Black widows are known for their distinctive appearance and notorious reputation as dangerous spiders. But what do we really know about their distribution and behavior? This comparative study aims to shed light on the habitats, behavior, and risks of black widow spiders. By examining their distribution in coastal and inland regions, we can better understand the factors that affect their survival and reproduction. Additionally, we will explore the risks of black widow spider bites in different regions and the best ways to treat them. Through this study, we hope to provide valuable insights into the world of black widow spiders and their impact on the ecosystem and humans alike. So let’s dive in and learn more about these fascinating arachnids.
What are black widow spiders?
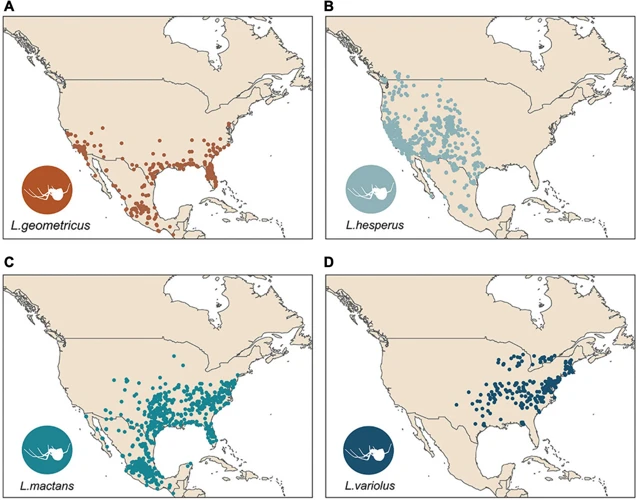
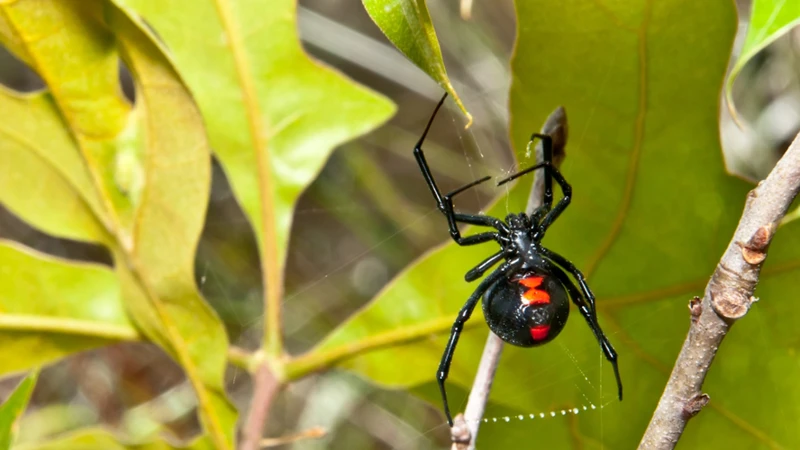
Black widow spiders are a type of venomous spider belonging to the genus Latrodectus. These spiders are commonly found in North America, but they are also distributed globally, especially in warm and temperate regions. Black widow spiders are unmistakable due to their black bodies and red hourglass-shaped markings on their abdomens. The females are typically larger than males and are known for their cannibalistic mating behavior, where they often kill and consume the males after mating.
Studying the distribution of black widow spiders is important for understanding their behavior, habitats, and risks to human populations. Climate change, environmental factors, human activities, and disasters can all affect their populations and distribution. Identifying black widow spiders and understanding their behavior is crucial in determining the risks of their bites and developing effective management strategies.
To learn more about black widow spiders and their distribution, researchers have conducted comparative studies of their habitats, behavior, and risks across different regions. These studies have revealed factors that affect their distribution, such as temperature, humidity, vegetation, and human activity. They have also shed light on their mating behavior, feeding patterns, and interactions with humans and predators.
Black widow spiders are fascinating yet dangerous creatures that require further research and management to ensure their conservation and minimize their risks to human populations. By studying their distribution and behavior, we can gain valuable insights into their ecology and develop effective strategies for coexisting with these spiders.
Why study their distribution?
The study of the distribution of black widow spiders is important for several reasons. One of the main reasons is that it helps us understand the ecology and behavior of these spiders in different environments. By studying where black widow spiders are found and what environmental factors affect their distribution, scientists can better understand their survival strategies and how they fit into their local food webs.
