Have you ever wondered about the impact of human development on the habitats of wolf spiders? These small but fascinating arachnids play an important role in our ecosystem, and their survival is closely tied to the health of our environment. Unfortunately, as human development continues to encroach on natural spaces, wolf spider populations are facing threats that could push them towards endangerment. In this article, we’ll explore the physical characteristics and behavior of wolf spiders, examine the impact human development is having on their habitats, and discuss ways that we can work to protect them. So, let’s delve into the world of these intriguing creatures and discover what we can do to help them thrive.
What are Wolf Spiders?
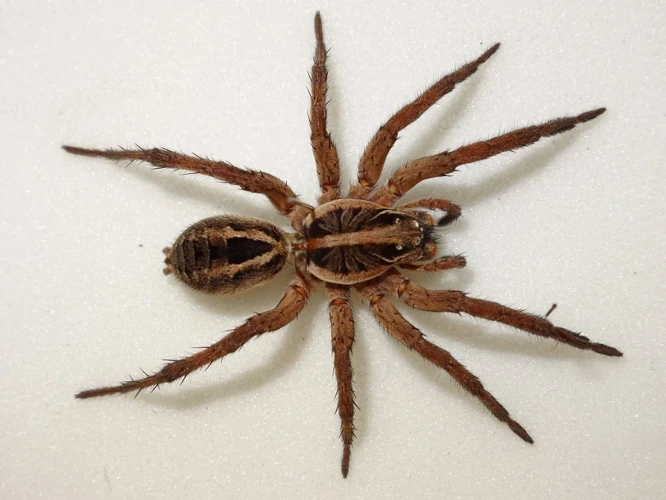

Wolf spiders are intriguing creatures that belong to the family Lycosidae. They are fascinating because of their unique traits and abilities that set them apart from other spiders. These spiders are found all over the world, including North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. In this section, we will delve deeper into the physical characteristics and behavior of wolf spiders. By understanding more about these creatures, we can gain insight into how human development affects their habitats. To learn more about the impact of human development on wolf spider habitats, please read on. If you want to know how to protect these fascinating spiders, head over to our article on the subject.
Physical Characteristics
Wolf spiders are a fascinating species that have many unique physical characteristics that set them apart from other spiders. They are also known for their incredible speed, agility, and hunting prowess. Here are some of the most notable physical features of wolf spiders:
- Eyes: Wolf spiders have eight eyes arranged in three rows. The top row contains four small eyes, the middle row has two large eyes, and the bottom row has two medium-sized eyes. This configuration of eyes gives wolf spiders excellent vision and the ability to see in almost all directions.
- Body: Wolf spiders have stout, hairy bodies that range in size from 0.04 to 1.18 inches in length. They are usually brown, gray, or black in color and have a distinctive pattern of stripes or spots on their abdomen.
- Legs: Wolf spiders have eight long, spiny legs that enable them to move quickly and jump considerable distances. They are often referred to as “wolf spiders” because their distinctive hunting behavior is similar to that of wolves.
- Fangs: Like all spiders, wolf spiders have two chelicerae (fangs) that are used to inject venom into their prey. These fangs are located at the front of the cephalothorax (head and thorax) and are connected to venom glands located in the abdomen.
Understanding these physical characteristics can help us appreciate and protect these fascinating creatures. However, several threats, such as pesticides and pollution, can cause harm to wolf spiders. For example, according to a recent study, the effects of pollution on wolf spider behavior and reproduction can be detrimental to their populations. To learn more about how pollution affects wolf spiders, check out our article on the effects of pollution on wolf spider behavior and reproduction, which provides in-depth information on this subject.
Behavior and Habitat
Wolf spiders are found throughout the world and make their homes in a wide range of habitats, from deserts to rainforests. They are a group of hunting spiders that do not rely on webs to catch their prey. Instead, they actively hunt by ambushing their prey or chasing after it.
Behavior: Wolf spiders are known for their hunting skills and have excellent eyesight, which helps them to locate and capture their prey. They are solitary creatures and prefer to hunt alone. These spiders are also known for their ability to jump, which they use to tackle prey that is out of reach or to escape danger.
