The world of spiders never ceases to amaze us. Among the many species of spiders that thrive in various environments, the wolf spider stands out with its unique parenting style. These spiders have evolved to not only survive but also take care of their young in the harshest of environments. However, like any other creature, wolf spiders are not immune to the effects of environmental factors. In this article, we will explore the impact of temperature, food availability, humidity, predators, and habitat destruction on the parenting practices of wolf spiders. Additionally, we will discuss how these spiders have adapted to changing environments, and what implications this has for wildlife conservation efforts. So fasten your seatbelts as we delve into the intriguing world of wolf spider parenting!
Understanding Wolf Spider Parenting
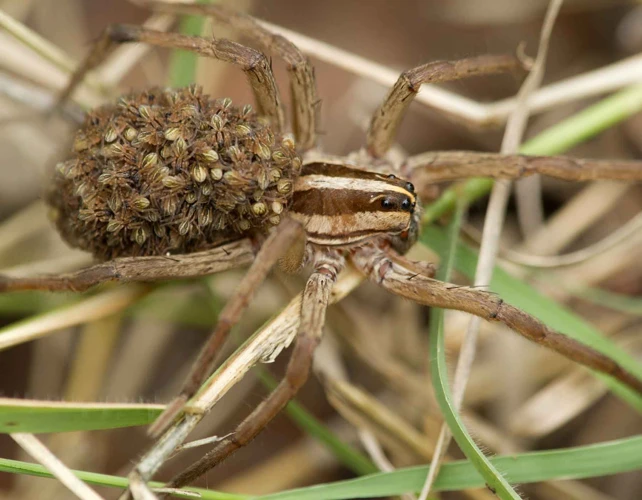

As the maternal instincts in the animal kingdom have always fascinated humans, wolf spider parenting is no different. These arachnids display unique behaviors that set them apart from other spider species. Understanding their parenting style can offer us insights into their survival mechanisms in the wild. In this section, we will explore what makes wolf spider parenting so unique, how they care for their young, and the role of both the mother and father in the spiderling’s survival. We will also discuss how researchers have observed and studied wolf spider parental behavior in the wild.
What is Wolf Spider Parenting?
Wolf spider parenting refers to the behaviors exhibited by female and male wolf spiders to ensure the survival of their offspring. Unlike many spider species, wolf spiders maintain a high degree of involvement in the care and protection of their young.
The female wolf spider typically lays her eggs in a silk-lined burrow, which she then covers with a layer of silk to protect them from predators and environmental factors. Once the eggs hatch, the spiderlings climb onto their mother’s back where they remain until they are mature enough to fend for themselves. This period of time can range from two weeks to several months depending on the species of wolf spider.
During this time, the female wolf spider will provide her young with food and protection. Wolf spider mothers are known to feed their young with partially digested insects, regurgitating the food to her spiderlings. This helps to ensure that the offspring receive the nutrition they need to grow and develop.
The role of the male in wolf spider parenting can also be significant. In some species, the male wolf spider will actively participate in the care and protection of the offspring. For example, the male may assist in carrying the spiderlings on his back while the mother is out hunting for food.
Wolf spider parenting involves a high degree of parental involvement and care, which is not commonly seen in many other spider species. This unique behavior has led to a great deal of research on the importance of maternal care for wolf spiders and the communication between males and females to coordinate parenting efforts.
Why is Wolf Spider Parenting Unique?
Wolf spiders have several unique characteristics when it comes to parenting their offspring. One of the most distinctive features is that they do not build webs to catch prey. Instead, they hunt for food and capture their prey directly. This means that wolf spiders cannot rely on large quantities of prey being trapped in their webs to feed their young. As a result, wolf spider mothers take on the role of primary caretaker for their offspring.
Mothers play a critical role in the survival of their young by providing them with food and protection. Wolf spider mothers will continue to feed and protect their young until they are old enough to fend for themselves. During this time, the young spiders will molt several times and develop into a fully mature adult.
Another unique feature of wolf spider parenting is the involvement of the father. Unlike many spider species, male wolf spiders play an active role in the care of their offspring. The male will often signal the female and guard the brood while she is away hunting for food. Once the female returns, the male will then go out to hunt. This shared responsibility demonstrates the cooperative parental care found in wolf spider families.
