As spider populations continue to adapt and evolve in response to changes in their habitats and surroundings, it is essential to understand the status of individual spider species. One such species that has been the subject of significant research and interest is the black widow spider. Known for their venomous bite, these spiders are found in various locations around the world and can cause severe reactions in humans. Understanding the current status and trends of black widow spider populations is crucial for conservation efforts, as well as preventing human encounters with these potentially dangerous creatures. In this article, we will delve into the global trends in black widow spider populations, examining their varieties, habitats, factors affecting their populations, and future predictions for their conservation.
Understanding Black Widow Spider Populations

When it comes to understanding the population of black widow spiders, there are multiple factors to consider. From their identification to their distribution and behavior, it’s important to take a closer look at these arachnids in order to grasp their global trends. By delving into their habitats and varieties, as well as the factors that affect their populations, we can gain insight into how these spiders are thriving or struggling in different regions. Let’s explore the world of black widow spiders and their populations. To learn more about the mapping of black widows populations around the world, check out this article.
What are Black Widow Spiders?
Black Widow Spiders are one of the most well-known and feared spiders in the world. They belong to the genus Latrodectus, which includes 32 recognized species, and are part of the family Theridiidae. These spiders get their name from the common belief that the female eats the male after mating, which is not always the case in all species.
Physical Characteristics
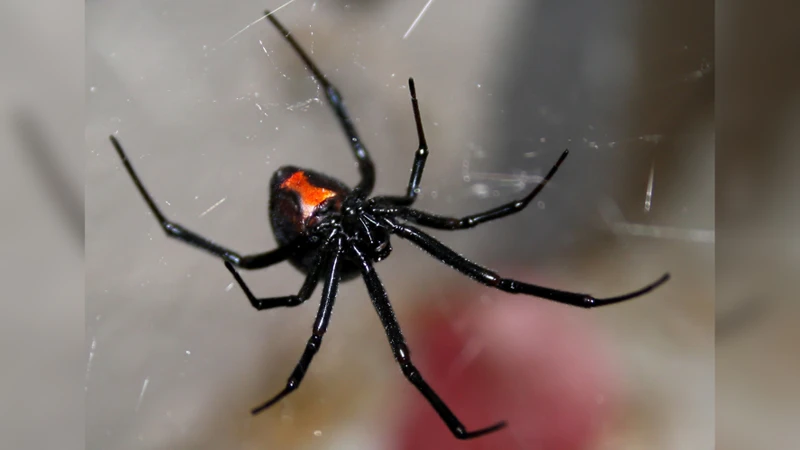
Black Widow Spiders are relatively small, typically measuring no more than 1.5 inches (3.8 cm) in length. They are identified by their shiny black body and their distinctive red or orange hourglass-shaped marking on the underside of their abdomen. Males are smaller than females and have longer legs. Black Widows are also known for their strong webs, which are used to catch prey and create egg sacs.
Habitat and Distribution
Black Widow Spiders can be found on every continent, except for Antarctica. They prefer warm climates and are commonly found in temperate regions. They have adapted to a variety of habitats, including deserts, forests, and even urban areas. In some places, they have become invasive and have displaced native species. For more information on the distribution of Black Widow Spiders, check out this article.
Behavior and Diet
Black Widow Spiders are solitary creatures and are most active at night. They are venomous and use their strong webs to trap insects, which they then immobilize with their venom. While they are not aggressive toward humans, they will bite if they feel threatened or if they are cornered. The bite of a Black Widow Spider can cause pain, muscle cramps, and other symptoms that vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity to the venom. For more information on identifying and understanding Black Widow Spider behavior, check out this article.
Black Widow Spiders are fascinating creatures that have adapted to a wide variety of environments and play an important role in the ecosystems they inhabit. They are also important to humans, as their venom has been used to develop treatments for a variety of medical conditions. However, it is important to understand and respect these spiders to avoid any potential negative interactions with them.
Where are Black Widow Spiders Found?
