The earth is constantly changing, and one of the most significant changes we are experiencing is climate change. With rising temperatures and extreme weather conditions, many species are facing challenges in adapting to their changing habitats. Wolf spiders, for instance, are greatly impacted by climate change. These fascinating arachnids play a key role in many ecosystems, and their decline would have far-reaching consequences. In this article, we will explore the impact of climate change on the distribution of wolf spiders in detail, examining their physical features, habitats, behaviors, adaptation, and survival. So, let’s delve into the world of wolf spiders and learn more about their lives and how climate change affects them.
Understanding Wolf Spiders
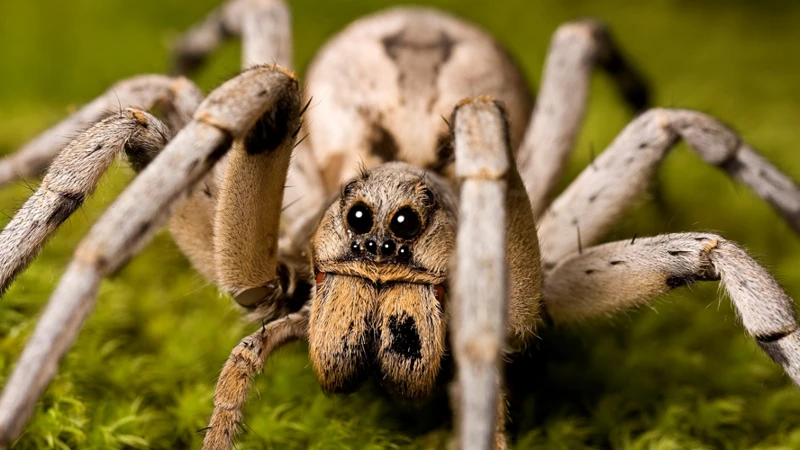

When people hear the words “wolf spider,” they might imagine a fearsome creature that preys on other animals. But wolf spiders are actually an important part of many ecosystems, thanks to their unique characteristics and behaviors. They are also among the most widely distributed spider species in the world, found on every continent except Antarctica. Let’s take a closer look at these fascinating arachnids and see what sets them apart from other spiders. To learn about how human activity can impact wolf spiders, check out our article on human activity and wolf spiders.
Physical Features
Wolf spiders are a diverse family of spiders with over 2,300 species found worldwide. As the name suggests, they are hunters and rely on their strength and agility to catch prey. They are known for their large size compared to other types of spiders. In fact, some species of wolf spiders can grow up to 5 cm in length!
| Physical Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Coloration | Wolf spiders have a range of colors, from brown to gray, with some even having stripes or spots. They use this coloration to blend into their surroundings and avoid detection by predators. |
| Eyes | Wolf spiders have eight eyes arranged in three rows, with four small eyes on the bottom row, two large eyes in the middle row, and two medium-sized eyes on the top row. These eyes provide excellent vision and allow them to hunt and avoid predators in low-light conditions. |
| Fangs and Chelicerae | Wolf spiders have large fangs, which they use to bite and subdue their prey. They also have chelicerae, which are mouthparts that help them tear apart their food. |
| Legs | Wolf spiders have four pairs of legs, which they use to run and jump. Their legs are covered in tiny hairs, which help them detect and capture prey. |
| Spinnerets | Wolf spiders have three pairs of spinnerets, which are used to produce silk. They use their silk to line their burrows and create egg sacs. |
Some species of wolf spiders in different regions have unique features such as rare habitat, abundance, or importance to agriculture. For example, the rarity of certain wolf spider species are affected by various factors, such as habitat loss and invasive species, which can drive them to extinction. Some wolf spider species are more abundant in certain habitats, such as moist forests, while others can be commonly found in agricultural fields.
Understanding the physical features of wolf spiders is important for understanding their behavior, habitats, and how they are adapting to climate change.