Wolf spiders also show a unique ability to adapt to environmental conditions. In times of food scarcity, they have been observed to cannibalize their own young to ensure the survival of the remaining offspring. Additionally, they are capable of behavioral thermoregulation, where they position themselves and their offspring in a way that maximizes warmth or minimizes heat stress.
Observing wolf spider parental behavior in the wild can be difficult, as they are primarily nocturnal and often hide during the day. However, researchers have been able to gain insight into their behavior by observing their interactions in a laboratory setting.
Understanding the unique aspects of wolf spider parenting can have important implications for wildlife conservation efforts. By recognizing their role in the ecosystem and the many ways in which they adapt to environmental changes, we can better protect and preserve these animals and their habitats for generations to come.
How Do Wolf Spiders Care for Their Young?
Wolf spiders are known for their unique method of parenting compared to other arachnids. Instead of laying eggs and leaving their offspring to fend for themselves, wolf spiders actually carry their eggs and later their spiderlings on their abdomen until they are old enough to survive on their own. This process of carrying their young is called “offspring brooding”.
Once the young wolf spiders hatch, their mother will continue to carry them around for a period of time. During this developmental stage, the mother will feed her young by regurgitating food for them to consume. It is interesting to note that wolf spider mothers provide this care on their own, with no help from the father, making maternal care crucial for the survival of the offspring.
As the spiderlings grow older, the mother will gradually leave them alone for longer periods of time, allowing them to begin hunting for their own food and learn necessary survival skills. However, it is not uncommon for the mother to still provide food for her offspring even after they have dispersed.
Wolf spider maternal care plays a fundamental role in the survival of the species. Without the mother’s care, the offspring would not have a high chance of surviving in the wild. It is fascinating to observe the behavioral adaptations wolf spiders have developed to ensure their young’s survival.
Environmental Impacts on Wolf Spider Parenting
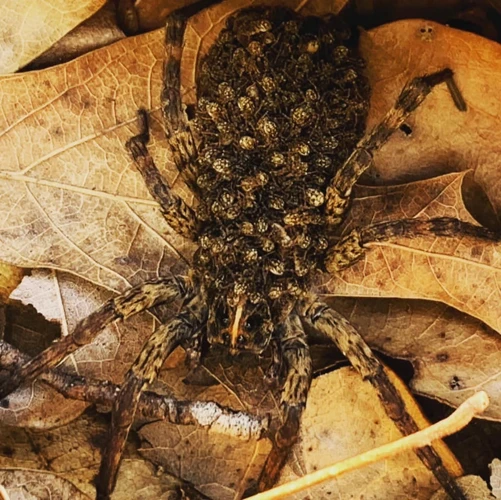

Wolf spiders are fascinating creatures that exhibit unique parental behaviors. There are several environmental factors that can have significant impacts on wolf spider parenting and the survival of their offspring. These factors range from temperature and food availability to the presence of predators and habitat destruction. Understanding the effects of these environmental factors is crucial in comprehending the behaviors and adaptations of these arachnids. In the following sections, we will delve into the different environmental impacts on wolf spider parenting and how they adapt to changes in the environment. This knowledge can have important implications for wildlife conservation efforts.
The Role of Temperature on Parenting
Temperature plays a crucial role in wolf spider parenting and influences various aspects of their behavior. The optimal temperature for wolf spiders to reproduce and care for their young is between 20 to 25°C. Temperature impacts maternal care and affects the wolf spider’s ability to feed and protect their young ones.
Effects of High Temperature: High temperatures can negatively affect wolf spider parenting by decreasing their energy levels and reducing the amount of time spent on parental care. Wolf spider mothers might have to move more to protect their offspring, which can cause them to spend less time in direct contact with their young. This can lead to less warmth and protection for the spiderlings, ultimately decreasing their chances of survival.
Effects of Low Temperature: Low temperature can significantly affect wolf spider parenting by reducing the spiderlings’ growth rate and decreasing the mother’s activity level. The reduced activity levels can lead to inadequate heat transfer and less protection for the spiderlings, increasing the likelihood of predation. Low temperature can decrease the spiderlings’ food consumption rate and hinder the mother’s ability to provide adequate nutrition, ultimately impacting their survival rates.
