As humans, our fascination with the natural world has led us to study and explore its many mysteries. One such mystery is the venom of the black widow spider and its effects on the brain. The powerful neurotoxin in the venom has proven to be both intriguing and deadly, and scientists have been studying its properties for years. In this article, we will delve into the composition of black widow spider venom, its effects on prey and humans, and the potential uses for the venom in neurology. But first, let’s take a closer look at what black widow spider venom really is.
What is Black Widow Spider Venom?

Black Widow Spider Venom is a potent toxin that is secreted by female black widow spiders. The mere thought of this venom can make one feel uneasy, but it is important to understand its composition and effects. The venom is a complex mixture of neurotoxins that attack the nervous system and can be fatal to small prey. While it may be toxic to some, others believe that the venom could hold powerful therapeutic potential. Let’s explore the composition of the venom and the effects it has on prey.
Composition of the Venom
Black Widow spider venom is a complex mixture of various proteins and enzymes that result in potent neurotoxic effects on its prey or victims. The venom also contains various nucleotides such as adenosine and guanosine, free amino acids, and monoamines. However, the specific chemicals present in the venom can vary depending on the species, location, and age of the spider.
According to research, there are six major components that make up Black Widow spider venom. These include α-Latrotoxin, α-Latroinsectotoxin, Latrodectin, Reductase, Hyaluronidase, and Neuropeptide α-latrotoxin. Each of these components has a different function and effect on the victim.
| Component | Description |
| ——————————- | ————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————- |
| α-Latrotoxin | One of the primary components of Black Widow spider venom and its most potent neurotoxin. It triggers the release of neurotransmitters from nerve endings, which can result in muscle rigidity, spastic paralysis, respiratory failure, and even death. |
| α-Latroinsectotoxin | Affects insects more than humans and other mammals. Causes flaccid paralysis, hindering the insect’s ability to move or fly, leading to its death. |
| Latrodectin | Disrupts nerve endings and causes excruciating pain to the victim |
| Reductase | Breaks down cell membranes and promotes the spread of venom throughout the victim’s body. |
| Hyaluronidase | Destroys hyaluronic acid, a substance that helps to hold cells together, leading to tissue damage. Additionally, Hyaluronidase speeds up the spread of venom throughout the victim’s body. |
| Neuropeptide α-latrotoxin | Similar to α-Latrotoxin, it affects neurotransmitter release, leading to rigid paralysis. It also affects blood pressure and the heart rate of the victim. |
The venom of a Black Widow spider is a complex mixture of various chemicals that attack different parts of a victim’s body. Understanding the composition of the venom is important for researchers who are working to find ways to treat victims affected by it. If you want to learn more about Black Widow spiders anatomy and their venom, check out this article about the anatomy of Black Widow fangs and its venom.
The Effects of the Venom on Prey
Black widow spiders use their venom to overpower and kill their prey. When attacking their prey, the spiders employ a unique method of injecting the venom into the body of the prey, then waiting for it to take effect before consuming it. The black widow spider venom is known to contain various compounds that affect its prey in different ways. One of the key effects of the venom is paralysis, which incapacitates the prey and renders it unable to escape.
Studies have shown that the neurotoxin in black widow spider venom can cause prolonged muscle contractions and spasms in the prey. This is due to the presence of α-latrotoxin, a toxic protein that, when introduced into the prey, causes widespread damage to the nervous system, leading to paralysis and death. The venom also contains a range of other toxins and enzymes that can cause tissue damage, disrupting normal cellular function in the prey, and disrupting the proper functioning of the immune system.
The venom has evolved to target certain types of prey, such as insects and other arachnids, which have specific physiological features that make them more vulnerable to the venom. For example, the venom is known to have a more pronounced effect on insects, which have simpler nervous systems than mammals. This makes them more susceptible to the neurotoxic effects of the venom, effectively rendering them defenseless against the black widow spider’s attacks.
The effects of the venom on prey are quite profound, and are a testament to the evolutionary adaptations that the black widow spider has developed over thousands of years. Understanding the venom’s composition and effects on prey can help scientists develop new treatments for various ailments, and can inform strategies for avoiding black widow spider bites, which can have serious health consequences if left untreated.