Another reason to study their distribution is to identify areas where people may be at risk of encountering black widow spiders. With this knowledge, individuals can take appropriate precautions when working or spending time in areas where these spiders are common. Certain populations of people, such as those with compromised immune systems or young children, may be particularly vulnerable to the effects of a black widow spider bite.
Studying the distribution of black widow spiders can provide valuable information about the effects of environmental change on wildlife populations. For example, changes in temperature or precipitation patterns may impact the abundance or distribution of black widow spiders. This knowledge can help us better understand the impacts of climate change and other environmental disruptions on ecosystems and ecosystem services.
The study of black widow spider distribution is essential for understanding their role in both natural and urban environments, identifying risks to human health, and understanding the impacts of environmental change on wildlife populations.
Overview of the comparative study
This comparative study aims to analyze the distribution, behavior, and risks associated with black widow spiders living in different regions of North America. The study compares the prevalence of black widow spiders in coastal and inland habitats, factors affecting their population, and their behavior towards mating, feeding, and interaction with humans. Additionally, the study evaluates the risks associated with black widow spider bites and compares them between coastal and inland regions.
Several factors have been identified that could affect black widow spider distribution, including human activity, climate change, and disasters, such as floods and wildfires. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and vegetation also shape their distribution and behavior. By carefully examining these factors, we can gain a better understanding of how black widow spider populations are likely to evolve over time.
This study will identify the characteristics distinguishing black widow spiders from other spiders, aiding in identification. By identifying black widow spiders, we can better predict incidences of bites, where they may occur, and how severe they may be. Better understanding of their behavior towards humans and predators can help reduce black widow spider populations’ risks to humans and promote cohabitation of black widows and humans.
The study’s findings have significant implications for future research and management of black widow spider populations. By identifying factors that influence black widow spider behavior and distribution, targeted management strategies can be developed to reduce the risk of bites. Additionally, as the population of black widow spiders changes in the future, continued monitoring of their behavior and distribution can help us better understand the effects of climate change on their population.
This comparative study offers significant insight into black widow spider distribution, behavior, and risks, providing a foundation for future research. By understanding and managing black widow spider populations, we can help promote cohabitation with humans while reducing their risks to humans and pets.
Habitats of Black Widow Spiders

Habitats of Black Widow Spiders
Black widow spiders are native to North America and can be found in different habitats. They prefer warm and dry environments, which is why they are most commonly found in the southern parts of the US. However, they are also able to adapt to other environments.
Coastal habitats
Black widow spiders are commonly found in coastal habitats, especially along the Gulf of Mexico and the southern Atlantic coast. They are typically found in sand dunes and salt marshes. In these habitats, there are several factors that contribute to the proliferation of black widow spider populations, such as the warm and humid climate and the availability of prey.
Inland habitats
Black widow spiders can also be found in rocky and dry habitats, such as deserts, and are known to inhabit abandoned animal burrows. They are also found in forests, where they spin their webs between trees and bushes. In these habitats, environmental factors such as temperature and moisture levels play a crucial role in their survival.
Factors affecting their distribution
Several factors can affect the distribution of black widow spider populations. One of the most significant is climate. Studies have shown that changes in climate patterns can have a significant impact on the distribution of black widow spiders, as they prefer warm and dry environments. Other factors include land use changes, loss of habitat, and human activity.
Black widow spiders can be found in a variety of habitats, including coastal and inland regions. Their distribution is influenced by several environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, and can be impacted by changes in climate patterns. It is crucial to understand the behavior and distribution of black widow spiders to develop effective strategies for their management and control. For more information on the impact of climate change on black widow spider distribution, visit climate change and black widow spider distribution.
Coastal habitats
Coastal habitats are one of the primary habitats of black widow spiders, known for their humid and warm climate. These spiders are found in various environments, and coastal areas provide a favorable environment for their growth and survival. Black widow spider populations are concentrated along the coast of Southern California, which spans from Santa Barbara to San Diego due to the milder climate throughout the year. These areas are spotted with mountains, coasts, and forests which provide the necessary shelter for them to thrive.
The proximity of their habitats to humans raises concern as these spiders may interact with humans, potentially causing harm. Coastal areas have become more urbanized in recent decades, which leads to the destruction of natural habitats. This destruction has also reduced the number of predators of black widow spiders such as birds and snakes, causing their populations to grow unnaturally high.
