Introduction

As spider enthusiasts, it’s fascinating to explore the world of wolf spider species, their behavior, habitats, and unique physical features. However, identifying wolf spider species can be a challenging task, as they share many common traits and characteristics. To help you navigate through this intricate process, we will introduce you to the concept of taxonomic keys, a crucial tool used by researchers and experts, and guide you through the steps involved in identifying various wolf spider species. So, roll up your sleeves and let’s dive into the world of wolf spiders!
Overview of Wolf Spider Species
Wolf spiders are a fascinating and diverse group of arachnids found all over the world. There are over 2,000 species of wolf spiders (family Lycosidae) worldwide, with more than 200 species found in North America alone. Wolf spiders are especially popular among researchers because of their unique hunting techniques and behaviors. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at some key facts about wolf spider species.
To start with, it is important to note that wolf spiders are very diverse when it comes to their appearance. They vary greatly in size, color, and markings. Some species are very small with a body length of only a few millimeters, while others can grow up to several centimeters long. Additionally, they may have stripes, spots, or other patterns on their bodies and legs. You can check out the specific species from our article about wolf spider classification.
Another important fact about wolf spider species is that they are terrrestrial spiders, which means that they live and hunt on the ground rather than in webs. They can be found in many different environments, from forest floors to deserts to grassy fields. Some species are adapted to living in very specific environments, such as near water sources or in rocky areas.
As for their behavior, wolf spiders are solitary hunters and do not form groups or colonies. They spend most of their time on the ground, hunting for prey. They are known for their agility and speed, which they use to chase and capture their prey.
Finally, it is worth mentioning that wolf spider species have undergone many changes in their taxonomy and nomenclature over the years. The scientific community has a long history of studying and classifying these spiders, and new species continue to be discovered and named. You can learn more about the taxonomic history of wolf spiders from our article.
Wolf spiders are an incredibly diverse group of spiders with fascinating physical, behavioral, and taxonomic features. Understanding the characteristics of these spiders is important for their identification and study. In the next section, we will explore how to use a taxonomic key to identify wolf spider species.
What is a Taxonomic Key?
A taxonomic key is a tool that helps in the identification of a particular species based on its characteristics and physical features. It acts as a guide for scientists and researchers to classify living organisms. Taxonomic keys are usually created by experts who have studied the species extensively.
The taxonomic key for identifying wolf spider species has three main categories:
- Family: This category includes distinguishing features that separate wolf spiders from other spider families. This feature helps in identifying the specific spider family to which the species belongs.
- Genus: This category provides specific details about the spider’s physical characteristics, such as leg size, shape, and type of eyes. These details help identify the genus to which the species belongs.
- Species: This category provides more detailed physical features such as color, patterns, markings, and measurements. These details help identify the specific wolf spider species.
Without the taxonomic key, identifying wolf spider species can be challenging and confusing. By using the taxonomic key, scientists and researchers are able to classify species accurately and consistently. This is especially important when it comes to studying wolf spiders’ behavior, ecology, and overall biodiversity.
It’s worth noting that the names of wolf spiders are also significant in the field of taxonomy. They aid in accurate identification and classification of the spider species. Wolf spider naming and identification are crucial for scientific studies that seek to understand these arachnids better. To learn more about wolf spider naming and identification, check out our article on Wolf Spider Naming and Identification. Additionally, the significance of wolf spider nomenclature for taxonomic studies is discussed in detail in our article on The Significance of Wolf Spider Nomenclature.
How to Use the Taxonomic Key?
When it comes to identifying wolf spider species, a helpful tool to use is a taxonomic key. However, the process of using a taxonomic key might seem daunting at first. Don’t worry! Here, we’ll guide you through the steps on how to use a taxonomic key effectively to identify wolf spider species. By the end of this section, you’ll be equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to identify wolf spider species using a taxonomic key. Let’s dive in!
