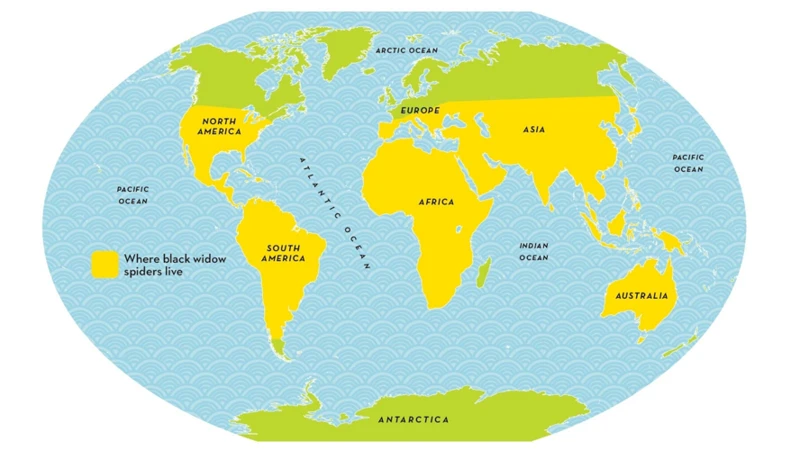
The black widow spider is notoriously known for its venomous bite and distinctive appearance with a red hourglass-shaped mark on its abdomen. But where exactly can you find black widows around the globe? And what about their behavior and characteristics? In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of black widow spiders, from their habitat to their geographic range and unique behavior. So, buckle up and discover with us the diverse geographic locations and behaviors of one of the most feared species of spider on the planet.
Black Widow Spider Habitat
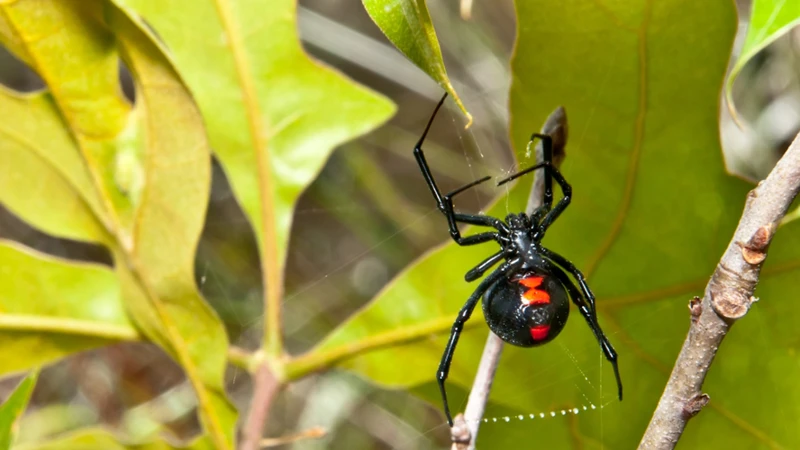

The habitat of the black widow spider is essential to understanding how and where these venomous creatures thrive. From their natural range to urban areas they’ve spread to, the black widow’s habitat is a significant factor in understanding their survival and proliferation. Factors such as climate, nesting sites, and adaptation play an essential role in the range and behavior of black widow spiders. In this section, we delve into the details of black widow spider habitats, including their range, migration, and distribution in various parts of the world.
Natural Habitat
Black widow spiders can be found in a variety of natural habitats around the world. These spiders thrive in warm and dry environments and are usually found in warm-temperate and tropical regions. They prefer to live in dark, secluded areas that provide hiding spots and ample prey.
The following table provides information about the natural habitats of black widow spiders:
| Habitat Type | Description | Geographic Range |
|---|---|---|
| Deserts | Black widow spiders can be found in deserts with sandy soil and rock formations where they can create burrows. | North America, South America, Africa, Asia, Australia |
| Forests | Black widow spiders are found in forests with dense vegetation, fallen logs, and leaf litter. They tend to build their webs near the ground or in hollow tree trunks. | North America, South America, Europe, Africa, Asia, Australia |
| Wetlands | Black widow spiders can be found in marshes, swamps and other wetland habitats with dense vegetation. They prefer to create their webs near the water. | North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Australia |
| Coastal Areas | Black widow spiders are often found in coastal areas with sandy soil and a warm climate. They prefer to make their nests in cracks and crevices or under rocks. | North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Australia |
Black widows are highly adaptable and can survive in a variety of environments. They have been known to live at elevations of up to 10,000 feet in some mountainous regions. Due to their adaptability, they are able to establish themselves in a wide range of ecosystems, including urban areas. In fact, they are often found in residential areas where they can hide in and around buildings and other structures.
