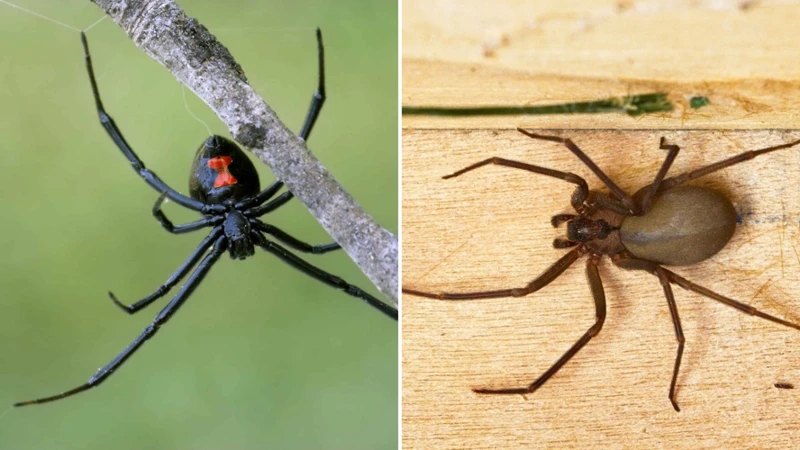
As humans, we have an inherent fear of dangerous creatures, and spiders are no exception. When it comes to venomous spiders, the black widow spider is often the first one that comes to mind. But how does it stack up against other dangerous spiders? Are they all as toxic and deadly as we’ve been led to believe? In this article, we’ll explore the world of venomous spiders and compare the black widow spider to its counterparts. We’ll take a closer look at their appearance, behavior, toxicity, lifespan, geographical range, prevention and treatment options, and debunk some common myths and misconceptions. So, sit tight and get ready to dive into the world of spiders.
Appearance
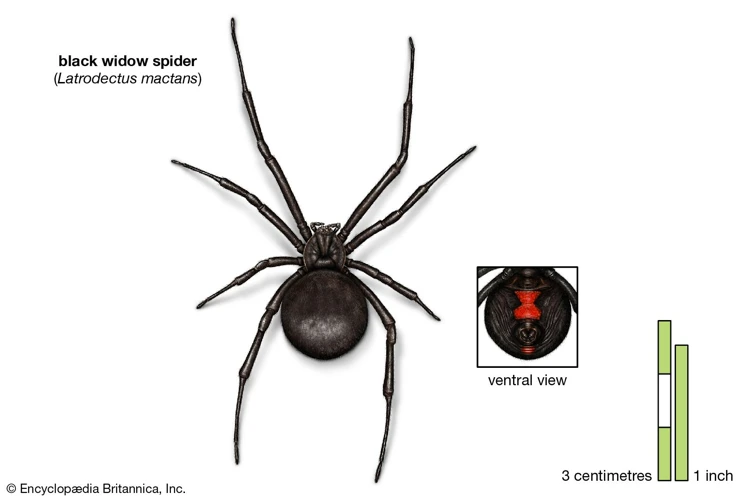

As one of the most recognizable and feared spiders in the world, the appearance of the Black Widow Spider is not easy to miss. However, how does it compare to other dangerous spiders in terms of appearance? In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the physical characteristics of the Black Widow Spider and compare them to those of other dangerous spiders. From the common misconceptions around the spider’s appearance to the myths that have long surrounded it, we will cover it all. So, before we get into the details, let’s first understand what the Black Widow Spider looks like.
Black Widow Spider
The black widow spider is a notorious and feared arachnid, known for its venomous bite and the distinctive hourglass marking on its abdomen. Here are some interesting facts about the black widow spider:
- The bite from a female black widow spider is considered particularly dangerous.
- The venom from a black widow spider is a neurotoxin, which can cause muscle spasms, cramps, and even paralysis in severe cases.
- Contrary to popular belief, not all female spiders kill and eat their male partners, and this only occurs occasionally with black widow spiders.
- The female black widow spider is larger than the male and is easily recognizable by the distinctive red hourglass marking on its abdomen.
- The black widow spider typically lives for about 1-3 years in the wild.
- Black widow spiders are found throughout North and South America, but mainly in warmer regions.
- Although the bite from a black widow spider can be dangerous, fatalities in healthy adults are rare, and medical treatment is usually successful.
