Introduction
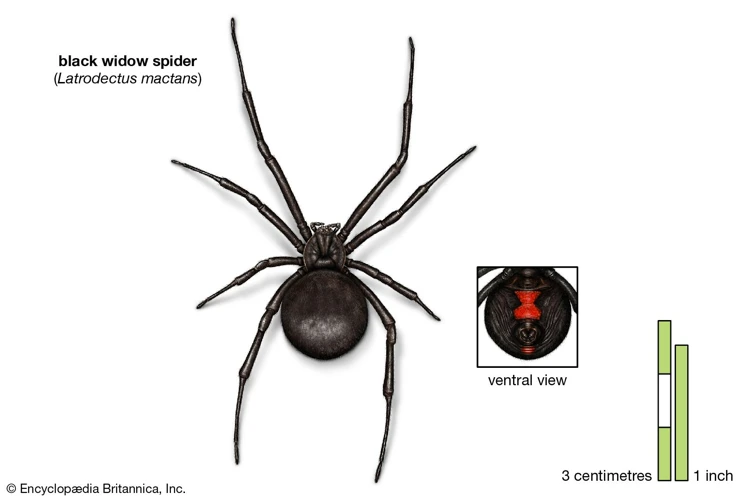

The mysterious and venomous black widow spiders have always sparked curiosity and fear in humans. These arachnids have a dark and glossy appearance and a deadly bite that can be fatal if not treated promptly. With their distribution spanning across continents, it’s crucial to understand the factors that influence their habitat, as well as the impact that climate has on their distribution. In this article, we will delve into the effect of climate on the distribution of black widow spiders, exploring regional climate impacts, and the factors that contribute to habitat shifts. So fasten your seatbelts and get ready to learn more about these fascinating creatures!
Overview of Black Widow Spiders
Black widow spiders are well-known arachnids that belong to the family of comb-footed spiders, Theridiidae. These spiders are widely distributed around the world, with different species inhabiting different regions. The three most common species are the western black widow, the northern black widow, and the southern black widow. They are characterized by a shiny, black body with a distinctive red hourglass shape on the underside of their abdomen. The male black widow spider is smaller than the female and has slightly lighter coloring.
Black widow spiders are considered venomous because they possess a potent neurotoxin that they use to subdue their prey. This neurotoxin affects the nervous system, causing muscle cramps, abdominal pain, and sometimes even paralysis. However, only female black widow spiders are known to bite humans, and even then, bites are relatively rare. These spiders generally avoid human contact and will only bite if they feel threatened.
Generally, black widow spiders prefer temperate climates and can be found in areas with moderate temperatures and high humidity. However, they have been known to adapt to different environments and are now found in a wide range of habitats, including deserts, forests, and even urban areas. Understanding the behavior and distribution of black widow spiders can provide important insights into the broader impact of environmental factors on spider populations.
Understanding the Climate Impact
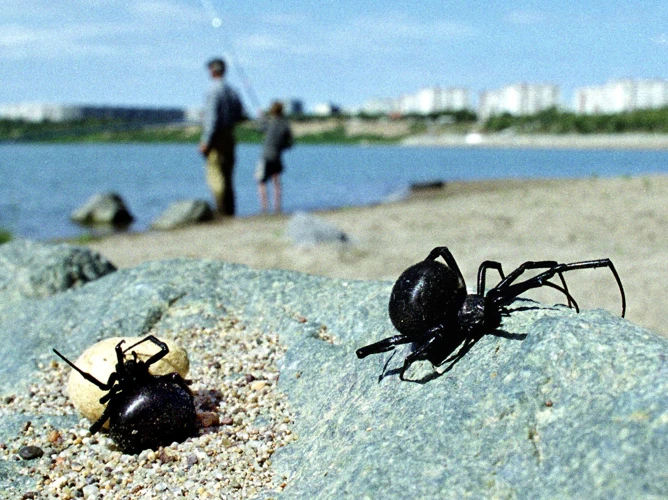

It is essential to understand the impact of climate on the distribution of black widow spiders. The behavior and distribution of these spiders are influenced by changes in temperature, precipitation, and humidity. Observing the impact of climate change on black widow spider populations is crucial to understand their distribution pattern, which can help in controlling and management of these spiders. Environmental factors such as temperature, precipitation, and humidity are known to affect the behavior of black widow spiders. In this section, we will discuss how climate change impacts the distribution of black widow spiders in detail.
1. Temperature
Temperature plays a significant role in the distribution of black widow spiders. These spiders prefer warm temperatures and are generally found in regions with a warm and dry climate. According to research, the ideal temperature range for black widow spiders is between 20°C to 32°C (68°F to 90°F). They are unable to tolerate very low temperatures as it hinders their metabolic processes, and extremely high temperatures reduce their body’s ability to retain moisture.