Temperature plays a crucial role in wolf spider parenting and affects offsprings’ development and survival rates. Temperature levels must remain optimal for wolf spiders to reproduce and care for their young. Environmental changes that affect temperature levels can significantly impact wolf spider parenting and lead to long-term ecological consequences.
Link: Importance of Maternal Care in Wolf Spiders
The Importance of Food Availability
Food availability is crucial when it comes to wolf spider parenting. Since wolf spiders provide their young with regurgitated food through an external digestion process, the availability of food is essential to the survival of their progeny. Wolf spider mothers are known to provide food to their young through initial regurgitation and subsequently bringing them larger prey once they are big enough.
A lack of food availability can result in the failure to thrive for the offspring. This lack of food can lead to lower growth rates and a high risk of predation. Without sufficient food, wolf spider young may not develop fully, rendering them vulnerable to environmental stressors. This can also result in early maturation and undersized progeny. Food availability is especially important in seclusive wolf spider species where the available prey is often limited.
Wolf spiders can adjust their feeding levels according to food availability. For example, when there is low prey density, wolf spiders tend to spend more time hunting and increase the size of prey they consume. In contrast, under higher prey density, wolf spiders are less aggressive and feed less frequently.
It is important to note that the availability of prey is not the only factor determining the availability of food for wolf spider progeny. The ability of wolf spider mothers to find and capture prey is a crucial factor and is influenced by a range of environmental factors, such as humidity, temperature, and habitat quality. The ability of wolf spiders to provide for their young and their success in doing so make them unique in the spider world.
Ensuring that food is available for wolf spider progeny is crucial for their survival. Studies show that in the presence of abundant prey, the wolf spider mother will have higher-quality offspring with increased growth rates. This highlights the importance of habitat conservation efforts in maintaining the necessary food availability for wolf spiders.
The availability of food is a critical factor that impacts wolf spider parenting. Food availability affects the sustainability and growth rate of wolf spider young. It is important to ensure that the necessary resources are available, including the continued presence of prey in the environment.
The Impact of Humidity on Offspring Survival
High humidity is critical for wolf spider parenting success. Wolf spider mothers often deposit their eggs in silk-lined burrows, and the humidity of the environment has a remarkable effect on offspring survival. One study conducted by researchers found that offspring survival rates were highest at a relative humidity of around 70% (source). In contrast, at lower humidity levels, offspring survival rates declined, with the highest mortality rates observed at humidity levels below 40%.
Additionally, the humidity level also has an impact on the growth and development of young wolf spiders. Higher humidity levels allow juvenile spiders to molt more effectively, leading to a more successful transition from one stage of development to the next. The table below summarizes the impact of humidity on the survival and growth of wolf spider offspring.
| Humidity level | Offspring survival rate | Effect on juvenile growth and development |
|---|---|---|
| Below 40% | Lowest survival rates | Difficulty molting leads to stunted growth and decreased survival |
| 40-70% | Moderate survival rates | Improved juvenile molting, leading to better growth and development |
| Above 70% | Highest survival rates | Optimal conditions for juvenile molting and growth |
Wolf spider mothers naturally gravitate towards soil with higher moisture content for egg deposition, but this is not always feasible or accessible. Deforestation, land use changes, and climate change impact the availability of moisture in the soil, leading to reduced offspring survival and decreased population density. Hence, it is crucial to understand and mitigate the impacts of environmental changes on wolf spider populations to maintain healthy ecosystems and prevent species from being lost (source).
The Effects of Predator Presence on Parenting
The presence of predators in the habitat of wolf spiders can have a significant impact on their parenting behavior. When predators are around, wolf spider parents may change their behavior to protect their young and ensure their survival.
1. Increased Aggression: One common effect of predator presence on wolf spider parenting is increased aggression towards potential threats. Wolf spider mothers, in particular, have been observed exhibiting aggressive behaviors towards predators in order to protect their young. This behavior can involve biting, hissing, and even attacking much larger predators in attempts to defend their young.
2. Decreased Foraging: Another potential effect of predator presence on wolf spider parenting is decreased foraging. In the presence of predators, wolf spiders may focus their energies on protecting their young instead of searching for food. This can lead to decreased food intake for both adults and young, potentially impacting their overall survival rates.