Black Widow Spiders are found in different regions all around the world. They prefer warm and dry habitats, which is why they are more common in the southern regions of the United States, Mexico, and South America. However, they can also be found as far north as Canada. The table below shows some of the locations where Black Widow Spiders have been found around the world:
| Region | Specific Locations |
|---|---|
| North America | Throughout the Southern United States, including California, Arizona, and Florida, as well as parts of Canada |
| South America | Brazil, Venezuela, Colombia, Argentina and other countries in the region |
| Europe | Greece, Turkey, and other Mediterranean countries |
| Asia | India, China, Japan, and other countries in the region |
| Australia & Oceania | Australia, New Zealand, and other countries in the region |
The presence of Black Widow Spiders varies depending on the region and the climate. They are most commonly found in dry, warm, and undisturbed habitats such as deserts, scrublands, and woodlands. However, they can also be found in urban areas such as outdoor garbage cans, mailboxes, sheds, and other places where they can find shelter. For more information about the prevalence of Black Widow Spiders in North America, you can read our article about Black Widow Spider Prevalence in North America.
Interestingly, the distribution of male and female Black Widow Spiders also varies by region. Some areas have a higher proportion of females compared to males, while others have a more balanced distribution. To learn more about this, you can visit our article about Male and Female Black Widow Spider Distribution. It is important to note that even though male Black Widow Spiders are less venomous than females, they are still potentially dangerous. It is important to take precautions when encountering them.
Climate is also a significant factor affecting the distribution of Black Widow Spiders. For example, they are less common in areas with colder temperatures and higher rainfall. To learn more about how climate affects the distribution of Black Widow Spiders, visit our article about Climate and Black Widow Spider Distribution.
In addition to their preferred habitats, Black Widow Spiders can also be found in unusual places due to human activity. For example, they have been found in boxes of grapes, shipped from one location to another. Additionally, natural disasters such as floods and wildfires can cause Black Widow Spiders to move to new areas. To learn more about how natural disasters affect Black Widow Spider populations and distribution, you can read our article about Black Widow Spider Populations and Disasters.
Black Widow Spiders can be found in various regions around the world, and their presence is associated with warm and dry habitats. While the distribution of males and females varies by region, it is always important to take precautions when encountering these venomous spiders. To learn more about identifying Black Widow Spiders and their behavior, visit our articles about Black Widow Spider Behavior and Identifying Black Widow Spiders.
What are the Varieties of Black Widow Spiders?
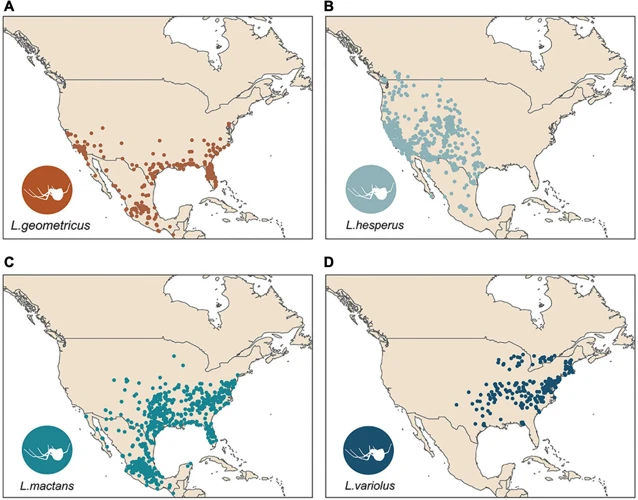
Black widow spiders consist mainly of five distinct species, each with its own unique characteristics and distribution. However, they all share one common trait that makes them easily identifiable, the hourglass-shaped marking on the abdomen.
1. Southern Black Widow (Latrodectus mactans)
The Southern Black Widow spider is the most commonly recognized black widow spider species. Found mainly in the Southern United States, it prefers warm climates. Although its venom is potent, it is not typically life-threatening to humans.
2. Northern Black Widow (Latrodectus variolus)
The Northern Black Widow spider, as its name implies, is mainly located in the northern regions of the United States and Canada. It is quite similar in appearance to the Southern Black Widow spider except for small differences.
3. Western Black Widow (Latrodectus hesperus)
The Western Black Widow spider is found in the western parts of the United States and western Canada. It has a more glossy appearance than the other species and, like the Southern Black Widow, has a red hourglass shape on its abdomen. It is considered more aggressive than the other black widow spiders.
4. Brown Widow (Latrodectus geometricus)
The Brown Widow spider is less commonly known, but it is spreading into more areas of the United States. It is mainly active during the daytime and has a brown color with a characteristic orange hourglass marking on the abdomen.
5. Red Widow (Latrodectus bishopi)
The Red Widow spider is the least known of the black widow species and is mainly located in Florida. It is recognizable by its red color, but it is not considered as dangerous as the other species of black widow spiders.