The impact of temperature on the distribution of black widows can be summarized in the following table:
| Temperature | Impact on Black Widow Spider |
|---|---|
| Below 10°C (50°F) | Black widow spiders become inactive and seek shelter |
| 10°C to 20°C (50°F to 68°F) | Black widow spiders remain dormant and less active |
| 20°C to 32°C (68°F to 90°F) | Black widow spiders are most active and thrive in this temperature range |
| 32°C and above (90°F and above) | Black widow spiders reduce their activity and seek shelter to avoid dehydration |
As temperature plays a vital role in the distribution of black widow spiders, the impacts of global warming and climate change cannot be ignored. Rising temperature levels in certain regions around the world can lead to the spread and increase in the number of black widow spiders in those areas. Hence, it is crucial to understand the climatic changes and its impact on the environment to predict and prevent any problematic shifts in black widow spider populations.
To learn more about factors contributing to black widow spider populations and the impact of human activity, click on this link for /human-activity-black-widow-spider-populations/.
2. Precipitation
Precipitation plays a crucial role in the distribution of black widow spiders. These spiders can adapt to a variety of environments, but they need a certain amount of moisture to thrive. If the environment is too dry, it can be challenging for them to survive and thrive.
1. Effects of High Precipitation
In areas with high precipitation levels, black widow spiders tend to be more abundant. Areas with consistent rainfall provide a suitable environment for these spiders to thrive. They can find shelter in the soil, plants, and bark of trees, which retain moisture and provide a suitable habitat for them.
On the other hand, areas with intermittent rainfall, such as deserts, do not provide the necessary conditions for black widow spiders to sustain their populations. In these areas, black widows may still be present but in lower densities.
2. Effects of Low Precipitation
In areas with low precipitation levels, black widow spiders have developed strategies to survive in arid conditions. They may form temporary shelters or remain dormant for extended periods until conditions improve.
Dry and arid environments are not ideal for black widow spiders because they need moisture to survive. Changes in precipitation patterns due to climate change can cause shifts in their distribution, which can alter the ecosystems they inhabit.
It’s been reported that a shift in climate patterns is one of the leading environmental factors that affect black widow spiders’ behavior, which in turn impacts their distribution. Some of these alterations directly influence the rate of precipitation, which would impact their population sizes.
3. Water Availability in Different Regions
The amount of precipitation that black widows need varies by region. In some areas, rainwater is sufficient to meet their needs, while in other areas, they may require additional sources of water, such as streams, ponds, or lakes. Climate change can impact the availability of these water sources, which can be detrimental to black widow spider populations.
For example, droughts caused by changes in precipitation patterns can lead to water scarcity, making it difficult for black widow spiders to survive and reproduce. Similarly, in areas that experience excessive rainfall and have standing water, their habitats may become flooded, which can lead to their displacement and affect their distribution.
While black widow spiders have adapted to variations in precipitation patterns, changes in climate can cause considerable disruptions to their populations, which in turn can affect the ecosystems they inhabit. By understanding the impact of precipitation on the distribution of black widow spiders across different regions, measures can be taken to mitigate the effects of climate change on these spiders.
3. Humidity
Humidity is another crucial factor that influences the distribution of black widow spiders. These spiders prefer dry environments, and high humidity levels can limit their numbers or prevent them from even surviving in the first place. Studies show that black widow spider abundance is lower in areas with high relative humidity, as the excess moisture affects their web-building abilities and egg development. Additionally, high humidity can promote the growth of mold and fungi, which can attract other insects, reducing the availability of prey for black widows.
In areas with low humidity, however, black widow populations can thrive, especially if there is a consistent source of moisture. This is because the dry conditions prevent the growth of mold and fungi and limit the number of potential predators. In North America, black widow populations are more common in arid or semi-arid regions such as the southwestern United States and Mexico. Similarly, in Europe and Asia, they are more commonly found in deserts, sandy loam soils, and dry grasslands.
With climate change causing shifts in weather patterns, there could be an impact on the humidity levels in affected regions that could lead to changes in black widow spider populations. Climate change can also have a ripple effect on other environmental factors, such as precipitation, temperature, and habitat fragmentation, which can further influence black widow distribution.
If you want to learn more about black widow spiders and climate change, check out our article on Climate Change and Black Widow Distribution.