Despite the fearsome reputation of the black widow spider, it is important to remember that these spiders usually only bite in self-defense, and are generally not aggressive towards humans unless threatened. It is important to take precautions to avoid getting bitten, such as wearing protective clothing when in areas where black widows are known to live and avoiding disturbing or handling these spiders unnecessarily. In case of a black widow spider bite, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial for successful treatment. More information about surviving black widow spider bites can be found through the following link.
Other Dangerous Spiders
There are several other species of spiders that are considered dangerous and potentially harmful to humans. One such spider is the Brown Recluse Spider, also known as the violin spider due to the characteristic violin-shaped marking on its body. These spiders are mostly found in the central and southern regions of the United States. The bite of a Brown Recluse Spider can cause tissue damage and even necrosis, but fatalities from their bites are rare.
Another dangerous spider is the Funnel Web Spider, which is native to Australia. These spiders are notorious for their aggressive behavior and their venom, which can be deadly. The male Funnel Web Spider is especially dangerous as their venom is more potent than that of the female.
The Redback Spider is another venomous spider found in Australia. Its venom is similar in potency to that of the Black Widow Spider, and it can cause pain, sweating, and nausea.
The Sydney Funnel Web Spider is another venomous spider found in Australia. Its venom is highly potent and can be deadly, especially in children. However, antivenom is available and has significantly reduced the number of fatalities resulting from their bites.
It is worth noting that despite their reputations, many of these dangerous spiders are not actively seeking to harm humans. They will only bite in self-defense or if they feel threatened. However, it is essential to be cautious around these spiders and to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect you have been bitten.
To learn more about myths and misconceptions surrounding the Black Widow Spider, check out the article ‘Myth of the Black Widow Spider Debunked‘.
Behavior
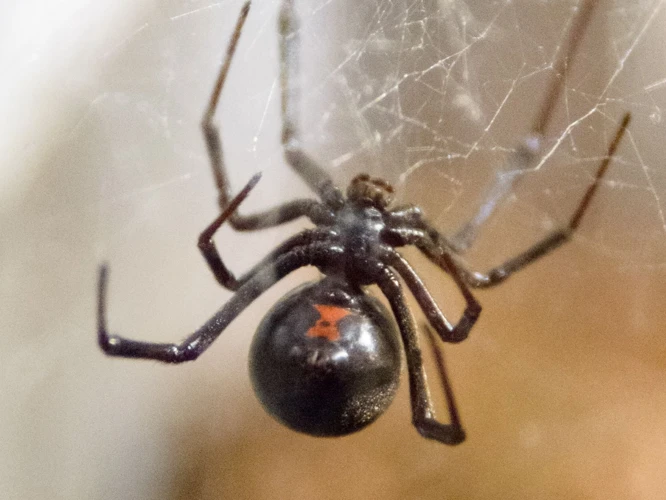

When it comes to behavior, spiders can exhibit both fascinating and terrifying tendencies. Understanding the behavior of dangerous spiders, such as the Black Widow Spider, is crucial in preventing potentially harmful encounters. From hunting patterns to mating rituals, these creatures are full of surprises. Let’s explore the behavior of dangerous spiders and shed some light on the myths surrounding them. To learn more about the myths and realities of Black Widow Spider hunting and feeding habits, click here.
Black Widow Spider
Black widow spiders are easily recognizable with their shiny black bodies and bright red hourglass-shaped marking on the underside of their abdomen. They typically measure about half an inch in body length and up to 1.5 inches including their long legs. Here are some additional details about black widow spiders:
- Habitat: They are commonly found in warm, dry regions around the world, including the United States, Mexico, and parts of Australia. They prefer to nest in dark, undisturbed areas such as garages, woodpiles, and outdoor furniture.
- Behavior: Black widows are solitary creatures and typically only come together for mating purposes. Female black widows are known to be cannibalistic and may even eat their male partners after mating.
- Toxicity: The venom of a black widow spider contains a neurotoxin that affects the nervous system. Symptoms of a black widow spider bite can include muscle pain and spasms, abdominal cramps, and difficulty breathing. While their venom is potent, deaths from black widow spider bites are relatively rare.
- Lifespan: Black widow spiders can live up to three years in the wild. Females tend to live longer than males and can produce multiple egg sacs during their lifetime.
- Geographical Range: Black widow spiders are found throughout the world, with several species native to the United States. The most common species in North America is the Southern black widow, which is found in the Southeastern U.S.
