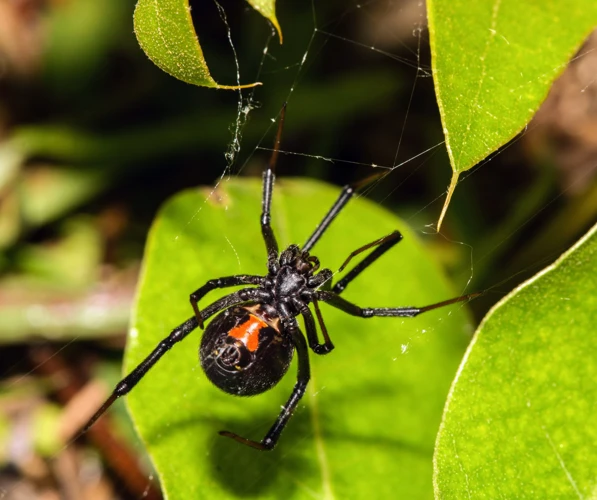
As we navigate through our daily routines, we often come across different species of spiders. While some may seem harmless, others can pose a serious threat to our health. Such is the case with the Black Widow Spider, a venomous creature well-known for its potentially lethal bite. However, not all Black Widow Spiders are the same. Some are native to certain regions, while others have been introduced as invasive species. In this article, we will explore the differences between Native and Invasive Black Widow Spiders, the physical and behavioral characteristics of each, their ecological and economic impacts, prevention methods, and how to deal with their bites. Let’s take a closer look.
What are Black Widow Spiders?
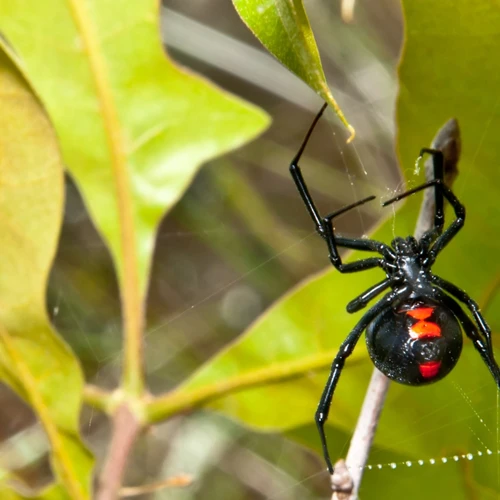

Black Widow Spiders are notorious arachnids that inhabit various parts of the world, including North and South America, Australia, and southern Europe. These spiders have distinct features that allow them to be easily identified from other spider species. The female Black Widow is larger than the male and has a shiny, jet-black body with a red or orange (hourglass) marking on the underside of her abdomen. However, not all Black Widows have this marking. Sometimes, their markings resemble stripes, dots, or even nothing at all. Adult males have longer, thinner legs and smaller bodies than females, and their markings are often less distinct.
Black Widow Spiders belong to the Latrodectus genus and are known for their distinctive, globular webs that are usually suspended between branches or rocks. These spiders are very territorial and will defend their web with aggressive behavior and venomous bites if disturbed. Black Widows are nocturnal hunters that prey on a wide range of insects, including flies, mosquitoes, grasshoppers, and beetles.
Interestingly, Black Widow Spiders exhibit cannibalistic behaviors, meaning that they sometimes eat their own species. Mating between Black Widows can often result in the female killing the male after copulation. This would explain why male Black Widdow’s life span is significantly shorter than females which can live about three years.
It’s essential to note that Black Widow Spiders are venomous, and their bites pose a significant threat to humans, especially children, elderly people and those who are immune-compromised. The severity of the reaction depends on the individual’s sensitivity to the venom, the amount of venom injected, and the location of the bite. Symptoms of a Black Widow bite can include pain, muscle cramps, chills, fever, headache, high blood pressure, and in rare cases, death. If you want to learn more about Black Widow Spiders, check out male-female-black-widows, identify-black-widow-spider-webs, and why-black-widow-spiders-bite-humans.
Physical Characteristics
The physical characteristics of black widow spiders are what set them apart from other spider species. These spiders have an unmistakable appearance and certain identifying features, making it vital to know what to look for when trying to distinguish whether a spider is a black widow or not. From their shiny black bodies to the distinctive red hourglass shape on their abdomens, the physical attributes of black widow spiders are worth exploring in greater detail. Let’s delve into the intricacies of what makes these spiders unique.
Biology and Behavior
Black widow spiders are well-known for their distinctive markings and potentially dangerous bite. Severe pain, muscle cramps, and spasms in the abdomen and back are some of the common symptoms associated with their bite. Understanding the biology and behavior of black widow spiders is essential for identifying and controlling infestations.
