and success of wolf spiders in their environment, and allow them to be highly effective predators.
Hunting Techniques
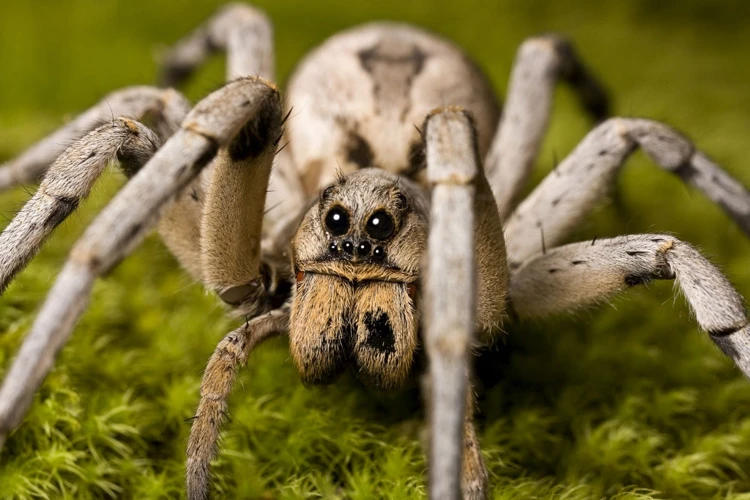

As cunning predators, wolf spiders have developed various techniques for hunting their prey. Their hunting abilities are honed over time, and they have become experts at chasing down fast-moving prey while also mastering the art of ambush tactics. Let’s delve deeper into some of the methods wolf spiders employ in their pursuit of prey.
Chase-and-pounce strategy
Wolf spiders are known for their effective hunting techniques, including the chase-and-pounce strategy. This tactic involves stalking and pursuing their prey until they are within reach, then swiftly launching an attack. The chase-and-pounce strategy requires a combination of speed, agility, and precise coordination.
Physical adaptations
Wolf spiders have several physical adaptations that aid them in their chase-and-pounce hunting technique. Their large, powerful legs enable them to move quickly, while their body shape and size allow them to navigate and maneuver through various terrains. Additionally, their sharp fangs and strong jaws can easily penetrate and immobilize their prey.
Behavioral aspects
In addition to their physical adaptations, wolf spiders also have behavioral traits that enhance their chase-and-pounce strategy. They are patient and strategic hunters, taking the time to observe their prey and assess their movements before initiating an attack. Wolf spiders also have excellent vision, allowing them to effectively track and pursue their prey across various distances and terrains.
Prey preference
While wolf spiders are generalist predators, they do have a preference for certain types of prey. Small insects, such as crickets, flies, and beetles, are common targets. However, they have also been known to hunt larger insects, as well as other spiders and even small vertebrates.
To summarize, the chase-and-pounce strategy is a highly effective hunting technique utilized by wolf spiders. Their physical adaptations, behavioral traits, and prey preferences all contribute to their success as hunters.
Ambush tactics
Wolf spiders are known for their impressive hunting skills and their ability to use a range of different tactics to catch their prey. One of the techniques employed by these spiders is ambush tactics, which involves lying in wait for prey to come near and then striking quickly to capture it.
To execute an ambush, wolf spiders often position themselves in areas with plenty of cover, such as foliage or rocks, where they can hide and wait. They remain motionless and patiently wait for an unsuspecting insect or other small animal to come near. Once their prey is close enough, the spider will pounce and make a quick kill.
The effectiveness of ambush tactics is greatly facilitated by the spider’s ability to remain undetected by its prey. To achieve this, wolf spiders use their camouflage capabilities, blending in with their surroundings. They can change their body coloration to match the environment, which allows them to remain hidden.
Additionally, wolf spiders have excellent eyesight, and they use it effectively to ambush their prey. They can detect prey from long distances using their large anterior median eyes, and the arrangement of their eyes allows for a broad field of view and depth perception. They are especially sensitive to movement, which makes it easier for them to spot prey.