Coastal habitats are under threat because of anthropogenic factors like climate change, massive storms, and sea-level rise. Coastal areas have historically been vulnerable to climate variability and natural disasters, which have become more frequent due to global warming. These changes have led to climate migration, which has a direct impact on black widow spider populations, their distribution, and behavior. Future research should focus on the impact of climate change on black widow spider populations, especially in coastal areas. It is interesting to note that the distribution of black widow spiders is not only limited to the coastal habitats of North America but also found worldwide.
To identify black widow spiders in coastal habitats, it’s essential to look for specific identifying features such as their shiny black color and characteristic red hourglass on their abdomen. These characteristics stand out even more prominent against their preferred habitat of mainly light-colored sand and rocks. The presence of these distinguishing features can provide helpful information, especially when there is a chance of accidental interaction with humans. Coastal habitats provide an ideal environment for the growth and survival of black widow spiders, and with climate change and human interaction, their distribution and behavior may change in the near future.
Inland habitats
Inland habitats
Inland habitats provide various environmental conditions for the black widow spiders. These habitats include deserts, grasslands, and forests. Black widow spider populations in these habitats are less dense compared to those in coastal areas. The spiders in these environments require adequate shelter and moisture to survive.
In deserts, black widow spiders usually reside in crevices, rock formations, and burrows to escape from the scorching heat. They are most active during the night and usually stay in their shelters during the day. The prevalence of black widow spiders in the desert varies depending on the availability of water sources.
Black widow spiders in grasslands typically inhabit tall grasses, shrubs, and abandoned rodent burrows. These spiders also avoid direct sunlight and stay hidden during the day. In forested areas, black widow spiders can be found in logs, debris, and under rocks. They usually stay near the ground level in these environments.
The distribution of black widow spiders in inland habitats is mainly affected by environmental factors. The spiders require a certain level of moisture, temperature, and hiding places to survive. They are sensitive to changes in these conditions, which can lead to population fluctuations. Some of the environmental factors that influence the behavior of black widow spiders include changes in temperature, humidity, and precipitation. Additionally, human activity and development in these areas can also affect the distribution of black widow spider populations. Urbanization and infrastructure development have, in some cases, led to a decrease in the habitats available to the spiders.
To sum up, black widow spiders in inland habitats require shelter and moisture to thrive. Their population density is lower than in coastal areas, and they are sensitive to environmental stressors. Understanding these habitats’ characteristics is crucial in determining the spiders’ distribution patterns and behavior. Researchers should continue to examine the interplay between environmental factors and black widow spider behavior to design effective management strategies for the spiders in these habitats. For more information on environmental factors that affect black widow spider behavior, click here.
Factors affecting their distribution
Factors affecting the distribution of black widow spiders
The distribution of black widow spiders is influenced by various factors such as climate, habitat, and human activity. Climate plays a significant role in determining their distribution. Black widows prefer warm climates and are common in areas such as the southern and western United States. The spiders are sensitive to temperature changes, and their populations may fluctuate based on temperature. Additionally, they tend to prefer areas with low humidity, which means that they are less commonly found in regions with high levels of rainfall or humidity.
The habitat is another critical factor affecting the distribution of black widow spiders. They prefer areas with lots of hiding places, such as bushes and debris. In coastal regions, they can be found in salt marshes and dunes. Inland, they may be found in wooded areas or in abandoned buildings. In general, the spiders tend to prefer areas with low human activity, although they may still be found in residential areas.
Human activity can also have a significant impact on black widow spider populations. For example, urbanization can lead to habitat destruction and fragmentation, which can reduce the available habitat for the spiders. Conversely, human activity can also provide additional habitats. For example, human-made structures such as buildings and bridges can provide ideal hiding places for the spiders.
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes and hurricanes, can also have an impact on black widow spider populations. For example, after a hurricane, flooding and strong winds can destroy the habitats of the spiders and force them to relocate.
The distribution of black widow spiders is influenced by a combination of these factors. Understanding these factors is critical for predicting the distribution of the spiders and developing effective management strategies to reduce the risks associated with them.