It is interesting to note that black widows can also adapt to various habitats and can now be found in urban areas, deserts, and even unusual habitats like underwater.
Factors Affecting Black Widow Spider Populations
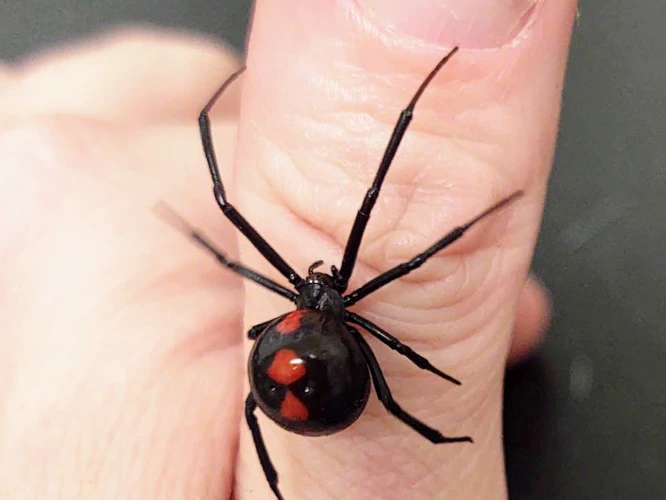

The survival and proliferation of black widow spider populations is largely dependent on various factors that can have both positive and negative impacts on their habitats. Environmental and human-induced factors affect their populations differently based on their location and variety. In this section, we will delve into the various factors that affect black widow spider populations and their consequences. Let us explore how natural predators, climate change, habitat loss, environmental pollution, and human intervention lead to a complex balance in black widow spider populations.
Climate Change and Habitat Loss
Climate change and habitat loss are two interrelated factors that have a significant impact on black widow spider populations. As the climate changes, habitats become either unsuitable or unavailable, leading to a loss of suitable breeding, feeding, and living spaces as well as a decline in prey availability.
Climate Change
The rise in temperature alters the seasonal cycle of the black widow spider, affecting the timing of breeding and egg-laying. This may lead to fewer offspring and reduced survivability of eggs and young spiders. Additionally, as warmer conditions encourage the expansion of the black widow spider’s range, it also increases the risk of competition with other spider species, further reducing the population.
Habitat Loss
Black widow spider habitats are rapidly declining due to human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, industrialization, and the conversion of natural habitats for agricultural purposes. The loss of natural habitats leads to fragmentation and isolation of populations, making it difficult for spiders to find mates and reduce gene flow. Additionally, this fragmentation can cause favorable habitats for the black widow spider to be isolated, resulting in dwindling populations that struggle to maintain genetic diversity.
The table below shows the impact of climate change and habitat loss on black widow spider populations:
| Factors | Impact on Black Widow Spider Populations |
|---|---|
| Rise in Temperature | Alters breeding and egg-laying, leads to fewer offspring and reduced survivability of eggs and young spiders, increases competition with other spider species. |
| Habitat Loss | Declining suitable breeding, feeding, and living spaces, decline in prey availability, fragmentation and isolation of populations making it difficult for spiders to find mates and reducing gene flow, loss of natural habitats and reduced genetic diversity. |
It is important to address these issues to prevent further decline of the black widow spider populations. Conservation efforts should focus on reducing habitat destruction and preserving natural areas and ecological corridors. Spreads in awareness about climate change and how it affects the environment should be taken to help mitigate the impacts.
Natural Predators and Competition
Natural Predators and Competition are one of the prime factors that affect the population of Black Widow Spiders. Due to the presence of a wide range of predators, including birds, reptiles, and mammals, the survival rate of Black Widow Spiders becomes quite challenging.
Competition from other spider species and even some insects can also limit the population of Black Widow Spiders in many regions. Interestingly, some species of ants have been observed attacking Black Widow Spider nests to claim the territory, further contributing to the decline.
A study conducted by researchers found that the presence of Orb Weaver spiders can greatly limit the population of Black Widow Spiders in shared habitats. According to the study report, Orb Weaver spiders tend to target the same prey as Black Widow Spiders, which leads to a suppressive effect on the latter’s breeding success rate.