The table below summarizes the key features of ambush tactics used by wolf spiders:
| Tactic | Description |
| Positioning | Spider hides in an area with plenty of cover and waits for prey to come near. |
| Motionlessness | Spider remains still and undetected until prey is close enough. |
| Camouflage | Spider can change body coloration to match surroundings and remain hidden. |
| Eyesight | Spider has excellent eyesight and can detect prey from long distances using their large anterior median eyes. |
| Movement sensitivity | Spider is especially sensitive to movement, making it easier to spot prey. |
Ambush tactics are a highly effective strategy used by wolf spiders to hunt and catch their prey. Their ability to remain undetected and their excellent eyesight make them formidable predators that can succeed even in challenging environments.
Web building and burrowing
Wolf spiders are known for their diverse hunting techniques, which include not only chase-and-pounce and ambush tactics but also web building and burrowing. These techniques allow different species of wolf spiders to hunt in a wide range of environments and habitats.
Some wolf spiders, like the nursery web spider, build a loose silk web around their eggs and guard them until they hatch. Other species, like the burrowing wolf spider, dig burrows in the ground and line them with silk. They may also build trapdoors or cover their burrows with leaf litter to hide from predators and wait for prey to pass by.
A few species of wolf spiders even build more elaborate webs, like the fishing spider, which creates a large, flat web on water surfaces to catch aquatic prey. They may also use their front legs to detect vibrations on the water surface created by struggling insects, allowing them to quickly locate and capture their prey.
The web building and burrowing techniques used by wolf spiders are effective for hunting in various environmental and ecological contexts, as they allow the spiders to adapt to different situations and prey types. However, the effectiveness of these techniques may be influenced by factors such as weather, soil composition, and other environmental conditions, which can affect the spider’s ability to build or maintain its shelter or web.
In terms of conservation and management concerns, there is limited research on the impact of human activity on wolf spider habitat and behavior. However, it is known that pesticides and habitat destruction can negatively affect spider populations and their prey, leading to potential ecological imbalances. It is important for researchers and conservationists to continue exploring the role of web building and burrowing in wolf spider hunting behavior and ensuring sufficient habitat protection and management practices.
Wolf spiders use a variety of techniques for hunting, including web building and burrowing, which allow them to adapt to various environments and prey types. These techniques involve silk production and can be influenced by environmental factors. To protect wolf spider populations, further research is needed on the impact of human activity on their habitats and behaviors.
Vision and Hunting Success
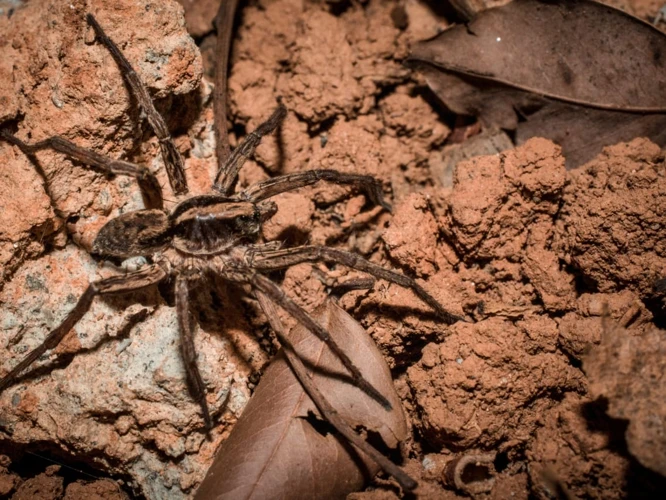

The way in which wolf spiders use their vision to hunt their prey is crucial to their survival. Visual acuity and range are particularly significant factors that contribute to their hunting success. Wolf spiders have some unique abilities such as the use of UV light and polarization that aid in prey detection and recognition. In this section, we will explore the fascinating role of vision in the hunting tactics of wolf spiders.
