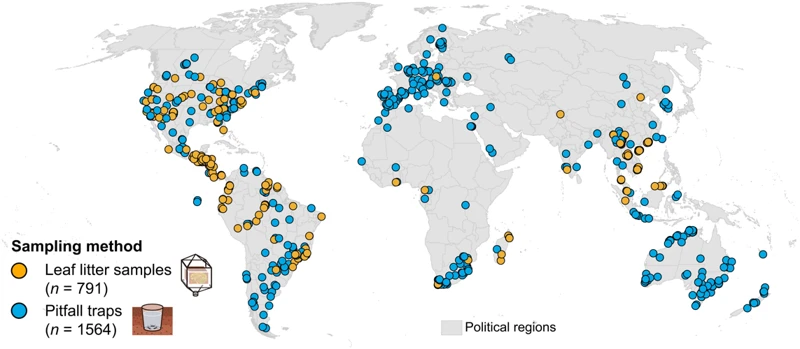
Wolf spiders are one of the most diverse and widespread spider families in the world, with over 2,000 species documented globally. Despite their ubiquity, mapping their distribution in certain regions is a complex and often understudied task. Factors such as habitat, climate, and food availability all impact their spatial distribution, presenting challenges to researchers attempting to better understand their ecology. This article will explore the various challenges in mapping wolf spider distribution in understudied regions, as well as potential solutions, including citizen science projects and improved technological efficiency.
Factors that Impact Wolf Spider Distribution
Understanding the factors that impact the distribution of wolf spiders is crucial in gaining insight into their ecology and biology. These factors can vary in different regions around the world, spanning across continents, whether we look at their geographical distribution across the globe, such as in wolf spider’s global perspective, North America, or tropical regions. The following sections will explore the habitat, climate, and food availability, all of which impact the distribution of wolf spiders.
Habitat
Wolf spiders are known to inhabit a wide range of ecosystems across the world, from deserts and grasslands to forests and wetlands. Habitat is a major factor affecting the distribution and abundance of wolf spiders. These spiders prefer habitats with moisture and cover, such as leaf litter, soil cracks, rocks, and logs. Some species of wolf spiders are also adapted to live in aquatic environments, like ponds and streams.
Different habitats have varying degrees of suitability for wolf spiders, which affects their presence and abundance. For instance, some studies have found that wolf spider density is higher in habitats with greater vegetation cover, while others have shown that they are more abundant in open areas. On a larger scale, the geographical distribution of wolf spiders is influenced by the availability of suitable habitats across different continents and regions.
Factors such as human activities and climate change can also have significant impacts on wolf spider habitat. Land use changes, such as deforestation, agriculture, and urbanization, can directly reduce the availability of suitable habitats for these spiders. Climate change can alter the moisture and temperature conditions in habitats, affecting wolf spider densities and distributions.
Understanding the impact of habitat on wolf spider distribution is crucial for designing effective conservation strategies and predicting the response of these spiders to global environmental changes.
Climate
Climate has a significant impact on the distribution of wolf spiders. These spiders are found in a wide range of climates, from tropical rainforests to deserts, and even in sub-Arctic regions. However, different species have different temperature requirements, and extreme temperatures can limit their distribution.
Temperature: One of the most important climate factors that influence the distribution of wolf spiders is temperature. These spiders are cold-blooded, so their body temperature is regulated by their environment. In general, wolf spiders thrive in areas with moderate temperatures. Extreme heat or cold can be detrimental to their survival.
Precipitation: Another important factor that affects the distribution of wolf spiders is precipitation. Wolf spiders are found in a variety of habitats, ranging from desert to rainforest. In many regions, sparse distribution of precipitation limits the habitat for wolf spiders, as they require some level of moisture to thrive.
Seasonal Variations: Wolf spider distribution can also be influenced by seasonal variations. In some regions, the wet and warm season creates a more hospitable environment for wolf spiders, who thrive in moist soil and can reproduce more rapidly. In other regions, the dry and cooler season can restrict their distribution, as they may not be able to find sufficient prey.