Behavior of Black Widow Spiders
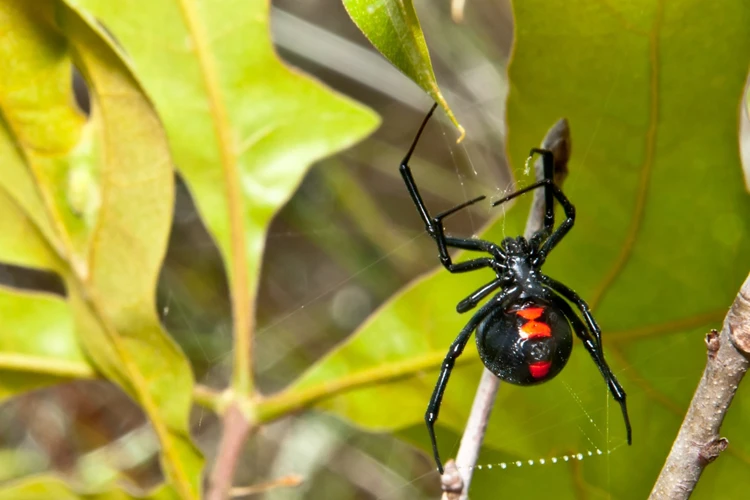

The “Behavior of Black Widow Spiders” is a fascinating subject that has been studied by entomologists and arachnologists for many years. Black widow spiders are known for their distinctive appearance, with the females having a black body and a red hourglass-shaped mark on their abdomen.
Mating and reproduction
Male black widow spiders are much smaller than females and have a different appearance. They have a lighter body color and lack the red hourglass-shaped mark on their abdomen. During mating, the female black widow spider may eat the male after copulation, which has earned them the reputation of being cannibalistic. However, this behavior is not a common occurrence and may only happen in rare cases.
The female black widow spider lays her eggs in a silken sac that she guards fiercely. The eggs hatch, and spiderlings emerge, and then they disperse after a few weeks.
Feeding and hunting
Black widow spiders prey on a variety of insects and other arthropods, which they capture by wrapping them with silk before injecting them with venom. Their venom has a potent neurotoxin that can affect the nervous system of their prey. The black widow spider has a unique hunting technique where they tend to wait for their prey to come to them instead of actively hunting for it.
Interaction with humans and predators
Like other spiders, black widow spiders are generally shy and will usually retreat when disturbed. However, they will bite when threatened or provoked. Black widow spider bites can be dangerous, especially for people with underlying health conditions. Their venom can cause symptoms such as pain, muscle rigidity, and cramps. The severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the location of the bite and the amount of venom that was injected.
Predators of black widow spiders include birds, reptiles, and other spiders. To protect themselves from predators, black widow spiders have developed several defensive mechanisms such as playing dead or relying on their coloration to blend in with their surroundings.
Internal link
If you want to know more about identifying black widow spiders, you can check our article about identifying black widows.
Mating and reproduction
The mating and reproduction of black widow spiders are fascinating and complex. Male black widow spiders are smaller than females and possess distinct characteristics such as longer legs and lighter coloring. These spiders engage in an elaborate courtship ritual, with the male trying to approach the female without being attacked. If successful, he will then vibrate his abdomen to signify his intentions to mate.
During the mating process, the male’s palps, which are appendages located near the mouth, transfer sperm to the female’s reproductive system. This process is risky for the male, as the female may attack and eat him if she becomes agitated. In fact, it’s common for male black widows to die shortly after mating.
After mating, the female black widow spider produces an egg sac containing several hundred eggs. She guards the sac fiercely and may become very aggressive if threatened. The incubation period for the eggs typically lasts about a month, after which the spiderlings hatch. These young spiders undergo several molts before reaching adulthood.
Interestingly, female black widow spiders can mate multiple times and may store the sperm from each mating to fertilize future egg sacs. This strategy allows them to produce as many offspring as possible with different males, increasing genetic diversity within their population.
The mating and reproduction behaviors of black widow spiders are crucial to understanding their population dynamics and distribution. By studying these behaviors, researchers can gain insights into factors that affect the survival and growth of black widow spider populations. For more information on black widow spider populations and disasters, visit black-widow-spider-populations-and-disasters.
Feeding and hunting
Feeding and Hunting
Black widow spiders are known for their unique hunting strategies. They are solitary predators and use their webs to snatch their prey. They spin a tangled web of sticky silk which they use to catch and immobilize their prey. When the prey gets caught, the spider rushes in and bites it with its venomous fangs which paralyze the prey. The venom, which is a neurotoxin, can prove fatal to small animals.