Visual acuity and range
Wolf spiders are known for their exceptional vision, which is a key component of their active hunting tactics. Their eyes are situated on the front of their cephalothorax, providing them with binocular vision that allows them to accurately perceive depth and distance. In this section, we will discuss the specific details of wolf spider visual acuity and range.
Visual Acuity:
Wolf spiders have a high visual acuity, which enables them to clearly focus on their prey. Studies show that the visual acuity of wolf spiders varies depending on the species and the size of their eyes. However, their visual acuity is generally sharper than that of most other spiders.
A study conducted on the wolf spider Lycosa rabida found that they have a visual acuity of approximately 0.3 cycles per degree (CPD), which is much higher than the visual acuity of 0.05-0.15 CPD found in most other spiders. This high visual acuity allows them to see small prey items from several centimeters away and to maintain focus while moving.
Visual Range:
Wolf spiders have a relatively high visual range, which enables them to scan their surroundings for potential prey. They can see objects at a distance of up to several meters, and their vision is particularly sensitive to motion. This allows them to detect prey from a distance, and to track it as it moves.
A study conducted on the wolf spider Hogna lenta found that they have a visual range of approximately 30 degrees. This means that they can see objects that are up to 30 degrees from their center of vision. Additionally, they have a field of view of approximately 140 degrees, which allows them to scan their surroundings for potential prey.
The table below summarizes the visual acuity and range of different wolf spider species:
| Species | Visual Acuity (CPD) | Visual Range (degrees) |
| ———————— | ————————— | —————————— |
| Lycosa rabida | 0.3 | – |
| Hogna lenta | – | 30 |
| Pardosa milvina | 0.15 | – |
| Arctosa tigerina | 0.15 | – |
Wolf spiders have exceptional visual acuity and range, which enable them to be successful hunters. They are particularly sensitive to motion and have a high field of view, allowing them to efficiently scan their surroundings for prey. Understanding the visual capabilities of wolf spiders is essential for developing effective conservation and management strategies for these ecologically important predators.
Use of UV light and polarization
Wolf spiders are known to use a range of visual cues to detect and track their prey, including ultraviolet (UV) light and polarization. Interestingly, they possess specialized eyes that can detect these cues despite the dim lighting conditions in which they usually hunt.
UV Light Detection
UV light is invisible to the human eye, but wolf spiders can see it due to the presence of specialized cells in their eyes known as UV photoreceptors. Research has shown that the spiders use this ability to navigate, locate prey, and identify potential mates.
One study found that wolf spiders were more successful at catching flies when under UV light compared to normal lighting conditions. This suggests that the ability to detect UV light provides them with a distinct advantage when hunting.
Polarization Detection
Polarization is the orientation of light waves as they travel in a particular direction. It is another visual cue that wolf spiders can detect using specialized cells in their eyes known as polarized light photoreceptors.
Research has shown that wolf spiders can use polarization to navigate, detect potential predators, and identify other wolf spiders of the opposite sex. Additionally, polarization may help them locate prey by enhancing the contrast between the prey and the background.
Combined Use of UV Light and Polarization
The use of UV light and polarization together may enhance the wolf spider’s ability to locate prey and navigate their environment. For example, one study found that wolf spiders use both cues to detect and track the movements of bees, which may help them to predict the bee’s flight paths and more accurately target them as prey.
The ability to detect and use UV light and polarization provides wolf spiders with a distinct advantage when hunting. This unique adaptation allows them to sense and respond to visual cues that are invisible to most other animals.
Prey detection and recognition
When it comes to detecting and recognizing prey, wolf spiders have several unique adaptations that give them an advantage in hunting. One of the most important adaptations is their keen eyesight, which allows them to detect movement and colors in their environment. They also have specialized eyes that allow them to see in low light conditions, making them effective hunters both day and night.
Another adaptation is their use of sensory hairs, which are located on different parts of their body. These hairs are extremely sensitive to vibrations and air movements, allowing the spider to sense its prey’s location and movements. In fact, the spider can even detect the sounds produced by its prey’s movements.