Habitats and Behaviors
Habitats and Behaviors
Wolf spiders are found all over the world, with over 2,300 species identified thus far. They are versatile and can adapt to different habitats, although they thrive in grassy and wooded areas. Wolf spiders are predatory creatures, and they are typically found in areas where their prey, such as insects, is abundant.
These spiders prefer to live in burrows or holes, which offer protection and shelter from predators. They are most active at night, where they hunt for prey. During the day, they hide in their burrows or under rocks, logs, or leaves. In general, wolf spiders are solitary creatures, although some species may occasionally come together.
Wolf spiders are also able to swim, which enables them to inhabit areas near water sources such as lakes, rivers, and streams. They have small hairs and grooves on their legs, which allow them to move through water. While some species prefer moist habitats, others can live in dry environments such as deserts and grasslands.
It’s important to note that habitat availability and type can greatly impact the abundance of wolf spider populations. For example, according to a study on the rarity factors of wolf spiders, habitat fragmentation caused by agricultural development can lead to a significant decrease in wolf spider abundance. This is because the fragmentation of habitats results in smaller, isolated populations, which can become more prone to local extinction.
Sources: /rarity-wolf-spider-factors/, /wolf-spider-abundance-habitats/, /wolf-spiders-agriculture/
The Role of Climate Change
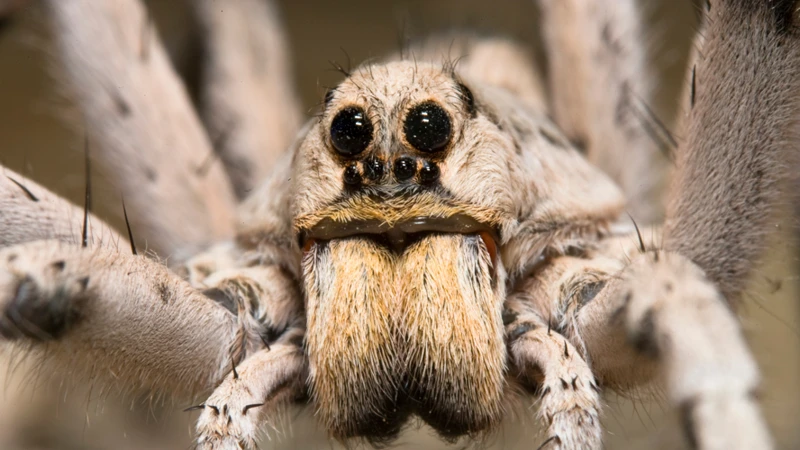

As scientists continue to study the impacts of climate change on different species, the role of this warming phenomenon on the distribution and behavior of wolf spiders has garnered increasing attention. With their varied habitats and behaviors, wolf spiders offer a unique case study for understanding the ways in which climate change is altering the natural world. In this section, we will explore the specific ways in which rising temperatures and extreme weather events are affecting wolf spiders and their ecosystems.
How Temperature Affects Wolf Spider Distribution
One of the most significant ways that climate change is impacting wolf spiders is through the alteration of temperature patterns. Wolf spiders are ectothermic, meaning that their body temperature is regulated by the temperature of their environment. As such, changes in temperature can have profound effects on their distribution patterns.
Increase in Temperature: As temperatures increase, wolf spiders tend to expand their range and move toward areas that were previously too cold for them. In fact, one study found that a warming climate in the Arctic tundra has led to an increase in the abundance and diversity of wolf spiders. This shift in distribution can have cascading effects on the ecosystem, as wolf spiders may interact more with other species they previously did not encounter.
Decrease in Temperature: Conversely, a decrease in temperature can lead to a contraction of wolf spider habitats. In areas where winters are becoming longer and colder, wolf spiders may struggle to survive and reproduce, leading to a decline in their populations. This, in turn, can impact the entire ecosystem as wolf spiders play a crucial role in controlling the population of other insects.