The following table provides a concise overview of the Natural Predators and Competitors of Black Widow Spiders:
| Natural Predators | Competitors |
|---|---|
| Birds | Orb Weaver Spiders |
| Reptiles | Jumping Spiders |
| Mammals | Wolf Spiders |
| Ants | Mantis |
To conclude, the presence of Natural Predators and Competition plays a crucial role in determining the population trends of Black Widow Spiders. In order to ensure their survival and conservation, it is vital to address these factors along with others affecting their population.
Environmental Pollution and Pesticides
The rampant use of pesticides and chemicals for agricultural purposes has been a major factor in the decline of black widow spider populations. Pollution resulting from industrial activities that emit toxic fumes and waste also contributes to the destruction of spider habitats. Here are some of the ways pesticides and pollution effects black widow spider populations:
- Decrease in Food Sources: Pesticides and chemicals can lead to a decrease in insect populations which are the primary source of food for black widow spiders. This lack of prey negatively affects their ability to survive and thrive.
- Direct Contact: When black widow spiders come into direct contact with pesticides and chemicals, there is a high likelihood that they will be negatively affected, leading to illness and death.
- Genetic Mutation: Exposure to pesticides and pollutants can result in genetic mutations in black widow spider populations, making them more vulnerable to disease and increasing the likelihood of extinction.
- Impact on Habitat: Chemical pollution and pesticides can harm the environment in which black widow spiders reside, making it difficult for them to find food, water, and shelter. This loss of habitat can lead to a significant decline in their overall population.
Protecting the environment from pollution and minimizing the use of harmful pesticides are essential measures for protecting black widow spider populations. Environmental organizations, scientists, and policymakers have identified these risks, and initiatives are being taken to minimize the damage. For example, many farmers are switching to organic farming methods, which minimize the use of pesticides and chemicals. Public awareness campaigns also play a vital role in promoting eco-friendly practices and reducing pollution.
Human Intervention and Ecological Imbalance
Human intervention and ecological imbalance are two major factors that negatively impact the populations of black widow spiders. The table below highlights the different types of human intervention and their effects on black widow spider populations.
| Type of Human Intervention | Effects on Black Widow Spider Populations |
|---|---|
| Urbanization and Habitat Destruction | The rapid pace of urbanization and habitat destruction has resulted in the loss of natural habitats for black widow spiders leading to a decline in their populations. |
| Deforestation and Agricultural Activities | Deforestation and agricultural activities have significantly affected black widow spider populations. Deforestation reduces the availability of natural habitats for these spiders, while agricultural activities such as the use of pesticides can negatively impact their survival and reproduction. |
| Introduction of Non-Native Species | The introduction of non-native species such as rats and cats has resulted in reduced prey populations for black widow spiders, which has led to a decline in their populations. |
| Pollution and Climate Change | Pollution and climate change have resulted in the degradation of habitats and the alteration of natural weather patterns that affect the survival of black widow spiders. Pollution also affects the quality of prey available to these spiders, which can impact their overall population. |
It is important to note that while human intervention has had negative impacts on black widow spider populations, conservation efforts can help to mitigate these effects. Strategies such as habitat restoration, the reduction and regulation of pesticide use, and the control of non-native species can help to improve the populations of black widow spiders.
Current Status of Global Black Widow Spider Populations
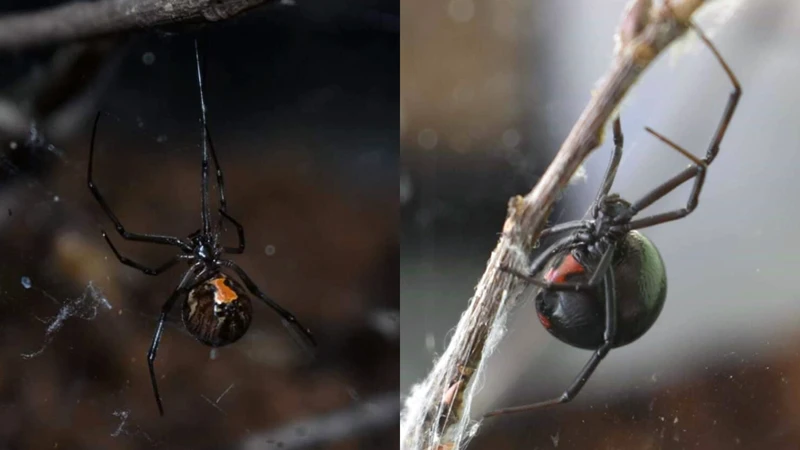

At present, it is crucial to analyze the current status of black widow spider populations worldwide due to the impact they have on humans and other species in their ecosystems. By examining the distribution and population trends of these venomous arachnids, researchers can gain valuable insights into the potential threats facing these species and devise appropriate conservation measures. Let us delve deeper into the current situation across various regions of the world and understand the fluctuations in black widow spider populations.
