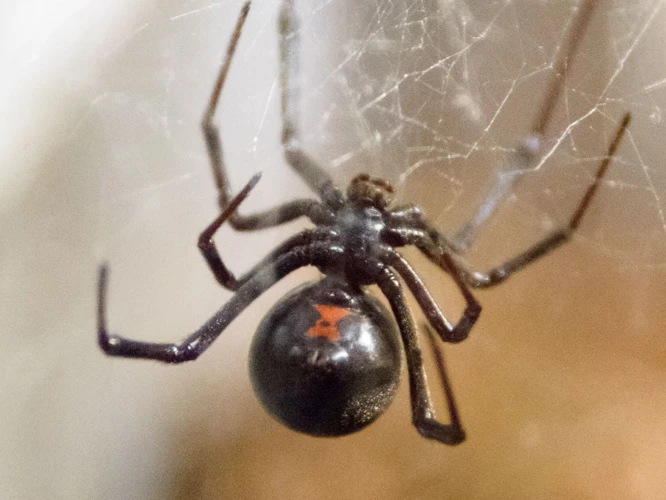
As humans, we often feel a sense of fear towards spiders, especially venomous ones like the Black Widow spider. However, what if we told you that the venom from these seemingly dangerous spiders could be used for medical purposes? It may seem perplexing, but the medical world has been studying Black Widow spider venom and its potential benefits for years. In this article, we will delve into the medical importance of studying Black Widow spider venom, its composition, effects on the body, current uses, future potential applications, and the ethical considerations surrounding spider conservation and safety for researchers and patients. Let’s explore this fascinating topic together.
What is a Black Widow Spider?
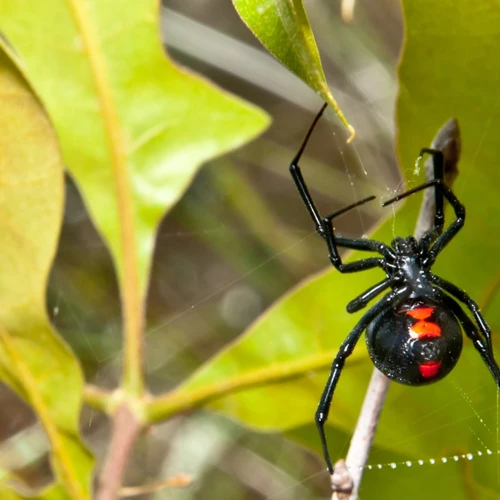

Black Widow Spiders are a group of venomous spiders belonging to the genus Latrodectus. These spiders are easily recognizable due to their iconic black color and red hourglass-shaped marking on their abdomen. The black widow spider has a particularly toxic venom, which can pose a severe threat to humans.
Black Widow Spiders have an average size of about 1.5 inches, and their coloration can vary from black to dark brown. Male black widow spiders are usually smaller and lighter in color than females. These spiders have eight legs and two body regions, the cephalothorax, also known as the prosoma, and the abdomen, also known as the opisthosoma.
Black Widow Spiders can be found in temperate regions around the world. They prefer warm and dry environments such as woodpiles, rubble piles, and abandoned buildings. These spiders are carnivorous and feed on various insects, including mosquitoes, flies, and grasshoppers.
It is essential to avoid black widow spider bites, as their venom can cause severe symptoms such as muscle spasms, abdominal pain, and difficulty breathing. Recovery time from a black widow spider bite depends on various factors, including the amount of venom injected, the location of the bite, and the health status of the individual bitten.
Evolutionary analysis has shown that black widow spider venom evolved as a means of self-defense against predators and as a way to capture prey. The venom of black widow spiders contains several neurotoxins which can target the nervous system of insects, small animals, and humans.
To better understand the effects of black widow venom on humans and to discover potential medical uses, research is currently being conducted on the chemistry and mode of action of their venom. This research has shown promise in the development of medications for chronic pain relief and heart disease treatment.
It is important to note the need for ethical considerations in studying Black Widow Spiders. Scientists should prioritize the conservation of these spiders and ensure that research is conducted in a manner that does not harm the spiders or other organisms. Additionally, safety protocols should always be implemented to protect both researchers and patients involved in any experimental treatments using black widow venom.
