Introduction

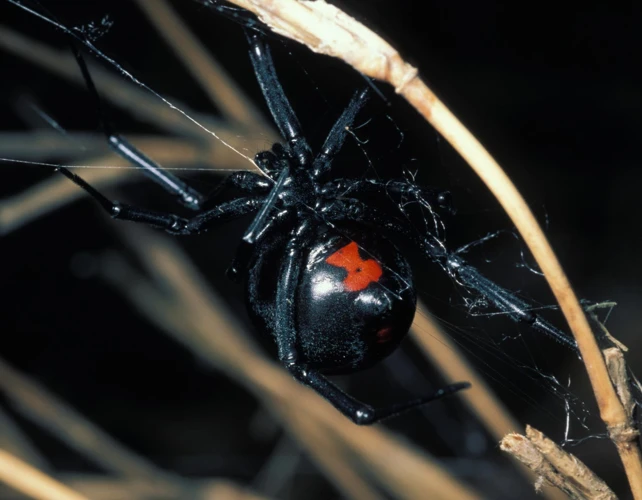
Black widow spiders are one of the most notorious arachnids in the world. Their frightful appearance and toxic venom have attracted fascination and fear among humans for centuries. In scientific circles, much has been studied about these creatures, including their physical and behavioral differences, distribution patterns, and impact on human societies. In this article, we will delve into one specific aspect of black widow spider research- the distribution patterns between male and female black widows. By exploring the geographical differences in behavior, we hope to gain a deeper understanding of these fascinating arachnids.
Background on Black Widow Spiders
Black widow spiders are a type of spider that are well-known for their venomous and dangerous bite. Here are some interesting facts about black widow spiders that you might like to know:
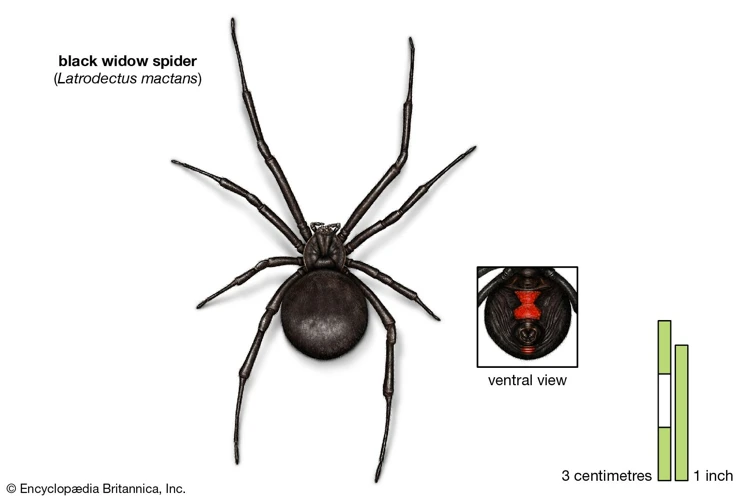
- Physical Characteristics: Black widow spiders are a type of arachnid that are typically black or dark brown in color. They are small in size, with females measuring about 1.5 inches (3.81 cm) in length, while males are around half that size. They are characterized by their distinctive red or orange hourglass-shaped mark on their abdomens.
- Lifespan: Black widow spiders typically live for about 1 to 3 years in the wild.
- Web-building: Black widow spiders are skilled at building webs, which they use to catch their prey. These webs are typically built in dark, secluded areas such as crevices or under rocks.
- Behavior: Black widow spiders are generally nocturnal and prefer to hide during the day. They are also known to be aggressive when provoked, and will bite humans if they feel threatened.
- Venom: The venom of black widow spiders is highly toxic and contains neurotoxins that attack the nervous system. While their bites are rarely deadly to humans, they can be extremely painful and may cause symptoms such as muscle cramps, nausea, and sweating.
Black widow spiders are found in many parts of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. To learn more about the distribution patterns of black widow spiders, check out our article on Black Widow Spider Distribution. It is important to take precautions if you live in an area where black widow spiders are present, to reduce the risk of being bitten.
Male and Female Black Widow Spiders: Differences

When it comes to black widow spiders, there are some clear differences between the males and females. These arachnids are well-known for their venomous bite and distinctive appearance, and knowing how to identify males and females can be important for staying safe around them. In this section, we’ll explore what sets male and female black widow spiders apart, both physically and behaviorally. We’ll also delve into some possible environmental factors that could affect their differences.