Even though black widow spiders are highly adaptable, their range is still affected by a variety of factors such as climate, prey availability, and habitat destruction. For more information on the factors affecting the distribution of black widow spiders, check out our article on factors affecting black widow spider distribution.
Urban Habitat
Black widow spiders are known for thriving in human settlements and urban habitats. They can be found in various environments, including abandoned buildings, storage areas, garages, barns, and woodpiles. Black widow spiders prefer to live in dark and secluded areas that are undisturbed and usually build their webs in the corners of rooms or under furniture.
It is important to note that while black widow spiders are found in urban habitats, they can also be found in natural habitats and have adapted to live in a range of environments. They have developed the ability to survive in a range of temperatures and climates, which has led to their wide distribution around the world.
The table below lists some common nesting sites for black widow spiders in urban areas:
| Nesting Sites | Description |
|---|---|
| Abandoned buildings | Black widow spiders are often found in abandoned buildings that provide a perfect environment for them to thrive. |
| Storage areas | Black widow spiders can be found in storage areas where they have access to a range of materials to build their webs. |
| Garages and barns | Black widow spiders tend to thrive in garages and barns where there is plenty of clutter and debris to make webs in. |
| Woodpiles | Black widow spiders are known to make their webs in woodpiles, which provide a dark and secluded environment. |
While black widow spiders are not usually aggressive towards humans, it is important to exercise caution when in their habitat. Black widow spider bites can be dangerous and should be treated immediately by a medical professional. If you suspect that you have been bitten by a black widow spider, seek medical attention right away.
Black widow spiders are found in both natural and urban habitats around the world. They have adapted to live in a range of environments, including urban areas, and can be found in a variety of nesting sites. It is important to exercise caution when in their habitat to avoid potential bites.
Migration
Migration is a natural phenomenon observed in many spider species. Similarly, black widow spiders also exhibit migratory behavior. They prefer to migrate during summer or fall to avoid cold weather. Migration is usually observed in those populations, which exist in the northern regions of North America.
During migration, black widows travel in search of food, mates, and ideal nesting sites. They are good at dispersal over long distances by air, water, or other means. Black widows spread to other locations with the help of humans in cars, trucks, or trains.
According to research, the migration of black widow spiders from one location to another depends on various environmental factors and their survival instincts. They move to the areas where food and shelter are in abundance. They can move easily through cracks and crevices in search of prey, avoiding predators and other dangers that come in their way.
The following table highlights some of the essential factors that influence the migratory behavior of black widow spiders:
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental conditions | Migration is commonly observed during summer and fall, as black widows try to escape the cold weather. |
| Nesting sites | Black widows are attracted to cool, dark, and dry places, such as woodpiles, rock crevices, sheds, and cluttered basements or attics. |
| Food availability | Black widows usually migrate to places where there is an abundant supply of insects, such as roaches, flies, and grasshoppers. |
| Clash with predators | Black widows can migrate to escape predators such as birds, lizards, and other insectivores. |
| Human intervention | Black widows can also move to new areas due to human activities like transportation. |
It is noteworthy that black widows play essential roles in their ecosystems. They are also an essential part of the food chain in various regions. To know more about the black widow role in ecosystems, click here.
Black Widow Spider Geographic Range

The black widow spider is a notorious arachnid, well-known for its venomous bite. While the spider is most commonly associated with North America, its geographic range extends far beyond the continent’s borders. Understanding where the black widow spider can be found and how it behaves in different environments is crucial for avoiding its potentially dangerous bites. Let’s explore the global range of the black widow spider in more detail.
North America
North America is the primary native habitat of black widow spiders. They can be found in most of the regions of the United States, including the southern and western parts of Canada and Mexico. These spiders are known for their preference for warm and dry environments.
Black widow spiders can be found in a variety of habitats in North America, ranging from deserts to forests. They are often found in areas with dense vegetation, where they can easily build their webs, and areas with loose soil, where they can create burrows.
