As I observe these eight-legged creatures crawling across my garden, I can’t help but wonder about the different sizes of male and female wolf spiders. Do they vary greatly in size or are they similar in dimensions? Why is size so important when it comes to these spiders? In this article, we’ll explore the intricate world of wolf spiders and uncover the differences in size, physical appearance, and behavior between male and female spiders. We’ll also delve into the impact that size has on their habitat, reproduction, and offspring development. So, grab a cup of coffee and let’s unravel this web of mystery together.
What are Wolf Spiders?
Wolf spiders are a fascinating and diverse group of arachnids that belong to the family Lycosidae. They are known for their large and hairy bodies, fast speed, and impressive hunting abilities. There are over 2,300 species of wolf spiders found around the world, with around 200 species of wolf spiders found in the United States alone. These spiders are solitary hunters that do not spin webs to capture their prey, but instead rely on their excellent eyesight and speed to catch insects, other spiders, and even small animals like lizards.
One of the most distinctive features of wolf spiders is their size. These spiders can range anywhere from 1/4 inch to 2 inches in length, making them one of the largest families of spiders in the world. In fact, some of the largest wolf spiders can reach lengths of up to 4 inches if you include their legs and body. This diverse range in size is due to a variety of factors, including genetics, geographic location, and environmental conditions.
Understanding the size of wolf spiders is essential for researchers who are studying this fascinating group of arachnids. Researchers must accurately measure and record the size of wolf spiders in order to better understand their hunting techniques, body size variations, and environmental impact. By doing so, we can gain a better understanding of how wolf spiders are adapting to changes in their habitat and how we can better protect them in the future.
To learn more about the size of wolf spiders, check out these helpful resources: /wolf-spider-size-hunting-techniques/, /accurately-measure-size-wolf-spider/, /wolf-spider-body-size-variations/, /environmental-impact-wolf-spider-size/.
The Importance of Size in Wolf Spiders
Size is an important aspect when it comes to wolf spiders. The body size of these arachnids can vary greatly depending on their sex, age, and species, which can have a significant impact on their behavior, habitat, and reproductive capabilities.
Behavior: The size of wolf spiders can affect their hunting and mating behaviors. Larger spiders are more aggressive and tend to have higher success rates in hunting prey, while smaller spiders may need to rely on stealth and cunning to catch their prey. Larger male wolf spiders tend to have a greater chance of successful mating due to their dominance over smaller males.
Habitat: Wolf spiders have a wide range of habitats, but their size can impact the specific environments they inhabit. Smaller spiders tend to live in smaller habitats, such as leaf litter and under rocks, while larger spiders may require more open spaces to move and hunt.
Reproduction: The size of wolf spiders also plays a significant role in their reproductive capabilities. Females often choose larger males as their mates, as they are more likely to produce healthier offspring. Larger females tend to be more fecund and can produce more eggs during reproduction, leading to a greater chance of successful reproduction.
The size of wolf spiders plays a critical role in their behavior, habitat, and reproductive capabilities. Understanding these differences can help us better understand and appreciate these incredible arachnids.
Male vs Female Wolf Spiders
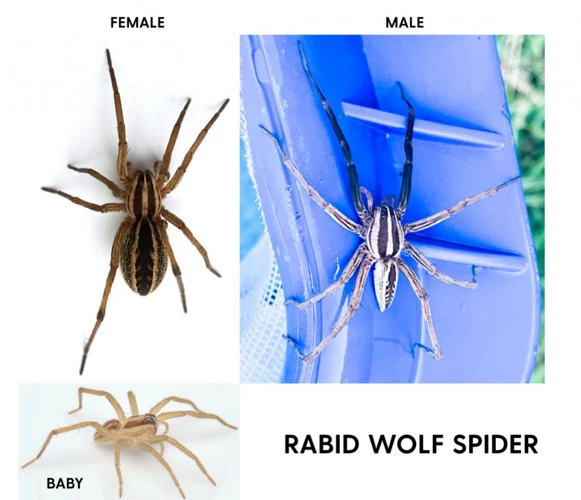

Male and female wolf spiders vary in size and appearance, as well as in their behavioral patterns. These differences play a vital role in their survival and reproduction in the wild.