Reproduction: Female black widow spiders are larger than males and typically have a shiny black body with a red hourglass marking on the abdomen. Male black widows, on the other hand, have a smaller body with longer legs and lack the distinctive red marking. The mating process of black widow spiders involves the male performing complex courtship rituals to avoid being eaten by the female. Once copulation is complete, the female may consume the male.
Nesting habits: Black widow spiders spin webs from silk, which they use for shelter and catching prey. The webs are usually found in secluded, dark areas, such as in woodpiles, garages, and attics. They can also be found outdoors in bushes, under rocks, and in hollow tree trunks.
Feeding habits: Black widow spiders are carnivorous and feed on various insects such as mosquitoes, beetles, and grasshoppers. Once a prey lands on their web, they use their strong jaws and venom to kill and digest it for nourishment.
Behavioral Adaptations: Black widows are primarily nocturnal, active during the night and hide during the day. These spiders are particularly sensitive to vibrations and movements and may become aggressive when their web is disturbed.
It is important to note that not all black widow spiders are the same. The biology and behavior of native black widow spiders differ from that of invasive black widow spiders. Understanding these differences and the associated risks can help you take the appropriate control measures to prevent infestations.
For more information about preventing black widow spider infestations and removing them if they do occur, check out our article on black widow spider infestation removal. If you are concerned about black widow spider safety in your home, read our article on home black widow safety. Outdoor precautions for black widow spider bites are discussed in our article on outdoor precautions for black widow spider bites. If you or someone you know has been bitten by a black widow spider, learn about first aid treatments in our article on black widow spider bite first aid.
Native Black Widow Spiders
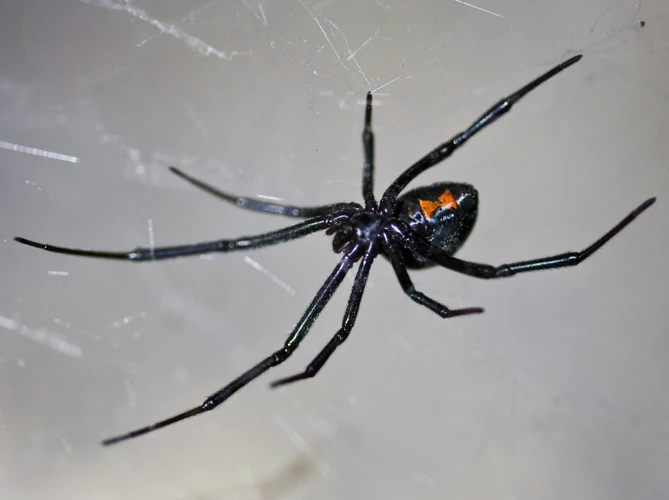

The Native Black Widow Spider is a venomous spider species found across North and Central America. While their bites can be dangerous, these spiders play an important role in their ecosystem as predators. In this section, we will explore the range, identification, behavior, risks, and control measures of these spiders. It’s important to note that if you have pets or are concerned about black widow spider bites, check our article on black widow spider bite prevention tips and black widow spiders as pets. If you’re interested in learning about the mating habits of these spiders, check our article on mating black widow spiders.
Range and Habitat
The range and habitat of Native and Invasive Black Widow Spiders differ greatly. Native Black Widow Spiders are found predominantly in the southern United States, particularly in warm and dry regions. They are also found in parts of Central and South America. On the other hand, Invasive Black Widow Spiders are found in various parts of the world.
| Native Black Widow Spiders | Invasive Black Widow Spiders | |
|---|---|---|
| Range | Native Black Widow Spiders are found predominantly in the southern United States, particularly in warm and dry regions. They are also found in parts of Central and South America. | Invasive Black Widow Spiders are found in various parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, and Australia. They have been introduced to these regions through human activity, such as the shipping of goods and materials. |
| Habitat | Native Black Widow Spiders are commonly found in outdoor habitats such as woodlands, deserts, and fields. They typically build their webs in sheltered, low-lying areas such as under rocks and debris. | Invasive Black Widow Spiders are more adaptable and can be found in a variety of habitats such as gardens, buildings, and even in cars. In urban environments, they often build their webs in areas such as playgrounds and outdoor furniture. |
It is important to note that while Invasive Black Widow Spiders may be found in a wider range of habitats, they can still be dangerous if encountered. It is recommended to take caution and avoid approaching or disturbing any Black Widow Spider, regardless of its native or invasive status.
