Are black widow spiders dangerous? This is a question that has been asked by many people around the globe. Known for their venomous bites, black widow spiders are a fascinating yet terrifying species. Although they are not aggressive towards humans, their bites can be deadly if not treated immediately. In this article, we will discuss the geographic distribution of black widow spiders across the globe, their habitat, behavior, and the impact of human activities on their populations. We will also cover prevention and treatment methods for black widow spider bites. So, let us delve into the world of black widow spiders.
Habitat and Behavior

The habitat and behavior of black widow spiders is as fascinating as it is dangerous. These arachnids can be found all around the world, and they have adapted to a wide range of environments. From dark basements to sunny gardens, black widows are a hardy and versatile spider species. Their behavior is generally solitary, and they will only interact with other spiders during mating season. However, their venomous bite and unique reproductive habits have made them a subject of fascination and fear. Understanding their habitat and behavior is key to avoiding dangerous interactions with these spiders. To learn more about black widow venom and their life cycle, check out our related article on the topic.
North America
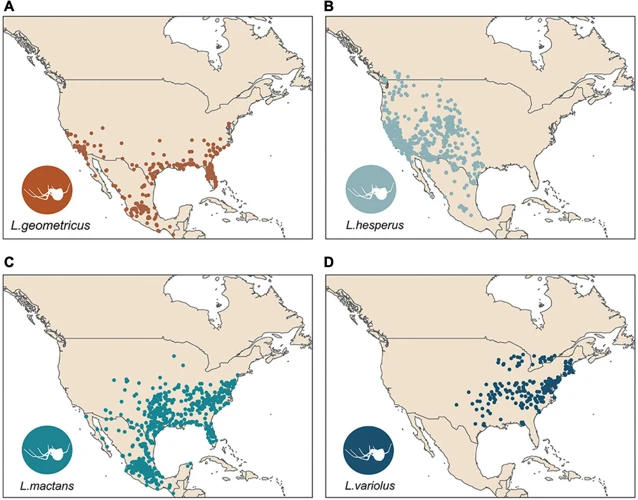
North America is the most well-known habitat of black widow spiders. These spiders are indigenous to the continent, and their populations range from Canada down to Mexico. In the United States, black widows can be found in all states, except Alaska. They thrive in warm, dry climates and commonly dwell in dark, sheltered areas such as garages, attics, and basements.
| Region | Species | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Eastern Black Widow | L. mactans | Most common species found; easily identified by the characteristic red hourglass shape on the female’s abdomen |
| Southern Black Widow | L. mactans | Similar to the Eastern species, but may have additional white or red markings on the abdomen; found in the southeastern US |
| Northern Black Widow | L. variolus | Darker in color than other species; found in northeastern US and southeastern Canada; less venomous than other species |
Research indicates that black widow venom is about 15 times more potent than that of a rattlesnake, yet only a small percentage of bites are fatal. Symptoms of a black widow spider bite may include mild to severe pain, muscle cramps, and spasms. Recovery time can range from a few days to several weeks, and medical attention may be required in severe cases.
To prevent black widow spider bites in North America, it is recommended to take proactive steps such as wearing gloves and protective clothing when working in areas that might harbor black widows, shaking out outdoor clothing and equipment before use, and properly storing outdoor gear. For more information on how to avoid black widow spider bites, check out our guide.
South America
South America is home to several species of black widow spiders, including the black widow Latrodectusmactans and the red-legged widow Latrodectus geometricus. The black widow Latrodectusmactans, also known as the South American black widow, is found throughout the continent, while the red-legged widow is found mainly in the southern regions of South America.
The South American black widow is mainly found in Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay, but can also be found in other countries such as Peru, Ecuador, and Bolivia. This species prefers warm and humid areas such as forests, agricultural fields, and urban areas. They are often found in darker areas such as under rocks or logs, or in sheds and garages.
The red-legged widow spider is known for its striking red legs and is found primarily in Chile and Argentina. This species is much less venomous than the South American black widow and is typically not considered a significant health threat to humans.
In terms of behavior, South American black widows are known to be relatively aggressive and will bite if disturbed. Their venom is similar to that of the North American black widow and can cause symptoms such as severe muscle cramps, abdominal pain, and respiratory distress. Fortunately, deaths from black widow spider bites are rare and can be treated with antivenom.