Difference in Size: The most apparent difference between male and female wolf spiders is their size. Male wolf spiders are usually smaller than their female counterparts, with an average body length of about 10-20 mm, whereas female wolf spiders can grow up to 35 mm or more. The size difference can be observed in their legs as well. Male wolf spiders have longer and thinner legs, while females have shorter and sturdier ones.
Physical Appearance: Apart from the size difference, male and female wolf spiders also have distinct physical appearances. The females are usually more colorful and have patterns on their bodies, while the males are relatively dull in color. Females have a rounder and bulkier appearance due to their larger size and the need for extra space to carry their eggs. In contrast, males have more elongated bodies and a streamlined appearance.
Behavioral Differences: Male and female wolf spiders have different behavioral patterns. Males are more aggressive than females when it comes to mating. They often engage in territorial battles with other males and may seek out females aggressively. In contrast, female wolf spiders are known for their excellent hunting skills, as they need to catch prey to feed themselves and their young.
The differences between male and female wolf spiders are crucial for their survival and reproduction in the wild. Size, physical appearance and behavioral patterns all play a role in their ability to survive and thrive in their diverse habitats.
Difference in Size
Male and female wolf spiders differ significantly in size. It’s an interesting subject to explore, and it’s especially fascinating how differences in size have a role in their behavior, habitat, and reproduction. The size difference between male and female wolf spiders is the key aspect that separates them. Let’s delve deeper into the world of wolf spiders and examine how they differ in size.
Physical Appearance
The physical appearance of male and female wolf spiders differs in many aspects. Let’s explore these differences in detail.
Size: The most apparent difference in physical appearance is in size. Male wolf spiders are generally smaller in body size than female wolf spiders. As an example, the average body size of a male wolf spider is about 1 inch, while the female wolf spider can grow to about 2 inches.
Coloration: Another noticeable difference is the coloration of the spider. Males are generally more colorful than females. Male wolf spiders are often adorned with bold patterns and brightly colored markings, while females are more muted in color.
Legs: The legs of male and female wolf spiders also have a few differences. The legs of male wolf spiders are often longer and more slender than the legs of females. Male wolf spiders have a bulbous tibia (second segment of the leg) that females lack.
Abdomen shape: The abdomen shape of male and female wolf spiders is also different. The abdomen of male wolf spiders is often elongated and thin, while females have a more rounded abdomen.
To summarize, male and female wolf spiders show significant differences in their physical appearance, including size, coloration, leg shape, and abdomen shape. These differences are essential for species identification and contribute to their survival in their respective habitats. Let’s explore how these differences and size impact the habitat and reproduction of male and female wolf spiders.
Here’s a table summarizing the physical appearance differences between male and female wolf spiders:
| Aspect | Male Wolf Spider | Female Wolf Spider |
| Size | Smaller, approx. 1 inch | Larger, approx. 2 inches |
| Coloration | Bold patterns and bright colors | Muted colors |
| Legs | Longer, more slender, with bulbous tibia | Shorter, thicker |
| Abdomen Shape | Elongated and thin | Rounded |
Behavioral Differences
Male and female wolf spiders are not only different in size and physical appearance but also in their behavior. In fact, the behavioral differences are one of the most striking distinctions between the two genders.
| Behavioral Differences |
|---|
| Male wolf spiders are generally more active than females. |
| Male wolf spiders tend to wander more frequently in search of mates, whereas females are more likely to stay in one place and wait for prey to come to them. |
| Females are typically more aggressive than males when it comes to defending their territory or offspring. |
| Males are often observed fighting each other for access to females, while females rarely engage in physical altercations outside of defending themselves or their clutch. |
| Male wolf spiders are also more prone to cannibalism, especially when in close proximity to females. |
These differences in behavior reflect the different roles that males and females play in reproduction and survival. Male wolf spiders have to be more active and risk-taking in order to locate females and engage in mating behaviors. They also engage in more competition over mates, which can increase the likelihood of risky behaviors such as cannibalism.