Black Widow Spider Bites on Humans

It’s important to understand the effects that a black widow spider bite can have on humans. The venom of these spiders can cause a range of symptoms and can even be deadly in some cases. In this section, you’ll learn more about these bites, including the common symptoms and the neurological effects of the venom on the human body. You’ll also find tips on how to protect yourself from black widow spider bites. So, let’s delve deeper into this intriguing and potentially dangerous topic. For more information on the anatomy and chemistry of black widow venom, check out this article.
Common Symptoms
Black widow spider bites on humans can cause several uncomfortable symptoms. These symptoms usually occur within an hour of the bite and can last up to 3 days. The most common symptoms of a black widow spider bite include:
- Sharp pain at the bite site
- Redness and swelling
- Muscle cramps and spasms
- Abdominal cramping and pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sweating
- Headaches
- Weakness and tremors
It is important to note that not everyone experiences the same level of symptoms from a black widow spider bite. Some people may have a mild reaction, while others may experience severe symptoms. In extreme cases, a black widow spider bite can be fatal, particularly in children and the elderly.
It’s important to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect you have been bitten by a black widow spider. The symptoms can be managed with proper medical treatment, but delaying treatment could lead to serious complications. Visit your doctor or seek emergency medical care if you experience any of these symptoms after a suspected black widow spider bite.
To learn more about the recovery time after a black widow spider bite, visit /black-widow-spider-bite-recovery-time/.
The Neurological Effects of the Venom
The venom of a black widow spider has significant neurological effects on humans, and can have severe impacts on the central nervous system. When injected into a human, the venom spreads rapidly throughout the body, affecting muscles, organs, and brain function. Some of the most common neurological symptoms associated with black widow spider bites include muscle cramps, severe pain, and stiffness in the shoulders, chest, and abdomen.
Other neurological symptoms may involve:
- Tremors and muscle spasms
- Excessive sweating and salivation
- Dizziness and fainting
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headaches and migraines
- Restlessness and anxiety
Black widow spider venom can also have significant psychotropic effects, leading to hallucinations, altered states of consciousness, and other cognitive disruptions. These impacts are due to the presence of neurotoxins in the venom that disrupt the normal functioning of nerve cells and neurotransmitters in the brain.
Research suggests that the venom works by interfering with calcium ion channels in nerve cells, which disrupts communication between neurons and causes them to fire abnormally. This can lead to the release of an excessive amount of neurotransmitters, which further disrupts normal brain function and can lead to seizures and other serious conditions.
Despite the potential dangers associated with black widow spider venom, recent studies have suggested that the neurotoxins in the venom may have some therapeutic applications in the field of neurology. For example, some researchers have explored the potential use of these toxins for treating certain types of seizures and other neurological disorders. However, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms underlying these effects and determine the potential risks and benefits of such treatments.
If you’re interested in learning more about black widow spider venom, there are a number of resources available online. For example, you may want to check out our article on the evolutionary history of black widow spider venom, which explores how and why these spiders developed such potent toxins. Other helpful resources include articles on the differences between black widow and brown recluse spiders and health risks associated with black widow spider bites. Additionally, if you live in an area where black widow spiders are common, it’s important to take steps to protect yourself from bites. Check out our guide on how to avoid black widow spider bites in your house and garden for more information.
How the Venom Affects the Brain
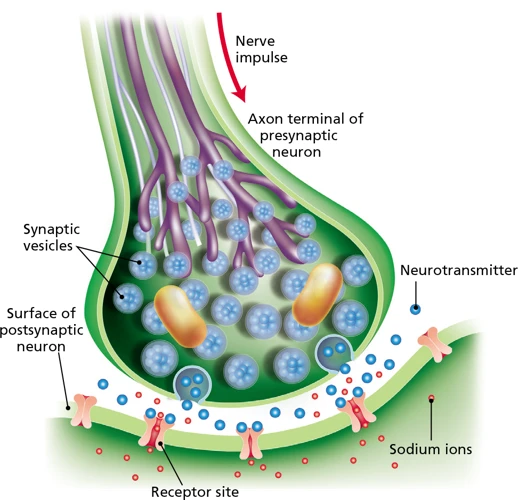
Black Widow spider venom affects the brain primarily by targeting nerve cells and blocking the release of neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemicals in the brain that transmit signals between individual nerve cells, allowing different regions of the brain to communicate with each other. The venom contains a specific toxin called alpha-latrotoxin, which triggers the release of these neurotransmitters in abnormal quantities. This unregulated release can cause overstimulation of nerve cells, leading to severe neurological symptoms.