- Prevention and Treatment: To prevent black widow spiders from nesting in your home or yard, keep areas clean and free of clutter. Wear gloves while gardening or working in areas where black widows might be present. If bitten, seek medical attention immediately.
- Myths and Misconceptions: There are several myths surrounding black widow spiders, including the idea that they always live in large clusters (debunked here) and that only female black widows are venomous (debunked here). Another myth is that black widow spiders always kill and eat their male partners (debunked here).
Black widow spiders are fascinating creatures that have garnered a lot of attention in popular culture. While they can certainly be dangerous, it’s important to understand the facts about them and take precautions to avoid bites. Additionally, there is ongoing research into the potential benefits of black widow venom for medical purposes (read more here) and there is no evidence to support the common myth that black widow spiders have a strong connection to witches (read more here).
Other Dangerous Spiders
When looking at other dangerous spiders, there are several that come to mind. Let’s take a closer look at some of them and compare them to the black widow spider.
| Spider | Appearance | Toxicity | Lifespan | Geographical Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown recluse spider | The brown recluse spider is usually light brown in color and has a distinctive violin-shaped marking on its back. | The brown recluse spider’s venom can cause tissue damage and in rare cases, death. However, fatalities are extremely rare. | Brown recluse spiders typically live up to two years. | Brown recluse spiders are primarily found in the Midwestern and Southern United States. |
| Hobo spider | The hobo spider is usually brown in color and has a chevron-shaped pattern on its abdomen. | Hobo spider bites can cause skin lesions, but are not considered fatal. | Hobo spiders typically live for about two years. | Hobo spiders are found in the Northwestern United States. |
| Sac spider | Sac spiders can vary in color from light yellow to beige and have a distinct round body shape. | The venom of sac spiders generally causes mild to moderate symptoms and is not considered fatal. | The lifespan of sac spiders is around one year. | Sac spiders are found worldwide. |
| Wolf spider | Wolf spiders are usually brown or gray in color and have stripe-like markings on their body. | Wolf spider venom is generally not considered dangerous to humans. | Wolf spiders can live up to several years. | Wolf spiders are found worldwide. |
It is important to note that while these spiders can be dangerous, most bites occur when the spider is provoked or feels threatened. It is important to exercise caution around spiders and take measures to prevent encounters with them. Additionally, it is important to seek medical attention immediately if you believe that you have been bitten by a dangerous spider.
While there are many myths and misconceptions about the black widow spider, it is important to understand the facts about its behavior and toxicity. To learn more about the truth behind black widow venom, check out our article on the truth behind black widow venom.
Toxicity
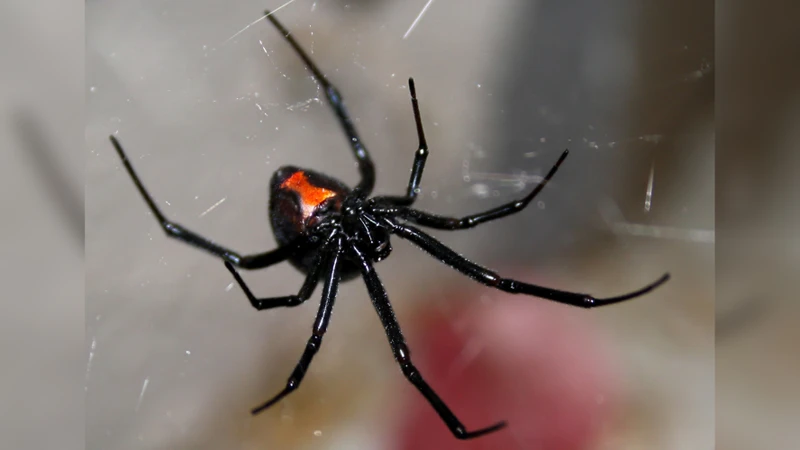

When it comes to venomous spiders, toxicity is a crucial factor to consider. The strength of the venom can determine the severity of the symptoms and ultimately impact the treatment required. Both the black widow spider and other dangerous spiders possess venom that can be harmful to humans. However, the types of venom and the effects it has on the human body may vary. It’s important to understand the toxicity of these spiders to determine the appropriate precautions and treatment methods. There are some myths circulating about the toxicity of black widows, including the belief that their venom is the deadliest of all spiders. Let’s debunk these myths and learn about the true toxicity of these spiders.