Regional Climate Impact on Distribution
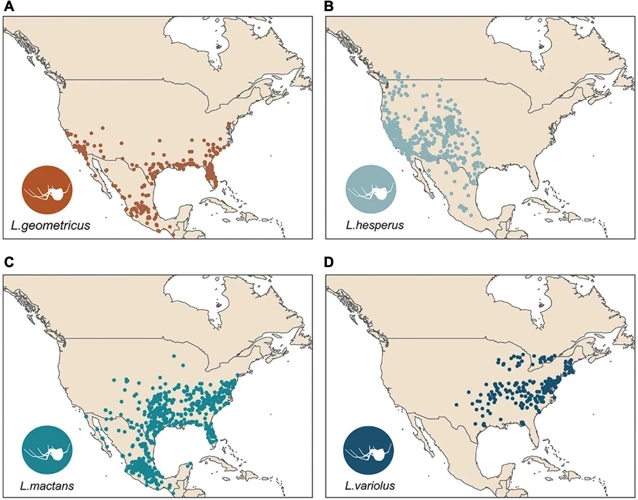
As black widow spiders are found worldwide, their distribution is influenced by a variety of environmental factors, including climate. This impact of climate on black widow spiders varies depending on the region they inhabit, and the spider populations can experience significant shifts in distribution as a result. In this section, we will explore how different regions around the world are affected by climate change, and how this affects the distribution of black widow spiders in those areas. We will examine three regions in particular- North America, Europe, and Asia- and investigate the various factors contributing to changes in black widow population.
1. North America
North America is the native home of the black widow spider, and there are five types of black widows found in North America. The black widow population is widespread throughout North America, inhabiting most of the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Although they have been seen in other areas, they are most commonly found in the southern states, including Texas, California, and Florida.
One notable characteristic of black widow spiders in North America is their preference for undisturbed habitats. They can be found in natural environments such as forests, fields, and prairies, but also in human-made structures like sheds, garages, and outdoor facilities.
Table 1: Distribution of black widow spiders in North America
| Region | States | Habitat |
|——–|——–|———|
| West | California, Arizona, Utah, Colorado, Texas| Dry, warm, and undisturbed environments such as desert regions|
| South | Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, Louisiana, Mississippi | Moist, warm environments such as marshlands and wetlands |
| Midwest | Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Kansas, Wisconsin | Undisturbed, cool environments such as forests and wooded areas|
| Northeast | Pennsylvania, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Maine, New York | Natural and human-made structures such as basements and outdoor areas |
The distribution of black widow spiders in North America is heavily influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, precipitation, and humidity. The varying climates within the continent offer diverse habitats for black widows. For example, western black widows prefer the hot and dry environment of the desert regions, while southern black widows prefer the humid and moist environment of marshlands and wetlands.
Factors such as urbanization, natural disasters, and habitat fragmentation also contribute to changes in the distribution of black widow spiders in North America. For instance, urbanization has led to more sightings of black widows in urban areas such as buildings and parks.
Despite the widespread presence of black widow spiders in North America, their populations have been affected by human activities. The use of pesticides and other chemicals to control pests has led to a decline in their population. Additionally, the introduction of invasive species and habitat destruction have also impacted their distribution.
It is essential to have a good understanding of the distribution and behavior of black widow spiders in North America to reduce their impact on ecosystems and human well-being. For more information on identifying black widows and their bites, please refer to our article on identifying black widows.
2. Europe
Europe, unlike North America, is not home to a large population of black widow spiders. However, they can still be found in some parts of southern Europe, namely in countries like Spain, Italy, and Greece. These spiders are known to thrive in warm climatic conditions and can be found in rocky or dry habitats. They are typically found in sites such as stone walls, rock crevices, or abandoned buildings. Although rare, black widow spiders may have the potential to become an invasive species in Europe.
The climate of Europe is characterized by a temperate oceanic climate in the north and a Mediterranean climate in the south. The temperate oceanic climate zone, which includes the United Kingdom, Ireland, and coastal areas of France and Spain, is characterized by mild temperatures and high precipitation throughout the year. On the other hand, the Mediterranean climate zone, which includes Spain, Italy, and Greece, is characterized by hot and dry summers and mild and rainy winters. Climate change may create new habitats for black widow spiders in Europe, allowing them to become invasive and establish populations in areas they have not been found before.
Human activities, such as urbanization and international trade, can also contribute to the introduction of black widow spiders into Europe. Shipping and transportation of plants and goods from countries where black widow spiders are established can increase the likelihood of these spiders being introduced to new habitats. Invasive species can impact ecosystems and potentially displace native species, creating a need for effective management strategies.