To illustrate the impact of temperature on wolf spider distribution, we can look at the following table:
| Temperature | Impact on Wolf Spider Distribution |
|---|---|
| Increasing | Expansion of range and increased abundance and diversity |
| Decreasing | Contraction of habitats and decline in populations |
It is clear that temperature is a crucial factor in determining wolf spider distribution, and changes in temperature patterns due to climate change can have significant impacts on these spiders and the ecosystems in which they live.
The Effect of Extreme Weather on Wolf Spiders
Extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, can have a significant impact on wolf spider populations. These spiders are sensitive to changes in their environment, and extreme weather can disrupt their food sources and mating patterns. Here are some of the effects of extreme weather on wolf spiders:
- Drought: A drought can cause wolf spider populations to decline, as their prey may become scarce or seek out water sources outside of the spider’s hunting grounds. Additionally, drought conditions can cause plants and other vegetation to dry up, reducing the cover and shelter that wolf spiders need to hunt and mate.
- Floods: Floods can have both positive and negative effects on wolf spider populations. On one hand, floods can wash away spider habitats and disrupt mating patterns. On the other hand, floods can also create new habitats and bring in new prey species for the spiders to hunt.
- Heat waves: Wolf spiders are heat-tolerant, but prolonged heat waves can still be detrimental to their health. High temperatures can cause the spiders to become dehydrated, stressed, and lethargic, which can reduce their hunting and mating success.
- Cold snaps: Wolf spiders are also adapted to cold temperatures, but sudden and extreme cold snaps can still have a significant impact on their populations. Frost and snow can damage spider habitats and reduce the availability of prey, while frigid temperatures can cause the spiders to hibernate or reduce their activity levels.
Extreme weather events can disrupt the delicate balance of the wolf spider’s ecosystem, affecting not only the spiders themselves but also their food sources and predators. As climate change continues to lead to more frequent and intense weather events, it is important to monitor wolf spider populations and take steps to mitigate their vulnerability to extreme weather.
Experts’ Opinions on Climate Change and Wolf Spiders
Numerous studies have been conducted to understand the impact of climate change on several species, including wolf spiders. Experts believe that wolf spiders are more susceptible to climate change than previously thought. According to Dr. Robert J. Warren, a research biologist at the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center, rising temperatures can alter the demographics of wolf spider populations, affecting their survival.
Another researcher, Dr. Amanda Koltz from Washington University in St. Louis, emphasizes that the combination of increased temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can lead to the decline in wolf spider populations. She also states that these factors can affect the spider’s prey and habitat, making it more challenging for the species to survive.
Furthermore, Dr. Jennifer Thaler, an ecological entomologist from Cornell University, suggests that climate change can alter the behavior of wolf spiders, making them less active and less successful in hunting prey. This behavioral shift could ultimately lead to the population decline.
These experts highlighted the potential threat climate change poses on wolf spider populations and emphasize the need for increased efforts to study, protect, and conserve the species.
Impact on Ecosystems
As the distribution of wolf spiders continues to be impacted by climate change, it’s important to consider the wider implications of this phenomenon. The delicate balance of ecosystems can be drastically altered by changes in the populations of key species such as the wolf spider. In this section, we explore how the impact of climate change on wolf spiders can have far-reaching effects on the ecosystems in which they live, and the different ways that experts are working to better understand and mitigate these impacts.
Wolf Spiders as a Keystone Species
Wolf spiders are not only important members of their ecosystem, but they are also classified as a keystone species. This means that their presence or absence has a significant impact on the structure and function of the ecosystem as a whole. Wolf spiders play a vital role in controlling the population of their prey, which can include many different types of insects and other small animals. Without wolf spiders, these prey populations could potentially get out of control and cause imbalances in the ecosystem.
The significance of wolf spiders as a keystone species extends beyond just their role in regulating prey populations. They are also an important food source for many other animals, such as birds, reptiles, and other insects. The loss of wolf spiders could potentially trigger a trophic cascade, leading to the decline or disappearance of other species as well.
