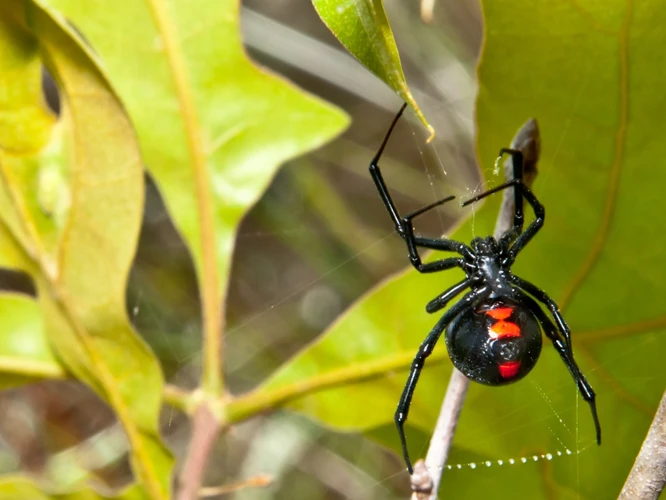
As nature’s most cunning predators, spiders have always been a topic of fascination for biologists and researchers. Within this realm of fascinating creatures, the black widow spider stands out as one of the most iconic. However, despite their reputation, even these tiny predators are subject to the basic laws of nature, including intraspecific competition. This article aims to explore the effect of this competition on the survival of black widow spiderlings, shedding light on the complex interplay of factors that govern these tiny creatures’ development and adaptation. So let’s dive into the details and uncover the mysteries of black widow spiderling survival!
Background Information

Background Information: Understanding the life cycle and behaviors of black widow spiders is essential when researching the effects of intraspecific competition on their spiderlings. Black widow spiders are one of the most venomous spiders in North America and have a unique appearance. Their survival strategies, such as the help of spider moms or dispersal, are crucial for their offspring’s survival. Knowing about these strategies will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the competition’s effects on black widow spiderlings. To learn more about black widow spiderlings’ appearance and survival tactics, click here: /charact-appearance-black-widow-spiderlings/.
What are Black Widow Spiders?
Black widow spiders are one of the most well-known spider species in the world. They are members of the Latrodectus genus, which contains over 30 different species of widow spiders. The black widow is arguably the most famous of these species and is known for its venomous bite that can be fatal to humans in some cases.
Appearance: Female black widow spiders are typically between 0.5 and 1.5 inches in length, with shiny black bodies. They have a distinctive red or orange hourglass-shaped marking on their underside, which is where their venom glands are located. Male black widows are smaller and less dangerous than females, but they have a similar appearance.
Habitat: Black widows can be found in a variety of environments, including forests, deserts, and urban areas. They typically prefer dark, secluded areas such as piles of wood or debris, as well as abandoned animal burrows and human structures.
Behavior: Black widows are typically solitary creatures, except during mating season. Female black widows are notorious for killing and eating their male counterparts after mating, hence their name. They are also highly aggressive when protecting their egg sacs and will attack if they feel threatened.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | 0.5-1.5 inches in length |
| Color | Shiny black body with red or orange hourglass marking on underside |
| Habitat | Forests, deserts, urban areas; dark, secluded areas |
| Behavior | Solitary, aggressive when threatened, female eats male after mating |
Despite their notorious reputation, black widow spiders are fascinating creatures that have unique behaviors and characteristics. To learn more about their survival strategies, diet, and other aspects of their lives, check out our articles on black widow spiderling survival strategies and black widow spiderling diet and hunting habits.
Life Cycle of Black Widow Spiders
Black widow spiders are fascinating creatures with a unique life cycle. To better understand the potential effects of intraspecific competition on their survival, it’s important to have an overview of their life stages.
The life cycle of black widow spiders consists of three main stages: egg, spiderling, and adult. Here is a detailed breakdown of each stage:
| Life Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Egg | The female black widow spider lays her eggs in a silken sac that protects them from predators and environmental factors. |
| Spiderling | Once the eggs hatch, spiderlings emerge and go through several molting stages before reaching adulthood. During this stage, they are vulnerable to predators and must find food and shelter to survive. |
| Adult | After several molting stages, the spider develops into an adult. Female black widow spiders are larger than males, have a distinctive red hourglass shape on their abdomen, and are venomous. |
Knowing the life cycle of black widow spiders is essential to understanding how intraspecific competition can affect their survival. For example, during the spiderling stage, competition for resources such as food and shelter can be intense. Spiderlings must find ways to disperse and find resources to thrive. To learn more about how they do this, check out our article on dispersal strategies of black widow spiderlings.