While black widow spiders have not established large populations in Europe, the potential for their range to expand due to climate change and human activities cannot be ruled out. Further research is necessary to understand the impact of environmental factors on black widow behavior in Europe and to develop management strategies to prevent the establishment of invasive populations.
3. Asia
Asia is a vast continent with diverse ecosystems and varied climate zones. Black widow spiders are distributed in several regions of Asia, such as Iran, Pakistan, and China. The highest populations of black widow spiders are found in warmer regions where temperatures remain high throughout the year.
Iran is home to three different species of black widow spiders, including Latrodectus revivensis, Latrodectus dahli, and Latrodectus tredecimguttatus. These species of black widow spiders can be located in arid and semi-arid regions of Iran.
In Pakistan, the black widow spider species Latrodectus elegans is found in the Sindh region. This species prefers warm and dry climates and can make habitats in crevices, burrows, and buildings.
In China, black widow spiders can be found in multiple regions of the country, including Xinjiang, Gansu, and Ningxia. These areas tend to have a hot and dry climate throughout the year, which is ideal for black widows to thrive.
One factor that contributes to black widow populations in Asia is urbanization. As cities in Asia continue to grow, urban areas become better habitats for these spiders. For example, black widow sightings in urban areas in Japan have significantly increased in recent years.
Another factor contributing to the distribution of black widows in Asia is habitat fragmentation. Destruction of natural habitats to make way for agriculture, industry, and urban areas can negatively impact these spiders’ habitats. Thus, it’s essential to maintain natural habitats to contain their populations.
Black widows in Asia thrive in hot and dry climates found in arid and semi-arid regions of the continent. Environmental factors and urbanization are contributing factors to their distribution. As black widow populations continue to increase, it’s crucial to understand their behavior and ecological impacts on ecosystems.
Factors Contributing to Distribution Shifts
As climate change continues to impact the environment, black widow spiders are finding themselves in new and unexpected locations. However, there are other factors contributing to the shift in distribution patterns. These include: urbanization, natural disasters, and habitat fragmentation. Each of these elements plays a significant role in how populations of black widow spiders move and change over time. Understanding these factors is essential in creating effective strategies for managing black widow populations and minimizing their impact on ecosystems. For more information on the impact of invasive black widow spiders on ecosystems, please read our article “Invasive Black Widow Spiders – Impact on Ecosystems.”
1. Urbanization
Urbanization, the process of creating and developing cities, has a significant impact on the habitat of the black widow spider. As cities continue to expand, natural habitats are destroyed to make way for buildings and infrastructure. This has resulted in a significant shift in the distribution of black widows.
The Effects of Urbanization on the Black Widow Spider Population
Studies show that urbanization has led to a significant increase in the number of black widow spiders in urban areas. Black widows are highly adaptable and have learned to survive in the unusual habitats created by urbanization. For instance, they can be found living in abandoned buildings, subway stations, and parking lots in urban areas.
One reason for this increase might be that the urban environment provides protection from natural predators. Urban areas may also have more food sources for spiders due to the presence of street lighting that attracts insects.
Despite their adaptability, urbanization has also caused a decline in the number of black widow spiders in some areas. Urbanization can lead to habitat fragmentation, where natural habitats are broken into smaller patches. This affects the distribution of black widows, as it becomes more difficult for them to move between habitats.
Climate Change and Urbanization
Climate change is another factor that has contributed to the shift in the distribution of the black widow spider. The increase in temperature due to climate change has created more favorable conditions for black widows to thrive.
Urban areas, which are often warmer than rural areas due to the urban heat island effect, provide the perfect conditions for black widows to thrive. This is because black widows require warmer temperatures to reproduce and thrive.
However, it is important to note that not all black widow populations are increasing in urban areas. Some urban areas do not provide adequate shelter or prey for black widows, resulting in a decline in their populations. Additionally, the presence of pesticides and other chemicals in urban areas may also affect the survival of black widow spiders.
The impact of urbanization on black widow spiders is complex and varies depending on location and other environmental factors. To learn more about how environmental factors impact black widow behavior, please see our article on Environmental Factors and Black Widow Behavior.
2. Natural Disasters
Natural disasters can have a significant impact on the distribution of black widow spiders. These events can shift populations to areas they previously did not inhabit and diminish their populations in areas where they were once present. Wildfires are a common natural disaster that can impact black widow spider populations. The destruction of vegetation that occurs during a wildfire can eliminate the spiders’ hiding places and disrupt their food supply, leading to a decline in population. However, some black widow populations have shown resilience, as they can quickly repopulate areas affected by wildfires.