Identification and Behavior
Black Widow Spiders are notorious for their distinctive physical appearance. Both Native and Invasive Black Widows have a unique black body with a bright red or orange hourglass-shaped marking on their bellies. However, the Native Black Widow Spiders have additional red or white spots on their backs, while the Invasive ones lack these spots. Another difference is in the shape of the hourglass – the Native Black Widows have a more hourglass-shaped marking, while in the Invasive ones it is more oval-shaped.
Behaviorally, Black Widow Spiders are shy and reclusive, prefering dark and hidden spaces. They tend to avoid human interactions as much as possible. These spiders are active all year round, but they tend to be more active during the warmer months. Both Native and Invasive Black Widows are nocturnal, and they search for prey at night.
One peculiar behavior that Black Widows exhibit is sexual cannibalism. The females are known to consume the males after mating. This behavior is more common in the Invasive Black Widow Spiders, where the male mating partner is much smaller than that of the females.
| Native Black Widow Spiders | Invasive Black Widow Spiders | |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Characteristics | Black Body Color, Red or White Markings on the Back, Hourglass-Shaped Red or Orange Marking on the Belly | Black Body Color, No Red or White Markings on the Back, Oval-Shaped Red or Orange Marking on the Belly |
| Behavioral Characteristics | Shy and Reclusive, Avoid Human Interaction, Active all Year Round, Nocturnal | Shy and Reclusive, Avoid Human Interaction, Active all Year Round, Nocturnal, Higher Frequency of Sexual Cannibalism |
It is essential to identify the type of Black Widow Spiders accurately since the risks and control measures can differ. But still, it is better not to interact with these spiders, and we should take necessary precautions to prevent infestations.
Risks and Control Measures
Black widow spiders are venomous and can pose significant risks to human health. Their bites can cause systemic symptoms that progress rapidly, including muscle cramps, nausea, and difficulty breathing. In rare cases, they can also be fatal. To avoid these risks, it’s essential to take steps to control and prevent black widow spider infestations in and around your home. Here are some control measures to consider:
1. Keep your home clean and clutter-free. Clutter provides hiding places for spiders and makes it difficult to detect infestations. Regular cleaning, including vacuuming and sweeping, can help reduce spider populations.
2. Seal any cracks or gaps in your home’s structure. Black widow spiders can enter through small openings. Cracks in walls, gaps around doors or windows, and holes in screens should all be sealed to prevent entry.
3. Remove any webs you find. If you spot a spider web, remove it immediately. This can help prevent additional spiders from inhabiting the area.
4. Store firewood away from your home. Black widow spiders are known to inhabit woodpiles, so it’s important to keep firewood away from the home.
5. Install yellow light bulbs outside. Black widow spiders are less attracted to yellow light than they are to white light. By installing yellow light bulbs outside, you can reduce the likelihood of black widow spider infestations.
6. Consider using insecticides. If you have a severe infestation, you may need to use insecticides to control the spiders. However, it’s important to use these products with caution and follow all label instructions.
7. Hire a professional pest control company. If you’re unable to control the infestation on your own, consider hiring a professional pest control company. They have the expertise and tools necessary to eradicate black widow spiders safely and effectively.
By taking these steps, you can reduce the risks associated with black widow spider infestations and keep your home safe for you and your family. Remember to always exercise caution when dealing with venomous spiders and seek medical attention immediately if you suspect you’ve been bitten.
Invasive Black Widow Spiders
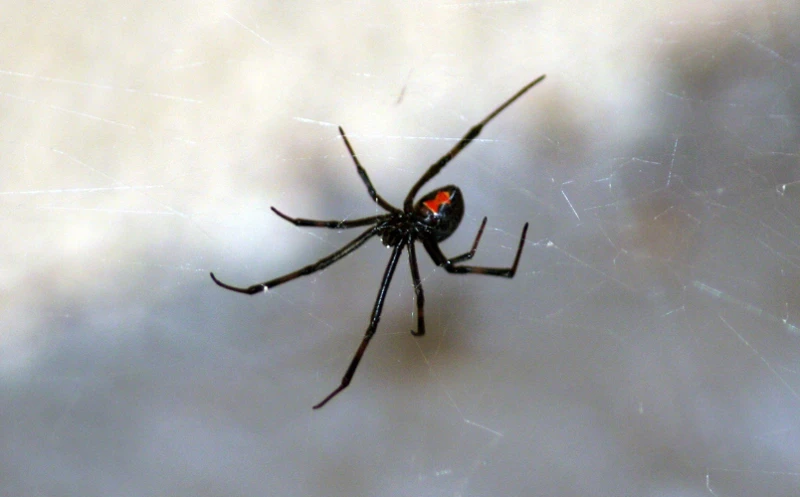

It’s no secret that invasive species can wreak havoc on ecosystems, and black widow spiders are no exception. The presence of these spiders can be alarming to homeowners and hikers alike due to their potentially dangerous bite. In fact, in recent years, the range of invasive black widow spiders has expanded, posing a threat to both native species and human health. Let’s take a closer look at the impact of invasive black widow spiders, as well as how to identify and control them.