In the table below is a summary of the key information about black widow spiders in South America.
| Species | Key Characteristics | Distribution | Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|
| South American black widow (Latrodectusmactans) | Mainly black with a red hourglass-shaped marking on the underside of the abdomen | Mainly in Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay, but also in Peru, Ecuador, and Bolivia | Warm and humid areas such as forests, agricultural fields, and urban areas, often in darker areas such as under rocks or logs, or in sheds and garages |
| Red-legged widow (Latrodectus geometricus) | Mainly black with bright red legs | Primarily in Chile and Argentina, but also in other parts of South America | Rocky areas, under logs and debris, typically in drier regions |
If you are interested in learning more about the health risks and effects of black widow bites, please check out our article on black widow spider bite health risks.
Europe
Europe is not home to any native species of black widow spider, but sightings have been reported in various countries across the continent. Although most of these sightings are of non-native species which have been introduced inadvertently with imported goods. Non-native species prevalent in Europe are the Latrodectus mactans, commonly known as the Southern Black Widow and Latrodectus hesperus, commonly known as the Western Black Widow.
These spiders are usually spotted in the warmer months, with more sightings in southern European countries such as Spain and Portugal. Many black widow spiders have also been found in the UK on imported goods, but these have usually been identified and destroyed before they become established in the wild.
It is important to note that black widow spider bites in Europe are rare, but they can occur and the bites can be dangerous. If you are bitten, seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms of a black widow spider bite include muscle pain and spasms, abdominal cramps, and nausea. The venom also affects the immune system, and can cause respiratory problems, as well as affecting brain function in severe cases.
Prevention: To prevent black widow spider infestations, it is important to inspect imported and stored goods regularly, as well as practicing good hygiene and sanitation measures. It is also recommended to wear protective clothing when handling materials that may be infested with spiders.
Treatment: If bitten, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. The treatment will depend on the severity of the symptoms, but it may include pain management, muscle relaxers, and antivenom medication.
It is always important to take necessary precautions when dealing with black widow spiders, as their bites can be dangerous. By being aware of their habitat and behavior, as well as taking preventative measures, you can greatly reduce your risk of being bitten.
Africa
The distribution of Black Widow spiders across Africa is relatively limited. These spiders are known to live in the southern parts of the continent, including countries such as South Africa and Namibia. The reason for their limited distribution could be due to the lack of suitable habitats and climates for them to thrive in.
In South Africa, the Black Widow spider is known as the “Button spider” due to its distinctive red or orange hourglass-shaped marking on the abdomen. This marking serves as a warning sign to potential predators, indicating the spider’s venomous nature. While the venom of Black Widow spiders found in Africa is similar to that of their North American counterparts, studies have shown that it may be less potent.
Table:
| COUNTRY | REGION | NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| South Africa | Southern parts of the country | Black Widow spider is known as the “Button spider” |
| Namibia | Northern parts of the country | Black Widow spider has been found in desert areas |
While there are not many reported cases of Black Widow spider bites in Africa, it is still important to exercise caution when in areas where these spiders are known to exist. As with all cases of spider bites, seeking medical attention is crucial for proper treatment and avoiding potential complications. To learn more about the effects of Black Widow spider venom on the human body, you can read about brain effects of Black Widow venom.
Asia
Asia is home to a variety of different black widow species. One of the most prevalent is the Latrodectus hasselti, which is commonly known as the redback spider. This spider species is found throughout Australia and its surrounding areas, including parts of Asia. The redback spider creates tangled webs in dry, sheltered areas such as beneath stones, logs, and outdoor furniture.
Another black widow species found in Asia is the Latrodectus elegans, which is commonly known as the elegant black widow. This spider resides in the northern regions of India, and its venom is more potent than that of many other black widow species. In fact, the venom of the Latrodectus elegans contains neurotoxins that can cause complete muscle paralysis and respiratory failure if left untreated.
Additionally, the Latrodectus tredecimguttatus, also known as the Mediterranean black widow, is found in parts of Europe, Africa, and Asia. This spider species is recognizable by its red hourglass marking, and can be found in a variety of habitats, from deserts to forests.
It’s important to note that while some black widow species in Asia can be dangerous to humans, they typically aren’t aggressive unless they are provoked. Avoiding outdoor clutter, wearing protective clothing, and using insect repellent can all be effective ways to prevent black widow spider bites.
The geographic distribution of black widow spiders in Asia mirrors the wide range of habitats and climates that can be found on the continent. While certain species may pose a threat to humans, these spiders generally play an important role in their ecosystems by helping to control pest populations.