The study of black widow spider venom is incredibly important in understanding and developing treatments for a range of medical conditions.
Physical Characteristics of Black Widow Spiders
Physical Characteristics of Black Widow Spiders
Black widow spiders, scientifically known as Latrodectus, are notorious for their venomous bites and distinctive appearance. They are usually jet black in color and are easily recognizable by the red hourglass-shaped marking on their abdomen. Females are typically larger than males and measure around 1.5 inches in length, while males are about half the size. Their bodies are round, and their legs are thin and long with spiny projections.
One notable characteristic of black widow spiders is their web. They spin irregular and tangled webs, with no set structure, which they use to catch their prey. The web is incredibly strong and sticky, making it effective at trapping insects and other small creatures.
Black widow spiders are found all over the world, but they are most commonly found in temperate regions, such as North and South America, Africa, and Australia. They prefer warm and dry environments, such as woodpiles, rocks, and crevices, but can also be found in man-made structures such as sheds and garages.
It is important to note that black widow spiders are shy and usually only bite humans when they feel threatened or cornered. If you encounter one in your house or garden, it is best to avoid them altogether and call in a professional to remove them safely. If you do get bitten by a black widow spider, seek medical attention immediately as their venom can be very dangerous. To learn more about black widow spider bites and recovery time, you can visit this resource.
Habitat and Feeding Habits of Black Widow Spiders
Black Widow Spiders can be found in diverse habitats, ranging from temperate forests to deserts. These spiders commonly build their webs in undisturbed areas, such as piles of debris or near the ground in dry habitats. They often hide in dark corners, crevices and woodpiles as well. Black Widow Spiders are nocturnal and eat other insects, such as mosquitoes, flies, and caterpillars. They also prey on other spiders, including males of their own species.
Interestingly, male Black Widow Spiders are known to be harmless to humans, as they don’t possess venom glands as female do. Females, on the other hand, are particularly venomous and can inject about 1 microliter of venom in a single bite. However, Black Widow Spiders don’t bite humans unless they feel threatened, in which case their venomous bite can be dangerous or even deadly.
It’s important for humans to avoid Black Widow Spider bites as much as possible, especially if living or working in areas where these spiders are common. There are specific precautions that can be taken to avoid bites, such as wearing long sleeves and pants when working in gardens or areas where spiders may be present. In case of a Black Widow Spider bite, it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Understanding the feeding habits and habitat of Black Widow Spiders is crucial for scientists researching the properties of their venom. For example, scientists have found that Black Widow Spider venom helps relieve chronic pain by targeting the same nerve channels as opioid drugs. Researchers have also experimented with Black Widow Spider venom to develop treatments for heart disease and cancer. By studying these spiders, researchers may continue to uncover new medical applications for Black Widow Spider venom.
Black Widow Spider Venom
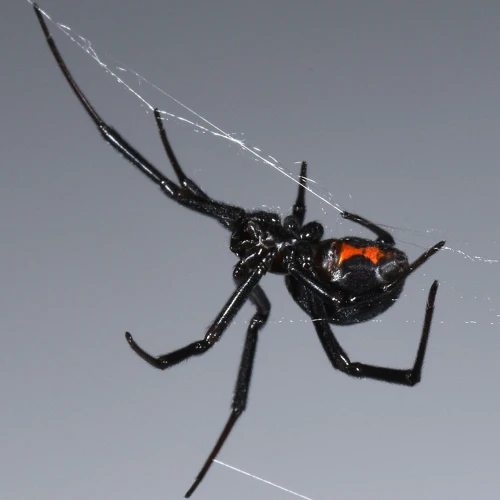

Black Widow Spider Venom is famous for being one of the most potent spider venoms in the world. The venom consists of various neurotoxins and enzymes that make it deadly to their prey. The venom is a clear liquid and is transmitted through the spider’s chelicerae, which are its fangs. When the spider bites, venom is injected into the victim’s tissue. Black Widow venom is a complex mix of toxins that affects the human body in several ways.