Black Widow Spider
The black widow spider is a highly poisonous arachnid found throughout the world. Here are some details about this dangerous spider:
- Appearance: Female black widow spiders are larger than their male counterparts with a shiny black body and a red hourglass marking on their abdomen. Males are usually smaller and lighter in color with no red markings.
- Behavior: Black widow spiders are shy and reclusive. They are most active at night and prefer dark and quiet places like woodpiles, garages, and sheds. They spin webs to catch their prey, which mostly includes other insects like ants, beetles, and flies.
- Toxicity: Black widow spider venom contains neurotoxins that affect the nervous system. The bite of a female black widow can cause serious symptoms like muscle spasms, cramps, and nausea. In extreme cases, it can even lead to death.
- Lifespan: Female black widow spiders can live up to 3 years in the wild, while males usually have a shorter lifespan of only a few months.
- Geographical Range: Black widow spiders are found throughout the world, with some of the most common species being the North American black widow and the European black widow.
- Prevention and Treatment: The best way to prevent black widow spider bites is to avoid areas where they are commonly found and to wear protective clothing and gloves when working in areas where they might be present. If bitten, seek medical attention immediately.
- Myths and Misconceptions: There is a common myth that female black widow spiders always eat their mates after mating. While this behavior does happen occasionally, it is not the norm.
If you want to learn more about the myth surrounding black widow spiders eating their mates, check out our article “Are Black Widows Really the Poisonous Spiders That Eat Their Mates?”.
Other Dangerous Spiders
When it comes to dangerous spiders, there are many different species that can pose a threat to humans. Here are some of the most notable ones:
- Brown Recluse Spider: Also known as the violin spider, the brown recluse spider is one of the most venomous spiders in the United States. They are typically found in the southern and central regions of the country and have a distinctive violin-shaped mark on their body. Their venom can cause severe tissue damage and, in rare cases, can even lead to death.
- Hobo Spider: The hobo spider is native to Europe but has also been found in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. They are often mistaken for the brown recluse spider but are less venomous. Their bite can still cause pain and swelling, and in rare cases, necrosis.
- Sydney Funnel-Web Spider: This spider is one of the deadliest in the world and is native to Australia. Their venom is highly toxic and can cause respiratory failure. Prompt medical attention is necessary after a bite from a Sydney funnel-web spider.
- Redback Spider: Another venomous spider found in Australia, the redback spider has a distinctive red mark on its body. Their bite can cause pain, swelling, and in some cases, can lead to serious illness.
- Wolf Spider: Wolf spiders are found throughout the world and are generally not considered dangerous to humans. However, some species do have venom that can cause pain, swelling, and other mild symptoms.
It’s important to note that while these spiders can be dangerous, bites are rare and can often be avoided with proper precautions. If you do encounter one of these spiders and are bitten, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately.
Lifespan
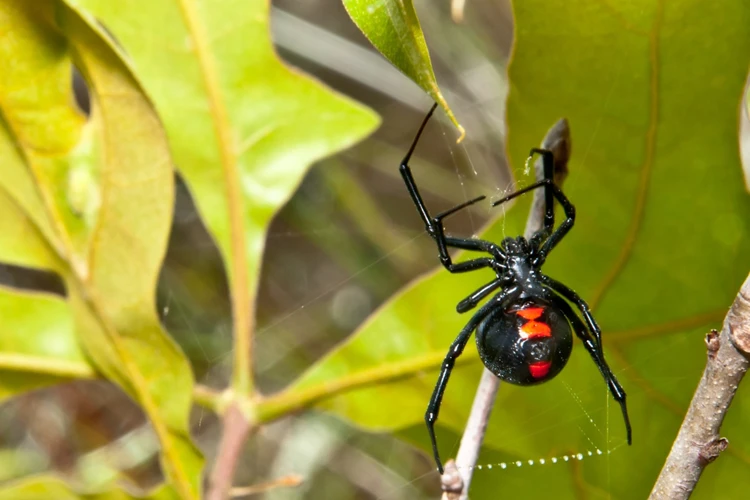

When it comes to spiders, lifespan is an important factor to consider. The amount of time a spider can live is influenced by various factors including diet, environment, and natural predators. As such, it’s interesting to compare the lifespan of black widow spiders and other dangerous spiders. Let’s take a closer look at their lifetimes and explore which species comes out on top.