On the other hand, female wolf spiders prioritize the defense of their territory and brood, which requires them to be more selective and strategic in their hunting and movement patterns. This emphasis on protection rather than exploration may help to explain why females are generally larger and stronger than males – they need to be able to defend themselves and their offspring against a variety of potential threats.
The behavioral differences between male and female wolf spiders are nuanced and complex, reflecting the unique ecological pressures and selection pressures that each gender faces. By understanding these differences, we can gain insights into the evolution and adaptation of these fascinating arthropods.
Impact of Size on Habitat
The size of a wolf spider can significantly impact their choice of habitat. The habitat of male wolf spiders tends to be larger and more expansive compared to female wolf spiders. Male wolf spiders are generally more active and require ample space to roam and hunt. They are often found in open fields, forests, and grasslands. They prefer areas with low vegetation where they can move around easily. Due to their larger size, male wolf spiders can tolerate extreme temperatures better than females and can be found in a wider range of habitats.
On the other hand, female wolf spiders have smaller and more restricted habitats. They are often found in burrows or cracks in the ground where they lay their eggs and protect their young. These burrows provide a safe and sheltered environment for the young spiderlings to develop. Females tend to prefer areas with higher vegetation where they can construct their burrows more easily. They are less active and mostly stay close to their burrows to protect their offspring.
The difference in habitat preference between male and female wolf spiders also influences their feeding habits. Male wolf spiders hunt and scavenge more openly whereas females tend to ambush their prey from their burrows. Due to their smaller size and fewer energy reserves, female wolf spiders need to conserve their energy and make efficient use of their surroundings.
The size of wolf spiders plays a crucial role in determining their habitat preference. Males require larger and more open spaces to roam and hunt, while females tend to choose sheltered and hidden burrows to protect their offspring. Understanding the habitat preferences of these creatures is crucial for their conservation and can help us create more suitable habitats for them to thrive in.
Habitat of Male Wolf Spiders
Male wolf spiders are solitary creatures that are commonly found in a variety of habitats. These arachnids are known for their impressive hunting skills and ability to thrive in different environments. However, their habitat preferences may vary depending on several factors such as their size, age, and reproductive status. In this section of the article, we will take a closer look at the different habitat requirements of male wolf spiders and explore the various environments that they occupy.
Habitat of Female Wolf Spiders
Female wolf spiders inhabit a wide variety of habitats, from grasslands and chaparral to forests and deserts. They prefer areas with abundant vegetation and ground litter, which offer ample shelter and hiding places from predators. Female wolf spiders are known to burrow in soil and leaf litter, making use of natural cavities or constructing their own retreats.
Some common habitats of female wolf spiders include:
- Leaf litter: Female wolf spiders are often found in leaf litter, which provides them with shelter and protection from predators. The fallen leaves provide a damp environment that helps them stay hydrated, especially during hot and dry weather.
- Grasslands: Female wolf spiders are commonly found in grassy areas, where they can hunt insects and spiders that live in the vegetation. They may also burrow in the soil in these areas, creating tunnels and retreats for themselves.
- Forests: Female wolf spiders can be found in both deciduous and coniferous forests, where they hunt insects and other arthropods that live in the soil and on trees. They may also build retreats among fallen logs and tree roots.
- Deserts: Some species of female wolf spiders are adapted to desert environments, where they can survive in hot and dry conditions. They may burrow in sand or soil, and seek refuge under rocks or vegetation during the day.
Female wolf spiders are well-adapted to their respective habitats, and their size and behavior can vary depending on the environment they live in. These spiders are important predators in their ecosystems and play a crucial role in controlling the populations of insects and other arthropods.
Impact of Size on Reproduction
The size of wolf spiders plays an important role in their reproduction. It affects their mating behavior, fecundity, and even parental care. Let’s take a closer look at how size impacts the world of wolf spider reproduction.