Composition of Black Widow Spider Venom
Black Widow Spider Venom is composed of several protein molecules that act on different body systems. Because of this, the venom has different effects on different animals and humans. The venom includes neurotoxins such as alpha-latrotoxin, which affects the nervous system, and Phospholipase A2, which affects the cell membranes. It also has enzymes such as Hyaluronidase, which breaks down the extracellular matrix in the body, and Proteases, which break down other proteins in the victim’s tissue.
How Does Black Widow Spider Venom Affect the Body?
Black Widow Spider Venom affects the body in various ways, depending on the person and how much venom they have been injected with. The venom mainly acts on the nervous system, causing pain, muscle spasms, and even paralysis in some cases. The venom can also affect the cardiovascular system, causing an increase or decrease in blood pressure and heart rate. People who are hypersensitive to the venom can experience more severe symptoms such as seizures, respiratory failure, and even death.
Despite being a potent venom and harmful to humans, Black Widow Spider Venom has several medical uses and current research studies. The venom is being used to help develop treatments for chronic pain, heart disease, and even cancer. Continued research and proper ethical considerations, including spider conservation and researcher protection in conducting studies, will continue to uncover the vast potential of this venom.
Composition of Black Widow Spider Venom
Black widow spider venom is a complex mixture of bioactive molecules that have the potential to cause a variety of symptoms in humans. The venom contains a large number of proteins and enzymes, including α-latrotoxin, which plays a major role in the spider’s toxic effects.
Other key components of black widow venom include neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, as well as low molecular weight peptides and organic molecules such as histamine, serotonin, and adenosine. These substances work together to cause the symptoms of black widow spider bites, including pain, muscle cramps, sweating, and nausea.
Interestingly, the composition of black widow spider venom can vary depending on the specific species and location of the spider. For example, the venom of Latrodectus mactans, a common species in North America, contains more potent neurotoxins than the venom of some other black widow spider species found in other parts of the world.
Scientists are continually studying the composition of black widow spider venom in order to better understand its mechanisms of action and potential medical applications. Research has shown that some of the proteins found in the venom may have therapeutic properties, such as pain relief or anti-tumor effects. This area of research is still in its early stages, but there is hope that further study of black widow spider venom could lead to new treatments for chronic pain, heart disease, and cancer.
For more information on the chemistry of black widow spider venom, check out this informative article on the subject.
How Does Black Widow Spider Venom Affect the Body?
Black widow spider venom affects the body in several different ways. When the venom enters the bloodstream, it travels to the nervous system and specifically targets the nerve endings. The venom contains neurotoxins that cause disruptions in the communication between neurons. This disruption can cause muscle cramps and spasms, as well as paralysis.
One of the most common symptoms of a black widow spider bite is intense, localized pain. This pain can spread to other parts of the body and may last for several hours. In some cases, the pain can persist for days or even weeks. Black widow venom has been studied extensively for its pain-relieving properties, and researchers believe that it may hold promise for the development of new pain medications.
In addition to pain relief, black widow spider venom has been studied for its potential effects on heart disease and cancer. The venom contains a protein called alpha-latrotoxin which has been found to increase blood flow to the heart and may help prevent heart attacks in some patients.
Research has also shown that certain compounds found in black widow venom can affect cancer cells. These compounds may be able to selectively kill cancer cells while leaving healthy cells unharmed, making them promising candidates for future treatments.
However, it’s important to note that black widow spider venom can be extremely dangerous and should always be handled with caution. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect that you have been bitten by a black widow spider. To avoid bites, it is important to take steps to reduce your risk of exposure, such as by wearing protective clothing and avoiding dark, cluttered areas where black widows may be hiding.
The study of black widow spider venom has great potential for medical research and the development of new treatments and medications. By understanding how the venom affects the body, researchers can work towards harnessing its beneficial properties while minimizing the risks associated with exposure. To learn more about the evolutionary history of black widow spider venom, check out this article on the topic .