Range and Habitat
Both native and invasive black widow spiders have distinct ranges and habitats.
Native Black Widow Spiders:
- The native black widow spider is primarily found in the United States, specifically in the southern and western parts of the country.
- They prefer hot, dry climates and are commonly found in arid or desert regions.
- The native black widow spider is typically found in outdoor habitats such as woodpiles, hollow stumps, and underneath rocks and other debris.
Invasive Black Widow Spiders:
- The invasive black widow spider is found in many parts of the world including Europe, Asia, South America, and Australia, but they are not native to those areas.
- They were introduced to these regions through human transportation, such as shipping and travel.
- The invasive black widow spider prefers warmer climates, but can also tolerate cooler temperatures.
- Invasive black widow spiders prefer to hide in secluded areas such as garages, sheds, crawl spaces, and other similar areas where there is minimal human activity.
It’s important to note that the range and habitat of black widow spiders can vary depending on the specific species, and environmental factors such as climate and food availability can also impact their range and habitat. However, when it comes to controlling and preventing black widow spider infestations, it’s crucial to understand their preferred habitats and take necessary precautions to avoid contact with these venomous spiders.
Identification and Behavior
When it comes to identifying black widow spiders, there are a few key characteristics that set them apart from other spider species. Firstly, black widow spiders have a distinctive jet-black coloration with a shiny, almost oily appearance. They also have a characteristic red or orange “hourglass” shaped marking on their underside, which can help distinguish them from other dark-colored spider species.
Additionally, female black widow spiders also tend to be larger than males, measuring up to 1.5 inches in length including leg span, while males typically only reach about half that size. Despite their large size, black widow spiders are known for their reclusive behavior and prefer to spend most of their time hiding in undisturbed areas.
In terms of behavior, black widow spiders are notorious for their venomous bites. They are known to be particularly aggressive when their web or nest is disturbed, so it’s important to exercise caution around any suspected black widow spider infestations.
Interestingly, while male black widow spiders are relatively harmless to humans and other animals, it’s the female black widow spiders that pose the greatest risk due to their potent venom. In fact, the venom from female black widow spiders contains a neurotoxin that can cause severe symptoms such as muscle cramps, spasms, and even paralysis. If you suspect that you may have been bitten by a black widow spider, seek medical attention immediately.
To summarize, identifying and understanding the behavior of black widow spiders is crucial in minimizing the risk of infestation and avoiding potentially dangerous encounters. Pay close attention to physical characteristics such as the distinctive black coloration and hourglass marking, and exercise caution around any suspected black widow spider presence. In the next sections, we will look at the differences between native and invasive black widow spiders, as well as effective control measures to prevent infestations.
Risks and Control Measures
Black widow spiders are among the most venomous spiders in the United States. Their bites can cause severe symptoms in humans, ranging from pain and swelling to muscle cramps, seizures, and even death in some cases. However, the risk of being bitten by a black widow spider is relatively low, as these spiders tend to avoid humans and will only bite if they feel threatened or cornered.
Control Measures
Prevention is key when it comes to controlling black widow spiders. Here are some effective control measures you can take to reduce your risk of infestation:
| Control Measure | How it works |
|---|---|
| Sealing cracks and gaps | Black widow spiders can enter your home through even the tiniest cracks and gaps. By sealing them up, you can prevent spiders from gaining access. |
| Reducing clutter | Black widow spiders are attracted to cluttered areas with lots of hiding spots. By reducing clutter in and around your home, you can make it less appealing to these spiders. |
| Removing webs | Regularly removing spider webs from your home and yard can help deter black widows from sticking around. |
| Using insecticidal sprays | Insecticidal sprays can be an effective way to kill black widow spiders and deter them from coming back. However, be sure to follow label instructions carefully and avoid using sprays in areas where children or pets may be exposed. |
| Professional pest control | If you have a severe infestation or are not comfortable dealing with black widow spiders on your own, professional pest control services can help eliminate the problem. |
Risks
The risks associated with black widow spider bites can vary depending on a number of factors, including the size and age of the person bitten, the amount of venom injected, and the location of the bite. Some of the most common symptoms of a black widow spider bite include:
– Pain at the bite site
– Muscle cramps and spasms
– Sweating and shaking
– Nausea and vomiting
– Difficulty breathing
In rare cases, a black widow spider bite can cause severe symptoms, such as seizures, paralysis, and even death. If you suspect you or someone else has been bitten by a black widow spider, seek medical attention immediately.