One study found that black widow spiders in North America tend to inhabit the following environments:
| Environment | Percentage of Black Widow Spider Populations |
|---|---|
| Forests | 39% |
| Deserts | 31% |
| Wetlands | 8% |
| Grasslands | 7% |
| Urban Areas | 6% |
| Other | 9% |
As can be seen, they have a preference for forest and desert environments, making up over two-thirds of all black widow spider populations in North America. However, they can also be found in wetlands, grasslands, and even in urban areas, particularly in dark and undisturbed places such as basements or garages.
If you live in an area where black widow spiders are common, it’s important to learn about their behaviors and habitats. This can help you avoid potential encounters with the spiders, which can be dangerous to humans. You can follow the link to learn more about the range and survival of black widow spiders in North America here.
South America
South America boasts a significant population of black widow spiders, specifically in countries such as Brazil, Chile, Argentina, and Uruguay. These spiders are known to thrive in a variety of habitats including tropical rainforests, deserts, and grasslands. As such, their adaptability to various climates and environments has contributed to their success in the region.
Black widow spiders in South America are typically found in undisturbed areas where they can build their webs, including in trees, shrubs, and under rocks. They are also known to build webs near human dwellings, particularly in dark and damp areas like basements and crawl spaces.
Due to the high humidity levels in South America, black widow spiders can easily find suitable environments to live and breed. They are known to seek out areas with clutter and debris to build their webs, specifically near common nesting sites such as woodpiles, storage areas, and brush piles.
In addition to their natural habitat, black widow spiders have also adapted to urban environments in South America, thriving in gardens and green spaces. They can often be found in gardens with debris, old furniture, and unused playground equipment.
The adaptability of black widow spiders to a range of climates and environments has enabled them to have a wide geographic range that extends to every continent except Antarctica. However, the potential risks they pose to humans should not be overlooked. If you live in an area with black widow spiders, it is essential to take precautionary measures to reduce the risk of bites and potential fatalities. For tips on how to survive a black widow spider bite, check out our article on black widow survival.
Europe
Europe is home to a variety of spider species, and the black widow spider has managed to establish a presence in several European countries. These countries include Spain, Portugal, Italy, and France. While the climate in Europe is generally unsuitable for black widow spiders, they are found in areas with warm and humid climates, especially in the Iberian Peninsula.
In Europe, the black widow spider prefers to live in natural habitats such as rocky crevices and forests. These habitats provide excellent hiding places for black widow spiders, as well as abundant prey items. Black widow spiders are also found in urban habitats such as gardens, attics, and storage sheds.
The distribution of black widow spiders in Europe is largely influenced by factors such as climate, human activity, and nesting sites. They are well-adapted to living in dark areas, and they tend to be found in areas with a lot of clutter and debris. They also tend to nest in areas that are protected from the elements, such as under rocks, in crevices, or in cracks and crevices in buildings.
While black widow spiders are not native to Europe, they have managed to establish themselves in various parts of the continent. Although their populations are not as widespread as in other parts of the world, they can still pose a risk to humans and animals if provoked or disturbed.
It is important to note that black widow spiders in Europe are generally not as dangerous as those found in North and South America. However, their bites can still be painful and can cause symptoms such as localized swelling, redness, and nausea.
While black widow spiders are not typically aggressive, they will bite if they feel threatened or cornered. It’s important to take precautions when working in or exploring areas where black widow spiders may be present. Wearing protective clothing and gloves and being aware of your surroundings can help minimize the risk of encountering a black widow spider.
While black widow spiders are not commonly found in Europe, they have managed to establish a presence in several countries. They prefer warm and humid climates and natural habitats, but can also be found in urban areas. While their bites can be painful, they are not typically aggressive and will only bite if they feel threatened.
Africa
Although black widow spiders are not commonly found in Africa, they do exist in some regions. These dangerous spiders are known to prefer environments that are dark and secluded, making them difficult to spot in their natural habitats. They often live in areas with moderate to high humidity levels, which is why they are most commonly found in the southern and western regions of the continent.
Factors such as climate and the adaptation of black widows to their environments play a significant role in determining their range in Africa. Black widow spiders are sensitive to temperature and require moderate to warm climates to thrive. This is why they are most commonly found in regions with tropical and subtropical climates, such as the southern parts of the continent. They also tend to adapt to their environments by building webs in common nesting sites, such as dark, secluded areas, including tree trunks, woodpiles, and crevices.