Current Medical Uses of Black Widow Spider Venom Research
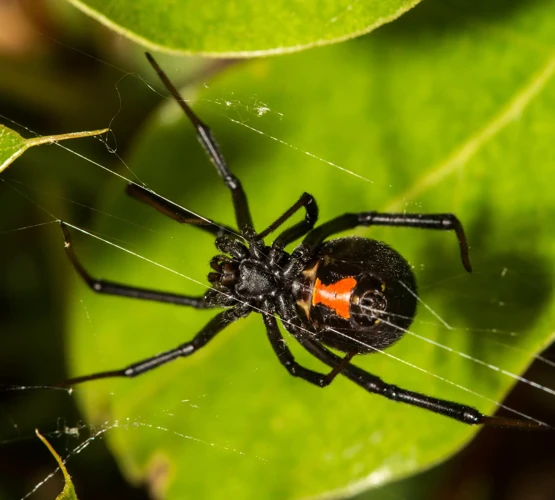

Research into black widow spider venom has revealed numerous medical applications. Due to its unique composition, black widow spider venom has the potential to be used for treating various medical conditions. Among the current medical uses of black widow spider venom research is chronic pain relief.
Chronic Pain Relief
Black widow spider venom contains a component called alpha-latrotoxin, which has been shown to activate pain-sensing neurons and produce pain-relieving effects. Alpha-latrotoxin triggers the release of neuropeptides, which play an essential role in controlling pain. As a result, black widow spider venom has been used to develop medication for chronic pain relief.
One example of medication derived from black widow spider venom is Prialt, which is used to treat severe chronic pain. Prialt provides long-lasting pain relief and has been found to be effective in patients who have not responded to other treatments. It is administered directly into the spinal cord via a catheter.
Heart Disease Treatment
Research has shown that black widow spider venom contains a compound called latrotoxin, which has been found to have cardio-protective effects. Latrotoxin can protect the heart and reduce damage to cardiac tissue during a heart attack. Scientists are exploring the use of black widow spider venom for the development of new drugs to treat heart disease.
Cancer Research
Black widow spider venom has shown promise in cancer research. Studies have revealed that venom contains peptides that can inhibit the growth of tumors and cancer cells. Research is ongoing in this area, and scientists believe that black widow spider venom may be a promising source of new cancer treatments.
Research into black widow spider venom has revealed exciting new medical applications. The components found in black widow spider venom have shown promise in treating chronic pain, heart disease, and cancer. The venom’s unique composition is what makes it such a valuable resource in medical research. Further research will likely uncover additional medical uses for black widow spider venom.
Chronic Pain Relief
Black widow spider venom has been found to have potential medical applications, including chronic pain relief. The venom of a black widow spider contains a compound called alpha-latrotoxin which is known to affect neurotransmitters in the body. This has led researchers to study the venom as a potential pain medication.
According to research, the alpha-latrotoxin compound in black widow spider venom may be effective in treating chronic pain. In fact, a synthetic version of the compound has been developed and tested in animal models. The compound was found to be effective in blocking pain sensation without affecting motor function. This could be a major breakthrough in chronic pain relief medication, as many current pain medications can cause unwanted side effects.
However, it’s important to note that because of the potency of black widow spider venom, caution must be taken when studying it for medical purposes. This venom can be deadly and can cause severe symptoms, including muscle pain, spasms, and respiratory distress. The use of synthetic compounds and careful research practices are necessary to ensure the safety of researchers and patients alike.
In the future, black widow spider venom research may lead to the development of even more effective and safe pain relief medications. While there is still much to learn about the effects of the venom on the body, its potential use in chronic pain relief is promising.
If you’re interested in learning more about the use of black widow spider venom for chronic pain relief, check out our article on Black Widow Venom for Pain Relief: Is It the Next Big Thing?.
Heart Disease Treatment
Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. While current treatments like bypass surgeries, stents, and drugs provide relief, they don’t always address the root cause of the heart problem. However, new research into black widow spider venom has uncovered potential treatments for heart disease.
Scientists have discovered that black widow spider venom contains a protein called latrotoxin, which causes the release of several neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine. Acetylcholine helps regulate the heart’s rhythm, which is essential for proper cardiovascular function. Researchers are exploring using latrotoxin to develop drugs that target the acetylcholine receptors in the heart, improving its function and reducing the risk of heart failure and arrhythmia.