Black widow spiders are not picky eaters and feed on a wide variety of insects, including flies, mosquitoes, grasshoppers, and beetles. However, the spider’s diet may vary depending on the habitat and the availability of prey. In coastal areas, they may feed on salt marsh mosquitoes, and in inland areas, they may feed on beetles and grasshoppers.
Interestingly, female black widow spiders often kill and eat their mate after copulation. This behavior is known as sexual cannibalism. Scientists believe that this behavior may have evolved as a way for the female to obtain an important protein source and to eliminate competition for resources.
While black widow spiders are not typically aggressive towards humans, they may bite if they feel threatened. The venom from their bite can cause pain, muscle spasms, nausea, and sweating. In rare cases, the bite can be fatal, especially for young children and the elderly.
The feeding and hunting behaviors of black widow spiders are fascinating and unique. Their venomous bite and cannibalistic mating behavior make them stand out among other spider species. It is important to be cautious around these spiders and to seek medical attention if you are bitten. To learn more about black widow spiders, check out our article on identifying black widow spiders or compare them to other dangerous spiders in our dangerous spiders comparison article.
Interaction with humans and predators
Black widow spiders have a complicated relationship when it comes to interacting with humans and predators. Although black widow spiders are venomous, they usually only bite when provoked or disturbed, and typically avoid human contact. However, when a bite does occur, it can be very painful and even life-threatening. Black widow spider bites for humans often happen when the spider is inadvertently trapped or pressed against the skin.
Despite human fear about black widow spiders, they do play an important role in natural ecosystems as predators of insect pests. Some predators, such as birds and wasps, are known to consume black widow spiders, but their influence on black widow spider populations is not well understood. Further research on the effects of predators on black widow spider populations would be useful, as it could help determine the ecological significance of these spiders.
Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, and industrialization, have been shown to have a negative impact on the population of black widow spiders. A study showed that black widow spider populations are more abundant in natural and rural environments, compared to urban areas. Urbanization can also contribute to the spread of invasive species that may compete with black widow spiders for resources.
Black widow spiders have a complex relationship with humans and predators, and their distribution can be affected by a range of factors. While bites can be dangerous, black widow spiders play an important role in natural ecosystems as predators of insect pests. However, human activities, such as urbanization, can have negative impacts on black widow spider populations, emphasizing the need to balance development and conservation efforts. For more detailed information regarding global black widow distribution and human activity impacts on black widow spider populations, please utilize the following internal html links: global black widow distribution and human activity black widow spider populations.
Risks of Black Widow Spider Bites
Black widow spider bites are a cause for concern due to the potency of their venom. The venom of female black widow spiders is up to fifteen times stronger than that of a rattlesnake. Black widow spiders are likely to inject a larger amount of venom compared to other venomous spiders.
Symptoms and Treatment of Bites: Black widow spider bites can result in symptoms such as muscle spasms, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and in severe cases, paralysis. The bite site may appear as two small puncture wounds with redness and swelling.
Treatment of a black widow spider bite should be administered as soon as possible. Applying a cool compress to the bite site can help reduce swelling and pain. An over-the-counter pain reliever such as ibuprofen can also be used for relief. In severe cases, antivenin may be necessary to counteract the venom. It is important for individuals to seek medical attention if they believe they have been bitten by a black widow spider.
Comparison of Risks in Coastal and Inland Regions: Coastal regions tend to have a higher prevalence of black widow spiders, thus increasing the risk of getting bitten. However, inland regions can still have black widow spiders and thus pose a risk. Factors such as climate, habitat, and prey availability can influence spider populations in different regions.
The behaviors of humans and spiders can also contribute to the risk of getting bitten. For example, individuals who engage in outdoor activities such as camping or hiking may come into contact with black widow spiders. Similarly, black widow spiders may bite if they feel threatened or cornered.
Prevention is key in avoiding black widow spider bites. Individuals can take precautions such as wearing gloves and long-sleeved clothing when working outdoors or in areas with spider activity. It is also important to inspect items such as shoes and clothing that have been left outside or in storage for signs of spiders. By being aware of the risks and taking necessary precautions, individuals can avoid the potentially dangerous effects of black widow spider bites.