Although black widows are not commonly found in Africa, it is important to remain vigilant and take appropriate precautions when living or traveling to regions known for their presence. Some common nesting sites for black widow spiders include abandoned rodent burrows and other underground spaces, such as crawl spaces and basements. It is important to minimize the presence of clutter around your home and keep areas well-lit to reduce potential nesting sites for black widow spiders. It is recommended to wear gloves and long-sleeved clothing when working outdoors or in areas where black widows may be present, such as woodpiles or underbrush.
While the black widow spider population is not as widespread in Africa as it is in other regions of the world, it is important to be aware of their habitats and potential risks. Factors such as climate and environment adaptation play a significant role in determining their range in Africa. It is important to take necessary precautions to reduce the potential nesting sites for black widows.
Asia
Asia is home to a few species of Black Widow Spiders, including the Latrodectus tredecimguttatus, L. lugubris, and L. pallidus. L. tredecimguttatus, also known as the Mediterranean Black Widow, is found in countries such as Turkey, Iran, and Israel. L. lugubris, or the Brown Widow, is found in countries such as India, China, and Japan. L. pallidus, also known as the White Widow, is found in southern regions of Russia and Central Asia.
These species of Black Widow Spiders in Asia prefer warm and dry environments. They can be found in a variety of habitats, including deserts, forests, urban areas, and agricultural fields. Some common nesting sites for these spiders in Asia are rocks, crevices, and woodpiles. They also may build webs in areas near human dwellings, such as garages, sheds, and basements.
Interestingly, the Black Widow Spiders in Asia have adapted to living in areas with high human activity. They have been known to construct webs under outdoor benches and in playground equipment in parks. They also tend to prefer dark areas, such as the corners of rooms and buildings, just like their counterparts in other parts of the world.
However, despite their adaptations, Black Widow Spiders in Asia face threats such as habitat destruction, pesticide use, and climate change. Climate change can affect the availability of prey and nesting sites for these spiders. Read more about the effects of climate change on the distribution of Black Widow Spiders in the previous section of the article.
Black Widow Spiders can be found across various regions in Asia. Despite their adaptability, they still face challenges in the changing environment. It is crucial to understand the natural history and behavior of these spiders to minimize potential risks to humans, and to preserve their natural habitats and ecosystems.
Australia
Australia is home to a specific species of black widow spider known as the Redback spider (Latrodectus hasseltii). These spiders are found throughout the mainland and commonly in urban areas, creating nests in warm and dry places. They are well-known for their distinctive red markings on their backs, with females having a larger, rounder abdomen than males.
Redback spiders are commonly found in hidden spots, such as inside shoes, under furniture, and in garden sheds. They also prefer to spin their webs in dark areas, such as under tree bark, rocks, and debris. Their preferred nesting sites include undisturbed locations like garden beds, low shrubs, and fence lines. Thus, it’s always important to thoroughly check the surroundings before unknowingly disturbing these spiders in their habitats.
Due to their ability to adapt in various environments, including extreme heat and dryness, redback spiders have established themselves in residential areas and become a potential danger to humans. According to an Australian study, these spiders are responsible for over 2,000 hospital admissions each year in the country.
However, despite their potentially harmful bites, redback spiders also play an important role in the ecosystem by preying on insects and other arthropods. Their specific role in the food chain and how they adapt to their environment is still an ongoing study in the country.
The Redback spider is the black widow species found in Australia, and it creates nests in warm and dry areas, indoor and outdoor. These spiders are commonly found in dark areas and prefer undisturbed nesting sites to avoid any harmful situations.
Non-Native Distribution
Black widow spiders are found all over the world. They are a species that adapt easily to new environments, and human activity has been an important factor in their proliferation in non-native regions.
Non-native distribution of black widow spiders:
| Region | Species Found |
|---|---|
| Europe | Latrodectus tredecimguttatus |
| Africa | Latrodectus indistinctus |
| Asia | Latrodectus erythromelas, Latrodectus cinctus |
| Australia | Latrodectus hasseltii (redback spider), Latrodectus mactans (black widow) |
In Europe, the most commonly found species is Latrodectus tredecimguttatus. This species is mainly found in Mediterranean countries such as Spain, Greece, and Italy. In Africa, the most commonly found species is Latrodectus indistinctus which is found in countries such as South Africa, Botswana, and Zimbabwe. In Asia, Latrodectus erythromelas and Latrodectus cinctus are the most frequently found species. In Australia, the most common species are Latrodectus hasseltii (redback spider) and Latrodectus mactans (black widow).