Additionally, black widow spider venom has been found to target specific regions of the brain. Researchers have discovered that the venom can bind to receptors in the brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord. These regions of the brain are responsible for controlling movement and regulating important bodily functions such as breathing and heart rate. By binding to these receptors, black widow spider venom can disrupt normal neurological function, resulting in muscle spasms, difficulty breathing, and even paralysis.
Although the exact mechanisms by which black widow spider venom affects the brain are still being studied, researchers have made significant strides in understanding the venom’s impact on neurotransmission and specific brain regions. These findings have important implications for the development of treatments for neurological disorders.
It should be noted that the effects of black widow spider venom on the brain are not fully understood and may vary depending on the individual and the amount of venom injected. To learn more about black widow spider venom and its effects, refer to our article on black widow spider venom chemistry.
Research Findings on the Venom’s Neurological Impact
Recent studies have shown that Black Widow spider venom has a profound effect on the neurological system of its prey and even humans. The venom contains latrotoxins, which target the nervous system’s synapses and nerve endings, causing a range of symptoms. To better understand the impact of Black Widow spider venom on the nervous system, several studies have been conducted.
One study published in the Journal of Proteomics examined the effects of Black Widow venom on rats. The researchers found that the venom altered the expression of specific proteins in the brain, which led to neurological dysfunction.
Another study published in the Journal of Neurochemistry focused on the action of the venom on synapses in the central nervous system. The study found that the venom caused extensive damage to nerve endings by opening up calcium channels that triggered the release of neurotransmitters.
A third study published in the Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins explored the effect of Black Widow venom on the brain’s neurotransmitters. The researchers found that the venom changed the levels of several neurotransmitters, including dopamine, acetylcholine, and GABA, leading to a range of neurological symptoms.
These studies suggest that Black Widow spider venom has a significant impact on the neurological system. It can cause a range of symptoms, including muscle spasms, paralysis, and even death, depending on the victim’s age and overall health.
Despite its dangerous nature, some researchers are exploring the potential benefits of this venom in neurology. One study published in the Journal of Experimental Biology found that latrotoxins in the venom could help treat neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s by promoting synapse repair.
As research into the effects of Black Widow spider venom on the nervous system continues, it offers valuable insights for medical professionals treating spider bites as well as researchers looking for new treatments for neurological diseases.
| Study | Journal | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Study 1 | Journal of Proteomics | Effects on protein expression in the brain |
| Study 2 | Journal of Neurochemistry | Actions on synapses in the central nervous system |
| Study 3 | Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins | Effect on neurotransmitters in the brain |
To learn more about Black Widow spider venom, be sure to check out our articles on the Life Cycle and Venom of this fascinating spider, and also some fascinating facts about their venomous bite.
Possible Uses for the Venom in Neurology
Studies have shown that black widow spider venom can potentially be used in treating neurological disorders. The neurotoxin in the venom specifically targets nerve cells, which can lead to paralysis or muscle spasms. However, scientists are researching ways to use the venom’s unique properties for positive effects.
One area of research is the potential use of the venom in pain management. The neurotoxin in the venom inhibits the release of neurotransmitters that transmit pain signals in the body. This has led to the development of medications that mimic the effects of the venom, which could potentially be used to treat chronic pain.
Another possible use for the venom is in treating neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Research has shown that the venom contains peptides that can cross the blood-brain barrier and regulate the activity of enzymes involved in the formation of amyloid plaques. Amyloid plaques are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease and can lead to the destruction of nerve cells.
Scientists are also studying the potential use of the venom in treating strokes. The neurotoxin in the venom can target nerve cells that have been damaged by a stroke and accelerate the healing process. This could potentially lead to faster recovery times and better outcomes for patients.
While these potential uses for black widow spider venom in neurology are exciting, more research is needed to fully understand the venom’s effects and to develop safe and effective treatments. However, these findings show that even dangerous substances like spider venom can have beneficial properties if used properly.