North America
As far as the global Black Widow Spider population is concerned, North America is one of the most significant areas to consider. North America has a diverse range of Black Widow Spiders species, including the Southern Black Widow, Western Black Widow, and Northern Black Widow. These spiders are widely distributed in the United States and parts of Canada. The comfortable climatic conditions in the southern states provide a suitable habitat for Black Widow Spiders, and as a result, their population is abundant in these regions.
According to recent reports, the population of Black Widow Spiders in North America has been steadily increasing over the past few years. This trend is mainly due to the rise in global temperatures, which has created a favorable environment for the spiders to thrive. Additionally, the growing human population and increased urbanization have led to habitat modification, which has further favored Black Widow Spider populations.
Despite the increase in their population, there have been several reports of Black Widow Spider infestations in residential areas in North America, posing a threat to human lives. The Northern Black Widow Spider species, in particular, are known to cause severe neurological symptoms in humans and pets through their venomous bite.
To manage the increasing North American Black Widow Spider populations and minimize the risks they pose to human lives, appropriate control measures need to be implemented. Integrated pest management (IPM) is a great approach that involves the use of various methods to manage pest populations effectively. These methods include biological, physical, and chemical control measures. Biological control measures involve using natural enemies such as wasps, parasitic flies, and birds that feed on Black Widow Spiders. Physical control measures include installing spider barriers and utilizing traps. Chemical control measures are often the last resort and involve the use of insecticides.
North America is home to several species of Black Widow Spiders, and their population is on the rise. This phenomenon is mainly due to climate change and human interference. However, with appropriate conservation measures, their population can be managed, minimizing the risks they pose to human life.
South America
When it comes to black widow spider populations, South America is one of the regions that has the highest number of species. According to recent research, South America is home to over 19 species of black widow spiders. These species can be found throughout different parts of the continent, from the humid rainforests of Brazil to the the dry and desert-like regions of Argentina.
One of the most common species found in South America is the Latrodectus geometricus, also known as the brown widow spider, which is found throughout the continent, including Brazil, Chile and Argentina. Another species found in South American countries is the Latrodectus curacaviensis, also known as the Chilean black widow spider. This species is native to Chile and is known for its distinct red hourglass marking on its abdomen.
However, despite having a high number of black widow spider species, South America is not immune to the threats facing these spiders. Climate change, habitat destruction, and pollution are some of the factors that are affecting black widow spider populations in the region.
To give you an idea of the current status of black widow spider populations in South America, the table below shows the number of species found in each country.
| Country | Number of Black Widow Spider Species |
|---|---|
| Brazil | 10 |
| Argentina | 5 |
| Chile | 3 |
| Colombia | 1 |
It is important to note that these numbers are subject to change due to ongoing research and studies. However, it is clear that South America plays a significant role in the global population of black widow spiders, and conservation efforts must be taken to ensure their survival.
Europe
Europe, with its widely varied habitat types, is home to several species of black widow spiders. The most common species found in Europe is the Northern black widow (Latrodectus variolus), which is also known as the European black widow. It is mainly found in North and Central Europe, but it can also be observed as far south as the Mediterranean region.
Another species that can be found in Europe is the Southern black widow (Latrodectus mactans), which is native to North America. It has been introduced to Europe, and some isolated populations have been found in the south of France, Italy, and Spain.
The brown widow (Latrodectus geometricus) has recently been reported in several regions of Europe, including the Mediterranean. This invasive species is believed to have been introduced to Europe through imported goods such as tires.
Although black widow spiders are present in Europe, their populations are relatively small compared to other parts of the world, such as North America and South America. This can be attributed to the cooler climate and fewer suitable habitats.
Despite this, black widow spider bites do occur in Europe, and they can lead to serious health problems. It is important for people living in or visiting Europe to be aware of the potential risks and take necessary precautions, such as wearing protective clothing and shoes when in areas where black widows may be present.