3. Changes to Reproductive Strategy: Some studies have also found that predator presence can cause wolf spiders to change their reproductive strategies. For example, some wolf spider species may produce fewer young in the presence of predators, while others may reproduce earlier or more frequently to compensate for potential losses.
The presence of predators can have a complex and varied effect on wolf spider parenting behavior. However, these changes ultimately aim to increase the survival of young wolf spiders and ensure the continuation of the species. To learn more about how wolf spiders care for their young, read our article on father wolf spider care and how wolf spider mothers feed their young.
The Role of Habitat Destruction in Parenting
The destruction of natural habitats is one of the biggest threats to many wildlife species, including wolf spiders. As habitats are destroyed due to human activity such as deforestation and urbanization, wolf spiders are forced to adapt to new environments which can have significant effects on their parenting behavior.
Loss of Shelter: When natural habitats are destroyed, wolf spiders lose their homes and shelters. This can lead to a decrease in the number of offspring they can successfully raise. Wolf spider mothers build silk nursery webs to protect their eggs from predators and the environment. Without adequate shelter, the eggs and spiderlings are vulnerable to harsh weather conditions, predators, and parasites that can decrease their survival rate.
Lack of Food: Habitat destruction not only affects shelter but also food availability. Wolf spiders are generalist predators, meaning they eat a variety of prey such as insects and other spiders. However, when their natural habitats are destroyed, their food sources become scarce, and this can lead to a decrease in their reproductive success. This can also affect the growth and development of their offspring, making them more susceptible to predation.
Invasive Species: Another impact of habitat destruction is the introduction of invasive species. Invasive species are non-native species that have the potential to cause harm to the environment and native species. As habitats are destroyed, invasive species can move in and outcompete the native prey that wolf spiders rely on. This can lead to a decline in the population of wolf spiders, and in some cases, may even cause local extinctions.
To address these issues, conservation efforts are needed to protect and restore natural habitats. This can include measures such as reforestation, creating corridors for wildlife movement, and preventing further habitat destruction. By protecting the natural habitats of wolf spiders and other wildlife, we can help ensure that their parenting behavior remains intact, and their populations continue to thrive.
Adapting to Changes in the Environment
It’s no secret that the environment can be unpredictable and ever-changing. For animals like Wolf spiders, adaptation is key to survival. These spiders have a unique ability to adjust to a variety of environmental factors that can impact their parenting strategies. In this section, we will explore how Wolf spiders are able to adapt to changes in their environment and the implications this has for wildlife conservation efforts. Let’s dive in and take a closer look at how these spiders manage to thrive in the face of environmental challenges.
Wolf Spiders’ Ability to Adjust to Environmental Changes
Wolf spiders are highly adaptive creatures that have the ability to adjust to various environmental changes. This adaptability is due to their behavioral and physiological mechanisms that allow them to respond to changes in their surroundings. Below are some ways in which wolf spiders adjust to changes in their environment:
1. Behavioral Plasticity: Wolf spiders exhibit behavioral plasticity, which means they have the ability to modify their behavior in response to environmental changes. For example, they may change their activity pattern, shift their hunting grounds, or move to a different location with more favorable conditions.
2. Physiological Adaptations: Wolf spiders also have several physiological adaptations that help them cope with different environmental conditions. For instance, they have the ability to adjust their metabolic rate and body temperature in response to temperature changes. Additionally, they can store water to survive in dry environments.
3. Genetic Variation: Genetic variation plays a crucial role in the adaptability of wolf spiders. Individuals within a population may have different genetic traits that help them to survive and reproduce in different environmental conditions. This genetic variation allows for natural selection to operate and favors the survival of individuals that are better adapted to changing conditions.
4. Phenotypic Plasticity: Phenotypic plasticity refers to the ability of an organism to change its physical characteristics in response to environmental cues. Wolf spiders exhibit phenotypic plasticity in response to food availability, which affects their body size, reproductive output, and survival rates.
The ability of wolf spiders to adjust to environmental changes is a key factor in their success as a species. Through behavioral plasticity, physiological adaptations, genetic variation, and phenotypic plasticity, they are able to survive and thrive in different environmental conditions. This adaptability has important implications for wildlife conservation efforts as it suggests that wolf spiders may be able to withstand certain environmental disturbances.