Wolf spiders are essential keystone species that help maintain the balance and health of their ecosystems.
Here are some examples of other keystone species:
- Sea otters, which help maintain the health of kelp forests by controlling populations of sea urchins.
- Beavers, which create and maintain wetland habitats that benefit many other plant and animal species.
- Elephants, which help maintain the diversity of savanna habitats by their grazing and selective browsing of vegetation.
Food Webs and Trophic Cascades
In any ecosystem, the wolf spider plays a significant role in the food chain. Being a predator itself, it preys on a variety of insects and pests, and hence maintains an ecological balance. However, climate change is disrupting these food webs and trophic cascades, ultimately affecting the survival of wolf spiders.
Food Webs: A food web is a complex web of interconnected food chains, where each organism plays a specific role in the food chain, either as a predator or as prey. Wolf spiders being predators, feed on a variety of insects like flies, ants, and beetles. At the same time, they also fall prey to larger predators like birds, snakes, and lizards.
Trophic Cascades: Trophic cascades refer to the indirect effects that a change in the population of one species can have on other species in the same food chain. For instance, if the wolf spider population decreases due to climate change, it will indirectly affect the population of its prey, which in turn will affect the populations of other organisms dependent on those prey species. This ripple effect can massively impact the entire ecosystem.
Other species that feed on wolf spiders as well as its prey could be affected. For example, birds of prey that prey on wolf spiders will experience a decrease in prey availability, which will worsen the food scarcity they already face due to climate change.
In effect, the wolf spider’s role in the food web is critical to maintaining ecological balance; without them, the food chain would be significantly disrupted. Conservation efforts must be undertaken to preserve wolf spider populations in changing ecosystems, as well as the entire ecosystem.
Adaptation and Survival
As climate change continues to impact the habitats of various species, adaptation and survival have become crucial factors in maintaining their populations. Wolf spiders, like many other organisms, are facing new challenges due to the changing environment. However, these arachnids have shown remarkable resilience and ingenuity in adapting to these changes. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which wolf spiders have managed to survive and thrive in the face of climate change. Keep reading to discover the fascinating and innovative methods that these creatures have developed to cope with their changing world.
Ways Wolf Spiders Are Adapting to Climate Change
Wolf spiders are one of the most adaptable creatures on the planet. As the planet’s climate continues to change, these spiders have developed various ways to adjust their behavior and adapt to the new environment. Here are some of the ways wolf spiders are adapting to climate change:
1. Range Expansion: Wolf spiders have been observed to slowly expand their ranges to cooler areas in response to rising temperatures. This means that they are adapting to the changing environment by migrating to places with cooler climates.
2. Behavioral Changes: Wolf spiders are becoming more active at night and during cooler temperatures. They are spending more time in shaded areas and less in the open sun. These changes allow them to avoid the hottest parts of the day and reduce their exposure to the sun’s heat.
3. Diet Changes: Wolf spiders are also changing their diet in response to changes in their environment. With rising temperatures, prey availability has shifted, and wolf spiders have been observed preying on new species. In some areas, they have become more opportunistic and have started eating smaller spiders, insects, and invertebrates.
4. Physiological Changes: Wolf spiders are also exhibiting physiological changes in response to the changing climate. For example, they are growing larger to better regulate their body temperature in response to higher temperatures. They also have developed adaptations to retain water in drier environments.
5. Hybridization: Some wolf spiders are hybridizing with other species in response to changing environments. Hybridization can help create new species that are better adapted to the changing climate and can survive in new habitats.
These adaptations to climate change are crucial for the survival of wolf spiders, as they help the species maintain their place in the ecosystem and continue to thrive amidst changing environmental conditions.
