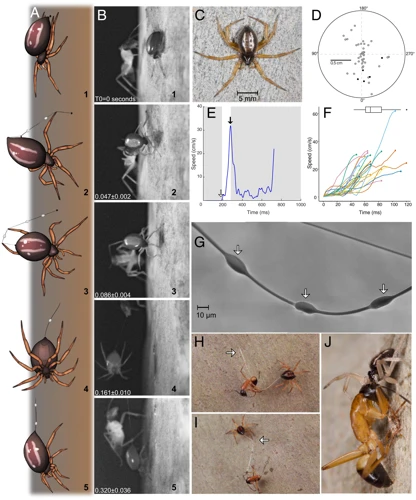
As we step into the natural world, we encounter a vast array of creatures, each with its unique adaptations to thrive in its environment. One of these remarkable creatures is the wolf spider. Despite their intimidating appearance, these arachnids are fascinating creatures that have developed a remarkable ability to assess and avoid predation risk. In this article, we will explore how wolf spiders detect and avoid danger, the mechanisms behind their predation risk assessment, and the adaptive significance of this behavior. So, let’s dive deep into the world of wolf spiders and uncover the secrets of how they survive in the wild.
Why Do Wolf Spiders Need to Assess Predation Risk?

As ambush predators, wolf spiders spend a significant amount of time waiting for their prey to come in range, making them susceptible to a wide range of predators. The ability to assess predation risk is therefore crucial for their survival and success as predators. Understanding the various predators of wolf spiders and parasitoid wasp threats highlights the importance of assessing predation risk in wolf spiders. In the following sections, we will explore the mechanisms of predation risk assessment in wolf spiders and how they utilize these mechanisms to avoid danger.
Predators of Wolf Spiders
Wolf spiders, like all other living organisms, are exposed to a variety of predators in their environment. These predators include both vertebrates and invertebrates, each of which poses a different type of threat to the wolf spider. Here are some of the most common predators of wolf spiders:
| Predator | Predator Type | Threat Posed |
|---|---|---|
| Birds | Vertebrate | Their excellent vision and flying abilities make them a formidable threat to wolf spiders. They can swoop down and catch a spider before it has a chance to react.
For more information on how birds are predators of wolf spiders, click here. |
| Other Spiders | Invertebrate | Other spider species, especially those that are larger than wolf spiders, can pose a significant threat. They can overpower wolf spiders and feed on them.
For more information on how wolf spiders use camouflage to avoid predators, click here. For more information on defense mechanisms of wolf spiders, click here. |
| Insects | Invertebrate | Insects such as mantises and beetles can be predators of wolf spiders. They have mandibles that are capable of grasping and crushing wolf spiders.
For more information on hunting strategies of wolf spiders, click here. |
As these predators pose real threats to wolf spiders, it is important that they effectively detect and avoid danger. Failure to do so can result in severe consequences, such as injury or death.
The Consequences of Failing to Detect Danger
Failing to detect danger can have serious consequences for wolf spiders. Below is a table outlining some of the potential outcomes of not properly assessing predation risk:
| Consequences of Failing to Detect Danger | Description |
| Increased risk of mortality | If a wolf spider fails to detect a predator, it may become an easy target and may not survive the encounter. |
| Energy loss | A wolf spider may spend significant energy on behaviors such as fleeing or hiding from a perceived threat, which can have negative impacts on its overall energy balance. |
| Missed opportunities for resources | If a wolf spider spends too much time engaging in predator avoidance behaviors, it may miss out on opportunities to hunt and capture prey, potentially impacting its ability to survive and reproduce. |
| Reduced fitness | As a result of the factors above, a wolf spider that repeatedly fails to detect danger may experience reduced fitness, potentially impacting its overall success in the ecosystem. |
It is crucial for wolf spiders to assess predation risk accurately in order to avoid these negative consequences and increase their chances of survival and reproduction.
Mechanisms of Predation Risk Assessment
As one of the most successful predators in the arthropod kingdom, wolf spiders are constantly faced with the challenge of avoiding becoming prey themselves. In order to detect and avoid danger, these spiders have evolved a multitude of mechanisms for assessing predation risk. Through a combination of visual, vibratory, and chemical cues, as well as behavioral responses, wolf spiders are able to quickly and accurately determine when they are in danger. In this section, we will explore the fascinating array of mechanisms that allow wolf spiders to assess and respond to potential threats.