Understanding the impact of climate on the distribution of wolf spiders is essential for accurate mapping and conservation efforts. To learn more about the geographic distribution of wolf spiders, check out our article on the topic.
Food Availability
Wolf spiders are known for being opportunistic hunters that will consume a wide variety of prey. However, the availability of prey can greatly impact their distribution. Studies have shown that wolf spiders are most abundant in areas with high prey densities, such as grassy meadows, wetlands, and forests with leaf litter. On the other hand, barren habitats like deserts or watersheds have lower spider densities.
| Factors that impact prey availability: | Impact on wolf spider distribution: |
|---|---|
| Vegetation structure and complexity | High vegetation complexity, such as tall grasses and shrubs, can provide shelter and habitat for prey, thus increasing the abundance of wolf spiders. |
| Climate and weather patterns | Prey activity levels can change based on weather conditions. For example, some insects may become less active during hot, dry weather, which can lead to a decrease in wolf spider abundance. |
| Seasonal changes | Wolf spider abundance may vary seasonally, depending on the life cycles of their prey. For example, invertebrate populations may increase during the spring and summer, leading to an abundance of wolf spiders during those seasons. |
Prey availability can also impact the size and behavior of wolf spiders. Studies have shown that wolf spiders will increase in size when prey is abundant, and decrease in size when prey availability is low. Additionally, prey availability can impact the hunting behavior of wolf spiders. For example, in areas with an abundance of prey, wolf spiders may hunt less aggressively and consume larger prey items, while in areas with lower prey densities, wolf spiders may be more aggressive and consume smaller prey items.
Overall, food availability is a crucial factor in wolf spider distribution, and can greatly impact population density, size, and behavior. Understanding the prey base of wolf spiders can provide valuable insights into their distribution patterns and help guide future research efforts.
Research Studies on Wolf Spider Distribution

As wolf spiders are an important member of ecosystems and play a role in controlling insect populations, researchers have conducted numerous studies on their distribution patterns. These studies have revealed crucial insights into the factors that impact their distribution, but certain regions still remain understudied. In this section, we will explore the areas that have been studied, the findings of these studies, and the lack of research in certain regions.
Areas That Have Been Studied
Research studies have been conducted on the distribution of wolf spiders in various regions around the world. Using a combination of field surveys, DNA barcoding, and environmental data analysis, these studies have shed light on the habitat preferences and climatic tolerances of different wolf spider species.
One such study was conducted by Stork et al. (2019) in the Australian tropical savanna. The researchers found that wolf spider species diversity was highest in open grassland habitats and that certain species had a preference for rock outcrops and termite mounds as microhabitats.
Another study was carried out by Vasconcellos-Neto et al. (2018) in the Brazilian Atlantic forest. This study focused on the influence of habitat fragmentation on wolf spider species richness and composition. The researchers found that species richness decreased in fragmented habitats, but certain species that are known to have a wide geographical range were able to persist in these areas.
In Europe, researchers have examined the effects of land use on wolf spider distribution. For example, Lang et al. (2017) investigated the impact of forestry practices on wolf spiders in Norway. The study found that clear-cut logging had a negative effect on wolf spider communities, while retention forestry (leaving some trees standing) increased species diversity.
Finally, in North America, Spagna et al. (2017) conducted a study on the factors affecting wolf spider distribution in grassland ecosystems. The researchers found that temperature and precipitation were the most important climatic variables driving species distributions, while habitat structure (including vegetation cover and moisture gradients) also played a role.
The studies conducted on wolf spider distribution have shown that habitat, climate, and food availability are important factors affecting these creatures. By understanding these factors, researchers can make more informed decisions about conservation efforts and potential challenges in understudied regions.
Insight From These Studies
Studies on wolf spider distribution have yielded valuable insights that can help us understand the factors that affect their distribution. A common finding from these studies is that wolf spiders exhibit a strong preference for certain types of habitats. For example, a study conducted in grasslands found that wolf spiders were more abundant in areas with taller vegetation and greater plant diversity. Similarly, a study conducted in Alaskan boreal forests found that wolf spiders were more common in areas with more complex vegetation and leaf litter.