Conservation Efforts to Protect Wolf Spider Populations
Wolf spiders are a critical part of many ecosystems, but they are vulnerable to the impacts of climate change and habitat destruction. As a result, there have been various conservation efforts taken to protect these populations. Here are some examples of such initiatives:
- Establishing Protected Areas: Creating protected areas is a common conservation strategy for many species, and it is no different for wolf spiders. These are areas of land where human activities are restricted, allowing the spiders and their habitats to remain intact without disturbance.
- Habitat Restoration and Management: Habitat restoration and management can be critical in ensuring that wolf spider populations remain stable or recover from previous losses. This can involve activities such as reforestation, planting native vegetation, protecting riparian corridors, and managing wildfire risks.
- Environmental Education and Awareness: Educating people about the importance of wolf spiders and their habitats can also be an impactful conservation effort. By raising awareness and understanding of the ecological roles that wolf spiders play, people can be motivated to protect them and their environments.
- Research and Monitoring: Investing in research and monitoring programs is also essential. This helps to better understand the current status and trends of wolf spider populations, identify potential threats and risks, and evaluate the effectiveness of conservation measures.
All of these conservation efforts and initiatives can help protect wolf spider populations and ensure that these unique creatures remain an important part of many ecosystems. However, there is still much that needs to be done to mitigate the impact of climate change on these populations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is clear that climate change has a significant impact on the distribution of wolf spiders. As temperatures rise, these spiders may shift their ranges further north or to higher elevations in search of more suitable habitats. Extreme weather events can also disrupt their behavior and populations, leading to declines in population sizes.
Furthermore, the impact of climate change on wolf spiders has cascading effects on ecosystems. As a keystone species, wolf spiders play an important role in controlling the populations of their prey, which in turn affects the entire food web. Changes in wolf spider populations can lead to shifts in predator-prey dynamics and trophic cascades.
However, there is some hope for the survival of wolf spider populations. These spiders are known for their ability to adapt to changing environments. With help from conservation efforts, including habitat restoration and protection, wolf spider populations can potentially recover and establish new ranges.
It is important to continue monitoring the impacts of climate change on wolf spider populations and their ecosystems as a whole. By understanding these changes, we can better inform policies and management strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change and protect the biodiversity of our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are wolf spiders?
Wolf spiders are a family of ground-dwelling spiders known for their hunting abilities. They are named for their wolf-like appearance and behavior.
What do wolf spiders look like?
Wolf spiders have stout bodies and hairy legs. They come in a variety of colors and patterns, but most have a distinctive eye arrangement with four small eyes in the bottom row and two large eyes on top.
Where do wolf spiders live?
Wolf spiders can be found all over the world, from deserts to forests to coastal areas. They prefer habitats with plenty of vegetation and moisture.
What do wolf spiders eat?
Wolf spiders are predators that feed on a variety of insects and other small creatures, including mosquitoes, grasshoppers, and even other spiders.
How does climate change affect wolf spiders?
Climate change can impact wolf spider populations by altering their habitats and food sources. Extreme weather events can also have a negative impact on their survival.
What is a keystone species?
A keystone species is a species that has a disproportionately large effect on its ecosystem compared to its abundance. Wolf spiders are considered a keystone species because of their role in controlling insect populations.
What are trophic cascades?
Trophic cascades occur when changes in the abundance of one species have indirect effects on other species in the ecosystem. For example, if wolf spider populations decline, this could lead to an increase in the population of their prey, which could then have negative impacts on other species in the food web.
How are wolf spiders adapting to climate change?
Some wolf spiders are adapting to climate change by shifting their range to cooler areas and altering their behavior to cope with changing conditions. However, their ability to adapt may be limited by their dependence on specific habitats.
What can be done to protect wolf spider populations?
Conservation efforts can be implemented to protect wolf spider populations, such as preserving their habitat and reducing the use of pesticides that can harm spider populations and their prey.
Why are wolf spiders important?
Wolf spiders play an important role in controlling insect populations and are a vital part of many ecosystems. By studying the impact of climate change on wolf spider populations, we can gain a better understanding of the potential effects of climate change on other species as well.