Conclusion
While black widow spiders can be a cause for concern, the risk of being bitten is relatively low if you take appropriate control measures. By following the prevention strategies outlined in this article and seeking medical attention if you suspect a bite, you can reduce your risk of a potentially dangerous encounter with these venomous spiders.
Differences Between Native and Invasive Black Widow Spiders
As fascinating creatures, black widow spiders have managed to capture the interest of many people around the world. Although they share some common traits, there are significant differences between native and invasive black widow spiders that people should be aware of. These spiders differ in various ways, from their physical characteristics to their behavioral tendencies and ecological impacts. By understanding these differences, we can better appreciate and manage the risks associated with their presence. So, let’s take a closer look at the disparities between native and invasive black widow spiders.
Physical Differences
When it comes to physical differences between native and invasive black widow spiders, there are a few key distinguishing features to look out for. These differences can help you identify which type of spider you are dealing with and take appropriate control measures.
Physical Differences Between Native and Invasive Black Widow Spiders
| Characteristic | Native Black Widow Spider | Invasive Black Widow Spider |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Adult females are typically 1/2 inch to 1 inch in length | Adult females are typically larger, measuring up to 1.5 inches in length |
| Coloration | Shiny black with a distinctive hourglass-shaped red or orange marking on the underside of the abdomen | May have variable markings, including a broken hourglass shape or even no markings at all |
| Webs | Built in undisturbed areas, such as brush or woodpiles | Built in human-made structures, including homes, sheds, and garages |
Native black widow spiders tend to be slightly smaller in size, with adult females typically measuring between 1/2 inch to 1 inch in length. They have shiny black bodies with a distinctive hourglass-shaped red or orange marking on the underside of the abdomen. These spiders usually build their webs in undisturbed areas, such as brush or woodpiles.
In contrast, invasive black widow spiders tend to be larger overall, with adult females measuring up to 1.5 inches in length. They may have variable markings on their bodies, including a broken hourglass shape or no markings at all, which can make identification more difficult. They are also more likely to build their webs in human-made structures, including homes, sheds, and garages.
It is worth noting that while physical differences can provide some clues as to which type of black widow spider you are dealing with, identification by a professional is always recommended. Additionally, if you are not experienced with identifying spider species, it is best to leave the task to trained professionals, as some spiders can be dangerous and should not be handled without proper training.
Behavioral Differences
When it comes to the behavioral differences between the native and invasive black widow spiders, there are a few key things to keep in mind. Firstly, native black widows are generally less aggressive than invasive black widows. However, both species are known to become more aggressive when they feel threatened or trapped.
Native black widows are also more likely to stay hidden away in their webs and only come out to hunt, while invasive black widows are more prone to wandering around looking for prey. This means that if you have an infestation of invasive black widows, you may be more likely to spot them out in the open.
Another important behavioral difference is that invasive black widows are more adaptable to different environments than native black widows. This means that they can thrive in a wider range of conditions and are more likely to spread to new areas where they may not originally have been found.
It’s important to note that while invasive black widows may be more adaptable and aggressive, both species are still dangerous and can pose a serious risk to humans. If you spot any black widow spiders in or around your home, it’s best to take action to have them removed as soon as possible.
Key takeaways:
- Native black widows are generally less aggressive than invasive black widows
- Native black widows are more likely to stay hidden in their webs, while invasive black widows are more prone to wandering around
- Invasive black widows are more adaptable to different environments than native black widows
- Both species are dangerous and should be removed if found in or near your home
Ecological and Economic Impacts
The ecological and economic impacts of Native and Invasive Black Widow Spiders are significant and far-reaching. Here are some of the key impacts:
Ecological Impacts:
- Native Black Widow Spiders can have a positive impact on ecosystem health by controlling insect populations, including agricultural pests.
- Invasive Black Widow Spiders can disrupt local ecosystems by outcompeting and preying on native spider species.
- Black Widow Spiders are not a significant food source for most predators due to their potent venom.
- Overuse of pesticides to control Black Widow Spider populations can harm beneficial insects and other organisms in the ecosystem.
Economic Impacts:
- Black Widow Spiders can pose a significant risk to human health and safety, resulting in medical expenses, lost productivity, and the cost of pest control services.
- Invasive Black Widow Spiders can damage crops and reduce agricultural yields, resulting in economic losses for farmers and the agriculture industry.