Habitat: Wolf spiders can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, coastal areas, and even inside homes. They prefer areas with plenty of ground cover, such as leaf litter, rocks, and vegetation. This provides them with places to hide and hunt for their prey. During the day, they often hide in burrows or under rocks.
Wolf spiders play an important role in controlling insect populations in their habitats. Unfortunately, human development can have a negative impact on their populations and their habitats.
The Impact of Human Development on Wolf Spider Habitats
As humans continue to develop land for residential, commercial, and agricultural use, there is a growing concern about the impact that these activities are having on wildlife and their habitats. Wolf spiders are no exception, as they rely on specific habitats for survival. The impact of human development on wolf spider habitats can result in a loss of suitable habitats and fragmentation of their existing habitat. This can have significant impacts on wolf spider populations and the ecosystems they belong to. It’s crucial to understand the effects of human development on wolf spider habitats and what can be done to protect them.
Loss of Habitat
The loss of habitat due to human development has had a negative impact on wolf spiders. Wolf spiders are ground-dwelling creatures that often make their homes in leaf litter or burrows. However, as human communities expand and forested areas are cleared for development, the habitats of these spiders are destroyed.
The greatest impact of habitat loss on wolf spiders is the loss of food sources and shelter, which can lead to a decline in population numbers. These creatures prey on a variety of insects, including mosquitoes and flies, and they rely on the vegetation and leaf litter in their habitats to provide shelter from predators and the elements. Without these resources, wolf spiders will struggle to survive.
To illustrate the effects of habitat loss, we can use an html table to show the correlation between human development and wolf spider populations:
| Development | Spider population |
|---|---|
| Low | High |
| Medium | Decreasing |
| High | Critically low |
As human development increases, wolf spider populations tend to decrease. This is due to the loss of habitat and resources that are vital to their survival.
To help prevent further loss of habitat and protect wolf spiders, it is important to take action. By limiting the amount of land that is cleared for development, or by setting aside areas for conservation, we can help to preserve the habitats of these creatures. Additionally, using eco-friendly practices such as minimizing pesticide use and reducing pollution can have a positive impact on the environment and the creatures that call it home.
To learn more about how to protect wolf spiders and their habitats, read our article on the effects of pesticides on wolf spiders.
Fragmentation of Habitat
Fragmentation of habitat refers to the breaking up of continuous habitats into smaller, isolated patches due to human activities such as urbanization, deforestation, and agriculture. This has a severe impact on the wolf spider population, leading to a decrease in genetic diversity and a higher risk of local extinctions.
For example: A study conducted by researchers at the University of Melbourne found that fragmentation of habitat affects the dispersal of the wolf spider population and results in smaller subpopulations and lower genetic diversity. This makes the wolf spider populations more vulnerable to disturbance events and environmental changes.
The fragmentation of habitat also has an impact on the wolf spider’s prey, which affects the spider’s food source. The wolf spider feeds on a variety of insects, and their decline in population due to fragmentation indirectly affects the wolf spider population.
To summarize: Fragmentation of habitat has a negative impact on the wolf spider population, which in turn affects the ecosystem as a whole. It is crucial to address the issue by minimizing land-use changes, promoting natural landscape conservation and connecting fragmented habitats through corridors. If we interfere with the natural habitat of wolf spiders, we are also threatening their prey, which can have far-reaching consequences on the food web and therefore the health and well-being of the entire ecosystem.
Internal link :Preventing wolf spiders
Ways to Protect Wolf Spider Habitats
As we’ve seen, wolf spiders are vital members of our ecosystem, but as human development continues to expand, their habitats are at risk. Fortunately, there are steps we can take to help protect these spiders and their environments. Here are some effective ways to safeguard wolf spider habitats. By implementing these techniques, we can help to ensure the continued survival of these fascinating creatures for generations to come.
Preserve Natural Landscapes
Preserving natural landscapes is crucial for the survival of wolf spiders, as human development often leads to the destruction of their habitats. Wolf spiders prefer undisturbed areas such as forests, fields, and wetlands, so preserving these areas is essential to protect their populations.