Visual Cues
When it comes to assessing predation risk, wolf spiders rely heavily on visual cues. They have keen vision and are able to detect objects and movements in their environment with great precision. In fact, studies have shown that wolf spiders can detect potential predators even before they enter their field of view. Here are some of the visual cues that help wolf spiders assess predation risk:
| Visual Cues | Description |
|---|---|
| Silhouette of predator | Wolf spiders are able to recognize the shape and size of predators even from a distance. They can discern between the silhouette of a predator and that of other objects or animals in their environment. |
| Movement of predator | Wolf spiders are highly attuned to the movement of predators. They can detect subtle changes in the speed, direction and intensity of movement, allowing them to predict the trajectory of the predator and respond appropriately. |
| Eye contact | When encountering a predator, wolf spiders often make eye contact with it. This allows them to assess the level of threat posed by the predator, as well as communicate their own level of aggression or fear. |
| Color and pattern | Some studies suggest that wolf spiders are able to distinguish between different colors and patterns of predators. This may be particularly important when encountering camouflaged or hidden predators. |
Wolf spiders use these visual cues to quickly assess the level of predation risk in their environment and take appropriate action to avoid danger. However, their ability to detect visual cues may be affected by a range of factors, including lighting conditions, time of day and the individual characteristics of the spider.
Vibratory Cues
Vibratory cues play an important role in the predation risk assessment of wolf spiders. These spiders have specialized hairs called trichobothria that are extremely sensitive to even the slightest vibrations in the air or ground. They use these vibrations to detect potential danger in their environment. Here are some ways in which vibratory cues help wolf spiders assess predation risk:
- Detecting approaching predators: When a predator is nearby, such as a bird or a lizard, it may create slight vibrations in the ground or air as it moves. Wolf spiders can pick up on these vibrations using their trichobothria and quickly recognize the danger.
- Distinguishing between predators and prey: Vibratory cues also help wolf spiders distinguish between predators and potential prey. For example, they can recognize the vibrations created by certain insects they hunt, versus the vibrations created by a predator that they need to avoid.
- Assessing the size of the predator: Vibratory cues can also provide useful information about the size of the predator. Larger animals generally create stronger vibrations, while smaller animals create weaker vibrations. This enables wolf spiders to make more calculated decisions about whether they can take on a predator or need to flee.
The importance of vibratory cues is also evident when considering the consequences of failing to detect danger. Without the ability to sense vibrations, wolf spiders would not be able to identify approaching predators or distinguish between predators and prey. This could lead to fatal consequences for the spider.
The ability of wolf spiders to detect vibratory cues is a crucial adaptation that allows them to better assess predation risk in their environment. By being able to quickly recognize and respond to potential danger, wolf spiders can better ensure their survival and pass on their genes to future generations.
Chemical Cues
Chemical cues play an important role in predation risk assessment for wolf spiders. These spiders can detect chemical cues from predators through their sense of smell. They use this ability to locate sources of danger and to avoid them. The following are some of the ways that wolf spiders use chemical cues to assess predation risk:
1. Predator-specific odors: Wolf spiders can detect the odor of specific predators and associate them with danger. For example, the odor of a bird might trigger an automatic behavioral response in a wolf spider, causing it to freeze, remain still, or move away. This response reduces the chances of being detected by the predator, giving the spider a better chance of survival.
2. Alarm pheromones: When a spider is attacked or threatened, it may release an alarm pheromone that alerts other spiders in the area to the presence of danger. This pheromone can stimulate a collective fear response among the spiders, causing them all to take evasive action.
3. Prey-specific chemicals: Wolf spiders can detect the chemicals produced by their prey and use them to locate potential food sources. By avoiding areas with high levels of prey chemicals, they can also avoid areas where predators are likely to be present.
4. Intraspecific odors: Male wolf spiders can detect the chemical signals produced by females to locate potential mates. This ability is particularly important during mating season when males wander in search of receptive females. However, this also creates a risk of predation, as predators can also use these chemical cues to locate their prey.
Chemical cues are an important mechanism for wolf spiders to detect and avoid danger. By using their sense of smell, they can identify predator-specific odors, alarm pheromones, prey-specific chemicals, and intraspecific odors. This ability allows them to reduce the risk of mortality, conserve energy, and increase their chances of reproductive success. However, further research is needed to fully understand the complex chemical communication systems in wolf spiders and their implications for ecology and evolution.