Other studies have focused on the impact of climatic factors on wolf spider distribution. One such study found that wolf spider abundance was positively correlated with temperature and precipitation levels, while another study found that wolf spider diversity was greater in areas with moderate temperatures and higher humidity levels.
Food availability is also an important factor influencing wolf spider distribution. A study conducted in the Great Basin Desert found that wolf spider abundance was higher in areas with more abundant insect prey. Similarly, a study conducted in a Brazilian savanna ecosystem found that wolf spider abundance was positively correlated with prey abundance and biomass.
These studies highlight the complex interplay between habitat, climate, and food availability in shaping wolf spider distribution. By gaining a better understanding of these factors, researchers can improve our ability to predict how wolf spiders will respond to changes in their environment, including those caused by human activities such as climate change and habitat fragmentation.
| Factor | Study Finding |
|---|---|
| Habitat | Wolf spiders more abundant in areas with taller vegetation and greater plant diversity |
| Habitat | Wolf spiders more common in areas with more complex vegetation and leaf litter |
| Climate | Wolf spider abundance positively correlated with temperature and precipitation levels |
| Climate | Wolf spider diversity greater in areas with moderate temperatures and higher humidity levels |
| Food Availability | Wolf spider abundance higher in areas with more abundant insect prey |
| Food Availability | Wolf spider abundance positively correlated with prey abundance and biomass |
Lack of Research in Certain Regions
Despite its ecological significance and potential benefits to understanding the dynamics of insect populations, there are many regions worldwide with little to no research on wolf spider populations. This lack of research can be attributed to several factors, such as insufficient funding, lack of scientific interest, or the difficulty of accessing remote areas.
Some of the regions with limited research include:
- The Amazon rainforest
- The Sahara desert
- Antarctica
- The Himalayas
- The Arctic tundra
This lack of research is particularly problematic because these regions are home to many endemic species of wolf spiders with unique adaptations to their environments. By failing to study wolf spider populations in these regions, we miss out on the opportunity to gain valuable insights into their ecology and behavior, and to potentially discover new species.
The lack of research in certain regions creates gaps in our understanding of wolf spider distribution and abundance, which can have wide-ranging consequences for conservation efforts and management decisions. For example, if we don’t know which regions are hotspots for wolf spider biodiversity, we may not prioritize these areas for conservation efforts or take measures to protect these populations from threats such as habitat destruction or climate change.
The limited research on wolf spiders in certain regions is a significant challenge that needs to be addressed. While funding and access remain major obstacles to conducting research in these areas, it is crucial that we prioritize and invest in these efforts, both to expand our understanding of wolf spider ecology and to protect these important arachnids for future generations.
Challenges in Studying Understudied Regions for Wolf Spiders

Studying wolf spider distribution in regions that are not well-studied can be a challenging and complex task. The lack of information and resources in these regions can make the task seem daunting. However, there are several factors that contribute to the challenge of mapping wolf spider distribution in these understudied areas. These factors include a lack of funding and resources, difficulty in accessing remote areas, the diversity of species, and seasonal variations. In this section, we will delve into each of these factors and explore their impact on the study of wolf spider distribution in understudied regions.
Lack of Funding and Resources
The lack of funding and resources is a major factor that has hindered research on mapping wolf spider distribution in understudied regions. Wolf spiders are found in a wide range of habitats, and the cost of conducting an accurate survey in any under-researched region can be high. The shortage of financial resources often makes it difficult for researchers to carry out detailed studies in areas where the spider population is scarce, but important from a conservation perspective.
Some of the difficulties researchers face due to the lack of funding and resources include:
- Insufficient funds to hire a team of scientists to work on the project for an extended period.
- Shortage of equipment, including cameras, microscopes, and traps, which are necessary to capture the spider’s images, analyze their anatomy, and monitor their movement patterns, respectively.