Step 1: Look at Physical Features
Before using the taxonomic key to identify wolf spider species, it is important to take note of their physical features. This step can be crucial in the identification process, as similar-looking species can be distinguished by minor variations in their physical characteristics. Below are the physical features that need to be considered in identifying wolf spider species:
| Physical Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | Wolf spiders vary in size, ranging from 0.04 to 1.18 inches in length. Take note of the spider’s overall size, including the legs. |
| Color | Wolf spiders come in a variety of colors, including brown, gray, black, and even orange or yellow. Take note of the color pattern and any markings on the spider’s abdomen and legs. |
| Eye Placement | Wolf spiders have eight eyes that are arranged in three rows. The top row contains four small eyes, while the bottom two rows each have two larger eyes. Note the arrangement of the spider’s eyes, as this can be a useful distinguishing feature. |
| Hairiness | Wolf spiders are typically covered in hair, which can be short and sparse or long and dense. Note the hair coverage and texture, as well as any unique hair patterns. |
| Leg Length | Wolf spiders have long, slender legs that can vary in length. Note the relative length of the spider’s legs, as well as any unique leg features such as stripes or spikes. |
| Cephalothorax Shape | The cephalothorax, or the front section of the spider’s body, can be round or elongated. Note the shape of the cephalothorax, as well as any unique features such as bumps or ridges. |
By paying attention to these physical features, you can quickly narrow down your selection of wolf spider species and move on to the next step of the identification process.
Step 2: Examine the Habitat
When examining a wolf spider for identification, the second step is to closely examine the habitat in which the spider was found. Wolf spiders can be found in a variety of environments, such as forests, fields, and even deserts. By examining the spider’s habitat, you can narrow down the possibilities of which species it could be.
Here are some important factors to consider when examining the habitat of a wolf spider:
- Geographical location: Different species of wolf spiders are found in different parts of the world. For example, the Carolina wolf spider is found in the southeastern United States, while the Tasmanian wolf spider is found only in Tasmania. Knowing the spider’s location can help you in identifying the species.
- Landscapes: Wolf spiders can be found in a variety of landscapes, from grasslands to forests. Some species are known to burrow and make dens, while others prefer to roam relatively freely. The type of landscape in which the spider was found can provide insight into its species.
- Microhabitats: Wolf spiders can also be found in specific microhabitats within their environment, such as under rocks, in leaf litter, or under tree bark. Examining the specific microhabitat can provide important information about the spider’s species.
- Prey: Wolf spiders are hunters, and their diet can vary depending on the species and environment. Some species prefer to hunt insects, while others may hunt small reptiles or even other spiders. Examining the prey available in the spider’s habitat can reveal clues about its species.
Taking into account all of these different factors can help you in identifying the species of wolf spider you have encountered. By examining the spider’s physical appearance and habitat, you can create a more accurate taxonomic key to help you in the identification process.
Step 3: Study Behavioral Patterns
When it comes to identifying wolf spider species, studying their behavioral patterns can be just as important as examining their physical features. Here are some things to look out for:
- Prey preferences: Different wolf spider species may have specific prey preferences, such as eating only insects or exclusively going after other spiders. Take note if you observe a particular type of prey in the spider’s habitat.
- Hunting behavior: Some wolf spider species are active hunters, chasing after their prey, while others use a sit-and-wait approach to ambush their meals. Observe the spider’s hunting behavior and take note of any unique strategies it employs.
- Mating rituals: Male wolf spiders often perform elaborate courtship displays to attract a mate. These rituals can involve distinctive movements and sounds. Observe any behaviors related to mating, and try to note any identifying characteristics of the males and females.
- Mobility: Some wolf spider species are excellent climbers, while others prefer to stay closer to the ground. Pay attention to how the spider moves around its environment, as this can also help determine its species.
Understanding these behavioral patterns can be essential to identifying wolf spider species correctly. By taking the time to observe and document a spider’s habitat, physical features, and behavior, you can increase your chances of accurately determining its species and contributing to scientific knowledge.