Behavioral Responses
Wolf spiders employ various behavioral responses to assess and avoid predation risks. These behaviors are honed through natural selection and have proven to be effective in increasing their chances of survival. Here are some of the behavioral responses utilized by wolf spiders to detect and avoid danger:
- Freezing: One of the most common behavioral responses of wolf spiders is to freeze upon detecting a potential predator. By freezing, wolf spiders blend in with their surroundings and remain undetected by predators. This strategy is particularly effective against predators who rely on movement to detect their prey.
- Retreating: Another common behavior of wolf spiders is to retreat when they detect danger. Wolf spiders are agile and swift, allowing them to escape from predators quickly. Retreating also helps wolf spiders avoid potential harm and conserves their energy.
- Feigning Death: When wolf spiders are in a dire situation where they cannot retreat or freeze, they sometimes resort to feigning death. By playing dead, wolf spiders hope to convince their predators that they are not viable prey. This behavior is particularly effective against predators that are attracted to movement or vibrations.
- Attacking: In some cases, wolf spiders may attack their predators if they feel threatened. This is a rare behavior, and wolf spiders usually resort to it only as a last resort. Some species of wolf spiders employ venomous bites as a means of self-defense and as a tool for capturing prey.
Wolf spiders exhibit a range of behavioral responses to assess and avoid predation risks, demonstrating their adaptability and survival skills. These behavioral responses are necessary for their survival, and their efficiency is a testament to the effectiveness of natural selection.
Factors Affecting Predation Risk Assessment
When it comes to assessing predation risk, there are a number of factors that can influence a wolf spider’s ability to detect and avoid danger. These factors range from individual characteristics such as age and sex, to environmental cues and learned experiences. Understanding these factors is crucial to gaining a better understanding of the mechanisms behind predation risk assessment in wolf spiders. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at some of the key factors that can impact a wolf spider’s ability to assess predation risk.
Age and Sex of the Wolf Spider
The age and sex of wolf spiders play a crucial role in their ability to assess predation risk. Here are some factors to consider:
Age:
- Young spiders lack experience and may not be able to recognize predators as easily as their older counterparts.
- Older spiders may have reduced sensory capabilities, making it harder for them to detect predation risk cues.
- However, research has also shown that older spiders may have a better ability to assess danger, as they have had more opportunities to develop more effective avoidance strategies.
Sex:
- Male wolf spiders have been observed to take more risks and have higher mortality rates than females, likely due to their increased movement and exploring behavior in search of mates.
- Females, on the other hand, tend to be more cautious and may have a better ability to assess predation risk, as their primary focus is protecting their young.
- Female spiders are often larger and may have more developed sensory systems, allowing them to better detect and respond to predation risk cues.
Age and sex are important factors to consider when examining predation risk assessment in wolf spiders. While experience and size may give older and female spiders an advantage, young spiders and males may still be able to effectively assess predation risk through other means, such as behavioral responses or chemical cues.
Experience and Learning
Experience and learning also play an important role in the ability of wolf spiders to assess predation risk. The more experience a spider has with a particular predator, the better equipped it is to recognize and avoid it in the future. Similarly, repeated exposure to non-threatening stimuli can result in habituation, where spiders become less responsive to those stimuli over time.
Table:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Experience | Spiders that have encountered a particular predator before are more likely to effectively assess the risks it poses in the future. |
| Learning | Spiders can learn to associate certain cues with danger, and modify their behavior accordingly (e.g. avoiding dark areas where predators may be hiding). |
| Habituation | Repeated exposure to non-threatening stimuli can result in habituation, where spiders become less responsive to those stimuli over time. |
This learning ability is especially important for juvenile spiders, who lack the experience of their adult counterparts. Juvenile spiders may be more likely to err on the side of caution, reacting to potential threats even if they turn out to be harmless. Over time, as they gain more experience, they are better able to fine-tune their predator detection abilities and become more efficient in their responses.