- Inability to conduct aerial surveys using drones or other means due to the high cost.
- Limited ability to gather long-term data on wolf spiders, which is necessary to observe changes over time and understand their population dynamics.
As a result of the lack of funding and resources, researchers have had to use more creative and resourceful methods to study wolf spider distribution in understudied regions. Some have relied on citizen science projects and collaborations with the local community to gather data. Nonetheless, without adequate funding and resources, it’s challenging to perform comprehensive research on wolf spider population and understand their distribution in understudied regions.
Difficulty of Accessing Remote Areas
Remote areas are typically difficult to access and this is a challenge in studying wolf spider distribution. Researchers often require fieldwork to identify and study these spiders. However, the difficulty of accessing these remote areas can pose a significant problem.
Challenges in Accessing Remote Areas
| Challenge | Implication |
| Geographical barriers | Difficult to travel to these areas, especially in extreme weather conditions. |
| Lack of transportation | Difficulty in transporting equipment and resources to remote areas. |
| Limited research stations | May not have established research stations in remote areas. |
| Safety concerns | Remote areas may pose risks to researchers’ safety. |
These challenges make it difficult and time-consuming to conduct studies in remote areas. It may require additional resources and funding to overcome these challenges. However, it is important to consider these challenges in order to have a comprehensive understanding of wolf spider distribution in understudied regions.
Diversity of Species and Similarity in Appearance
Wolf spiders are a highly diverse group, with over 2,300 species known worldwide. However, many of these species share a similar physical appearance, which makes it difficult to identify and differentiate them.
The challenge of identifying individual species of wolf spiders is compounded by the fact that these spiders have a wide range of morphological variations within each species. The variations can range from differences in coloration, to size, to markings on their bodies, making the identification of different species a daunting task for researchers.
This diversity of species and similarity in physiques not only makes it challenging to study wolf spider distribution but also creates difficulties in accurately tracking changes in their populations. Even trained experts can have a hard time distinguishing between species, leading to inaccuracies in the data collected.
To overcome this challenge, researchers have had to employ new and innovative techniques to identify and differentiate between species, such as DNA sequencing and morphometric analysis. These techniques help in identifying physical variations between the species, enabling researchers to create a more accurate database of wolf spider species in a particular area.
However, these methods can be time-consuming, expensive, and require specialized expertise, which further highlights the challenges associated with studying wolf spider distribution especially in understudied regions.
To summarize, the diversity of species and similarity in appearance among wolf spiders make studying their distribution a challenging task. Researchers have to be innovative and use advanced methods to accurately identify and differentiate between species. These challenges emphasize the need for more funds and resources to enable the development of advanced techniques to study these spiders in understudied regions.
Seasonal Variations
One of the major challenges in mapping wolf spider distribution in understudied regions is the impact of seasonal variations. These variations can significantly influence the behavior and distribution of wolf spiders. Some of the seasonal changes that can affect wolf spider distribution include changes in temperature, humidity levels, and precipitation.
Temperature: Wolf spiders are ectothermic, which means that their body temperature depends on the environment in which they live. During the colder months, wolf spiders may become less active, and may even hibernate to conserve energy. In warmer months, they are more active, and their distribution may shift to areas with cooler temperatures.
Humidity levels: Wolf spiders require a certain level of humidity to survive, and this can vary depending on the species. In arid regions, where humidity is low, some wolf spider species may have a limited range. In areas with high humidity, wolf spiders may be more abundant and widespread.
Precipitation: The amount of precipitation in an area can affect wolf spider distribution by affecting their food supply. In areas with high rainfall, there may be more insects for wolf spiders to feed on, leading to a larger population. Conversely, areas with low rainfall may have less food and, therefore, a smaller population of wolf spiders.
Different species of wolf spiders may have different seasonal habits, such as breeding or molting during certain times of the year. All these factors add to the complexity and difficulty of studying wolf spider distribution, especially in understudied regions.