Mating Behavior of Male Wolf Spiders
Size is a crucial factor in the mating behavior of male wolf spiders. Smaller males are often outcompeted by larger males for access to female mates. This is because larger males have physical advantages such as longer legs and larger pedipalps, which are used to grasp the female during copulation. These traits give larger males a competitive edge in the mating arena.
However, smaller males have developed a unique strategy to increase their chances of mating. They approach the female when she is ready to mate and tap her legs with their pedipalps. This tap creates a vibration that the female can sense, and if she’s receptive, she’ll allow the male to approach and mate. This strategy allows smaller males to bypass the competition and have a chance to reproduce.
Fecundity in Female Wolf Spiders
Female wolf spiders’ size also plays a critical role in their fecundity, or their ability to produce offspring. Larger females typically produce more eggs than smaller ones and are more fecund. This is because they have more energy reserves to allocate towards egg production and have a larger reproductive tract to carry and nourish the eggs.
However, larger females face higher risks during the reproduction process. They may have difficulty finding enough food to sustain themselves and their offspring, and they may be less agile and more vulnerable to predators. Smaller females, on the other hand, may produce fewer eggs, but they are more agile and can evade predators more efficiently.
Offspring and Parental Care
Wolf spider parents provide exceptional parental care for their offspring, and the size of the parent has a direct impact on that care. The larger the parent, the longer it takes for the offspring to hatch and grow fully. Large females produce larger offspring, which require more food and take longer to mature. The parents must provide food and protection for the young, so larger females may provide better care.
Smaller females, on the other hand, produce smaller offspring, which require less food and take less time to mature. This means that they have a shorter period of parental care, but they may be better suited to survive in harsher environments.
Size matters when it comes to the reproduction of wolf spiders. It affects their mating behavior, fecundity, and parental care. The size of wolf spiders is not just a physical characteristic; it has a significant impact on their survival and reproduction.
Mating Behavior of Male Wolf Spiders
Among the different species of spiders, wolf spiders are unique in their mating behavior. Male wolf spiders play an active role in courtship and mating, which involves a series of intricate behaviors that are fascinating to observe. In this section of the article, we will explore the intriguing mating behavior of male wolf spiders and the impact of their size on their reproductive success. So, let’s dive in and discover the intricate world of wolf spider mating rituals!
Fecundity in Female Wolf Spiders
Female wolf spiders are known for their ability to produce large broods of spiderlings. This trait is known as fecundity, which refers to the reproductive potential of a female spider. The size of the female wolf spider is strongly correlated with fecundity, as larger females are able to produce more eggs.
Studies have shown that female wolf spiders can produce anywhere from 100 to 1,000 eggs in a single reproductive season. These eggs are typically carried in an egg sac that the female attaches to her spinnerets. The egg sac is made of silk, which the female produces using glands in her abdomen.
After the eggs are laid, the female wolf spider provides maternal care by guarding and protecting the egg sac. She may also carry the egg sac with her as she moves around. This level of parental care is unusual among spiders and is thought to contribute to the success of the wolf spider as a species.
It’s interesting to note that the fecundity of female wolf spiders can be impacted by environmental factors such as temperature and availability of food. Higher temperatures have been shown to increase the number of eggs produced, while reduced food availability can result in smaller clutch sizes.
The fecundity of female wolf spiders plays a crucial role in the reproductive success of the species as a whole. By producing large numbers of spiderlings, female wolf spiders are able to ensure the survival of their offspring in a harsh and competitive environment.
Offspring and Parental Care
When it comes to offspring and parental care, there are some notable differences between male and female wolf spiders. Female wolf spiders are known to be incredibly protective of their offspring, resulting in a higher survival rate for their offspring compared to males who have little to no involvement in offspring care.
Females: Once a female wolf spider lays her eggs, she will wrap them in a protective sac that she carries with her. She will continue to carry the sac with her until the eggs hatch, at which point she will actively protect her spiderlings. The female will help them disperse and hunt for food until they are capable of hunting for themselves. This level of parental care ensures that the spiderlings have a higher chance of survival in their early stages of development.