Australia
Australia is home to a small population of black widow spiders, known as the Southern black widow (Latrodectus mactans hasseltii). These spiders are mainly found in the warmer regions of the country, such as South Australia, Western Australia, and New South Wales. While the Southern black widow typically prefers dry environments, it can also be found in backyards and gardens.
Unlike their North American counterparts, female Southern black widows do not always have a distinctive hourglass shape on their abdomens. They are typically dark brown or blackish in color with some lighter markings, and measure about a centimeter in length.
Southern black widows in Australia typically prey on insects, but have also been known to feed on small lizards and frogs. When threatened, they will bite and inject venom into their prey or predators. The venom of the Southern black widow is relatively potent, and can cause severe pain and muscle spasms in humans.
It is important to note that there have only been three recorded deaths from Southern black widow spider bites in Australia since the discovery of the species in the 1800s. This is possibly due to widespread education about the dangers of these spiders and the availability of antivenom.
One interesting fact about Australia’s Southern black widows is that they have been found to have a unique chemical in their venom that tricks the immune system into not recognizing the venom as harmful. This adaptation may allow the spider to inject more venom without triggering an immune response in their prey or predators.
While the risk of encountering a Southern black widow in Australia is relatively low, it is still important to be aware of their presence and take precautions when camping or exploring in spider-prone areas. If you suspect that you have been bitten by a black widow spider, seek medical attention immediately and consider using a topical pain relief cream or taking pain medication. Do not attempt to treat the bite on your own.
To learn more about black widow spider bites and how to prevent and treat them, check out our articles on related topics, including /black-widow-venom-pain/ and /black-widow-spider-bite-recovery-time/.
Native vs. Non-Native Species

Native vs. Non-Native Species
Black widows have adapted exceptionally well to their environments, which allows them to thrive in their native habitats. Native species tend to have specific adaptations that help them acquire food, shelter from predators, and other essential resources easily. This adaptability has allowed the black widow to become one of the most successful venomous spiders in the world.
However, due to human intervention, non-native black widow species have been introduced to various regions across the globe, causing a potential threat to native ecosystem and other species. For instance, people often transport goods, cars, and other commodities between countries, which could inadvertently lead to the transport of non-native black widows across borders. Agricultural practices might also be responsible for black widows’ expansion into non-native areas.
Non-native species often struggle to survive in their new environment, but the black widow can adapt and thrive in foreign regions just as well as native ones. This is an alarming trend because it poses a threat to native species, especially insects, and the ecosystem as a whole.
Black Widow Spider Bites and Immune System
Human Interaction and Impact on Black Widow Populations

Human interaction has a considerable impact on the black widow spider populations across the globe. Some people regard these spiders as dangerous and venomous, which often leads to fear and hatred towards them. Consequently, humans try to eliminate black widow spider populations, either through direct killing of the spiders or by destroying their habitats. Unfortunately, such actions threaten the survival of these spiders in some regions.
It is important to note that black widow spiders have a significant ecological role in controlling the population of insects such as mosquitoes, flies, and cockroaches. Hence, their elimination can lead to an increase in the number of these pests, which can cause a range of health problems. Additionally, the use of toxic pesticides to kill these spiders can also lead to environmental pollution and harm other non-target organisms.
Despite their aggressive reputation, black widow spiders rarely bite humans, unless they feel threatened or cornered. In most cases, bites occur when people accidentally come into contact with the spiders or disturb their webs. It is crucial to understand that not all bites result in fatalities. Still, in some severe cases, the bites can cause a range of symptoms, including muscle pain, nausea, seizures, and even death.
People can reduce their chances of getting bitten by black widow spiders by wearing protective clothing while working in areas prone to these spiders’ infestation. Additionally, it is advisable to avoid leaving clothes, towels, or shoes outside, as these spiders can lurk in such items. If someone gets bitten by a black widow spider, they must seek medical assistance immediately. There are antivenom treatments available for black widow spider bites, and a prompt response can save lives.
Ignoring the importance of black widow spiders in their environment can be detrimental to ecosystems and lead to negative health outcomes. Rather than fearing and eliminating these spiders, it is essential to learn about their ecology, behavior, and role in maintaining ecological balance. Doing so will allow humans to coexist with black widow spiders and other organisms in a harmonious manner.
To learn more about the dangers of black widow spider bites, visit /death-by-black-widow-spider-bite/. For more information about the anatomy of black widow spiders’ venom and fangs, check out our article on /anatomy-black-widow-fangs-venom/.