Did you know? Spider venom can also have a positive impact on the immune system. Click here to read more about black widow spider bites and the immune system.
| Possible Uses of Black Widow Spider Venom in Neurology | Effects on the Body |
|---|---|
| Pain management | Inhibition of pain signal transmission |
| Treating neurological diseases | Crossing blood-brain barrier, regulation of enzyme activity |
| Treating strokes | Accelerating healing process in damaged nerve cells |
How Can We Protect Ourselves from Black Widow Spider Bites?
It’s important to take precautions to protect ourselves from black widow spider bites, as they can have severe neurological effects. Here are some tips on how to avoid being bitten:
1. Wear Protective Clothing: When outdoors, especially in areas where black widows are known to live, wear gloves, long-sleeved shirts, and boots to protect your skin from contact with the spiders.
2. Be Careful When Moving Objects: Black widows often like to hide in dark, secluded places such as under rocks, in woodpiles and in debris. When moving objects that have been sitting for a while, such as lumber, rocks, or gardening equipment, wear gloves and use caution.
3. Use Pest Control Strategies: Regular pest control maintenance can aid in decreasing the prevalence of black widows and other dangerous spiders in your living areas. It’s important to keep your living spaces clean and clutter-free to prevent spiders from making themselves at home in your living space.
4. Use Insect Repellent: Products containing DEET provide protection against spiders and other insects that can bite or sting. Be sure to apply these products according to the instructions in order to avoid accidental side effects.
5. Seek Professional Removal: If you notice a spider that you believe is a black widow spider in your living quarter, do not try to remove it yourself. Instead, call a professional pest control service that can safely and effectively remove the spider without placing you at additional risk.
By taking these precautions, we can decrease the likelihood of being bitten by a black widow spider and minimize the risk of the neurological effects of the venom.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the neurotoxic effects of black widow spider venom on the human brain are significant and can cause serious health complications. The venom contains a cocktail of chemicals that work together to target the nervous system of the prey and cause paralysis. This is achieved by interfering with the release and uptake of neurotransmitters which are essential for proper brain function.
When a human is bitten by a black widow spider, the neurological effects can be severe and may cause muscle contractions, seizures, and even death. Although advances in medical treatment have improved the prognosis for those bitten by a black widow spider, prevention is the most effective way to avoid the dangers of their venom.
Awareness of the black widow spider and its habits is the first step in protecting oneself from their bites. Precautions such as wearing protective clothing and avoiding outdoor activities during peak spider season can help reduce the risk of being bitten. If a bite does occur, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
In addition to its harmful effects, black widow spider venom may have potential applications in the field of neurology. Research has shown that the compounds found in the venom have an affinity for specific receptors in the brain. This could potentially lead to the development of new drugs that target these receptors and could be used to treat neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease.
Overall, the study of the neurological effects of black widow spider venom is an important area of research that has the potential to improve our understanding of the brain and lead to the development of new therapies for neurological disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I do if I get bitten by a Black Widow Spider?
You should seek medical attention immediately, especially if you’re experiencing severe symptoms such as muscle spasms or difficulty breathing.
How can I identify a Black Widow Spider?
Black Widow Spiders are black with a distinctive red hourglass shape on their abdomen.
How toxic is Black Widow Spider Venom?
Black Widow Spider Venom is highly toxic, and can be fatal if left untreated.
What are the common symptoms of a Black Widow Spider bite?
Symptoms can include muscle cramps, abdominal pain, nausea, and difficulty breathing.
Why is the Black Widow Spider Venom so effective?
The venom is made up of neurotoxins that attack the nervous system, ultimately paralyzing the prey.
Can Black Widow Spider Venom be used for medical purposes?
Yes, researchers are studying the potential for the venom to treat neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
How do Black Widow Spiders catch their prey?
They use their webs to ensnare prey, and then bite them with their fangs to inject venom.
Where are Black Widow Spiders typically found?
They are found throughout the world, but are most common in warm and dry climates.
Can children and pets be affected by Black Widow Spider bites?
Yes, children and pets can be affected by the bites, and may be more vulnerable to severe symptoms.
What is the mortality rate for Black Widow Spider bites?
The mortality rate is less than 1%, but severe symptoms can lead to hospitalization and potential long-term effects.