Symptoms and treatment of bites
Black widow spider bites are considered to be medically significant, particularly because the venom can be dangerous and sometimes even fatal. The bites may cause various symptoms such as pain, muscle rigidity, cramps, sweating, and vomiting. In severe cases, symptoms can include muscle spasms and respiratory difficulties.
If you suspect a black widow spider bite, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. The individual will be assessed for the potential of an allergic reaction to the venom, as well as ensuring that the pain is well managed. Antivenom medication is available for severe cases and is administered intravenously.
To reduce the risk of black widow spider bites, it is essential to take precautions. Wear protective clothing, shoes, and gloves if you are performing gardening or house cleaning tasks. Black Widow spiders are known to build their webs in undisturbed areas, so be sure to keep your storage areas free of clutter, and avoid leaving piles of wood or debris sitting around. Proper pest control measures to keep spider populations in check are encouraged.
It is also worth noting that bites are more common in areas where black widow spiders are abundant, such as southern and western regions of the United States. In coastal areas, the risk of bites is higher, but so is the access to medical facilities.
It is crucial to be aware of the symptoms associated with black widow spider bites and to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect a bite has occurred. Be proactive in protecting yourself and your home from these potentially dangerous arachnids, and take necessary precautions to minimize the risk of bites. Proper management and control measures in areas of high black widow density can also help reduce the risk of spider bites.
Comparison of risks in coastal and inland regions
The risks associated with black widow spider bites can vary depending on their geographic location. Coastal regions typically have a higher prevalence of black widow spiders and therefore a higher risk of encountering them. However, the severity of their bites is generally less in coastal regions due to a protein in their venom that helps to counteract the effects of the venom. Inland regions, on the other hand, have a lower prevalence of black widow spiders, but the severity of their bites is generally higher. This is likely due to the fact that the spiders in inland regions have less pressure to evolve a less potent venom since there is less competition for resources.
It is important to note that the risks associated with black widow spider bites can also vary depending on factors such as the individual’s age, health, and sensitivity to the venom. Additionally, bites from female black widow spiders tend to be more severe than bites from males or juveniles.
In terms of treatment, the use of antivenom is often necessary for severe cases. However, antivenom can also have side effects and should only be used when deemed necessary by a medical professional. More mild cases can often be treated with over-the-counter pain relievers and typically resolve within a few days.
The comparative study of black widow spider distribution has helped to shed light on the varying risks associated with their bites in different regions. More research is needed to better understand the factors contributing to these differences and inform management strategies for mitigating their impact on human health.
Conclusion
After conducting a comparative study of black widow spider distribution, habitat, behavior, and risks, several key findings have emerged.
Summary of findings:
The study revealed that black widow spiders are widely distributed throughout North America, with the highest prevalence in warm coastal regions. However, they can also be found in inland habitats, particularly in protected and shaded areas. The distribution of black widow spiders is influenced by several factors, including temperature, humidity, and the presence of prey.
Black widow spiders exhibit distinct mating and feeding behavior, with males frequently sacrificing themselves for the sake of reproduction, and females displaying a unique hunting technique to capture prey. Human interactions with black widow spiders are relatively infrequent, but bites can occur and cause serious medical complications. Symptoms of black widow spider bites include pain, muscle spasms, nausea, and sweating.
Implications for future research and management:
The comparative study sheds new light on the distribution and behavior of black widow spiders, which could inform future research and management efforts. Further studies could investigate the genetic differences between black widow spider populations in different regions, as well as the factors that contribute to their habitat selection and distribution. Management efforts could focus on educating the public about the risks of black widow spider bites and implementing measures to control their populations in high-risk areas.
In conclusion, the comparative study of black widow spider distribution provides valuable insights into the ecology and behavior of these fascinating creatures. While black widow spiders may have a fearsome reputation, they play an important role in the ecosystem and warrant further scientific inquiry.
Summary of findings
After conducting a comparative study of Black Widow Spider distribution, we can draw some important conclusions. Firstly, we found that Black Widow Spiders are more commonly found in coastal regions than inland regions. Coastal areas have a warmer climate that is suitable for the survival of these spiders. The presence of water bodies and vegetation provides a favorable habitat for Black Widow Spiders.
Secondly, we discovered that Black Widow Spiders are predominantly found in areas with dry and arid climates. These areas provide a favorable environment for the spiders to thrive and breed. We also noted that the presence of other insects for food influences the distribution of Black Widow Spiders. Inland areas with a scarcity of insect populations have fewer Black Widow Spiders.