Prevention and Treatment of Black Widow Spider Bites
One of the best ways to prevent black widow spider bites is to avoid areas where they are commonly found, such as dark and cluttered spaces like garages, sheds, and outdoor storage units. If you do need to enter these areas, wear protective clothing like long-sleeved shirts and pants, sturdy gloves, and closed-toe shoes. Additionally, using an insecticide spray or dust in these areas can help to reduce the spider population.
If you do happen to get bitten by a black widow spider, seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms of a black widow spider bite can include muscle cramps, spasms, and pain that may spread to the chest, abdomen, or back. In some cases, these symptoms can be severe and even life-threatening, so it is important to get treatment as soon as possible.
Treatment for black widow spider bites may include anti-venom medication, pain relievers, muscle relaxants, or anti-seizure medications, depending on the severity of the symptoms. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary for more severe symptoms.
It is important to note that not all spider bites are from black widow spiders, and some bites may not require medical attention. If you are unsure if a spider bite requires medical attention, it is always safer to seek the advice of a healthcare professional.
To prevent future spider bites, regular cleaning and decluttering of storage areas can help to reduce the spider population. Additionally, sealing up cracks and gaps in doorways and windows can also help to keep spiders out of the home. Taking preventative measures and seeking medical attention if necessary can help to reduce the risk and severity of black widow spider bites.
Conclusion
After exploring the geographic distribution of black widow spiders across the globe, it is evident that these spiders have a wide range and can adapt to various habitats. From the deserts of North America to the rainforests of South America, and from the Mediterranean countries of Europe to the savannas of Africa and the forests of Asia and Australia, black widow spiders can be found in many regions.
Despite their reputation as venomous spiders, black widows are not aggressive towards humans and tend to retreat when they sense danger. However, caution should be exercised when handling objects in spaces commonly inhabited by these spiders, such as woodpiles, dark corners, and unused outdoor furniture.
It is also important to note that not all species of black widow spiders are native to the regions where they are found. Some species, such as the western black widow in Europe and the redback spider in Japan, were introduced and have established populations in these regions.
Human impact has also affected the behavior and reproduction patterns of black widows in urban areas. Eliminating potential habitats and food sources, such as insects, can lead to a decrease in the spider population.
In the event of being bitten by a black widow spider, seeking medical attention is crucial. Antivenom is available in areas where black widows are prevalent, and early treatment can prevent serious complications.
Overall, the distribution of black widow spiders is widespread, and they are a notable predator in many ecosystems. While their venom can be dangerous to humans, their importance in controlling insect populations should not be overlooked. Awareness of their habitats and understanding of their behavior can lead to coexisting peacefully with these fascinating creatures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a black widow spider?
A black widow spider is a venomous species of spider known for its shiny black body and red hourglass-shaped markings on its abdomen.
What is the habitat of black widow spiders?
Black widow spiders can be found on all continents except Antarctica. They prefer to live in dark, dry places such as wood piles, sheds, and other outdoor structures, as well as in undisturbed areas in and around homes.
What does a black widow spider eat?
Black widow spiders are carnivorous and primarily prey on insects, but they may also eat other spiders and small animals like lizards and frogs.
How potent is black widow venom?
Black widow venom is highly potent and contains neurotoxins that can cause severe symptoms like muscle pain, cramping, and spasms, as well as fever and sweating. In rare cases, it can even be fatal, particularly in young children and the elderly.
What is the difference between a male and female black widow spider?
Male black widow spiders are typically much smaller and have lighter coloration than females. They also lack the red hourglass marking on their abdomen that is characteristic of females.
How can I identify a black widow spider?
In addition to their shiny black body and red hourglass marking, black widow spiders also have shorter legs than other spider species and a round, bulbous abdomen.
What should I do if I am bitten by a black widow spider?
If you are bitten by a black widow spider, seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms can worsen over time and cause serious health complications, so prompt treatment is essential.
How can I prevent black widow spiders from entering my home?
To prevent black widow spiders from entering your home, seal all cracks and openings in doors and windows, keep outdoor structures like sheds and wood piles clean and clutter-free, and use insecticides and spider repellents as needed.
What is the most effective treatment for a black widow spider bite?
The most effective treatment for a black widow spider bite is antivenom, which can help neutralize the venom and reduce symptoms. Pain medication and muscle relaxants may also be used to manage symptoms.
Are black widow spiders endangered?
No, black widow spiders are not currently endangered. They are a relatively common species and can adapt to a variety of habitats and environments.