Wolf spiders are also capable of recognizing their prey by its shape and movement patterns. This recognition occurs in the spider’s brain, where it can decipher the size, shape, and behavior of the prey. This allows the spider to determine whether or not a moving object is a potential meal, and whether or not it’s worth pursuing.
To better understand their prey, wolf spiders have the ability to move their eyes independently, giving them a wider field of vision. They can focus their eyes on different objects at the same time, allowing them to track multiple potential prey items at once.
The combination of sharp eyesight, sensory hairs, and recognition abilities make wolf spiders formidable hunters. They use these adaptations to detect and track prey, providing them with a high success rate in capturing food.
| Adaptations for Prey Detection and Recognition |
| Keen eyesight, specialized for low light conditions |
| Use of sensory hairs to detect vibrations, air movements, and prey sounds |
| Recognition of prey by its shape, movement patterns, and behavior |
| Independent eye movement and focus, allowing for a wider field of vision and tracking of multiple prey items |
Environmental and Ecological Factors
As with any living organism, wolf spiders are influenced by a variety of environmental and ecological factors which shape their behavior and survival. Understanding these factors is essential for gaining insight into their role in the ecosystem and for effective conservation and management efforts. From their preferred habitats to their interactions with other organisms, this section delves into the intricate web of factors that influence wolf spider behavior and success. Let’s explore the complex interplay of the environment and ecology in the fascinating world of wolf spiders.
Habitat preferences
Wolf spiders are found in a wide range of habitats, from forests and grasslands to deserts and even wetlands. However, their specific habitat preferences depend largely on their species, size, and stage of development. Some species prefer moist habitats near streams, ponds, or marshes, while others live in drier habitats such as rocky or sandy areas.
Factors affecting habitat preferences
The following factors may influence the habitat preferences of wolf spiders:
- Temperature and moisture: Wolf spiders are cold-blooded and rely on the environment to regulate their body temperature. They tend to prefer habitats with moderate temperatures and sufficient moisture, which allows them to remain active and hunt for prey.
- Vegetation and substrate: Wolf spiders use vegetation and substrate for shelter, camouflage, and hunting. Some species prefer open areas with low vegetation, while others prefer dense vegetation or rocky crevices.
- Prey availability: As active hunters, wolf spiders need access to prey in their preferred habitats. They may select habitats that have a high abundance and diversity of prey.
- Competition and predation: Wolf spiders may also avoid habitats with high competition from other spider species or predators such as birds, lizards, or small mammals.
Examples of wolf spider habitat preferences
Here are some examples of wolf spider species and their preferred habitats:
- Tigrosa helluo: This large and colorful wolf spider is found in wooded areas and grasslands of North America. It prefers to live near the edges of forests, under logs or stones, and in burrows.
- Lycosa tarantula: Also known as the tarantula wolf spider, this species is found in Mediterranean countries and North Africa. It prefers dry and warm habitats with sandy or rocky soil, where it may build deep burrows.
- Hogna carolinensis: This wolf spider is found in the southeastern US, where it inhabits sandy or loamy soils in open fields, lawns, or farms. It may also climb trees or shrubs to hunt.
- Alopecosa pulverulenta: This wolf spider is found in temperate and boreal forests of Europe and Asia. It prefers to live in leaf litter or under rocks near streams, where it hunts for aquatic insects and spiders.
Wolf spiders are adaptable to a variety of habitats, but their survival and reproductive success depend heavily on finding suitable environments with sufficient resources and minimal competition and predation.
Predator-prey relationships
The predator-prey relationships of wolf spiders are complex and can vary depending on the species and habitat. Wolf spiders themselves are predators, preying on a variety of insects and other small arthropods. However, they also face predation from larger animals such as birds, lizards, and small mammals.