Black Widow Spider
The Black Widow Spider is a venomous species known for its notorious reputation. They are primarily found in warm regions and are recognizable by their black-colored body with a signature red hourglass-shaped marking on the underside of their abdomen. Here are some more details about them:
| Appearance: | The Black Widow Spider is typically black with a shiny, hairless body. The females have a red hourglass marking on the underside of their abdomen. |
| Behavior: | Black Widows are known for being solitary and nocturnal. They typically build their webs near the ground in dark, secluded areas such as basements, garages, and other undisturbed areas. |
| Toxicity: | The venom of the Black Widow Spider contains a neurotoxin that can cause severe pain, muscle spasms, and cramps. In extreme cases, it can lead to paralysis and even death. |
| Lifespan: | The lifespan of a Black Widow Spider is typically around 1-3 years, but can vary depending on environmental factors. |
| Geographical Range: | Black Widow Spiders can be found in the warmer regions of the United States, as well as in other areas including Mexico, Central America, and South America. |
| Prevention and Treatment: | Prevention measures include sealing up cracks and crevices in buildings, removing clutter and debris from around the property, and wearing protective clothing when working in areas where Black Widows may be present. Treatment for a Black Widow bite may include pain medication, antivenom, and muscle relaxants. |
| Myths and Misconceptions: | One common misconception about Black Widow Spiders is that they always kill their male partners after mating. While this can happen, it is not always the case. |
While encounters with Black Widow Spiders can be frightening, it is important to remain calm and seek medical attention if you are bitten. With proper prevention and treatment measures in place, it is possible to minimize the risk of a Black Widow encounter.
Other Dangerous Spiders
When it comes to other dangerous spiders, there are quite a few species that can pose a threat to humans. Here are some noteworthy examples:
- Brown Recluse Spider: Also known as the “violin spider” due to the shape on its back, the brown recluse spider is found in the southern and central United States. Its venom can cause necrosis, or the death of living tissue, and can be especially dangerous to children and the elderly.
- Hobo Spider: Native to Europe but now found in the Pacific Northwest of the United States, the hobo spider is often confused with the brown recluse spider due to their similar appearance. Its bite can cause tissue necrosis but is rarely fatal.
- Sydney Funnel-Web Spider: Found in Australia, the Sydney funnel-web spider is considered one of the deadliest spiders in the world. Its venom can cause seizures, respiratory distress, and even death if left untreated.
- Redback Spider: Another spider found in Australia, the redback spider is related to the black widow spider and has similar neurotoxic venom. Its bite can cause intense pain, muscle weakness, and sometimes even paralysis.
- Yellow Sac Spider: Common in North and South America, the yellow sac spider is known to bite humans but its venom is not as potent as some other dangerous spiders. However, its bite can cause pain, redness, and swelling.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples of the many dangerous spiders found throughout the world. If you believe you have been bitten by a spider, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately.
Geographical Range
The distribution of Black Widow spider and other dangerous spider species can vary greatly depending on environmental factors. From the bustling cities of North America to the remote corners of Australia, these spiders have adapted to a wide range of habitats. Interestingly, the presence of these spiders does not necessarily indicate a lack of cleanliness; they can be found in both urban and rural areas. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at where these venomous spiders can be found across the globe and what factors contribute to their distribution.
Black Widow Spider
The black widow spider, scientifically known as Latrodectus mactans, is a venomous species that is found throughout North America. They are easily recognizable for their unique appearance; females have a shiny black body with a characteristic red hourglass-shaped marking on their abdomen. Males are smaller and have a lighter coloration with yellow and red bands on the abdomen.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | The black widow spider has a shiny black body with a characteristic red hourglass-shaped marking on its abdomen. Males have a lighter coloration with yellow and red bands on the abdomen. |
| Behavior | Black widow spiders are known to be reclusive and generally prefer dark, secluded areas to live in. They are known to be nocturnal and will only come out to hunt or explore at night. |
| Toxicity | The venom of the black widow spider is highly toxic to humans and can cause a wide range of symptoms, including muscle pain, cramps, sweating, and nausea. In severe cases, it can cause muscle spasms, respiratory failure, and even death. However, fatalities from black widow bites are rare, thanks to the availability of antivenom. |
| Lifespan | The lifespan of a female black widow spider can range from one to three years, while males only typically live for a few months. |
| Geographical Range | Black widow spiders are found throughout North America, particularly in the Southern United States and parts of Mexico. They can also be found in some parts of South America. |
| Prevention and Treatment | To prevent a black widow spider infestation, it is important to keep your surroundings clean and clutter-free. Seal up any entry points in your home, and avoid sticking your hands into dark crevices without proper protection. If you do get bitten by a black widow, seek medical attention immediately as their venom can be fatal without proper treatment. |
| Myths and Misconceptions | One of the most common myths surrounding black widow spiders is that females always eat their male counterparts after mating. While this can happen in some cases, it is not a common occurrence. Additionally, it is a common misconception that black widow spiders are aggressive and will attack humans unprovoked. In reality, they will typically only bite if they feel threatened or are disturbed. |
The black widow spider is a fascinating but dangerous creature that should be treated with caution. While their venom can be fatal, with the right precautions and treatment, the risk of a deadly encounter with a black widow is relatively low.