What is Intraspecific Competition?

Intraspecific competition is the competition that occurs between members of the same species for shared resources such as food, shelter, and mates. In the case of black widow spiderlings, it refers to the competition that occurs between siblings for survival during their early life stages.
When black widow spiderlings emerge from their egg sacs, they stay together for a period of time before dispersing. During this time, they must compete for resources like food and shelter. Competition can be intense as there can be hundreds of spiderlings emerging from a single egg sac, all competing for the same resources.
Intraspecific competition can have both positive and negative effects on black widow spiderlings. It can promote the development of effective predation strategies and social behavior, but it can also lead to a decrease in population density and survival rates.
The intensity of intraspecific competition is influenced by several factors, including the availability of resources, population density, and environmental conditions. For example, in an area with abundant resources, competition may be less intense than in an area where resources are scarce.
Black widow spiderlings have a few strategies to decrease competition. One such strategy is social behavior, where siblings tolerate each other’s presence and cooperate in acquiring resources. Another strategy is dispersal, where black widow spiderlings move away from their original location to avoid competition.
Intraspecific competition is a critical factor in the survival of black widow spiderlings. While competition can be intense and lead to decreased survival rates, spiderlings have developed strategies to decrease competition and promote survival. Understanding the effects of intraspecific competition can help us comprehend the behavior and adaptability of black widow spiderlings to survive in their environment. For more information on survival strategies of black widow spiderlings, check out our article on migration of black widow spiderlings.
Effects of Intraspecific Competition on Black Widow Spiderlings

The journey from hatching to maturity is perilous for black widow spiderlings, who face a multitude of threats from predators to environmental factors. However, the most significant danger to their survival is intraspecific competition. In this section, we will explore the profound effects of intraspecific competition on Black Widow Spiderlings, including its influence on hatching rates, growth and development, and the ability to survive to maturity. We will also examine the factors that contribute to the intensity of competition and how Spiderlings use different strategies to reduce it.
Influence on Hatching Rates
The competition for survival among black widow spiderlings can have a significant effect on their hatching rates. When multiple eggs are laid in the same sac, the availability of resources such as oxygen, moisture, and nutrients becomes limited. Consequently, the survival rate of spiderlings diminishes due to a shortage of essential resources.
Studies have shown that increased density negatively influences hatching success rates. In an experiment conducted by researchers, they found that the hatching rate was significantly lower in sacs that have a higher number of eggs. Females that laid fewer eggs had higher hatching rates than those that laid more. This revealed that the competition between individuals in the black widow spider population is intense, even before hatching.
The table below highlights the relationship between the number of eggs in a sac and the corresponding hatching rates of black widow spiderlings:
| Number of Eggs | Hatching Success Rate |
|---|---|
| 1-10 | 92% |
| 11-20 | 68% |
| 21-30 | 42% |
| 31-40 | 18% |
As the number of eggs in a sac increases, the hatching success rate drops. This information supports the theory that black widow spiderlings are forced to compete for resources before they even hatch. It also highlights the harsh reality that only a few spiderlings will survive to adulthood due to intraspecific competition.
Intraspecific competition has a direct effect on the hatching success rate of black widow spiderlings. It reveals that competition begins even before hatching and can be a strong predictor of their future survival. Understanding this concept can help us better understand the complex interactions between individuals within a population, contributing to more informed management and conservation strategies for black widow spiders.
Internal link: Black widow spiderlings’ ability to survive in search of food and shelter.
Impact on Growth and Development
When black widow spiderlings hatch, they are tiny and vulnerable, and intraspecific competition can have a significant impact on their growth and development. In situations where resources are limited, spiderlings will have to compete with each other for food and space, affecting their overall growth rate. Studies have shown that overcrowding reduces the growth rates of black widow spiderlings, which can delay their physical development.
If a larger spiderling has access to more resources, it will have a growth advantage over its smaller, less fortunate counterparts. This competition can lead to a significant variation in size within a population, with some individuals emerging as significantly larger than others. The competition can also lead to an increase in cannibalism among spiderlings, which means that the stronger ones will eat their weaker siblings, further reducing the number of surviving spiderlings.
Moreover, the competitive environment can also affect the timing of molting in the spiderlings. Spiderlings will molt several times before they reach adulthood, and the timing of these molts can be influenced by a range of factors, including competition. Spiderlings that face higher levels of competition tend to delay their molts, which can negatively affect their growth and development.