Implications for Wildlife Conservation Efforts
The findings of research on the effects of environmental factors on wolf spider parenting have important implications for wildlife conservation efforts. As wolf spiders are a crucial component of many ecosystems and play an essential role in controlling pest populations, it is essential to protect them from environmental threats.
| Challenge | Implications for Conservation |
|---|---|
| Climate Change | The rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can affect the availability of food and water, which can have significant impacts on wolf spider populations. Conservation efforts must focus on maintaining and protecting the habitat of wolf spiders to ensure their survival. |
| Habitat Destruction | As wolf spider’s lifestyle is closely linked to their environment, the destruction of their natural habitat can significantly impact their ability to breed and provide proper care to their young. Efforts targeting habitat protection and restoration are essential to sustain viable populations of wolf spiders and maintain the balance of ecosystems. |
| Predator Control | As predators influence wolf spider’s behavior and maternal care, the excessive predator population can lead to a decline in wolf spider population. Effective predator control measures must be implemented to mitigate the effect of predation on Wolf spider’s biomass and population dynamics while preserving a healthy balance of ecosystems. |
| Biocontrol pesticides | The widespread use of pesticides in agriculture can disrupt the balance of ecosystems and pose a threat to wolf spider populations. The use of biocontrol pesticides can be an effective alternative to chemical pesticides and contributes to maintaining the diversity of the ecosystem. |
Conservation efforts must take into account the unique parenting behaviors and environmental requirements of wolf spiders to create effective management strategies for their populations. By protecting wolf spider’s habitat and controlling environmental threats, we can ensure the survival of this essential species and preserve the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
Conclusion
Through studying wolf spider parenting and the environmental factors that can impact it, we have gained a better understanding of the intricacies of nature and the delicate balance that exists within ecosystems. It is evident that temperature, food availability, humidity, predator presence, and habitat destruction can all have significant effects on wolf spider parenting and the survival of their offspring.
However, it is essential to note that wolf spiders have shown an ability to adapt to changes in their environment. They have evolved to be resilient and can adjust their parenting behaviors based on the environment they find themselves in. This is a crucial adaptation that allows these spiders to survive in a variety of habitats and climates.
The implications of this are significant for wildlife conservation efforts. By understanding how species like the wolf spider adapt to environmental changes, we can better predict how other species may respond to similar pressures. This information is incredibly valuable in creating effective conservation strategies that can help protect vulnerable ecosystems and the species that inhabit them.
In conclusion, studying wolf spider parenting and the environmental factors that impact it has provided valuable insights into the complexity of nature and the importance of maintaining a delicate balance within ecosystems. By recognizing the resilience of species like the wolf spider, we can work towards preserving the diversity of life on our planet for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the lifespan of a wolf spider?
Wolf spiders typically live for one to two years.
Do all wolf spider mothers care for their young?
No, not all wolf spider species exhibit maternal care for their offspring.
What do wolf spider mothers do for their young?
Wolf spider mothers carry their egg sacs with them and continue to provide protection and care for their spiderlings after hatching.
How do environmental factors affect wolf spider parenting?
Environmental factors such as temperature, food availability, humidity, predator presence, and habitat destruction can all have negative impacts on wolf spider parenting and survival rates of their offspring.
What is the impact of temperature on wolf spider parenting?
Temperature can affect the development and survival of wolf spider offspring, with hotter temperatures potentially reducing survival rates.
Why is food availability important for wolf spider parenting?
Food availability can impact the growth and survival of wolf spider offspring, with a lack of food leading to reduced survival rates of the spiderlings.
How does humidity impact wolf spider offspring survival?
Humidity can affect egg development and spiderling survival rates, with lower humidity resulting in decreased survival rates.
What is the effect of predator presence on wolf spider parenting?
Predator presence can impact the behavior of wolf spider mothers, leading to reduced protection and care of their offspring.
Why is habitat destruction a threat to wolf spider parenting?
Habitat destruction can eliminate necessary resources and shelter for wolf spider mothers and their offspring, reducing survival rates.
Can wolf spiders adapt to environmental changes?
Yes, wolf spiders have the ability to adjust their behavior and physiology in response to environmental changes, although the extent of their adaptation may be limited.