One interesting study found that some species of wolf spiders have developed coloration patterns that mimic the appearance of ants, which are common prey items for many predators. By mimicking ants, these spiders may be able to avoid predation by appearing less appetizing or dangerous to potential predators.
Another study found that wolf spiders living in high predation risk environments were more likely to exhibit bold behavior when hunting, potentially increasing their chances of successfully capturing prey. This kind of behavioral adaptation is an important part of the predator-prey relationship in many species, including wolf spiders.
Additionally, the presence of predators in an ecosystem can have a significant impact on the population dynamics of wolf spiders and their prey. For example, if a predator population declines, the prey population may increase, leading to increased predation pressure on the wolf spider population. These kinds of ecological relationships are complex and interdependent, highlighting the need for comprehensive conservation and management strategies that take into account the needs of all species in an ecosystem.
The predator-prey relationships of wolf spiders are an important area of study in ecology and can provide valuable insights into the adaptations and behaviors of both predators and prey. Understanding these relationships is essential for effective conservation efforts and for maintaining healthy ecosystems for future generations.
| Predators | Prey |
|---|---|
| Birds | Small and medium-sized wolf spiders |
| Lizards | Small and medium-sized wolf spiders |
| Small mammals | Small and medium-sized wolf spiders |
| Other predators | Small and medium-sized wolf spiders |
Conservation and management concerns
The conservation and management of wolf spiders is becoming increasingly important as their habitats face anthropogenic threats such as deforestation, urbanization, and climate change. These threats can cause significant declines in wolf spider populations, which can have negative effects on local ecosystems.
One of the main concerns for wolf spider conservation is the loss of suitable habitat as a result of human activities. Wolf spiders typically inhabit areas with dense ground cover, like forest floors or grasslands, and are therefore at risk due to deforestation and other land-use changes. Such habitat loss can lead to population declines and even extirpation of certain species.
Another concern is the use of pesticides and other harmful chemicals, which can have negative impacts on both wolf spiders and their prey. These chemicals can reduce the availability of prey, affect reproductive success, and even cause direct mortality of wolf spiders. To mitigate these impacts, it is necessary to implement farming and land management practices that minimize the use of harmful chemicals.
Climate change is also a significant concern for wolf spider conservation. As temperatures and precipitation patterns shift, this can affect the availability of prey and impact the suitability of habitat. Additionally, shifts in climatic conditions may lead to the spread of invasive species that compete with wolf spiders for resources.
An important aspect of wolf spider conservation is to raise public awareness about these concerns and the importance of protecting these spiders and their habitats. This can be done through education and outreach programs, as well as through the establishment of protected areas and other conservation measures.
The conservation and management of wolf spiders is crucial for the preservation of local ecosystems. To address the threats facing these spiders, it is important to implement measures that protect their habitats, minimize the use of harmful chemicals, and mitigate the impacts of climate change. By working towards these goals, we can ensure that wolf spiders continue to play their important roles in their respective ecosystems.
| Concerns | Impacts |
| Habitat loss | Population declines, extirpation of certain species |
| Use of harmful chemicals | Reduction in prey availability, affect reproductive success, direct mortality |
| Climate change | Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns, invasive species competition |
Conclusion
As we come to the end of our exploration into the active hunting tactics of wolf spiders, it becomes increasingly clear that these small but mighty predators play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of their ecosystems. From their unique body structure to their diverse hunting techniques, these creatures possess a remarkable range of adaptations that enable them to thrive in their environments. Having delved into the factors that contribute to their hunting success, let us now take a moment to reflect on what we have learned and consider what future research may unveil.