Despite these challenges, researchers continue to make progress in understanding wolf spider distribution through detailed field studies, improved technological efficiency, and citizen science projects. By working together, we can better understand and protect these important members of our ecosystem.
Potential Solutions
As with any complex challenge, identifying potential solutions for mapping wolf spider distribution in understudied regions can require creativity, ingenuity, and collaboration. While this task may seem daunting, there are several strategies and tools that researchers and communities can utilize to fill knowledge gaps and innovate more efficient methods for data collection. By exploring these approaches, we can better understand how to effectively study wolf spider populations and their impact on ecosystems.
Citizen Science Projects
Citizen Science Projects
Citizen science projects have proven to be valuable tools for mapping wolf spider distribution in understudied regions. These projects involve volunteers from the local community who collect data on wolf spider sightings and habitat conditions. The data collected is then shared with researchers, who use it to gain a better understanding of population distribution and trends.
Here are some examples of how citizen science projects can help:
- Engaging local people in the research process helps raise awareness of wolf spiders and their role in the ecosystem. This increased awareness can help foster conservation efforts in the area.
- By involving more people in the data collection process, researchers are able to gather more information than they would be able to on their own.
- Citizen science projects can help fill data gaps in regions where research is lacking, giving researchers a more comprehensive view of wolf spider populations.
- Volunteer data collectors can cover a greater geographic area than researchers working alone, which can help improve data accuracy and representativeness.
However, there are some challenges to using citizen science projects for studying wolf spider distribution:
- Ensuring data quality can be a challenge when relying on volunteers with varying levels of experience and training. To overcome this, projects may involve training and certification programs to ensure that data collectors are following best practices.
- Sampling bias can be an issue when relying on volunteer data collectors. For example, the data collected may come from areas that are easily accessible, rather than those that are truly representative of the region.
- There may be a lack of standardization in data collection protocols across different projects, which can make it difficult to compare data across regions.
Despite these challenges, citizen science projects can provide a valuable source of data for studying wolf spider distribution in understudied regions. By engaging with local communities and using technology to streamline data collection and analysis, researchers can better understand these important predators and their role in the ecosystem.
Improved Technological Efficiency
One potential solution for mapping the distribution of wolf spiders in understudied regions is to improve technological efficiency. This would involve utilizing advanced technology and innovative methods to help researchers identify and study these elusive creatures.
Technology has played a significant role in advancing our understanding of wolf spider distribution. With the help of drones, remote sensing technologies, and geographic information systems (GIS), researchers have been able to gather data on wolf spider population density and habitat distribution in a more efficient and accurate manner.
Another useful technique is DNA barcoding, which enables researchers to identify wolf spider species based on their DNA sequences. This method has helped identify previously unknown species and elucidate the genetic relationships between different wolf spider populations.
In addition to these methods, there are other advanced technologies being developed to aid in mapping wolf spider distribution. For example, researchers are exploring the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to identify wolf spider species from photographs and other forms of data. This technology could potentially make it easier and faster to gather accurate data on wolf spider populations in understudied regions.
Improved technological efficiency also involves collaboration between researchers and technologists. By working together, researchers can develop new technologies and tools specifically designed to aid in mapping wolf spider distribution.
Here’s a table summarizing the different technological methods that have been developed to aid in mapping wolf spider distribution:
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Drones | Remote-controlled aircraft equipped with cameras that can capture aerial images and video footage of wolf spider habitats. |
| Remote sensing technologies | Equipment that can detect and measure various physical properties of wolf spider habitats, such as temperature, moisture, and topography. |
| Geographic information systems (GIS) | Software that captures, stores, and analyzes geographical data, which can be used to create detailed maps of wolf spider distribution. |
| DNA barcoding | A method of identifying species using DNA sequences, which has helped identify previously unknown wolf spider species. |
| Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms | Computer programs that can analyze large amounts of data and identify patterns that are difficult for humans to detect, making it easier to gather accurate data on wolf spider populations. |
Improving technological efficiency is an important step in accurately mapping the distribution of wolf spiders in understudied regions. By leveraging advanced technology and collaborating with technologists, researchers can gather more precise data on wolf spider habitats and populations.