Some studies have already shown promising results in using black widow spider venom for heart treatment. Researchers at the University of Leeds in the UK found that parts of the venom could treat heart cell damage caused by heart attack or stroke. They discovered that the protein knottin, extracted from the black widow spider venom, had a regenerative effect on heart cells, which could help in repairing the damaged tissues of the heart.
However, it is important to note that this research is still in its early stages, and more studies need to be conducted to understand the effects of black widow spider venom on the heart fully. At the same time, researchers need to explore the potential side effects and risks of using venom-based drugs for heart treatment. Nonetheless, black widow spider venom shows immense potential in treating heart disease and offers a ray of hope to the millions of people suffering from it.
If you want to know more about how to avoid black widow spider bites in your house and garden, you can check out our article on how to avoid black widow spider bites in your house and garden.
Cancer Research
Cancer Research: In recent years, scientists have been studying the potential of black widow spider venom in treating cancer. The venom contains compounds known as ‘alpha-latrotoxins’ that have shown to be effective against cancerous cells. These toxins work by disrupting calcium ion flow in the targeted cells which results in cellular death. While still in the early stages of research, tests have shown that these toxins can be effective in killing a variety of cancer cells including melanoma, leukemia, and breast cancer.
One study conducted at the University of Queensland found that the venom was able to significantly reduce the growth of breast cancer cells by up to 98%. However, research in this area is still ongoing, and further study is needed to understand the full potential of black widow spider venom in treating cancer.
The potential of black widow spider venom in cancer research has opened up new avenues for developing cancer treatments. Researchers are now exploring the possibility of using venom as a delivery system for cancer drugs. By injecting the drugs into the venom, it can target specific cancer cells in the body more effectively.
However, it is important to note that the use of spider venom in cancer treatment is still in the early stages of research. While it shows great promise, it is not a cure for cancer, and its effectiveness is still being investigated.
Internal link: To learn more about the mechanisms of black widow spider venom, read our article on how Black Widow spider venom works.
Future Medical Applications of Black Widow Spider Venom
Research on black widow spider venom has uncovered promising applications for the future of medicine. Neurodegenerative disease treatment is one area of potential application that has garnered significant interest. The venom contains a compound called latrotoxin, which has been shown to affect neurotransmitters in the brain and could potentially be used to treat conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Another potential application for black widow spider venom research is anti-venom development. Anti-venom is a critical treatment for individuals who have been bitten by venomous spiders, including black widows. Currently, the only available anti-venom for black widow spider bites is made by collecting venom from live spiders and extracting the proteins. However, this process is time-consuming, expensive, and potentially harmful to the spiders. By studying the venom’s composition, researchers may be able to develop a synthetic anti-venom that is more effective, less expensive, and does not require the use of live spiders.
It is important to note that while the medical applications of black widow spider venom research are promising, there is still much work to be done before any treatments are available to the general public. Spider conservation is an important consideration in this research, as black widows are crucial to many ecosystems and play a vital role in controlling pest populations. Additionally, protecting researchers and patients from potential harm is paramount, as black widow spiders are highly venomous and can cause severe illness or death in some cases.
Future research on black widow spider venom has the potential to significantly impact the field of medicine. From treating chronic pain and heart disease to developing anti-venom and treating neurodegenerative diseases, the possibilities are vast. However, ethical considerations, including spider conservation and patient safety, must be carefully considered in any future developments.
Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment
The potential for black widow spider venom to be used in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases is an exciting area of research. Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, are characterized by a gradual loss of brain function over time. While there are medications available to manage symptoms, there is currently no cure for these diseases.
Studies have shown that black widow spider venom may hold promise in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. The venom contains compounds that can interact with neurotransmitters in the brain, potentially improving cognition and slowing disease progression. Additionally, black widow spider venom has been found to have neuroprotective properties that may prevent or slow the death of brain cells.
While research is still in the early stages, the potential for using black widow spider venom in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases is an exciting prospect. However, it’s important to note that these studies are still in the preclinical phase, meaning they have not yet been tested on humans.
As with any area of research involving venomous animals, there are risks involved in studying black widow spider venom. It’s important for researchers to take necessary precautions to protect themselves and their patients. This includes wearing protective clothing and equipment, as well as following established safety protocols.