Experience and learning are critical factors in the ability of wolf spiders to assess predation risk. This ability helps spiders to reduce their risk of mortality and conserve energy, ultimately contributing to their reproductive success and fitness. Further research into the interplay between experience, learning, and predation risk assessment in wolf spiders could provide valuable insights into the broader ecology and evolution of these fascinating creatures.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in the predation risk assessment of wolf spiders. These factors include:
- Presence of prey: The availability of prey affects the predation risk assessment behavior of wolf spiders. When prey is plentiful, wolf spiders tend to take more risks and are less cautious in their behavior.
- Light: Light is an important environmental factor that influences the activity and behavior of wolf spiders. They tend to be more active at night when light levels are low. During the day, they tend to seek shelter and stay hidden from potential predators.
- Temperature: Temperature also affects the behavior and activity of wolf spiders. They are more active in warmer temperatures and tend to stay hidden when temperatures are too cold.
- Humidity: Humidity levels can affect the activity and behavior of wolf spiders. They tend to be more active in humid conditions and may seek out moist environments to reduce water loss from their bodies.
- Presence of predators: The presence of predators can affect the behavior of wolf spiders. When predators are present, wolf spiders tend to be more cautious and may spend more time hiding or searching for safe places.
- Vegetation: Vegetation can provide cover and shelter for wolf spiders, which can reduce their predation risk. They may also use vegetation for hunting or as a means to move around without being seen.
It is important to note that these environmental factors can vary depending on the specific habitat and geographical location of the wolf spider. Understanding how these factors influence their behavior and activity can provide insight into their ecology and evolution.
Adaptive Significance of Predation Risk Assessment
As with many other organisms in nature, the ability of wolf spiders to detect and avoid predation risk has played a crucial role in their evolution and survival. This section will explore the adaptive significance of this trait in more detail. By understanding why wolf spiders undertake predation risk assessments and how they benefit from doing so, we can gain insight into the ecology and evolution of these fascinating arachnids. So, let’s dive in and explore the importance of predation risk assessment in wolf spiders.
Reducing Risk of Mortality
Survival is the highest priority for any living organism, and wolf spiders are no exception. Predation risk assessment is critical for reducing the risk of mortality for these spiders. They employ various mechanisms to detect danger and respond appropriately. Let us take a closer look at how these mechanisms work and how they help in reducing the risk of mortality for wolf spiders.
One of the main mechanisms for reducing the risk of mortality is by detecting potential predators early. Wolf spiders have excellent vision and can detect visual cues from predators such as birds, lizards, and other spider species. They use their keen eyesight to scan their surroundings for potential threats and quickly move away from them. Vibratory cues are also important in detecting predators, especially when they are hidden or camouflaged. When predators move, they create vibrations in the environment, which the spiders can sense through the hairs on their legs.
Chemical cues also play a significant role in reducing the risk of mortality. Wolf spiders can detect chemical cues from predators, which can include scents and pheromones. Chemical cues help wolf spiders detect predators that are out of sight or smell predators that are camouflaged in their surroundings. They can quickly move away from areas where they sense the presence of predators.
Another mechanism for reducing the risk of mortality is behavioral responses. Wolf spiders have different behavioral responses to potential predators, depending on the situation. When threatened by a predator, they may freeze in place, which helps them to blend in with their surroundings and avoid detection. They can also leap away to escape from a predator quickly.
The following table summarizes the mechanisms and adaptive significance of predation risk assessment in reducing the risk of mortality for wolf spiders.
| Mechanisms of Predation Risk Assessment for Reducing Risk of Mortality | Adaptive Significance |
|---|---|
| Visual Cues | Early detection and avoidance of predators |
| Vibratory Cues | Detection of hidden or camouflaged predators |
| Chemical Cues | Detection of predators out of sight or smell |
| Behavioral Responses | Quickly responding to potential threats, including freezing in place or leaping away |
Wolf spiders employ various mechanisms for assessing predation risk to reduce the risk of mortality. These mechanisms include visual, vibratory, and chemical cues, as well as behavioral responses. The adaptive significance of predation risk assessment for reducing mortality risk includes the ability to detect and avoid predators early, detect hidden or camouflaged predators, detect predators out of sight or smell, and quickly respond to potential threats.
Conserving Energy
Conserving Energy is one of the adaptive significances of Predation Risk Assessment in Wolf Spiders. Wolf Spiders, like other animals, have limited energy reserves, which they need to allocate efficiently to different activities such as foraging, mating, and molting. The risk of predation can be high in certain environments, such as open fields, where wolf spiders are more exposed to predators, or during the night, when their visual cues are limited. In such situations, wolf spiders need to invest more energy in assessing the risk of predation and avoiding danger.