- Tourism and outdoor recreation industries can be impacted by Black Widow Spider infestations, as people may avoid areas with high spider populations.
- Legal and liability costs can arise if someone is bitten by a Black Widow Spider in a public area or on someone’s property.
It is important to consider both the ecological and economic impacts of Black Widow Spiders when developing control measures and making management decisions. While it is important to ensure human safety and protect agriculture, it is also important to minimize negative impacts on the environment. Integrated Pest Management strategies can help achieve these goals by using a combination of techniques that avoid or minimize pesticide use and prioritize non-toxic control measures.
How to Prevent Black Widow Spider Infestations

Preventing black widow spider infestations is essential for the safety and well-being of your household members and pets. These venomous spiders are prevalent in areas with warm climates, especially in regions with high moisture levels. Although it may seem challenging to keep these spiders out of your home and outdoor spaces, there are simple and effective measures you can take to prevent infestations. In this section, we will explore various preventative measures that will keep your home and backyard safe from black widow spider invasions. So, let’s dive in and learn about some practical ways to prevent these dangerous spiders from entering your domain.
Outdoors
To prevent a black widow spider infestation outdoors, certain measures should be taken. These measures are especially important if you live in an area where black widow spiders are common.
1. Eliminate Spider Habitats: Start by getting rid of places where black widow spiders might like to live. This includes piles of wood, clutter, and debris. Keep the outside of your home, your basement, attic, and garage clean and free from clutter, especially if you live in an area where black widow spiders are common.
2. Caulk and Seal All Cracks and Crevices: Inspect the exterior of your home for any cracks or crevices in the foundation, walls, around windows, and doors. Seal these areas with caulk to prevent black widow spiders from getting inside your home.
3. Use Yellow Bug Lights: Black widow spiders are attracted to light and can often be found around outdoor lighting fixtures. Consider using yellow bug lights to reduce the number of black widow spiders in your yard.
4. Keep Firewood Away: Store firewood away from your home, preferably at least 20 feet from your home if possible. This will help keep black widow spiders and other pests away from your home.
5. Use Insecticides as a Last Resort: If you have to use insecticides outdoors, use them as a last resort and follow the instructions carefully to avoid harming beneficial insects or your pets. It’s best to seek the help of a professional pest control service to ensure the safe and effective use of insecticides.
Preventing black widow spider infestations outdoors is essential to keeping your family and pets safe. By eliminating spider habitats, sealing all cracks and crevices, using yellow bug lights, keeping firewood away from your home, and using insecticides as a last resort, you can greatly reduce the risk of black widow spider infestations.
Indoors
When it comes to preventing black widow spider infestations indoors, there are several steps you can take. These include:
- Sealing Entry Points: Black widow spiders can enter your home through gaps around windows and doors, so it’s important to seal these areas with caulking or weatherstripping. Make sure all vents and pipes entering the home are also sealed.
- Decluttering: Cluttered areas provide hiding spots for spiders, so it’s important to declutter your home regularly. Pay attention to areas such as closets, basements, and garages, where clutter tends to accumulate.
- Cleaning: Keeping your home clean is a key step in preventing spider infestations. Vacuum regularly to remove cobwebs and spider egg sacs, and use a dehumidifier to reduce moisture levels in your home – this will make the environment less hospitable to spiders and other pests.
- Using Pesticides: If you’re dealing with a severe spider infestation, you may need to use pesticides to control the problem. However, keep in mind that some pesticides can be toxic to humans and pets, so it’s important to use them responsibly. Always follow the instructions on the label and use protective gear if instructed.
- Seeking Professional Help: If you’re having trouble controlling a spider infestation on your own, it may be time to seek professional help. An exterminator can assess the situation and recommend the best course of action. They can also use specialized tools and techniques to remove spiders and other pests safely and effectively.
By following these steps, you can reduce the risk of black widow spider infestations in your home. Remember to be diligent and proactive, and don’t hesitate to seek help if you need it. With a little effort and attention, you can keep these potentially dangerous spiders at bay.
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management, or IPM, is an environmentally friendly and effective approach to controlling black widow spider populations. It involves a combination of prevention measures, non-chemical methods, and targeted pesticide applications when necessary.
Here are some ways to implement IPM for black widow spider control:
- Inspection: Regularly inspect your property for signs of black widow spider activity, and remove any egg sacs, webs, or spiders you find.
- Exclusion: Seal up any cracks or gaps in your walls, doors, windows, and foundation to prevent black widow spiders from getting inside.