Other Dangerous Spiders
When it comes to dangerous spiders, there are a few other species that are worth mentioning. These spiders may not be as well known as the black widow, but they should still be taken seriously.
Brown Recluse Spider: also known as the violin spider, the brown recluse can be found in the southern and central United States. It has a distinctive dark brown violin-shaped marking on its head. Their venom can cause necrosis of the skin, and in severe cases can lead to organ failure and death. It’s important to seek medical attention if you have been bitten by a brown recluse.
Hobo Spider: found in the Pacific Northwest, the hobo spider is often mistaken for the brown recluse. They have a brown body with a lighter stripe down their back. Their venom can cause skin lesions and necrosis, but it’s still debated whether their bites can lead to death.
Sydney Funnel-Web Spider: native to Australia, the Sydney funnel-web spider has fangs strong enough to bite through shoes. Their venom attacks the nervous system and can quickly lead to death if left untreated. It’s important to seek immediate medical attention for anyone who has been bitten by a funnel-web spider.
Here’s a table summarizing the key information about these other dangerous spiders compared to the black widow:
| Spider | Appearance | Behavior | Toxicity | Lifespan | Geographical Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown Recluse Spider | Dark brown with a violin-shaped marking on its head | Usually shy and not aggressive towards humans | Venom can cause necrosis and in severe cases, organ failure and death | 1-2 years | Southern and central United States |
| Hobo Spider | Brown with a light stripe down their back | May be aggressive if provoked | Venom can cause skin lesions and necrosis, possible death | 1-2 years | Pacific Northwest |
| Sydney Funnel-Web Spider | Shiny black with large fangs | Aggressive towards humans and will attack if provoked | Venom attacks the nervous system and can quickly lead to death | 1-2 years | Australia |
While these spiders may be less common than the black widow, it’s important to be aware of their presence and take necessary precautions to avoid being bitten. If you suspect that you’ve been bitten by any of these spiders, seek medical attention immediately.
Prevention and Treatment

Prevention: It is always better to prevent bites from dangerous spiders rather than treating them later. One should be cautious and take some steps to avoid spider bites. The following are some preventive measures that can be taken:
1. Keep your home and surroundings clean and free of clutter. Spiders tend to hide in dark and cluttered places, so it is crucial to maintain cleanliness.
2. Use insecticides and repellents in your home regularly. Ensure that the products are pet-friendly if you have pets at home.
3. Seal all the cracks and gaps in your home, as spiders can enter through these spaces.
4. If you have an outdoor area or garden, ensure that it is well-maintained, and there are no places for spiders to hide. Clean up any debris or piles of leaves that might attract spiders.
5. Wear long-sleeved clothes and gloves when working in areas that spiders might inhabit.
6. Be cautious when handling rocks or firewood, as spiders tend to hide under them.
Treatment: If you get bitten by a black widow or any other dangerous spider, seek medical attention immediately. The following are some first-aid measures that can be taken before reaching a medical facility:
1. Wash the affected area with soap and water.
2. Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and pain.
3. Elevate the affected area to reduce swelling.
4. Take painkillers to ease the pain.
Remember not to apply home remedies like garlic, salt, or vinegar to the affected area. These remedies do not help and may cause further harm.
In severe cases, medical treatment may include antivenom, pain medication, and antibiotics. It is crucial to follow the doctor’s instructions and take the prescribed medication. Do not ignore any spider bites, even if they seem small, as they can cause severe complications.
Myths and Misconceptions
Despite their fearsome reputation, black widow spiders and other dangerous spiders often fall victim to myths and misconceptions. It’s important to separate fact from fiction when it comes to these arachnids.