The spread of black widow spiders around the world has been largely influenced by human activity. International trade, transportation, and tourism have helped spread the spider to regions where they were not native. Climate change is another factor that has led to the migration of certain species of black widow spiders to new areas.
It is important to note that though black widow spiders are a potentially dangerous species, they also serve an important role in their ecosystems. They help control populations of other insects and pests, and in some areas, they are even used as a form of biological control.
To learn more about ways that black widow spiders adapt to new environments, check out our article on ways black widows adapt.
Black Widow Spider Behavior
When it comes to the behavior of black widow spiders, there are several intriguing factors to consider. From their feeding habits to their webbing, these arachnids have unique characteristics that set them apart from other species. Additionally, their potential risks to humans make them an important topic of study. To better understand the behavior of black widow spiders, it’s important to explore their environments and common nesting sites, as well as the role that climate plays in their distribution. Let’s dive deeper into the fascinating behavior of black widow spiders.
Feeding Habits
Black Widow Spiders have interesting feeding habits, which include a carnivorous diet of insects, and other arachnids. They immobilize their prey with their venomous bite and then wrap them in silk before consuming them. Black Widow Spiders are known to feed on mosquitoes, grasshoppers, beetles, flies, and other spiders. Female Black Widow Spiders are known to eat their male counterparts after mating, which has earned them the reputation of being cannibalistic.
Black Widow Spiders are more active during the night, and their vision is not well-developed. They use their webs to detect prey and wait in dark corners for their prey to get ensnared in their sticky webs. They prefer to live in undisturbed areas where their webs won’t be damaged, like dark areas, crevices, and edges of structures.
Black Widow Spiders can go without food for several months, and can even survive without water. They can also adapt to different environments and change their feeding habits, depending on the availability of prey. Studies have shown that they tend to feed more during warmer months and during the breeding season.
Black Widow Spiders have unique feeding habits that have helped them to thrive in diverse environments. With their carnivorous diet, they play an important role in controlling insect populations. If you’re interested to learn more about the environments they thrive in, check out our article on common nesting sites Black Widow Spider.
Webbing
Black Widow spiders have a unique webbing pattern compared to other spiders. The shape of the web is irregular and tangled because the spider does not use it to capture prey. Instead, it serves as a retreat area for the female spider. The silk is much stronger than steel of the same diameter and is elastic, which allows it to absorb the vibrations caused by trapped prey. The webbing is made up of seven types of silk, each having a different purpose.
When males are searching for a mate, they follow the silk trail laid down by the female. The males then tap the silk to identify a receptive female. This tapping behavior of male spiders is known as ‘web vibrations.’
Black Widow spiders are known for their ability to reproduce rapidly, and webbing plays an important role in ensuring the survival of their offspring. After the female lays her eggs, she covers them with a loosely woven silk. This silk creates a spherical egg case that protects the eggs from predators and harsh environmental conditions. The eggs hatch within a month, and tiny spiderlings emerge from the protective webbing.
Black Widow spiders often choose dark, secluded areas to construct their webs. The spiders are nocturnal hunters and prefer to remain hidden during the day. They can often be found in woodpiles, cluttered areas, or abandoned buildings. Common nesting sites for the spider include hollow tree stumps, rodent burrows, or crevices in rocks.
Although Black Widow spiders are notorious for their venomous bites, they only do so when threatened. The spider’s bite is incredibly painful and can be fatal if not treated promptly. However, despite the risks, these spiders play an important role in the ecosystem by providing natural pest control.
The webbing of Black Widow spiders serves multiple functions, from protecting the spider’s offspring to attracting potential mates. The unique shape of the web and the strength of the silk make it an essential tool for the spider’s survival. Understanding the spider’s behavior and preferred habitats can help humans to coexist with these creatures safely. If you’re interested to know more about the climate Black Widow spiders thrive in, find more information by following this link.
Reproduction
Black widow spiders reproduce sexually. The males use their pedipalps to transfer sperm to the female during mating. The female then stores the sperm in a special receptacle called the spermatheca.