Collaboration with Local Communities
Collaboration with local communities can be an effective way to overcome some of the challenges of mapping wolf spider distribution in understudied regions. By working with people who are familiar with the area and its wildlife, researchers can gain valuable insights and information that might be difficult to acquire otherwise. Here are some examples of how collaboration with local communities can be beneficial:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Local Knowledge | Local communities can provide valuable information about the presence or absence of wolf spiders in certain areas. This can include knowledge of specific habitats or behaviors that are unique to the area. |
| Increased Access | Collaborating with local communities can also help researchers to gain access to remote or hard-to-reach areas. Local guides or volunteers can provide transportation and logistical support, making it easier to conduct fieldwork. |
| Community Outreach | Working with local communities can also help to build awareness and support for research efforts. By involving community members in the research process, scientists can help to foster a sense of ownership and investment in protecting the local environment and its inhabitants. |
Of course, collaboration with local communities also comes with its own set of challenges. For example, researchers must be sensitive to the cultural norms and practices of the communities they are working with, and respect their perspectives and knowledge. However, when done appropriately and respectfully, collaboration with local communities can be an effective strategy for mapping wolf spider distribution in understudied regions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mapping the distribution of wolf spiders in understudied regions is a complex and challenging endeavor. There are various factors that have an impact on their distribution, including habitat, climate, and food availability. While there have been research studies conducted on the distribution of wolf spiders, much of the focus has been on certain regions, leaving a lack of information on other areas. Additionally, studying understudied regions poses its own set of challenges such as resource and funding limitations, difficulty accessing remote areas, and seasonal variations.
Despite these challenges, solutions such as citizen science projects, improved technological efficiency, and collaboration with local communities offer potential avenues for progress. By working together and utilizing these solutions, researchers can gain a better understanding of wolf spider distributions in understudied regions, which can not only contribute to scientific knowledge but also have practical applications in conservation and management efforts.
Overall, while mapping wolf spider distribution in understudied regions is not without its obstacles, the benefits of gaining this knowledge are significant. With continued effort and collaboration, researchers can overcome these challenges and uncover important information about the ecology of these fascinating creatures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are wolf spiders?
Wolf spiders are a family of spiders that are unique from other spiders due to their hunting behavior and large eyes.
Why is mapping wolf spider distribution important?
Mapping wolf spider distribution can help scientists understand their ecology, behavior, and the effects of environmental factors on their populations. It can also aid in conservation efforts and pest management.
What factors impact wolf spider distribution?
Habitat, climate, and food availability are the primary factors that impact wolf spider distribution.
What types of habitats are preferred by wolf spiders?
Wolf spiders prefer habitats with vegetation and cover such as forests, grasslands, and shrublands. They can also be found in urban areas.
How does climate affect wolf spider distribution?
Wolf spiders are typically found in regions with moderate temperatures and humidity. Extreme temperature fluctuations or extended periods of drought can negatively impact their populations.
What do wolf spiders eat?
Wolf spiders are carnivores and primarily eat small insects and other arthropods. They are known to be important in pest control.
Why are some regions understudied for wolf spiders?
Some regions may be difficult to access or lack funding and resources for research. Additionally, wolf spiders can be difficult to identify due to their similarity in appearance to other spider species.
What is a citizen science project?
A citizen science project involves members of the public in scientific research by collecting and reporting data on a particular topic. It can help increase the amount of data collected and promote public engagement.
How can improved technological efficiency aid in studying wolf spider distribution?
New technologies such as DNA barcoding and remote sensing can help increase accuracy and efficiency in identifying and mapping wolf spider populations.
How can collaboration with local communities benefit wolf spider research?
Collaboration with local communities can help increase the amount of data collected and provide valuable insight into the ecology and behavior of wolf spiders in the area. It can also aid in promoting conservation efforts and awareness.