Myth: Black widow spiders are aggressive and will attack humans unprovoked.
This is a common misconception about black widows. In reality, they only bite in self-defense and are not naturally aggressive toward humans. Bites usually occur when the spider is accidentally disturbed, such as when a person puts on clothes that have been hanging outside.
Myth: All black spiders are black widows.
While it’s true that black widow spiders are black, not all black spiders are black widows. There are many harmless spider species that also have a black coloration, such as the cellar spider or the black jumping spider. It’s important to know the distinct physical characteristics of each species to properly identify them.
Myth: Only female black widow spiders are venomous.
This is a popular misconception, but in reality, both male and female black widow spiders are venomous. However, females are more frequently encountered because males are smaller and less conspicuous.
Myth: All spider bites are dangerous and require medical attention.
This myth can be dangerous because not all spider bites are harmful. In fact, many spider bites are harmless and cause only mild irritation. However, it’s important to seek medical attention if you develop symptoms such as swelling, fever, or severe pain after a spider bite.
Myth: You can always tell if a spider is venomous by its appearance.
It’s not always easy to tell if a spider is venomous just by looking at it. Some venomous spiders have distinct markings, such as the red hourglass on the black widow spider, but others may be less noticeable. Always err on the side of caution and take appropriate precautions when encountering any spider.
It’s important to separate fact from fiction when it comes to black widow spiders and other dangerous spiders. By educating ourselves and dispelling these myths, we can better understand and coexist with these fascinating arachnids.
Conclusion
After comparing the Black Widow Spider to other dangerous spiders, it’s clear that while all spiders pose a certain level of risk, the Black Widow Spider is among the most venomous in North America. Its distinctive appearance, behavior, and toxicity make it a formidable opponent for any potential victim.
However, it’s important to remember that there are misconceptions about the Black Widow Spider and other dangerous spiders that can lead to unnecessary fear and panic. It’s also crucial to understand that bites from these spiders are rare, and most spiders will not attack unless provoked or threatened.
To prevent encounters with Black Widow Spiders and other dangerous spiders, it’s important to take precautions, such as wearing long sleeves and pants when in areas where they may reside, shaking out shoes and clothing before wearing them, and using caution when moving gardening materials or outdoor equipment.
If a bite does occur, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms of a Black Widow Spider bite can range from mild to severe, and a healthcare professional can provide the appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, while the Black Widow Spider may be a top contender in the world of dangerous spiders, it’s important to understand that there are steps that can be taken to avoid encounters and seek appropriate treatment if necessary. With knowledge and caution, it’s possible to coexist with the natural world, including these potentially dangerous creatures.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can any spiders defeat the Black Widow Spider in toxicity?
There are several spiders known for their venom, such as the Sydney funnel-web spider or the Brazilian wandering spider, that have more potent toxins than the Black Widow Spider.
What is the size of a Black Widow Spider?
An adult female Black Widow Spider typically ranges from half an inch to one and a half inches in length.
Do other dangerous spiders have red markings like Black Widow Spiders?
Yes, some spiders such as the Redback Spider found in Australia or the False Widow Spider found in Europe have red markings similar to the Black Widow Spider.
How long do Black Widow Spiders usually live?
The average lifespan of a Black Widow Spider is around one to three years.
Can the venom of a Black Widow Spider be fatal to humans?
While deaths from Black Widow Spider bites are rare, the venom can be fatal to young children, elderly individuals, or people with compromised immune systems.
What is the most effective way to prevent spider bites?
The most effective way to prevent spider bites is to wear protective clothing, use insect repellent, avoid areas where spiders may be present, and keep your home free of clutter.
Is it true that male Black Widow Spiders are more dangerous than females?
No, male Black Widow Spiders are not considered dangerous to humans as they rarely bite, and even if they do, their venom is much less toxic than that of the female.
Do Black Widow Spiders always eat their mates?
No, while cannibalism in the Black Widow Spider is a common occurrence, not all females will consume their mate after mating.
Can you die from a spider bite if left untreated?
If left untreated, some spider bites, such as the Brown Recluse or some species of Funnel Web spiders, can lead to severe tissue damage or even death.
Are Black Widow Spiders aggressive towards humans?
No, Black Widow Spiders are not typically aggressive towards humans and will only bite if they feel threatened or provoked.