More research is needed on the black widow spider populations in Europe to fully understand their distribution and behavior. Conservation efforts should also be implemented to better protect these populations and their habitats.
Here are some notable points regarding black widow spiders in Europe:
- The Northern black widow is the most common species of black widow found in Europe.
- The Southern black widow has been introduced to Europe and can be found in isolated populations in some areas.
- The invasive brown widow has recently been reported in several regions of Europe.
- Compared to other parts of the world, black widow spider populations in Europe are relatively small.
Asia
Asia is home to a few species of black widow spiders, namely the Lactrodectus hasseltii, Lactrodectus erythrurus, and Lactrodectus tredecimguttatus. The black widow spider population in Asia has been significantly influenced by environmental factors, as well as human intervention and ecological imbalance.
Below is a table summarizing the current status of black widow spider populations in Asia:
| Species | Status | Threats |
|---|---|---|
| Lactrodectus hasseltii | Stable | Habitat loss, human intervention, competition with other spider species |
| Lactrodectus erythrurus | Endangered | Habitat loss, natural predators, environmental pollution |
| Lactrodectus tredecimguttatus | Vulnerable | Habitat loss, environmental pollution, competition with other spider species |
As shown in the table, the black widow spider population in Asia is facing numerous threats, ranging from habitat loss and environmental pollution to natural predators and competition with other spider species. The Lactrodectus erythrurus species is particularly vulnerable, with its population decreasing rapidly due to various environmental factors.
Conservation measures are crucial to protect the black widow spider population in Asia. Protecting their habitats, monitoring and controlling the use of pesticides and pollutants, and raising awareness about the importance of these spiders in the ecosystem are necessary steps for their survival.
Australia and Oceania
Australia and Oceania host a variety of Black Widow Spider species. In Australia alone, 18 species of Black Widow Spiders have been identified, including the Redback Spider, the Karakurt Spider, and the Cupid’s Dart Spider. These spiders can be found throughout the country, from the coastal areas to the deserts and even the rainforests.
The distribution of Black Widow Spiders in the Pacific Islands of Oceania is more limited, with only a few species identified. The Fijian Widow Spider and the Marsh Spiders are notable examples. These spiders are mainly found in coastal areas and are adapted to the humid environments of the islands.
One of the main threats faced by Black Widow Spiders in Australia and Oceania is the spread of invasive species. The Cane Toad is a significant threat to native populations of Black Widows, as they devour them without ill effect. Pesticides and habitat loss due to urban development and deforestation are also contributing factors.
Researchers predict that Black Widow Spider populations in Australia and Oceania will continue to face significant challenges in the coming years. However, conservation measures such as the introduction of predator-free zones and the use of environmentally friendly farming techniques may help to mitigate the effects of these threats and ensure the survival of these fascinating arachnids.
Future Predictions and Conservation Measures
As we look towards the future, it is essential to make informed predictions about the fate of black widow spiders. These venomous arachnids continue to face numerous threats that impact their populations worldwide. To ensure their survival, it is vital to implement appropriate conservation measures that can mitigate these challenges. Let’s dive deeper into the predictions for the global trend in black widow spider populations and discuss the possible conservation measures that can be taken to support their survival.
Global Black Widow Spider Population Trends for the Next Decade
Looking ahead to the future, it is crucial to understand the trends and predictions for the global black widow spider population in the next decade. Based on current research and analysis, the following are some possible outcomes:
- The black widow spider population is expected to decrease in some regions due to climate change and habitat loss.
- On the other hand, in areas where black widow spiders are not native, there could be an increase in their population due to human activities such as globalization and international trade.
- The use of pesticides and environmental pollution is likely to continue to have negative impacts on the population of black widow spiders.
- Due to the threatened status of the black widow spider, conservation efforts will become increasingly important in the next decade to protect their natural habitats and maintain their populations.
- There may be fluctuations in the population of black widow spiders in different regions, depending on factors such as competition with other species and predation from natural enemies.
It is clear that there is much to be done in order to protect and preserve black widow spider populations in the years to come. With the right conservation strategies and implementation of eco-friendly practices, it is possible to ensure that these creatures continue to thrive in their natural habitats.