In addition to physical safety, it’s important to consider the ethics of using black widow spider venom in research. These spiders play an important role in their ecosystems, and it’s important to ensure that their populations are not threatened by research efforts. This can be accomplished through responsible collection and handling practices, as well as supporting conservation efforts.
As we continue to learn more about black widow spider venom and its potential medical applications, it’s important to approach this research with a sense of responsibility and ethical consideration. By doing so, we can maximize the potential benefits of this venom while minimizing any potential risks to researchers and spiders alike.
References:
- https://spiders.ucr.edu/black-widow-spider
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2017.00733/full
Anti-Venom Development
One of the most important medical uses of black widow spider venom research is the development of anti-venom. When someone is bitten by a black widow spider, the venom can have serious and potentially deadly effects on their body. The symptoms of a black widow spider bite can include muscle pain and spasms, as well as nausea, vomiting, and difficulty breathing. Without proper treatment, these symptoms can worsen over time and can lead to long-term health problems.
Anti-venom is a treatment that has been developed to counteract the effects of black widow spider venom. The anti-venom is created by extracting venom from black widow spiders and then purifying it to remove any harmful toxins. Once the venom has been purified, it is injected into animals like horses or sheep. The animal’s body then produces antibodies to the venom, which are collected and used to create an anti-venom serum.
This serum can then be used to treat people who have been bitten by a black widow spider. When the serum is injected into the patient’s bloodstream, it neutralizes the venom and helps to relieve the symptoms of the bite. It’s important to note that anti-venom is only effective if it is given soon after the bite. Delayed treatment can result in permanent damage to the patient’s body.
As with any kind of medical treatment, the development of black widow spider anti-venom has been a long and complex process. However, it has already saved countless lives since its introduction. It’s worth noting that not all spider bites require anti-venom treatment. In fact, most spider bites are harmless and don’t require any medical intervention. However, for those who do suffer from a black widow spider bite, the existence of anti-venom is a lifesaver.
For more information on how to differentiate a black widow spider bite from those of other venomous spiders, check out our article on black widow spider bites vs venomous spiders. And for more information on the surprisingly dangerous habits of male black widow spiders, you can read our article on male black widow bites on humans.
Studying Black Widow Spiders Ethically
When it comes to studying Black Widow Spiders for their venom, it is essential to approach the research in an ethical manner. Spider conservation is an important consideration, as these creatures play a vital role in the balance of the ecosystem, and they are often overlooked and misunderstood by humans. Researchers must ensure that their work does not have a negative impact on spider populations or their habitats.
Another aspect of ethical spider research is protecting both researchers and patients from the dangerous effects of Black Widow Spider venom. Safety measures must be in place to prevent bites from occurring during the handling of spiders, as well as the collection and transportation of venom.
It is vital to consider the welfare of the spiders themselves during the venom extraction process. Researchers find themselves in a precarious situation because removing spider venom can potentially harm or kill the spider. However, recent advancements in technology have allowed for a more humane approach to venom extraction. Rather than manually milking spiders, scientists can now obtain venom samples via a non-invasive technique that does not harm the spider. This approach helps to ensure the ethical treatment of Black Widow Spiders in research.
Studying Black Widow Spiders for their venom provides valuable insights for medical research. Still, it is also essential for researchers to approach the study ethically. They must balance the benefits of the research with the importance of spider conservation and the safety of both humans and spiders. By doing so, researchers can make significant contributions to medical advancements while also promoting responsible and ethical scientific practices.
Importance of Spider Conservation
The study of black widow spider venom has provided valuable insights into potential medical applications. However, it is important to note that spider conservation efforts must also be considered. The black widow spider is often labeled as dangerous and harmful, leading to unnecessary fear and human-driven population decline.
Spider conservation is important for maintaining ecosystem balance and diversity. Spiders play a crucial role in controlling insect populations, preventing overpopulation and crop damage. Without spiders, the balance of ecosystems could be disrupted and lead to detrimental consequences.
Furthermore, black widow spider venom research depends on the existence of black widow spiders. They are essential for conducting ethical research and the development of anti-venom. If the spider populations continue to decline, research would become more difficult, ultimately hindering medical advancements that could benefit human health.