- Cultural Controls: Keep the area around your home free of clutter and debris, and reduce moisture sources, such as standing water or leaky pipes, which attract insects that black widow spiders prey on.
- Biological Controls: Encourage natural predators of black widow spiders, such as birds or mantises, by providing habitat or installing bird feeders.
- Pesticides: As a last resort, use targeted pesticide applications to eliminate black widow spider populations. Choose products that are labeled for use on these spiders, and follow the instructions carefully.
Remember, IPM is a long-term solution that requires ongoing monitoring and maintenance to be effective. By implementing these practices, you can reduce the risk of black widow spider infestations and keep your home and property safe.
Dealing with Black Widow Spider Bites
Finding a black widow spider bite can be a distressing experience. These pesky arachnids can deliver a venomous, painful bite that can cause a range of symptoms. Knowing how to deal with black widow spider bites is crucial in minimizing the effects and promoting faster healing. In this section, we will discuss the treatment options available for black widow spider bites and what steps you can take to prevent them from occurring in the first place. So, if you have been bitten by a black widow spider or are interested in learning how to deal with these bites, keep reading.
Symptoms and First Aid
When bitten by a black widow spider, it’s important to know the symptoms and take appropriate first aid measures. Here are the symptoms to look out for:
- Pain – The bite may cause immediate sharp pain that can intensify over the next few hours.
- Muscle cramps – The affected area may experience muscle spasms, especially in the abdomen and back.
- Sweating – The bitten person can experience sweating, especially around the bite area.
- Nausea and vomiting – Some people may experience nausea and vomiting after being bitten by a black widow spider.
- Headaches and dizziness – People can experience headaches and dizziness after being bitten by a black widow spider.
- Difficulty breathing – In rare cases, people can have difficulty breathing due to severe muscle cramps.
If you or someone you know has been bitten by a black widow spider, the first aid measures include:
- Clean the bite area – Wash the area with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Apply a cold compress – Placing a cold compress over the bite area can help reduce swelling and pain.
- Take pain relievers – Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help relieve pain.
It’s important to seek medical attention immediately if the symptoms are severe or worsen over time. Additionally, black widow spider bites can be dangerous for young children, elderly people, and people with weakened immune systems, so medical attention should be sought immediately in these cases.
Remember to always take caution when dealing with black widow spiders and their bites, and seek medical attention if needed.
Medical Treatment
If you are bitten by a black widow spider, seeking medical treatment is paramount. The venom of a black widow spider is highly toxic and can cause serious symptoms and complications if left untreated. In this section, we will discuss medical treatments for black widow spider bites.
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Antivenom | Antivenom is the most effective treatment for black widow spider bites. It is made from antibodies that neutralize the venom. Antivenom is administered intravenously and is typically only used for severe cases of envenomation. |
| Pain Management | Pain from a black widow spider bite can be severe and may require prescription pain medication such as opioids. Over-the-counter pain medications may also be used to manage mild to moderate pain. |
| Muscle Relaxants | Black widow spider venom can cause muscle spasms and cramps. Muscle relaxants may be prescribed to reduce these muscle symptoms. |
| Hydration | It is important to remain hydrated after a black widow spider bite. This can help reduce the risk of complications such as kidney failure. Intravenous fluids may be necessary in severe cases. |
| Monitoring | After a black widow spider bite, patients should be closely monitored for symptoms such as muscle cramps, spasms, and abdominal pain. Blood tests may also be performed to monitor kidney function. |
It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you are bitten by a black widow spider. Any delay in treatment may increase the risk of complications and make the treatment less effective. With prompt and appropriate medical care, the prognosis for black widow spider bite is generally good.
Conclusion
As we come to the end of our exploration of native and invasive black widow spiders, it’s clear that caution and prevention are key when dealing with these venomous arachnids. Both species share similar physical characteristics and behaviors, but their range, habitat, and ecological impact distinguish them from each other. While bites from these spiders can be dangerous, there are steps you can take to prevent infestations and protect yourself. In this final section, we’ll summarize the key points we’ve covered throughout the article and provide some final thoughts and recommendations for dealing with black widow spiders.