Benefits of Preserving Natural Landscapes for Wolf Spiders
| Benefits | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Protection from Predators | Preserving natural landscapes allow wolf spiders to hide and avoid predators that may prey on them. |
| Access to Food | Protecting their natural habitat ensures that wolf spiders have access to their prey, such as insects, that are crucial for their survival. |
| Maintaining Ecosystem Balance | Wolf spiders play an important role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem they inhabit. By preserving their natural habitats, the entire ecosystem can thrive. |
Human encroachment into natural habitats, such as deforestation and urbanization, can lead to the destruction of natural landscapes. This can cause a significant decline in wolf spider populations. Additionally, human activities such as heavy use of pesticides and herbicides can further reduce their numbers.
To protect wolf spider habitats, it is crucial to preserve natural areas and limit human intrusion. This can be done through legislation and regulations that protect natural habitats from development. However, preserving natural landscapes alone may not be enough to ensure the survival of wolf spiders.
Linking to Relevant Anchor Text: If you want to learn more about the effects of pollution on wolf spider behavior and reproduction, click here.
Create Habitat Corridors
One effective way to protect the habitat of wolf spiders is to create habitat corridors. These corridors are essentially strips of land that connect larger areas of natural habitat. By creating these corridors, we enable wolf spiders to move between different areas of habitat more easily, which can help to reduce the negative impact of habitat fragmentation.
How do habitat corridors help?
Habitat corridors can help wolf spiders in a number of ways. Firstly, they allow the spiders to migrate and disperse more easily. This helps to maintain healthy populations by allowing individuals to find new mates and new sources of food.
Additionally, habitat corridors can help to increase genetic diversity. By allowing individuals to mix from different populations, the gene pool is broadened, which can improve the overall health of the species.
What are some considerations when creating habitat corridors?
When creating habitat corridors, it’s important to consider the needs of the wolf spider. Ideally, the corridor should be wide enough to allow for movement, and should be free from any major obstacles that might impede the spider’s progress. Additionally, the plants within the corridor should be appropriate for the spider’s needs, providing sufficient cover and sources of food.
It’s also crucial to consider the impact of human development on the corridor itself. For example, roads or buildings around the corridor can increase the risk of roadkill or other negative impacts on the spider population. Careful planning and management of the corridor is therefore essential.
Why are habitat corridors important in reducing the impact of human development?
As humans continue to develop natural habitats, we inevitably fragment the landscape, reducing the space available for wolf spiders and other wildlife. By creating habitat corridors, we can help to re-connect these fragmented areas and provide a sustainable solution to the issue of habitat loss.
Creating habitat corridors can also help to mitigate the impact of light pollution on wolf spiders. By providing an alternative habitat that is away from artificial lighting, the spiders can continue their natural behavior patterns and remain protected from the negative effects of light pollution.
Creating habitat corridors is an effective way to protect the habitat of wolf spiders and other wildlife. By providing a sustainable solution to habitat loss and fragmentation, we can help to secure the future of these important species.
To learn more about the impact of pollution on wolf spider behavior and reproduction, check out our previous article on the effects of pollution on wolf spider behavior and reproduction.
Reduce Light Pollution
Wolf spiders are nocturnal creatures and they rely heavily on natural light to navigate through their habitats. The increase of artificial light due to human development has a significant impact on their behavior and ultimately their survival. Reducing light pollution can play a crucial role in the preservation of their habitats.
One way to reduce light pollution is to use properly shielded outdoor lighting fixtures. These fixtures should be designed in a way that directs the light downward, preventing it from spilling over into areas where it is not needed. This not only helps to reduce light pollution but also saves energy and reduces costs.
Another way to reduce light pollution is to use motion sensors for outdoor lighting. These sensors can detect movement and switch on the lights only when necessary, rather than having them on all night. This not only saves energy but also helps to reduce the amount of light pollution and its impact on nocturnal wildlife.
Moreover, switching to LED lights can also help reduce light pollution. LED lights are more energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. This not only reduces the carbon footprint, but also helps reduce light pollution as they emit less light pollution.