It is necessary to prioritize spider conservation through education and environmental protection. This includes creating public awareness campaigns about spiders and their important role in our environment. Governments and organizations should also prioritize conservation efforts and initiatives to protect spider populations.
While studying black widow spider venom can lead to groundbreaking medical advancements, it is critical to consider spider conservation efforts to protect the overall ecosystem and ensure the future of venom research.
Protecting Researchers and Patients
Due to the potentially dangerous nature of black widow spiders and their venom, it’s important to take proper precautions when studying them and using their venom for medical research. Researchers who work with black widow spiders must be properly trained and take appropriate safety measures to protect themselves.
One essential precaution is the use of protective gear such as gloves and goggles. Researchers must also be careful when handling and extracting venom from the spiders to avoid being bitten and injected with the venom themselves. The venom can cause serious health effects, including muscle spasms, cramps, and breathing difficulties.
Patients who receive black widow spider venom as part of medical treatment must also be closely monitored for any adverse reactions. While the venom has potential therapeutic benefits, it can also cause harmful side effects if not administered properly.
To ensure safety, researchers and medical professionals must adhere to strict ethical guidelines and regulations when working with black widow spider venom. Any experimentation or treatment must undergo rigorous testing and approval processes to protect the well-being of both researchers and patients.
In addition to protecting people, it’s also important to protect black widow spiders and their habitats. These spiders play an important role in ecosystem balance and should be respected and conserved. Policies and regulations must be put in place to prevent the destruction of natural habitats, and researchers must work to minimize their impact on local ecosystems when conducting studies. Ethical considerations must be a top priority when studying black widow spider venom for medical research.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of black widow spider venom is a crucial field with vast potential in the world of medicine. This venomous substance, composed of a complex cocktail of enzymes and proteins, has been shown to have significant effects on the body, including pain relief and anti-cancer properties. While current medical applications are limited, ongoing research is showing promise in the treatment of heart disease, chronic pain, and potentially even neurodegenerative diseases.
However, it is important to approach the study of black widow spiders ethically. This means taking into account the importance of spider conservation and protecting both researchers and patients. It is also crucial to develop proper safety protocols when handling venomous spiders and their venom.
Further research is needed to fully understand the potential of black widow spider venom, and to develop safe and effective medical treatments. Nevertheless, the continued study of this venomous substance has the potential to revolutionize medicine and positively impact many lives. It is imperative for researchers and medical professionals to continue to explore the possibilities and ethical considerations surrounding the medical uses of black widow spider venom.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common species of Black Widow Spider?
The most common species of Black Widow Spider is the southern black widow (Latrodectus mactans).
Can Black Widow Spider venom kill a human?
While the venom of a Black Widow Spider can be toxic to humans, fatalities are rare and typically only occur if left untreated.
What are the symptoms of a Black Widow Spider bite?
Symptoms of a Black Widow Spider bite include muscle pain, tremors, sweating, nausea, and vomiting.
How is Black Widow Spider venom extracted for research purposes?
Black Widow Spider venom is extracted using a technique called “milking” where a glass pipette is placed on the spider’s fangs to collect the venom.
What is the future potential of Black Widow Spider venom research?
Black Widow Spider venom has the potential to be used in the development of treatments for diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis.
What is the role of calcium in Black Widow Spider venom?
Calcium plays a vital role in the toxic effects of Black Widow Spider venom, as it can cause the release of neurotransmitters that lead to muscle spasms.
Are there any current FDA-approved medications that contain Black Widow Spider venom?
Yes, there is a medication called Prialt which is made from a synthetic form of Black Widow Spider venom and is used to treat chronic pain.
Why is ethical treatment of Black Widow Spiders important?
Black Widow Spiders are an important part of the ecosystem and help to control insect populations. Ethical treatment is necessary to protect both the spiders and the researchers who study them.
What kind of habitat do Black Widow Spiders prefer?
Black Widow Spiders prefer dark, secluded areas such as woodpiles, garages, and sheds.
How can Black Widow Spider bites be prevented?
Black Widow Spider bites can be prevented by wearing protective clothing when working in areas where spiders may be present, and by carefully inspecting items like firewood and outdoor furniture before bringing them inside.