Another natural disaster that can affect the distribution of black widow spiders is hurricanes, particularly in coastal regions. These events can cause flooding and strong winds, both of which can impact black widow populations by flushing spiders from their habitats or damaging their webs and nests. The aftermath of hurricanes can also attract more spiders to urban areas in search of shelter and food.
Earthquakes can also affect black widow spider populations by altering the structure of their habitats – often in unexpected ways. For example, an earthquake may cause land to shift, exposing previously underground nests or causing the collapse of man-made structures where spiders were residing.
Natural disasters are unpredictable and can cause significant shifts in the distribution of black widow spiders. However, these spiders are adaptable and may be able to thrive in new habitats created as a result of these events. To learn more about the impact of natural disasters on black widows, check out this article.
3. Habitat Fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation is another significant factor that affects the distribution of black widow spiders. Fragmentation of habitat means breaking up of continuous habitat into smaller, isolated patches which can no longer support the same species or population. For black widow spiders, habitat fragmentation can lead to population decline and even local extinction.
Black widow spiders prefer undisturbed and hidden habitats. The fragmentation of their habitat can decrease the availability of their preferred natural habitats, causing them to search for new habitats, including urban areas. Urbanization is a significant contributor to habitat fragmentation as it causes loss and fragmentation of natural habitats.
According to a study conducted in California, urbanization has resulted in the increased presence of black widow spiders in urban areas. Black widow spiders are capable of adapting to unusual habitats, and urban areas provide suitable conditions for their survival. In such urban areas, black widow spiders can be found in structures, gardens, green belts, and similar habitats.
Another impact of habitat fragmentation is the loss of genetic diversity, which can have severe consequences on the population’s survival. Fragmentation can cause genetic isolation and bottleneck effect, leading to the loss of genetic variation. This can make black widow populations more vulnerable to environmental stressors or diseases.
Habitat fragmentation is a significant factor affecting the distribution of black widow spiders, causing population declines, and even local extinction. Urbanization is a notable type of fragmentation that can have positive consequences for black widow spiders, leading to unusual habitats the spiders can inhabit. However, habitat fragmentation generally causes loss of genetic diversity and can put species at risk of stressors and diseases. Understanding the impact of habitat fragmentation can help in conservation efforts to protect black widow spiders and their habitats.
Reference: unusual habitats black widow spider
Conclusion
Summing up the Effect of Climate on the Distribution of Black Widow Spiders
In conclusion, it is evident that the distribution of black widow spiders across the world is influenced by climate factors, specifically temperature, precipitation, and humidity. As a result of climate change, the distribution of the species has been observed to shift in many regions.
In North America, black widows have been seen moving into northern territories, while in Europe, sightings of the spider are increasing in countries previously thought to be unsuitable habitats. In Asia, the species has been expanding its range into new territories.
Climate change is not the only factor that impacts the distribution of black widow spiders. Urbanization, natural disasters, and habitat fragmentation also contribute to distribution shifts. With more people moving into urban areas, black widow sightings are increasing in cities across the globe.
Furthermore, the importance of understanding the distribution and threat of black widow spiders cannot be overemphasized. Knowing where the spiders are located can help in the development of effective management strategies.
In addition, understanding the symptoms and treatment of black widow bites is critical in saving lives from this venomous spider. While the spiders’ bites are venomous, fatalities are rare. However, medical attention is necessary in the event of a black widow bite to prevent severe reactions.
In conclusion, awareness of the global black widow distribution, black widow bites, and black widow sightings in urban areas is crucial for everyone in identifying the potential threat and taking appropriate precautions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common type of black widow spider?
The most common type of black widow spider is the southern black widow (Latrodectus mactans).
Can black widow spider venom be deadly?
Yes, black widow spider venom can be deadly, particularly for children, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems.
Do black widow spiders only live in hot climates?
No, black widow spiders can live in a variety of climates, but they typically thrive in warm and moist environments.
How do black widow spiders catch their prey?
Black widow spiders use their webs to catch their prey, which typically consists of insects.
Can black widow spiders be found in urban areas?
Yes, black widow spiders can be found in urban areas, particularly in areas with gardens or other green spaces.
Are male black widow spiders venomous?
Male black widow spiders are venomous, but their venom is not as potent as that of the females.
What should you do if you are bitten by a black widow spider?
If you are bitten by a black widow spider, seek medical attention immediately.
Can black widow spiders be kept as pets?
While black widow spiders can be kept as pets, it is not recommended due to the potential danger of their venom.
Are black widow spiders nocturnal?
Black widow spiders are not strictly nocturnal, but they are most active at night.
Can black widow spiders be found in every continent?
No, black widow spiders are primarily found in North and South America, but they can also be found in parts of Europe, Asia, and Australia.