Here are some ways that Predation Risk Assessment helps Wolf Spiders conserve energy:
- Identifying Safe Areas: Wolf spiders use their sensory cues to detect areas where the risk of predation is low. For example, they may choose to stay hidden in leaf litter, under rocks or in crevices during the day, when predators are active. By minimizing their exposure to danger, they can conserve energy that would have been lost in an encounter with a predator.
- Reducing Unnecessary Movements: Wolf spiders are active hunters that rely on visual cues to detect prey. However, they are also vulnerable to predators when they move around. By assessing the risk of predation, they can minimize unnecessary movements, conserve energy and reduce the likelihood of being detected by predators.
- Optimizing Foraging Strategies: Wolf spiders need to forage efficiently to meet their energy requirements. However, they cannot just forage anywhere, as they risk exposure to predators. Predation Risk Assessment helps them to choose areas where the risk of predation is low and optimize their foraging strategies. For example, they may choose to forage in areas where there are fewer prey, but also fewer predators, thereby conserving energy while still meeting their energy requirements.
Predation Risk Assessment in Wolf Spiders has adaptive significance in conserving energy. Through various mechanisms such as identifying safe areas, reducing unnecessary movements, and optimizing foraging strategies, Wolf Spiders can conserve energy and allocate it efficiently to other activities such as mating and molting.
Reproduction and Fitness
One of the most critical factors affecting the evolutionary success of any species is its reproductive output, which can be significantly impacted by predation risk assessment in wolf spiders. Strong predation risk avoidance behaviors can result in reduced energy expenditure for predator detection and escape, enabling wolf spiders to allocate more resources towards reproduction and fitness.
Research has demonstrated that female wolf spiders allocate more resources to reproduction when they perceive low predation risk, resulting in larger clutch sizes and higher offspring survival rates. Male wolf spiders are known to engage in costly mate search behaviors for successful reproduction, but limited predation risk can reduce these costs and enable males to allocate more resources to reproduction and mating success.
Additionally, predation risk assessment can influence mate choice decisions in wolf spiders. Females often base their mate choices on male physical traits, such as body size, coloration, and courtship displays. However, in the presence of high predation risk, female wolf spiders are more likely to choose males with faster and more efficient escape responses, which can reduce the risk of predation during copulation and ultimately improve their reproductive success.
Predation risk assessment plays a crucial role in shaping the reproductive strategies and fitness of wolf spiders. By reducing the energy expenditure associated with predator detection and escape, wolf spiders can allocate more resources towards successful reproduction and mating. Predation risk can impact mate choice decisions, necessitating careful consideration of ecological factors when studying the evolution of reproductive traits in this critical group of arachnids.
- Predation risk avoidance behaviors can result in reduced energy expenditure
- Female wolf spiders allocate more resources to reproduction when they perceive low predation risk
- Male wolf spiders can allocate more resources to reproduction with limited predation risk
- Predation risk assessment can influence mate choice decisions in wolf spiders
Conclusion
As we reach the end of our exploration into predation risk assessment in wolf spiders, it’s clear that these small arachnids have developed remarkable strategies for avoiding danger and ensuring their survival. Throughout this article, we’ve looked at the different mechanisms and factors that shape their ability to detect and respond to potential threats. By understanding the adaptive significance of these behaviors, we can gain important insights into the complex interactions between predators and prey in natural ecosystems. As we move forward, it’s crucial to continue studying these fascinating creatures to further our knowledge of their behavior and the role they play in our environment.
Implications of Predation Risk Assessment in Wolf Spiders for Ecology and Evolution
The predation risk assessment abilities of Wolf Spiders have significant implications for both ecology and evolution. Firstly, their survival behavior and potential for avoiding predators can affect the population dynamics of not only themselves, but also their prey and predator species.
The mechanisms and factors involved in predation risk assessment are likely to have evolved over time. This is because the ability to detect and avoid danger has allowed Wolf Spiders to survive and reproduce while minimizing risk. Thus, their predatory risk assessment can contribute to evolutionary processes by promoting the survival of individuals with better risk assessment abilities and allowing for the evolution of more efficient mechanisms and factors involved in the process.