Identification of Male and Female Black Widows
Male and female Black Widow Spiders can be distinguished by a few key physical characteristics. The identification of male and female spiders is essential for understanding the behavior, mating patterns, and distribution patterns of these arachnids. The following table summarizes the differences between male and female Black Widow Spiders:
| Features | Female Black Widows | Male Black Widows |
| Size | Large, up to 1.5 inches (38 mm) | Small, about half the size of the female |
| Coloration | Glossy black, with a red or orange hourglass-shaped mark on the underside of the abdomen | Lighter in color, usually brown, with no distinctive markings |
| Abdomen shape | Globular | Long, slender, and cylindrical |
Female Black Widow Spiders are generally larger than males and have a round, globular abdomen. They are also darker in color, with a distinctive red or orange hourglass-shaped marking on the underside of the abdomen. The females are the only ones to pose the infamous risk of venomous bites.
On the other hand, male Black Widow Spiders are smaller, about half the size of females, and usually brown in color. They do not possess any distinctive markings like the hourglass shape found on the females. Instead, they have longer, slender, cylindrical abdomens.
Understanding the differences between male and female Black Widow Spiders is crucial for researchers, wildlife managers, and the general public. Male spiders may also be confused with other spider species, but being able to identify the female spider is important when controlling their populations, given the potential harm to humans and ecosystem.
Physical and Behavioral Differences
Male and female black widow spiders exhibit significant physical and behavioral differences, which are crucial in distinguishing between the two sexes. One of the most noticeable differences is their size. Females are significantly larger than males, with a shiny black body that can reach up to 1.5 inches in length. Males, on the other hand, are smaller and less shiny and are often brown or gray in color.
Another physical difference between males and females is their venom potency. Despite their smaller size, males possess venom that is more potent than that of females. This difference in venom potency is thought to have evolved to aid males in subduing their larger female counterparts during courtship and mating.
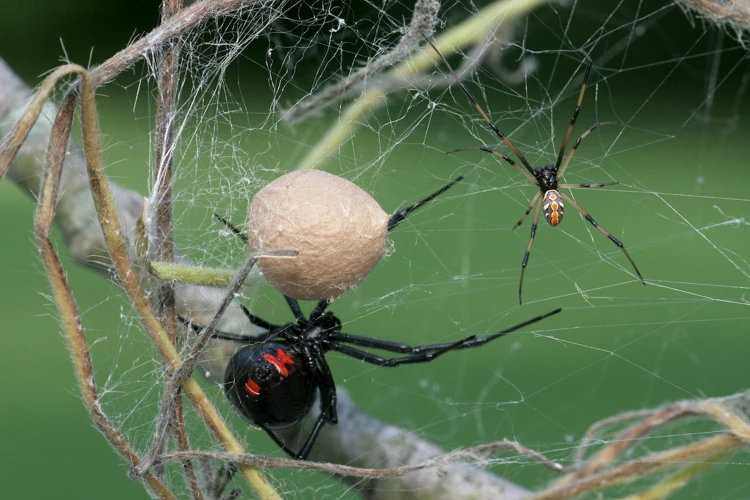
Behaviorally, male black widows exhibit a “shyness” towards females, while females are known to be highly aggressive towards potential threats. Females also exhibit maternal instincts and will protect their egg sacs aggressively. Male black widows, on the other hand, are solitary and are not known for protecting their young.
Also, male black widow spiders tend to have a shorter lifespan than females, which can live up to three years. Males only live for a few months after their final molt. This could be because mating is a hazardous process for males. They insert their palps into the female genitalia, where they are at risk of becoming trapped and devoured, or running afoul of her potent venom.
The physical and behavioral differences between male and female black widow spiders have significant implications not only for their survival but also for their impact on human society. Understanding these differences can help researchers understand how the black widow spider has adapted to its environment and how it is impacted by a changing environment.
Geographical Distribution Patterns
The geographical distribution of black widow spiders is a crucial aspect of understanding their behavior and impact on ecosystems. The patterns of distribution differ significantly between species and are influenced by various environmental and human factors. In this section, we will explore the prevalence, global trends, and unusual habitats of black widow spiders. Additionally, we will examine the impact of human activity and climate change on their distribution patterns. Keep reading to learn more about the fascinating distribution patterns of male and female black widow spiders. To learn about the behavior of black widow spiders, check out our article on black widow spider behavior.