Wolf Spider Species Identification

Once you have gathered all the necessary information about wolf spiders, you can begin the process of identifying the spider species. This can be a bit perplexing at first, as there are many different species of wolf spiders, each with their own unique physical features, habitats, and behavioral patterns. However, with a little patience and the right tools at hand, you can start identifying the wolf spider species in no time. In this section, we will explore the different methods for identifying common and uncommon wolf spider species. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of wolf spider species identification!
Common Wolf Spider Species Identification
Wolf spiders are incredibly diverse and come in many different species. Identifying common wolf spider species can be challenging, but with the right tools and knowledge, it can become a lot easier. Here are some common wolf spider species and their distinctive features to help you in your identification process.
| Common Wolf Spider Species | Distinctive Features |
|---|---|
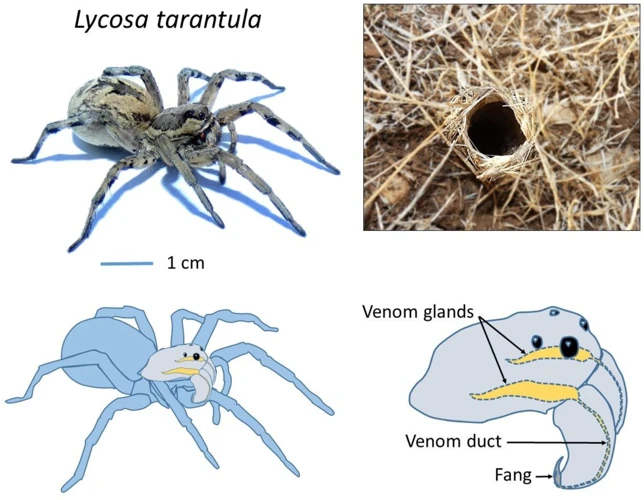
| Lycosa Tarantula | Large size, with a distinct pattern of stripes and spots on its abdomen |
| Trochosa Terricola | Dark brown or black body, with white markings on the legs |
| Gladicosa Pulchra | Distinctive eye pattern, with two large eyes in the center and two smaller eyes above them |
| Hogna Carolinensis | Large size, with a hairy body and a distinct ridge on the cephalothorax |
| Pardosa Milvina | Small size, with a light brown or gray body and distinctive black stripes on the legs |
When trying to identify these common wolf spider species, it’s important to note their distinctive features. The Lycosa Tarantula, for example, is a large spider with a striped and spotted abdomen. The Trochosa Terricola has a dark body and white markings on its legs. The Gladicosa Pulchra has a unique eye pattern with two large eyes in the center and two smaller eyes above them. The Hogna Carolinensis is a large, hairy spider with a ridge on its cephalothorax. Lastly, the Pardosa Milvina is a small spider with stripes on its legs and a light brown or gray body.
Identifying common wolf spider species can be challenging, but with a little practice, you can begin to recognize the distinctive characteristics of different species. Of course, it’s always helpful to use additional resources, such as identification guides and literature, as well as seek expert advice if you’re having trouble identifying a specific species.
Uncommon Wolf Spider Species Identification
Identifying uncommon wolf spider species can be a bit more challenging than their common counterparts. However, by using careful observation and comparison with identification guides, it is possible to distinguish one species from another.
One uncommon species is the Hawaiian wolf spider (Alopecosa nothofagi). This species is found only in Hawaii and has unique physical features such as a hairy body and two distinct black stripes on the cephalothorax. It typically inhabits forested areas and can be found active at night, hunting for prey.
Another uncommon species is the Six-spotted Fishing Spider (Dolomedes triton). As the name suggests, this wolf spider species is frequently found near water sources. It has a distinctive six-eyes pattern, and its body is covered in dense hair. Unlike most wolf spiders, this species does not build a burrow or lair but relies on water and shelter from the bank. They also feed on a variety of prey including amphibians and small fish.