Summary of key points
After exploring the role of vision in the active hunting tactics of wolf spiders, the following key points have been revealed:
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Wolf spiders use their vision to locate prey | They have excellent visual acuity and can detect prey movement from far distances |
| UV light and polarization aid in prey detection | Wolf spiders can detect UV light and utilize polarization to enhance their prey detection abilities |
| Size and coloration of wolf spiders vary based on their habitat and environmental factors | Adaptations such as camouflage and mimicry aid in their hunting success |
| Wolf spiders use a variety of hunting techniques including chase-and-pounce, ambush, web-building, and burrowing | Each technique is tailored to their prey and environmental conditions |
| Habitat preferences and predator-prey relationships greatly impact the success and survival of wolf spiders | Conservation and management efforts should take these factors into consideration to protect and preserve wolf spider populations |
| Future research could focus on the genetic and evolutionary aspects of wolf spider vision and behavior | This could provide further insight into their unique abilities and ecological roles |
Wolf spiders rely heavily on their vision for hunting and survival. Their unique adaptations and hunting techniques make them successful predators in their environments. Understanding the role of vision in their behavior can aid in conservation and management efforts to protect these fascinating arachnids. Ongoing research could shed more light on the evolutionary and genetic aspects of wolf spider behavior.
Future research directions
As wolf spiders are an important predator in many ecosystems and play a crucial role in keeping pest populations in check, there is no doubt that further research into their hunting tactics and behaviors would be beneficial.
Currently, there is a limited understanding of the role of other sensory modalities, such as touch and chemical perception, in wolf spider hunting. Future studies could investigate the relative importance of these senses in prey detection and recognition and how they may be used in conjunction with vision.
Another area of research could focus on the impact of environmental factors such as temperature and humidity on wolf spider hunting success. By examining how different abiotic factors affect their behavior, we gain a better understanding of how they may respond to ongoing climate change and habitat alteration.
In addition, studies examining the genetics underlying variation in wolf spider eyesight and hunting prowess would shed light on the evolution of hunting tactics in these spiders and could inform conservation efforts.
Lastly, the development of new and more advanced imaging technologies could allow for more detailed investigations of the neural circuits responsible for vision and sensory processing in wolf spiders, revealing new insights into their behavior and ecology.
There is still much to be learned about these fascinating arachnids, and further research into their hunting behaviors and ecology will undoubtedly yield new discoveries and insights.
| Possible future research directions |
|---|
| Examining the role of touch and chemical perception in wolf spider hunting |
| Investigating the impact of environmental factors on wolf spider hunting success |
| Studying the genetics underlying variation in wolf spider eyesight and hunting prowess |
| Developing new and more advanced imaging technologies to study wolf spider sensory processing |
Frequently Asked Questions
How big can wolf spiders get?
Wolf spiders can reach sizes of up to two inches in length.
What do wolf spiders eat?
Wolf spiders prey on a variety of insects and other small animals including beetles, crickets, ants, and even other spiders.
Do wolf spiders bite humans?
While wolf spiders are not aggressive towards humans, they may bite if provoked or threatened. Their bites are usually not serious and only result in mild pain and swelling.
What is unique about wolf spider vision?
Wolf spiders have excellent vision and are able to detect movement from a distance. They also have specialized eyes that can detect ultraviolet light and polarization.
How do wolf spiders hunt?
Wolf spiders use a variety of hunting techniques including chase-and-pounce, ambush, web building, and burrowing to catch their prey.
Are wolf spiders dangerous to pets?
While wolf spiders are not typically dangerous to pets, their bites may cause discomfort and swelling. It is best to monitor your pet and seek veterinary care if necessary.
Do wolf spiders live in groups or alone?
Wolf spiders are solitary animals and generally do not live in groups. However, they may share territories with other wolf spiders.
How do environmental factors affect wolf spider behavior?
Environmental factors such as light, temperature, and humidity can impact wolf spider behavior and habitat preferences. For example, some species of wolf spiders are more active at night while others are more active during the day.
Are wolf spider populations declining?
There is limited data on wolf spider populations, but some species may be impacted by habitat loss and fragmentation, as well as pesticide use in agricultural areas.
What can I do to help protect wolf spiders?
Protecting the habitats of wolf spiders, reducing pesticide use, and minimizing human disturbances in natural areas can help preserve wolf spider populations and their role in ecosystem functioning.