North American Black Widows
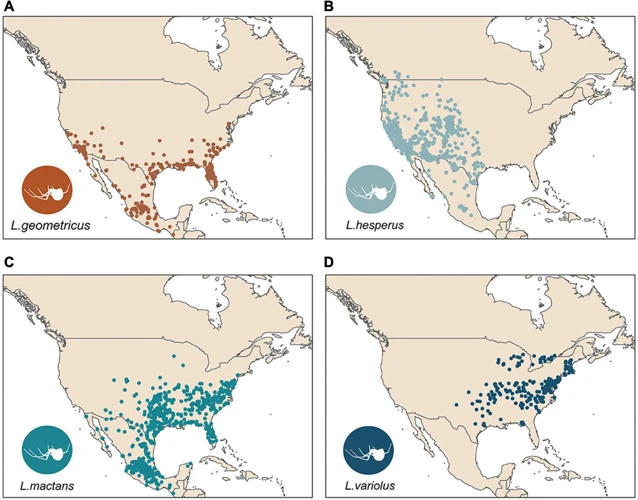
North America is home to three species of black widow spiders: the southern black widow (Latrodectus mactans), the northern black widow (Latrodectus variolus), and the western black widow (Latrodectus hesperus). These venomous arachnids are notorious for their distinctive shiny black bodies with a red hourglass-shaped marking on the underside of the abdomen.
The prevalence of black widow spiders in North America is high, with these creatures found in a variety of habitats including forests, shrublands, deserts, and urban areas. According to a recent study, the southern black widow is the most commonly encountered species in the southeastern United States, while the northern black widow is primarily found in the northeastern part of the country.
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and availability of prey have a significant impact on black widow spider behavior and distribution patterns. They prefer to live in warm and dry environments and tend to be more active during the warmer months of the year. Climate change is expected to have an effect on the distribution of black widow spiders in North America in the future.
Human activity can also impact black widow spider populations. Urbanization and construction can lead to the destruction of natural habitats, which can in turn lead to the disruption of black widow spider populations. On the other hand, some invasive species such as the brown widow (Latrodectus geometricus) have been found to thrive in urban environments and may be displacing some populations of native black widow spiders.
Please have a look at the table below for a summary of the three North American black widow species and their distribution patterns:
| Species | Habitat | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Southern black widow | Low-lying areas, forests, urban areas | Southeastern United States, Mexico, Central America, South America |
| Northern black widow | Forests, fields, and grasslands | Eastern and central United States, eastern Canada |
| Western black widow | Deserts, dry areas | Western United States, western Canada, Mexico |
It is important to note that while black widow spiders are venomous and can cause serious symptoms, they are not an aggressive species and will usually only bite if they feel threatened or cornered. Proper precautions should be taken when encountering a black widow spider, and medical attention should be sought immediately if bitten.
Global Distribution
Global Distribution of Black Widow Spiders
Black widows are found all over the world, with the exception of a few countries such as Antarctica and some islands. They are more common in tropical and subtropical regions, but can also be found in temperate regions. The global distribution of black widows is influenced by many factors such as climate, environmental conditions, human activity, and invasive species.
Climate change is also affecting the distribution of black widows. As temperatures rise, black widows are expanding their range into new areas. In fact, a recent study has shown that black widows are moving farther north in the United States due to warming temperatures. This could have significant implications for ecosystems and human health.
The table below summarizes the global distribution patterns of various species of black widow spiders.
| Species | Distribution |
|---|---|
| Lactrodectus hesperus (Western black widow) | Western United States, Canada, Mexico |
| Lactrodectus mactans (Southern black widow) | Southeastern United States, Mexico, Central America |
| Lactrodectus variolus (Northern black widow) | Eastern and Central United States, Southeastern Canada |
| Lactrodectus katipo (Katipo) | New Zealand |
| Lactrodectus geometricus (Brown widow) | Native to South Africa, but now found in many parts of the world including United States, Japan and Australia |
In addition to the species listed in the table, there are many other species of black widow spiders found around the world. Some of these species are endemic to certain regions, while others are invasive species that have been introduced to new areas through human activity.
The distribution patterns of black widows are constantly changing due to environmental factors and human activity. As scientists continue to study these spiders, we will gain a deeper understanding of their behavior and distribution patterns, which will help us better protect ourselves and the environment.
Impact on Human Society
The Dark Side: Impact of Black Widow Spiders on Human Society
Apart from their intriguing behavior and distribution patterns, black widow spiders pose a significant threat to humans. As venomous arachnids, the spiders have gained notoriety due to their potent venom and the potential harm that can result from their bites. Impact on human society emanates from black widow spider bites and concerns about their presence, population growth, and distribution. Several aspects make black widows a concern for human populations, including their geographic distribution, environmental factors for their behavior, and human activities that impact their populations. This section explores the implications of black widow spiders to human society and methods for mitigation.
Reports of Black Widow Bites
Reports of black widow bites are numerous and widespread, predominantly in areas where these spiders are common. The majority of black widow bites occur when humans accidentally disturb a female spider’s web or come into direct contact with the spider. The venomous bite of a black widow spider can cause a range of symptoms including intense pain, swelling, muscle cramps, nausea, and even paralysis. In rare cases, bites can be fatal, particularly in vulnerable individuals such as the elderly, young children, and those with weakened immune systems.
Some interesting statistics about black widow bites include:
- Between 1950 and 1959, there were over 63,000 recorded black widow bites in the United States alone.