Males: Males, on the other hand, have no role in parental care. Once they have mated, they are not concerned with the offspring and move on to find another mate. This lack of involvement in offspring care is common in many spider species, as males prioritize mating over parental responsibilities.
It is important to note that the amount of care given to offspring ultimately impacts the overall success of the species. In the case of wolf spiders, the higher survival rate of spiderlings under female care plays an important role in maintaining healthy population levels.
The differences in parental care between male and female wolf spiders highlights the unique roles each gender plays in the survival and success of the species.
Conclusion
After exploring the different sizes of male and female wolf spiders, it’s clear that size plays a crucial role in various aspects of their behavior and survival. While there are some similarities between the two sexes, there are also significant differences that are worth noting.
From a behavioral perspective, male wolf spiders are often more active and aggressive when it comes to finding a mate. They tend to wander more and cover greater distances in order to find a receptive female. Female wolf spiders, on the other hand, tend to be more selective and choose mates based on specific traits.
In terms of habitat, male and female wolf spiders also have slightly different preferences. Male wolf spiders tend to inhabit more open and exposed areas, while female wolf spiders prefer sheltered and protected environments where they can lay their egg sacs.
Reproduction is another area where size can have a significant impact on wolf spiders. Male wolf spiders engage in complex courtship displays and must be large enough to overpower potential rivals and impress females. Female wolf spiders, on the other hand, produce larger eggs and egg sacs as they grow larger, resulting in greater fecundity.
Overall, the differences in size and behavior between male and female wolf spiders highlight the fascinating intricacies of the natural world. While they may seem small and insignificant to some, these creatures play an essential role in maintaining ecological balance and are worth studying and protecting.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average size of male and female wolf spiders?
The average size for male wolf spiders is around 9 mm, while the average size for female wolf spiders is around 18 mm. This size can vary depending on the species.
Why do male wolf spiders have smaller bodies than females?
Male wolf spiders have smaller bodies than females because they have smaller reproductive organs, which require less space in the body. This allows for a more streamlined body, making it easier for the males to move around and hunt.
How can you differentiate male and female wolf spiders?
The easiest way to differentiate male and female wolf spiders is by size. Typically, females are much larger than males. Additionally, males have longer legs and smaller abdomens, while females have shorter legs and larger abdomens.
What is the significance of size in wolf spiders?
The size of wolf spiders is significant because it affects their ability to hunt prey, find mates, and survive in their environment. Larger spiders have a greater likelihood of finding food and attracting mates, while smaller spiders may be more agile and better able to avoid predators.
Do male and female wolf spiders have different hunting strategies?
Yes, male and female wolf spiders have different hunting strategies. Female wolf spiders tend to be ambush hunters, waiting for prey to come within striking distance. Male wolf spiders, on the other hand, are active hunters that actively roam their environment in search of prey.
Where do male and female wolf spiders typically live?
Male and female wolf spiders can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, fields, and deserts. However, females are generally more likely to live in burrows or hiding places, while males are more often found out in the open.
How do male wolf spiders attract female partners?
Male wolf spiders attract female partners by using pheromones and vibration signals. They will often wave their front legs and perform a courtship dance to signal their interest to nearby females.
How many offspring do female wolf spiders typically have?
Female wolf spiders can have anywhere from a few dozen to over one hundred offspring at a time, depending on the species. They produce egg sacs which they carry with them until the spiderlings hatch.
How do wolf spiders care for their offspring?
Wolf spiders exhibit maternal care, with the mothers carrying their egg sacs and spiderlings on their bodies for protection. The mothers will provide food and protection for their spiderlings until they are able to fend for themselves.
Are wolf spiders dangerous to humans?
While wolf spiders are venomous and may bite humans if threatened, their venom is not typically dangerous to humans. They are also not aggressive towards humans and will generally only bite if provoked.