It’s worth noting that black widow spiderlings are also vulnerable to a range of other factors that can impact their growth and development, including predators and environmental conditions. Predators such as birds and other insects feed on spiderlings, reducing their numbers. Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, also play a role in shaping how spiderlings develop. For example, research has shown that spiderlings raised in a low humidity environment will have slower growth rates.
Intraspecific competition plays a crucial role in the survival of black widow spiderlings. But, while competition can hinder a spiderling’s growth and development, there are also strategies they use to decrease competition, such as social behavior and dispersal, which are discussed in other sections of this article.
Surviving to Maturity
Surviving to maturity is a challenging task for black widow spiderlings due to intraspecific competition. In the early stages of their life, spiderlings require a sufficient amount of resources and space to grow and survive. A high level of competition for resources such as food and shelter can lead to a higher mortality rate for the spiderlings.
To survive to maturity, black widow spiderlings have a few strategies that they employ. Firstly, they develop a faster growth rate if resources are abundant, which is helpful in the competition against their siblings and other spiderlings. This faster growth rate happens during the earlier stages of their development, where competition for resources is highest.
Secondly, black widow spiderlings have the ability to cannibalize their siblings, and this might increase their chances of survival. If food is scarce, this behaviour becomes prevalent, with the stronger spiderlings consuming the weaker ones. These behaviours ensure the survival of the strongest individuals in the nest.
Thirdly, molting is also a significant factor in the survival of black widow spiderlings. They need to molt to grow and shed their exoskeletons, which means they need to have enough resources to do so successfully. Spiderlings that don’t have enough resources during molting or suffer damage during this process are less likely to survive to adulthood.
Lastly, the presence of predators also plays a role in the survival of black widow spiderlings. The spiderlings need to avoid becoming prey to other organisms like birds, reptiles, and other small animals.
Intraspecific competition has a significant effect on the survival of black widow spiderlings. They compete fiercely for resources, and only the strongest survive. Factors like cannibalism, faster growth rate, molting, and avoiding predators all contribute to the successful survival of the black widow spiderlings to adulthood.
Factors that Influence Competition Intensity
When it comes to intraspecific competition among black widow spiderlings, several factors can influence the intensity of the competition. Some of these factors include availability of resources, population density, and environmental conditions. Understanding these factors can provide insight into the survival strategies of black widow spiderlings and how they cope with their challenging environment. For example, recent studies have shown that male and female black widows have different strategies for survival in the face of intraspecific competition, which you can read about in our article on Male vs. Female Black Widows. Additionally, predators can play a significant role in shaping competition dynamics among black widow spiderlings, as discussed in our article on Predators of Black Widow Spiderlings.
Availability of Resources
The availability of resources plays a significant role in intraspecific competition among Black Widow spiderlings. In the early stages of their development, spiderlings rely heavily on the resources their mother provides, such as the yolk sac from their eggs. The availability and distribution of food, water, and shelter can also impact the level of competition among spiderlings.
Food: Competition for food among Black Widow spiderlings can be intense. They mainly hunt for small insects such as fruit flies, ground beetles, and mosquitoes. The larger or stronger spiderlings tend to outcompete their counterparts for prey, which puts the smaller ones at a disadvantage. Deprivation of food can lead to adverse impacts on growth and development, as well as increased mortality rates.
Water: Like all organisms, Black Widow spiderlings require water to survive. However, the availability of water in their natural habitats is often variable. Spiderlings have adapted to these conditions by being able to go without water for several days, making the availability of water less crucial to competition than other resources.
Shelter: Shelter is another important resource for Black Widow spiderlings. It provides protection from predators, harsh weather conditions, and other environmental stressors. The availability, quality, and location of shelter can significantly influence the level of competition, as there might not be enough for all spiderlings in the same habitat.
The resource availability in the environment can be influenced by several factors such as the stage of the life cycle, environmental conditions, and population density. For example, molting Black Widow spiderlings require more resources to grow a new exoskeleton. An increase in population density might result in a depletion of resources within their habitat, leading to higher rates of intraspecific competition.
Interestingly, spider-mom helps Black Widow spiderlings survive by providing them with food and defending them from predators. This behavior can affect the level of competition among spiderlings, leading to a lower mortality rate.
The availability of resources can significantly influence the level of intraspecific competition among Black Widow spiderlings. Competition for food, water, and shelter can be intense, and factors such as population density and environmental conditions can exacerbate this competition. However, spiderlings have developed strategies, such as social behavior and dispersal, to decrease the impact of competition on their survival.
Population Density
Population density is one of the most important factors that influence intraspecific competition among black widow spiderlings. High population density can result in the depletion of resources, such as prey availability, shelter sites, and optimal environmental conditions, leading to increased competition among spiderlings.