Understanding the predation risk assessment abilities of Wolf Spiders has larger implications for the study of animal behavior in general. It can offer insights into the sensory capabilities and cognitive processes of animals, and how they might have evolved in response to particular ecological pressures.
The predation risk assessment abilities of Wolf Spiders can provide a unique and valuable perspective on the relationships between ecological processes and evolutionary processes. By understanding the mechanisms, factors, and adaptive significance of risk assessment, we can gain a deeper understanding of how animals interact with their environment and how they evolve over time.
| Ecological Implications | Evolutionary Implications |
|---|---|
| Population Dynamics – Wolf Spiders’ ability to avoid danger can have an impact on the population dynamics of themselves, their prey, and their predator species. | Evolutionary Mechanisms – Predation risk assessment mechanisms and factors have likely evolved over time and contribute to the survival and fitness of individuals. |
| Ecological Pressures – The study of predation risk assessment can provide insights into the sensory and cognitive processes of animals, and how they have evolved in response to environmental pressures. | Survival and Reproduction – Predation risk assessment abilities can contribute to the survival and reproductive success of individuals with better risk assessment skills. |
Areas for Future Research
There are several areas that warrant further research in the field of predation risk assessment in wolf spiders. These include:
| Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Neural mechanisms involved in predation risk assessment | While it is known that wolf spiders use visual, vibratory, and chemical cues to detect predators, there is still much to learn about the neural mechanisms involved in this process. |
| Effect of prey density on predation risk assessment | Studies have shown that prey density can affect the behavior of predators, but it is unclear how this affects the ability of wolf spiders to detect and avoid danger. |
| Interaction between predation risk assessment and mate choice | It is known that female wolf spiders use visual cues to evaluate potential mates, but it is unclear how predation risk assessment influences this process. |
| Impact of climate change on predation risk assessment | As the climate changes, the behavior of predators and prey may change as well, which could have implications for the ability of wolf spiders to assess predation risk. |
Additional research in these areas would improve our understanding of the adaptive significance of predation risk assessment in wolf spiders, as well as shed light on the mechanisms underlying this important behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do wolf spiders detect predators?
Wolf spiders detect predators through various mechanisms such as visual cues, vibratory cues, and chemical cues. They also exhibit behavioral responses to minimize the risk of predation.
What are the predators of wolf spiders?
Some of the predators of wolf spiders include birds, lizards, rodents, and other spiders. Even some larger invertebrates such as mantids and centipedes can also prey on them.
How do wolf spiders assess predation risk?
Wolf spiders assess predation risk through various mechanisms such as detecting potential predators, choosing suitable microhabitats, and modifying their behavior in response to the presence of predators.
What are the consequences of failing to detect danger?
The consequences of failing to detect danger can be fatal for wolf spiders. They may get eaten by predators or suffer injuries that can negatively impact their survival and fitness.
How do environmental factors affect predation risk assessment?
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, and vegetation cover can affect the ability of wolf spiders to detect and respond to predators. Changes in these factors can alter the frequency and intensity of predation events.
What is the role of experience and learning in predation risk assessment?
Experience and learning can play a critical role in predation risk assessment in wolf spiders. Through repeated exposure to predators and their cues, spiders can learn to recognize and avoid dangerous situations.
Why is predation risk assessment important for wolf spiders?
Predation risk assessment is important for wolf spiders because it helps them minimize the risk of mortality, conserve energy, and increase their reproductive success. By avoiding predation, spiders can allocate more resources towards growth and reproduction.
How do wolf spiders use chemical cues to detect predators?
Wolf spiders use chemical cues in the environment to detect potential predators. They can detect pheromones and other chemical signals that are released by predators or their prey. These cues can help spiders determine the location and identity of predators.
Can wolf spiders recognize specific predators?
Yes, wolf spiders can recognize specific predators through various cues such as chemical, visual, and vibratory cues. They may modify their behavior in response to the presence of certain predators to minimize the risk of predation.
How does predation risk assessment in wolf spiders impact the ecosystem?
Predation risk assessment in wolf spiders can impact the ecosystem by regulating the populations of both predators and prey. The presence of wolf spiders may deter some predators from preying on other organisms, while the spiders themselves may indirectly contribute to nutrient cycling and decomposition through their feeding activities.