To protect wolf spider habitats, it is important to reduce light pollution, which can be achieved by using properly shielded outdoor lighting, motion sensors, and switching to LED lights. By implementing these measures, humans can reduce light pollution and help preserve the natural habitats of wolf spiders and other nocturnal species.
| Ways to Reduce Light Pollution | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Use properly shielded outdoor lighting | Reduces light pollution, saves energy and costs, directs light downward preventing spillage. |
| Use motion sensors for outdoor lighting | Saves energy, reduces light pollution, detects movement, switches on lights only when necessary. |
| Switch to LED lights | Reduces carbon footprint, saves energy and costs, has longer lifespan and emits less light pollution than incandescent bulbs. |
Conclusion
After exploring the topic of the impact of human development on wolf spider habitats, it is clear that these arachnids face significant challenges as their natural habitats continue to be destroyed and fragmented. This could have serious consequences for the populations of these important predators, which play a vital role in maintaining the health and balance of ecosystems. However, there are steps that can be taken to protect wolf spider habitats and ensure their continued survival.
Preserving natural landscapes is one of the most effective ways to protect wolf spiders and their habitats. This involves setting aside large areas of land for conservation and making sure that human activities are limited in these areas. By maintaining a healthy natural environment, we can support the complex interactions between wolf spiders and their prey, as well as other species that depend on the same habitats.
Creating habitat corridors can also help to connect fragmented habitats and allow wolf spiders to move between different areas. This involves creating strips of natural vegetation that link different patches of land, providing safe pathways for animals to travel. By creating these corridors through urban and suburban areas, we can help to mitigate some of the effects of development and ensure that wolf spiders can continue to thrive.
Reducing light pollution is another important step that can be taken to safeguard wolf spider habitats. Artificial light can disrupt the natural rhythms of these arachnids, making it harder for them to hunt, navigate, and reproduce. By reducing the amount of light that is present in and around wolf spider habitats, we can minimize these disruptions and help these creatures to maintain their natural behavior.
In conclusion, while the impact of human development on wolf spider habitats is significant, there are ways to protect these important predators and ensure their continued survival. By preserving natural landscapes, creating habitat corridors, and reducing light pollution, we can help to support these arachnids and the ecosystems in which they play a critical role. It is important that we take these steps now, before it is too late to save these fascinating creatures and the vital services they provide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do wolf spiders look like?
Wolf spiders are usually large and hairy, with long and spiny legs. They range in color from dark brown to gray or even black, usually with contrasting markings on their bodies.
Where do wolf spiders live?
Wolf spiders can be found all over the world, in a variety of habitats from forests and grasslands to deserts and wetlands. They prefer to live in humid and dark environments.
Are wolf spiders dangerous?
Most species of wolf spiders are not dangerous to humans. While they do have venom, it is not typically harmful to people and they rarely bite unless provoked.
What do wolf spiders eat?
Wolf spiders are carnivores and primarily eat insects and other small arthropods. They are known to be quite effective hunters, using their excellent eyesight and speed to capture prey.
How do wolf spiders reproduce?
Wolf spiders mate through a process called courtship, where the male will perform various displays to attract the female. The female will lay her eggs in a sac and carry it around with her until the young are ready to hatch.
What is habitat fragmentation?
Habitat fragmentation refers to the process where large, continuous areas of habitat are divided into smaller and more isolated patches. This can disrupt the natural movements of species and impact their ability to find food, mates, and suitable habitat.
What is light pollution?
Light pollution refers to the excessive or misdirected artificial light that can interfere with natural ecosystems. It can cause confusion and disorientation among nocturnal animals, and disrupt their natural behavior patterns.
Why is preserving natural landscapes important?
Preserving natural landscapes is important because it helps to maintain biodiversity and protect important ecosystems. It can also provide important ecological services like clean air and water, soil stabilization, and carbon sequestration.
What are habitat corridors?
Habitat corridors are areas of habitat that connect otherwise fragmented habitats. They can help to maintain the movement and gene flow of species, and reduce the negative impacts of habitat fragmentation.
What can individuals do to protect wolf spider habitats?
Individuals can help protect wolf spider habitats by supporting conservation efforts, reducing their own environmental impact, and advocating for policies that promote sustainable land use and development.