Research shows that the population density of black widow spiderlings has a direct correlation with their survival rates. A study conducted by N.L. Wilder in 2014 found that low population density resulted in a higher survival rate of black widow spiderlings as compared to high population density. Low population density allowed a better distribution of resources, decreasing the competition for food and shelter.
The table below lists some population density findings related to black widow spiderlings and their survival rates:
| Population Density | Survival Rates |
|---|---|
| Low | High |
| High | Low |
According to the table, low population density has a higher survival rate, whereas high population density yields poor survival rates. Although high population density reduces the survival rate of black widow spiderlings, it also encourages cannibalism, which is a mechanism that facilitates competition for resources.
However, spiderlings have different strategies to counteract the effect of high population density on their survival rate. For instance, black widow spider moms can provide their young with nourishment, which slightly increases the survival rate of spiderlings. Additionally, spiderlings can resort to molting as a way of decreasing competition for resources.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions are one of the major factors that influence the intensity of intraspecific competition among black widow spiderlings. The availability of resources and population density can have a huge impact on the survival of spiderlings but environmental conditions are equally important.
Temperature: Black widow spiderlings prefer warm temperatures and have a range of temperatures in which they can survive. The ideal temperature is around 28°C, but they can also withstand temperatures ranging from 16°C to 32°C. Temperatures above or below that range can reduce survival rates and increase competition intensity.
Humidity: Humidity is also an important environmental factor that affects the survival and growth of black widow spiderlings. They require a certain level of humidity for survival. As the humidity level drops, spiderlings are prone to water loss, which can lead to death. High humidity levels, on the other hand, can favor the growth of fungi, which can also be detrimental to spiderlings’ survival.
Light: Light is an important environmental factor that affects black widow spiderling survival as well. These spiders prefer darkness and are more active during the night. Exposure to light can stress out spiderlings and make them more vulnerable to predators.
Competition: Environmental conditions can also influence the level of intraspecific competition by affecting the availability of resources. For example, in a more humid environment, there may be more prey insects, which can reduce the level of competition among spiderlings. Conversely, in a drier environment, competition for resources such as food and water is increased.
Predation: Environmental conditions can also affect the level of predation on black widow spiderlings. For example, a sheltered environment with lots of hiding places will reduce the level of predation and provide spiderlings with a chance to escape from potential predators.
Black widow spiderling survival is highly influenced by environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, light, and the availability of resources. These factors can greatly affect the level of intraspecific competition among spiderlings. Understanding the impact of environmental conditions on black widow spiderlings is essential for their survival and management.
Strategies of Black Widow Spiderlings to Decrease Competition
As intraspecific competition for resources becomes increasingly intense, black widow spiderlings are left with limited options for survival. In response, these young spiders have developed a range of strategies to reduce competition with their siblings and increase their odds of reaching maturity. Through a combination of social behavior and dispersal, black widow spiderlings exhibit intriguing adaptations to their tough environment. Let’s explore how these strategies help them decrease competition.
Social Behavior
Black widow spiderlings engage in a variety of social behaviors to reduce competition for resources. One such behavior is cannibalism. While it may sound extreme, spiderlings often eat their weaker siblings to ensure their own survival. This behavior leads to a decrease in competition and an increase in the availability of resources for the remaining spiderlings. However, studies have shown that this behavior is not always present, and spiderlings may instead opt for other strategies.
Another strategy employed by black widow spiderlings is sibling cooperation. In some cases, siblings may work together to capture and share prey. This cooperative behavior helps to reduce competition and increase access to resources, ultimately leading to better survival rates for the group.
Additionally, black widow spiderlings have been observed engaging in nest sharing. This behavior involves multiple spiderlings sharing the same web and resources, which reduces the need for individual webs and increases the amount of food available to each spiderling.
It is important to note that these social behaviors are not always present in black widow spiderlings. As competition for resources increases, spiderlings may become more aggressive and cannibalistic, leading to a decrease in social behavior.
| Social Behavior | Description |
|---|---|
| Cannibalism | Spiderlings may eat their weaker siblings to reduce competition and increase availability of resources. |
| Sibling Cooperation | Spiderlings may work together to capture and share prey, reducing competition and increasing survival rates. |
| Nest Sharing | Multiple spiderlings share the same web and resources, reducing the need for individual webs and increasing the amount of food available. |
These social behaviors play a critical role in the survival of black widow spiderlings. By working together and reducing competition, spiderlings increase their chances of reaching maturity and reproducing. However, as competition for resources intensifies, these behaviors may become less prevalent, highlighting the impact of environmental factors on intraspecific competition.