- In California, there have been over 2,000 reported black widow bites from 2011 to 2015.
- In Australia, it is estimated that there are around 2,000-10,000 cases of black widow spider bites each year.
- Black widow spiders are responsible for around one-third of all reported spider bites in the United States.
Although bites from black widow spiders can be very painful and potentially deadly, they are relatively rare and can be prevented with proper precautions. To avoid getting bitten by a black widow spider, it is important to wear protective clothing and gloves when working outside, avoid reaching into dark crevices and waste piles where spiders may reside, and vigilant when cleaning and working in areas that are known to have black widows.
If a bite does occur, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. In most cases, treatment for black widow bites will involve the application of an antivenom and pain management medications. However, prevention is always the best course of action when it comes to avoiding the dangers of black widow spider bites.
Looking for more information on black widow spiders? Check out our article on unusual habitats of black widow spiders or read about the global trends in black widow spider populations.
Prevention and Treatment of Black Widow Spider Bites
Prevention and Treatment of Black Widow Spider Bites:
Preventing Black Widow Spider Bites:
- Wear gloves and long-sleeved shirts when working in areas where black widows are likely to live.
- Shake out clothing and shoes before wearing them, especially if they have been left outside.
- Keep garages, basements, and attics clean and clutter-free to reduce areas where black widows can live.
- Seal cracks and crevices in buildings to keep spiders from entering.
Treating Black Widow Spider Bites:
- If you experience a black widow spider bite, seek medical attention immediately.
- Try to capture the spider and bring it with you to the hospital for proper identification.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used to manage pain and reduce swelling.
- In severe cases, antivenom may be required to treat the bite.
It is important to note that human activities can have an impact on black widow spider populations, which can in turn affect the risk of bites. To learn more about this topic, read our article on human activity and black widow spider populations. Additionally, climate change may also impact the distribution of black widows. Check out our article on climate change and black widow spider distribution to learn more about this issue.
Conclusion
Strong research and analysis have been conducted on the black widow spider, revealing a lot of information about its behavior, distribution patterns, and impact on humans. The black widow spider is considered to be one of the most venomous spiders in the world, and its presence in North America and other parts of the world has led to a significant concern for human safety.
Through this study, we have learned about the differences between male and female black widow spiders, both in terms of physical appearance and behavior. The identification of male and female black widows is crucial, especially in areas where they are frequently found. The geographical distribution patterns of black widow spiders have also been examined, revealing that their population is more concentrated in certain regions. Environmental factors play a significant role in black widow spider behavior and distribution, and further research in this area can help us understand their habitat requirements better.
Apart from their ecological importance, the study of black widow spiders demonstrates their potential impact on human society. Black widow bites can cause severe health problems, especially in people with pre-existing medical conditions, children, and the elderly. While there have been reports of black widow bites, prevention and treatment measures are available to minimize the risk.
In conclusion, the study of black widow spiders provides a wealth of information about their behavior, distribution patterns, and impact on human society. As global temperatures continue to rise, scientists are observing changes in black widow behavior that may pose additional threats to human health and ecosystems. Hence, it is crucial to stay aware of the global trends of black widow spiders, the environmental factors affecting their behavior, and their invasive tendencies to prevent further negative impacts on the world around us.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the scientific name for Black Widow spiders?
The scientific name for Black Widow spiders is Latrodectus.
Can male Black Widows bite humans?
Yes, male Black Widows can bite humans, but it is less likely to happen as they are smaller in size and not as aggressive as females.
What is the lifespan of a Black Widow spider?
A female Black Widow spider can live up to three years, while males typically live only a few months.
What is the mating behavior of Black Widows?
After mating, female Black Widows often eat the male. This is believed to benefit the female in terms of nutrition and reducing competition for limited resources.
Do Black Widow spiders have predators?
Yes, some predators of Black Widow spiders include birds, lizards, and other spiders.
Can Black Widow spiders be kept as pets?
It is not recommended to keep Black Widow spiders as pets due to their venomous bite and potentially dangerous nature.
How do Black Widow spiders catch their prey?
Black Widow spiders create webs that are strong enough to catch insects and other small prey. They also use their venom to immobilize their prey.
What is the venom of a Black Widow spider like?
The venom of a Black Widow spider is a neurotoxin that affects the nervous system. It can cause muscle pain, spasms, and in rare cases, death.
Are Black Widow spiders endangered?
No, Black Widow spiders are not considered endangered. They are a common species found in many parts of the world.
How can I prevent Black Widow spider bites?
To prevent Black Widow spider bites, avoid touching or disturbing their webs or nests. Wear gloves and protective clothing when working outside in areas where Black Widows may be present.