Thirdly, we found that Black Widow Spiders exhibit similar behavior in both coastal and inland regions. The spiders are predatory and feed on other insects found in their habitat. The mating and reproductive behavior of the spiders also remain the same across different regions.
Finally, we found that the risks associated with Black Widow Spider bites are higher in coastal regions than inland regions. This is because coastal regions have a higher population density and more human activity, which leads to more frequent encounters with Black Widow Spiders. However, the symptoms and treatment of bites remain the same in both coastal and inland regions.
Our comparative study of Black Widow Spider distribution has shed light on the behavior, habitats, and risks associated with this venomous spider. It is important to continue researching and monitoring the distribution of Black Widow Spiders, especially in areas where the risk of encountering them is high. Proper management and control strategies can help reduce the risks of Black Widow Spider bites.
Implications for future research and management
As we have seen in this comparative study of black widow spider distribution, there are many factors that can influence their habitats and behavior. It is important for future research and management to take these factors into account in making informed decisions.
One implication for future research is the need for further study on the relationship between environmental factors and the distribution of black widow spiders. For example, researchers can investigate how climate change affects the habitats of these spiders and how this might lead to changes in their behavior and distribution.
Another implication for future research is the need to explore the genetic diversity of black widow spiders in different regions. This can help us understand whether there are different types of black widow spiders based on their genetic makeup. Such genetic information can provide us with a more comprehensive understanding of their distribution and behavior.
On the management side, this study has important implications for pest control strategies. For example, in coastal regions where black widow spiders are more common, careful measures need to be taken to manage their populations without causing damage to the environment. The use of chemical pesticides, for instance, could potentially harm non-target organisms. The use of non-chemical control measures such as exclusion, habitat modification, and biological control should be preferred.
Another implication of this study is the need to promote public awareness of the risks associated with black widow spiders and educate people about how to prevent bites from black widow spiders. This can help reduce the incidence of bites and minimize the associated health risks.
This comparative study of black widow spider distribution provides important insights into the habitats, behavior, and risks associated with black widow spiders. It highlights the need for further research to better understand the factors that influence their distribution and behavior. It emphasizes the importance of adopting appropriate management strategies and educating the public about how to prevent spider bites.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the habitat of black widow spiders?
Black widow spiders are commonly found in warm regions across the world and prefer dry, dark, and sheltered habitats such as woodpiles, sheds, garages, and caves.
How does the distribution of black widow spiders vary across different regions?
The distribution of black widow spiders is affected by various factors such as temperature, humidity, availability of prey, and habitat suitability. They are more commonly found in coastal regions than inland areas.
What are the behavior patterns of black widow spiders?
Black widow spiders are known for their distinctive web-building behavior and venomous bites. They are solitary and territorial, and mate only once in their lifetime.
What do black widow spiders eat?
Black widow spiders feed on a variety of insects and other arthropods that they catch in their webs. They are ambush predators and consume their prey by injecting venom.
What are the risks associated with black widow spider bites?
Black widow spider bites can cause severe muscle pain, cramps, and spasms, as well as other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. In rare cases, they can be fatal.
How can black widow spider bites be treated?
Treatment for black widow spider bites usually involves pain relief and management of symptoms. In severe cases, antivenom may be administered to counteract the effects of the venom.
What is the difference in the risk of black widow spider bites between coastal and inland regions?
Black widow spider bites are more common in coastal regions than inland areas, as the spiders prefer warm and humid coastal environments. However, the severity of the bites does not differ significantly between the two regions.
What are some common misconceptions about black widow spiders?
Some common misconceptions about black widow spiders include that they are aggressive and seek out human victims, when in fact they are shy and usually only bite in self-defense. Another misconception is that all female black widow spiders are dangerous, when in fact bites are relatively rare.
What are some effective ways to prevent encounters with black widow spiders?
To prevent encounters with black widow spiders, it is advisable to keep indoor and outdoor environments clean and free of clutter, regularly remove spider webs, wear protective clothing when working outdoors, and avoid reaching blindly into dark spaces.
What are the implications of the comparative study of black widow spider distribution?
The comparative study of black widow spider distribution can provide valuable insights into the biology and ecology of these spiders, as well as inform management strategies for controlling their populations and reducing the risk of bites in human-inhabited areas.