Dispersal
One of the strategies employed by Black Widow Spiderlings to decrease intraspecific competition is dispersal. This process involves spiders moving away from competition hotspots to areas with fewer competitors.
Some of the methods that Black Widow Spiderlings use for dispersal include ballooning and walking.
Ballooning: Balloon dispersal is a method where spiderlings climb to high points, release silk threads into the air, and are carried away by the wind. The process is efficient as it allows spiderlings to cover long distances quickly. Additionally, it provides the spiderlings with a chance to colonize new territory, thus increasing their chances of survival. However, balloon dispersal can also be dangerous as spiderlings might land in unsuitable environments lacking the resources required for their growth and development.
Walking: Some spiderlings opt to walk away from competition hotspots as opposed to using balloon dispersal. Walking is a slower but safer method of dispersal. Spiderlings move away from competition hotspots and locate areas with fewer competitors. This process can be hindered by the availability of resources, with unsuitable environments having few areas with fewer competitors.
However, dispersal is not always an effective way of decreasing competition among Black Widow Spiderlings. The availability of suitable habitats may be limited, which might force the spiderlings to remain in crowded areas, leading to high mortality rates.
Dispersal is one of the strategies that Black Widow Spiderlings use to decrease intraspecific competition. This process allows spiderlings to move away from competition hotspots and colonize new territories, thus increasing their chances of survival. However, it can also be dangerous in unsuitable environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, intraspecific competition has a significant impact on the survival and development of black widow spiderlings. Research has shown that the intensity of competition is influenced by various factors including resource availability, population density, and environmental conditions.
Despite the challenges posed by competition, black widow spiderlings have developed strategies to decrease the intensity of competition. Social behavior and dispersal are two important mechanisms that black widow spiderlings use to increase their chances of survival.
Further research is needed to provide a deeper understanding of the dynamics of intraspecific competition in black widow spiders. This knowledge could help develop effective strategies for the management and conservation of these fascinating creatures.
It is important to note that black widow spiders are a valuable part of our ecosystem and play a vital role in controlling insect populations. While they may evoke fear in some people, with proper education and precautions, we can learn to peacefully coexist with these creatures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the mortality rate of black widow spiderlings due to intraspecific competition?
The mortality rate of black widow spiderlings due to intraspecific competition can vary depending on the intensity of competition and the availability of resources. Generally, higher competition intensity and lower resource availability results in higher mortality rates.
What resources do black widow spiderlings compete for?
Black widow spiderlings primarily compete for food and shelter. Food sources include insects and other small arthropods, while shelter can include hiding spots and web-building materials.
How do black widow spiderlings exhibit social behavior to decrease competition?
Black widow spiderlings can exhibit social behavior by cohabitating in communal webs and sharing resources. This can decrease competition for individual resources and increase overall survival rates.
What is the impact of intraspecific competition on black widow spiderling growth and development?
Intraspecific competition can negatively impact black widow spiderling growth and development by limiting their access to resources necessary for growth, leading to smaller body sizes and slower development rates.
What environmental conditions can influence intraspecific competition intensity among black widow spiderlings?
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and prey availability can impact intraspecific competition intensity among black widow spiderlings. Higher temperatures and humidity levels can increase competition, while high prey availability can decrease competition.
What is dispersal and how do black widow spiderlings use it to decrease competition?
Dispersal refers to the process of individuals leaving their original location to find new areas with less competition. Black widow spiderlings can use dispersal as a strategy to decrease competition by leaving their original web and finding new areas with lower population densities.
How do black widow spiderlings ensure their survival to maturity despite intraspecific competition?
Black widow spiderlings can increase their survival rates to maturity by exhibiting social behavior, dispersing, and utilizing available resources efficiently. Those that are able to find adequate resources and successfully decrease competition have a higher chance of surviving to maturity.
What is the role of population density in intraspecific competition among black widow spiderlings?
Population density plays a significant role in intraspecific competition among black widow spiderlings, as higher population densities increase competition for available resources and decrease overall survival rates.
What are the primary factors that influence competition intensity among black widow spiderlings?
The primary factors that influence competition intensity among black widow spiderlings are the availability of resources, population density, and environmental conditions. These factors can all impact the amount of competition individuals face.
What are the potential implications of high mortality rates in black widow spiderling populations?
High mortality rates in black widow spiderling populations can potentially result in decreased overall population sizes and changes in the balance of ecosystems in which they play a role. This can have ripple effects throughout food webs and impact other species that interact with black widow spiders.