Conservation Measures for Black Widow Spiders
Black Widow Spiders are an important species in the ecosystem and their conservation is crucial for maintaining the balance of nature. Here are some conservation measures that can be implemented to ensure the survival of black widow spider populations:
1. Habitat preservation: One of the most effective conservation measures for black widow spiders is habitat preservation. Black widow spiders generally prefer undisturbed habitats such as forests, shrublands, and meadows. It is important to protect and preserve their natural habitat by reducing deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion.
2. Integrated Pest Management: The use of chemical pesticides is harmful not only to black widow spiders but also to other organisms in the ecosystem. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an effective and eco-friendly method of pest control that can reduce the use of pesticides. IPM involves the use of non-toxic pest control methods such as crop rotation, habitat modification, and biological pest control.
3. Public Awareness: Educating the public about the importance of black widow spiders and their role in the ecosystem can generate awareness about the need for conservation. By creating public awareness campaigns, people can learn about the spiders and take steps to avoid harming them.
4. Research and Monitoring: Conducting research and monitoring black widow spider populations can help in understanding their behavior, habitat requirements, and factors affecting their populations. Regular monitoring can provide valuable data to assess their population status and implement appropriate conservation measures.
5. Captive breeding and reintroduction: In cases where black widow spider populations have been severely depleted, captive breeding programs can be implemented to release spiders back into the wild. This enables the population to recover from previous losses and can aid in the conservation of the species.
These conservation measures can be effective in the conservation of black widow spiders and their populations. However, implementing them requires the collaboration of governmental organizations, non-governmental organizations, and the public. By working together, it is possible to save the black widow spider and to preserve our planet’s rich biodiversity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is evident that black widow spider populations around the world are facing a variety of challenges that affect their survival and existence. Factors such as climate change, habitat loss, natural predators, competition, environmental pollution, pesticides, and human intervention have all contributed to the decline of black widow spider populations in various regions.
Despite these challenges, efforts should be made to conserve black widow spider populations around the world. Conservation measures that can be implemented include reducing the use of pesticides, protecting and restoring habitats, and implementing policies that promote ecological balance. Additionally, engaging in further research on black widow spider populations and their ecology can provide insights into how best to protect them.
It is important to note that black widow spiders play a vital role in their ecosystems, and preserving them is crucial for the maintenance of healthy and balanced ecosystems. As such, it is the responsibility of individuals, governments, and organizations to take action towards conserving and protecting black widow spider populations for the benefit of all. By implementing conservation measures and prioritizing the protection of black widow spider populations, future generations can continue to reap the benefits that these remarkable creatures offer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the lifespan of a Black Widow Spider?
A female Black Widow Spider can live for up to three years, while the lifespan of a male Black Widow Spider lasts only a few months.
What is the venom of a Black Widow Spider like?
The venom of a Black Widow Spider is highly toxic but rarely leads to death in humans. Its effect on victims includes muscle spasms, high blood pressure, and, in severe cases, paralysis.
Why are Black Widow Spiders predominantly found in warm environments?
Black Widow Spiders prefer warm environments because they are more active in warmer temperatures, which allows them to hunt more efficiently and successfully.
What is the mating behavior of Black Widow Spiders?
After mating, the female Black Widow Spider often kills the male and feeds on him. This behavior is called sexual cannibalism and is observed in many species of spiders.
How can individuals protect themselves from being bitten by a Black Widow Spider?
Individuals can protect themselves from being bitten by a Black Widow Spider by wearing protective clothing and shoes, shaking out clothing and bedding before use, and keeping their surroundings free from debris and insects that spiders prey upon.
What is the importance of Black Widow Spiders in the ecosystem?
Black Widow Spiders play an important role in the ecosystem by controlling populations of insects such as flies, mosquitoes, and cockroaches, which are considered household pests.
How are climate change and habitat loss impacting Black Widow Spider populations?
Climate change and habitat loss are threatening Black Widow Spider populations by altering their natural habitats and exposing them to new predators and disease.
What are some of the natural predators of Black Widow Spiders?
Some of the natural predators of Black Widow Spiders include birds, lizards, and other spider species.
How can individuals contribute to the conservation of Black Widow Spiders?
Individuals can contribute to the conservation of Black Widow Spiders by educating themselves and others on the importance of their role in the ecosystem and avoiding the use of harmful pesticides and chemicals that may harm them.
What is being done on a global scale to protect Black Widow Spiders?
On a global scale, there is no widespread effort to protect Black Widow Spiders. However, some organizations and individuals are working to raise awareness of their importance and promote conservation efforts.