Summary of Key Points
After considering the differences between Native and Invasive Black Widow Spiders, as well as the risks and control measures associated with them, it’s important to summarize the key points to ensure that readers understand the main takeaways from the article. We have compiled a list of the most important points in the table below:
| Key Points | Details |
| Native Black Widow Spiders | – Range limited to certain regions of the United States – Found in natural habitats like forests and deserts – Recognizable by their hourglass-shaped markings on their abdomen – Rarely encountered, but can be dangerous if provoked or threatened – Prevention and control measures include removing debris and sealing entry points |
| Invasive Black Widow Spiders | – Widespread throughout the United States – Found in both natural and man-made habitats – Recognizable by their hourglass-shaped markings on their abdomen – More aggressive than native species and pose a greater risk to humans – Prevention and control measures include keeping indoor spaces clean and sealing entry points |
| Differences between Native and Invasive Black Widow Spiders | – Physical differences: invasive species are larger and more colorful – Behavioral differences: invasive species are more aggressive and prolific – Ecological and economic impacts: invasive species can displace native species and cause damage to crops – Prevention and control measures should be tailored to the species present in the area |
| Preventing Black Widow Spider Infestations | – Outdoors: keep outdoor spaces clean and free of debris – Indoors: keep indoor spaces clean and clutter-free, and seal entry points – Integrated Pest Management: use a combination of prevention measures and chemical treatments for effective control |
| Dealing with Black Widow Spider Bites | – Symptoms include pain, swelling, and nausea – First aid measures include applying ice and seeking medical attention – Medical treatment may include antivenom, pain management, and supportive care |
By keeping these key points in mind, readers will be better equipped to understand the risks associated with Black Widow Spiders, and what steps they can take to prevent infestations and deal with bites if necessary. It’s important to remain vigilant when it comes to these potentially dangerous spiders, but with the right knowledge and tools, anyone can protect themselves and their homes from harm.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
After reading about the differences, risks, and control measures for native and invasive black widow spiders, it is clear that they pose a significant threat to humans and the environment. It is important to take preventative measures to reduce the likelihood of an infestation, and to be aware of the symptoms and first aid for black widow spider bites.
Recommendations
To prevent black widow spider infestations, we recommend the following measures:
| Outdoors | Indoors |
|---|---|
| Regularly remove debris and clutter from your yard to eliminate potential hiding places for black widows. | Seal cracks and gaps around doors and windows to prevent spiders from entering your home. |
| Trim back vegetation to reduce the risk of spiders moving indoors. | Keep your home clean and clutter-free to decrease the likelihood of spiders taking up residence. |
| Use yellow or sodium vapor lights outside to reduce their attractiveness to insects and their predators, like black widows. | Use insecticide sprays to target any black widow spiders that are seen indoors. |
Dealing with Black Widow Spider Bites
If you or someone you know is bitten by a black widow spider, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. The venom from black widows can cause serious symptoms, including abdominal pain, muscle cramps, and difficulty breathing. While awaiting medical help, follow these first aid recommendations:
- Wash the bite area thoroughly with soap and water.
- Apply a cold compress to the bite area to reduce swelling and pain.
- Keep the affected limb elevated to slow the spread of venom.
- Avoid taking any medication unless directed to do so by a healthcare professional.
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a sustainable approach to controlling pests that includes a variety of methods, including biological, cultural, and chemical control measures. IPM can be an effective way to control black widow spiders, as well as other pests in and around your home.
By taking preventative measures to reduce the likelihood of an infestation, and by being aware of the symptoms and first aid for black widow spider bites, we can minimize the risks associated with these dangerous arachnids. By following the recommendations provided, we can keep ourselves and our homes safe from black widow spiders.
Frequently Asked Questions
How venomous are black widow spiders?
Black widow spiders are highly venomous and their venom can cause severe reactions in humans, especially in children and the elderly.
Can black widow spiders be found throughout the world?
No, black widow spiders are only found in certain regions of the world, including North and South America, Europe, Australia, and Africa.
What is the typical habitat of black widow spiders?
Black widow spiders prefer dark and secluded areas like garages, attics, basements, and outdoor spaces like woodpiles and rock piles.
What should I do if I suspect a black widow spider infestation in my home?
It is recommended to seek professional help from a pest control service to safely and effectively remove the infestation.
Are all black widow spiders dangerous to humans?
No, only female black widow spiders have venom that is considered dangerous to humans.
How can I distinguish between native and invasive black widow spiders?
Native black widow spiders have a red hourglass mark on their abdomen, while invasive black widow spiders have an orange or yellow hourglass mark.
What are the economic impacts of black widow spider infestations?
Black widow spider infestations can cause significant economic losses due to medical expenses and decreased worker productivity in affected areas.
Are there natural predators of black widow spiders?
Yes, some natural predators of black widow spiders include birds, ants, and spider wasps.
How can I prevent a black widow spider bite?
Avoiding contact with black widow spiders and taking preventative measures like wearing gloves while gardening or cleaning can help prevent bites.
What should I do if I suspect a black widow spider bite?
Seek medical attention immediately and try to capture the spider to help with identification and treatment.