The Burrowing Wolf Spider (Geolycosa rogersi) is another uncommon species that can be found living in underground burrows in the southeastern United States. They have a brownish-gray coloration with distinctive chevron markings on the cephalothorax. These spiders are nocturnal, emerging from their burrows at night to hunt for prey.
A helpful way to organize and compare physical features of uncommon wolf spider species is to use an identification table. Below is an example of a table that can be used to compare and identify these species.
| Species Name | Physical Features | Habitat | Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alopecosa nothofagi | Hairy body, two distinct black stripes on cephalothorax | Forested areas | Nocturnal hunter |
| Dolomedes triton | Six-eyes pattern, dense hair on body | Near water sources | Feeeds on amphibians and small fish |
| Geolycosa rogersi | Brownish-gray coloration, chevron markings on cephalothorax | Underground burrows | Nocturnal hunter |
By using an identification table and carefully examining the physical features, habitat, and behavior of uncommon wolf spider species, it is possible to distinguish one species from another and gain a better understanding of the diversity within the wolf spider family.
Expert Tips for Identification
When it comes to identifying wolf spider species using a taxonomic key, it’s easy to get lost in the details. Even with the three-step process we’ve outlined, it can still be challenging to distinguish one species from another. This is where expert tips for identification come in handy. In this section, we’ll share some useful tips from seasoned experts that you can use to boost your chance of success in identifying wolf spider species. So, grab your magnifier and let’s get started!
Use a Magnifier
For a more detailed and accurate identification of wolf spider species, it is recommended to use a magnifier or a hand lens when examining their physical features. This can help you see even the tiniest details, such as hair patterns and eye arrangements, which are crucial for identifying the species.
When using a magnifier, it is important to position it properly and use it adequately to avoid any errors in identification. Here are some tips to help you use a magnifier effectively:
1. Choose the Right Magnifier
Select a magnifier that provides enough magnification without affecting the quality of the image. A magnifier with a magnification power of at least 10x is recommended.
2. Position the Magnifier
Hold the magnifier close to the spider to get a clear view of the features. You may also need to adjust the distance between the magnifier and the spider to achieve optimal focus.
3. Use Sufficient Light
Make sure there is enough light surrounding the spider, as this will help illuminate the fine details. Natural daylight or a bright lamp can provide the necessary light.
4. Observe Carefully
Examine the spider’s physical features under the magnifier carefully, noting any unique patterns or unusual characteristics that may distinguish it from other wolf spider species.
Using a magnifier is particularly helpful when identifying uncommon wolf spider species, as these species may have subtle physical features that require a closer look to notice. By using a magnifier and taking note of unique patterns and characteristics, you will be more likely to accurately identify the species of wolf spider you are examining.
Mark Unique Physical Features
When identifying wolf spider species using a taxonomic key, it is important to pay attention to unique physical features. One way to ensure you don’t miss any important details is to mark those features that stand out to you during your observation. This will help you remember what to look for and allow you to refer to your notes as needed.
Here are some unique physical features to look for when identifying wolf spider species:
- Size: Pay attention to the spider’s size relative to other wolf spider species. Size can be an important factor in distinguishing between different species.
- Color: Look at the spider’s overall color, as well as any distinct color patterns or markings that may be present.
- Eyes: Wolf spiders have eight eyes arranged in three rows. Pay attention to the arrangement of the eyes and any unique eye patterns that may be present.
- Legs: Check the length and thickness of the spider’s legs, as well as any unique leg patterns or dimples that may be present.
- Abdomen and cephalothorax: Look at the shape and overall appearance of the abdomen and cephalothorax, as well as any distinct markings or patterns that may be present.
- Hairs: Wolf spiders have hairs on their bodies, legs, and pedipalps. Pay attention to the density, color, and shape of the hairs.
- Spines: Check for any unique spine patterns or arrangements on the spider’s legs or body.