A female black widow spider can lay up to 900 eggs at a time in her egg sac. The eggs are round and white and can be up to 1/3 inch in diameter. The female black widow will often make several egg sacs in a year. The eggs hatch after about 30 days, and the spiderlings emerge. The spiderlings are cannibalistic and will eat each other if they get the chance.
The spiderlings are very small and fragile at first. They will stay in the egg sac or on the mother’s web until they are big enough to hunt and fend for themselves. Female black widows will often eat their own offspring if they feel threatened or stressed.
It’s interesting to note that male black widow spiders have a relatively short lifespan and generally pass away soon after mating. Female black widow spiders are longer-lived and can live up to 3 years in the wild.
During the mating process, the female is known to sometimes kill and eat the male. This has earned the black widow spider a reputation as a mating cannibal. However, this behavior is not always the case, and some males are able to mate without being eaten.
It’s important to note that black widow spiders are not typically aggressive towards humans, but they will defend themselves if threatened. It’s best to stay away from dark areas and common nesting sites of black widow spiders to avoid contact with these potentially dangerous spiders.
Potential Risks to Humans
Black widow spiders are widely considered to be one of the most dangerous spiders in the world. Potential risks to humans are significant and can cause serious harm. Black widow spiders are known for their toxicity, with venom that can be fatal, especially to children and the elderly.
The venom of a black widow spider can cause a range of symptoms, which can vary depending on the age and health of the person who has been bitten. Common symptoms of a black widow spider bite include nausea, severe abdominal pain, muscle cramps, headaches, fever, chills, and hypertension. If left untreated, the bite can lead to respiratory failure, paralysis, and even death.
Black widow spiders are usually found in quiet, dark areas such as rock piles, logs, and crevices. They will usually hide in or around objects, waiting for their prey to come to them. Common nesting sites for black widow spiders include cluttered basements, attics, and storage areas with poor lighting. (source)
The best way to protect oneself from black widow spider bites is to avoid potentially infested areas. If you live in an area where black widows are common, take steps to reduce hiding places around your home, such as trimming back clutter and removing debris. If you need to work or spend time in an area where black widows are known to live, wear protective clothing, including gloves and long sleeves.
In the event of a black widow spider bite, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. (source) Remember that black widow spider bites can be fatal and should be taken seriously.
Conclusion
As we come to the end of this article, it is clear that black widow spiders can be found in a variety of habitats around the world. From natural landscapes to urban areas, these spiders have adapted to survive in many different environments. Their geographic range is extensive, and they can be found on every continent except for Antarctica.
While black widow spiders may elicit fear in some individuals due to their venomous bite, it is important to remember that they play an important role in their ecosystems by controlling the populations of other insects. It is also important to note that bites from these spiders are rarely fatal, and medical treatment can effectively manage symptoms.
Overall, it is clear that black widow spiders are fascinating creatures that have adapted to thrive in a variety of habitats throughout the world. While caution should be exercised around these spiders, they should also be appreciated for their important ecological role.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can black widow spiders be found in all parts of the world?
No, black widow spiders are not found in all parts of the world. Their range is limited to certain areas around the globe.
What does the natural habitat of black widow spiders look like?
The natural habitat of black widow spiders can vary depending on the species, but generally they prefer areas with plenty of vegetation, such as forests, fields, and deserts.
Do black widow spiders live in urban areas?
Yes, black widow spiders can be found in urban areas, such as gardens, parks, and abandoned buildings.
Do black widow spiders migrate?
Yes, black widow spiders are known to migrate seasonally in search of food, water, and shelter.
Are black widow spiders only found in North America?
No, black widow spiders are also found in South America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and Australia.
What are the feeding habits of black widow spiders?
Black widow spiders primarily feed on insects, but they have been known to prey on small mammals and reptiles as well.
How do black widow spiders build their webs?
Black widow spiders build webs that are strong and sticky. They position themselves in the center of the web and wait for prey to become trapped.
How do black widow spiders reproduce?
Black widow spiders reproduce through sexual reproduction. The female often eats the male after mating, which is why the species is often associated with sexual cannibalism.
Are black widow spiders dangerous to humans?
Yes, black widow spiders are venomous and their bites can be dangerous to humans. Symptoms can include pain, muscle cramps, and spasms.
Can black widow spiders be kept as pets?
While some people may keep black widow spiders as pets, it is not recommended. They are venomous and can be dangerous, especially to children and pets.