Marking unique physical features is a helpful tool in identifying wolf spider species, but it is important to remember that these features may vary within a species depending on age, sex, or location. The more you practice identifying wolf spiders using a taxonomic key, the easier it will become to recognize important physical features.
Refer to Identification Guides and Literature
When it comes to identifying wolf spider species using a taxonomic key, referring to available identification guides and literature can be extremely helpful. These resources provide valuable information on the characteristics of different wolf spider species, allowing for easier identification.
Here are some of the best identification guides and literature available for identifying wolf spider species:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| The Wolf Spider Taxonomic Inventory | This online resource provides a comprehensive list of known wolf spider species and their taxonomic classifications. It is regularly updated with new information and research. |
| Wolf Spiders of the World | This book by expert spider biologist, Jonathan A. Coddington, provides detailed information on wolf spider species found around the world. It includes high-quality photographs and illustrations for easier identification. |
| Spider Identification: An Introduction | This guide, created by the Australian Museum, provides an introduction to spider identification and includes information on common spider families, including wolf spiders. It features detailed descriptions and photos for each family of spider, including wolf spiders. |
| Field Guide to Spiders of California and the Pacific Coast States | For those interested in identifying wolf spider species found on the Pacific Coast, this field guide is an excellent resource. It includes photographs and detailed descriptions of more than 300 species found in the region, including wolf spiders. |
Using these resources in conjunction with a taxonomic key can help you identify wolf spider species with greater accuracy. Remember to take note of the physical features, habitat, and behavioral patterns of each species to properly identify it. By following the steps outlined in this guide and utilizing the available resources, you can become skilled in identifying wolf spider species in no time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, identifying wolf spider species can be a challenging but rewarding task. By using a taxonomic key, individuals can easily distinguish between different types of wolf spiders based on their physical traits, habitat, and behavior.
It’s important to note that some species of wolf spiders may be more difficult to identify than others, and experts in the field may need to be consulted.
However, with the use of a magnifier and careful examination of unique physical features, as well as referring to identification guides and literature, even the most elusive species can be identified.
By understanding the characteristics of different wolf spider species, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for these fascinating creatures and their role in the ecosystem. So the next time you come across a wolf spider in the wild, take a closer look and see if you can identify which species it belongs to using the techniques outlined in this taxonomic key guide. Happy spider hunting!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a wolf spider and other spiders?
Wolf spiders have an exceptional ability to hunt down their prey while other spiders, like orb weavers, sit and wait for their prey to come to them.
How can I tell if a spider is a wolf spider?
Wolf spiders have unique eye structures and a hairy body that sets them apart from other spider species. They also have a habit of burrowing in the ground.
What is a taxonomic key used for?
A taxonomic key is a guide used to identify species of plants, animals, and other organisms. It relies on physical characteristics and scientific classification to help classify organisms.
What are the benefits of using a taxonomic key?
It can help you quickly identify different wolf spider species and accurately classify them, as well as improve your understanding of the different traits that distinguish one species from another.
Can I use a taxonomic key to identify other spider species?
Yes, you can use a taxonomic key to identify different spider species. However, you should be aware that different spider species may have different physical characteristics and identification features.
What are some common wolf spider species in North America?
Some common wolf spider species in North America include Hogna carolinensis, Rabidosa rabida, and Pardosa lapidicina.
Where do wolf spiders typically live?
Wolf spiders can be found all over the world, but they are most commonly found in grassy or wooded areas.
Are wolf spiders dangerous to humans?
While wolf spiders are venomous, they generally pose no danger to humans. Their bites can be painful and cause swelling, but they are not life-threatening.
How can I safely capture and release a wolf spider?
You can safely capture a wolf spider using a jar or container. Be sure to release the spider back into its natural habitat, away from human dwellings.
What should I do if I find a wolf spider in my home?
If a wolf spider has made its way into your home, you can safely capture it using a jar or container and release it outside. Be sure to seal off any entry points to prevent further intrusions.






