As humans, we have a natural fascination with significant predators of the animal kingdom. Among them is the notorious black widow spider, known for its venomous bites and hourglass-shaped red markings on its abdomen. But how much do we know about the distribution of black widow populations across the world? This is where mapping comes in. By understanding where and how black widows thrive, we can better inform conservation efforts, recognize potential threats, and track changes in their populations. So, let’s explore the fascinating world of black widow spiders and their global distribution.
The Importance of Mapping Populations
Mapping populations is a crucial step in understanding the distribution and abundance of a species. By tracking the locations where a species is found, scientists can gain valuable insights into its behavior, habitat needs, and potential threats. This information is particularly important when it comes to black widow spiders, whose venomous bite can be harmful to humans and other animals. If you’re interested in learning more about the distribution of black widow spiders across the world, there are several reasons why population mapping is necessary. In this section of the article, we’ll explore these reasons in more detail.
Understanding Habitat and Range
Understanding the habitat and range of black widow spiders is essential to comprehending the behavior and habits of these venomous creatures. They are found in a variety of locations globally, including North America, South America, Africa, Asia, and Australia. Black widows prefer hiding in dark, secluded areas, and they can adapt to various environments such as forests, deserts, and urban landscapes. They are known to create webs in garages, sheds, wood piles, and underneath outdoor furniture.
Identifying the species is also important, as there are several types of black widows, with varying distributions. The female black widow is the most well-known variety due to its distinctive, shiny black color and red hourglass marking on its abdomen. Males, on the other hand, generally have a lighter brown color with less distinct markings.
Various factors affect black widow distribution, including climate, habitat preferences, and competition with other species. Warmer climates tend to be conducive to their survival, which is why they are more prevalent in regions such as Southern California. They have also been known to thrive in areas with high population densities and human activity, such as cities and suburban environments.
The impact of human activity on black widow spider populations is significant. Development leads to habitat loss, which can cause populations to decline. Additionally, black widows are often considered a harmful pest and are killed on sight, which can lead to localized extinctions.
Understanding the habitat and range of black widows is critical for better management and prevention of their negative impacts. By studying their distribution patterns and behavioral tendencies, we can develop strategies for minimizing their impact on ecosystems and human health.
Assessing Potential Threats
Assessing Potential Threats
One of the most important reasons for mapping black widow spider populations is to identify potential threats that they may pose to humans or the environment. This information is especially important for areas where black widow spiders are invasive or where human activity has increased in recent years.
To assess potential threats, researchers must first identify the types of threats that black widow spiders might present in a given area. These threats can include bites to humans and animals, as well as impacts on the surrounding ecosystem (for more information about black widow spider behavior, check out our article on identifying black widow spiders).
Once potential threats have been identified, researchers can begin to gather data on black widow spider populations and their behavior. This data can help to identify whether black widow spiders are more prevalent in areas with certain environmental factors (such as high temperatures or low humidity) or in areas with a high concentration of prey species. Researchers can also use this data to determine whether human activity has had an impact on black widow spider populations.
The table below shows some of the potential threats that black widow spiders can pose and some of the factors that can contribute to these threats.
| Potential Threats | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|
| Bites to humans and animals | Presence of black widow spiders in areas with a high level of human activity |
| Invasive species | Presence of non-native black widow spider populations in areas where they have no natural predators or competitors (for more information about invasive black widow spiders, see our article on invasive black widow spiders and their impact on ecosystems) |
| Impacts on ecosystem | Changes in the behavior of black widow spiders due to environmental factors (for more information about how environmental factors can affect black widow spider behavior, see our article on environmental factors and black widow spider behavior) |
By assessing potential threats posed by black widow spider populations, researchers can provide valuable information to policymakers and conservationists, who can use the data to make informed decisions about how best to protect humans and the environment.
Informing Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts for black widow spiders can be informed by mapping their global populations. These efforts are crucial in maintaining healthy ecosystems, as black widows help control insect populations. It is important to identify areas where black widow populations are thriving and areas where they are declining. This information can be used to create conservation plans and reintroduce black widows to areas where their populations have decreased.
For example, in North America, where black widow populations are prevalent, conservation efforts can focus on preserving their natural habitats and educating the public about identifying black widow spiders to prevent accidental bites. Meanwhile, in areas where their populations are declining, such as parts of Africa and Asia, conservationists can work to alleviate human activities that may have contributed to their decline, such as deforestation or pesticide use.
Climate change can also impact black widow populations, as it alters their natural habitats. By assessing the impact of climate change on black widow distribution, conservationists can adjust their conservation plans accordingly. Factors such as habitat preferences and competition with other species must also be considered when creating conservation plans for black widows.
Ultimately, the goal of conservation efforts is to ensure the long-term survival of black widow spiders and their crucial role in the ecosystem. By mapping their populations and tracking population changes, conservationists can make informed decisions on how to best protect black widows and their habitats.
Table: Conservation Efforts for Black Widow Spiders
| Actions to Take | Impact on Conservation Efforts |
|---|---|
| Preserving natural habitats in areas of high black widow populations | Ensures long-term survival and prevents population decline in these areas |
| Educating the public on identifying black widow spiders | Prevents accidental bites and further harms to the population |
| Halting human activities that contribute to population decline | Helps maintain black widow populations in areas where they are endangered |
| Assessing impact of climate change on black widow distribution | Allows conservationists to adjust conservation plans based on changing habitats and ecosystems |
In summary, informing conservation efforts for black widow spiders through population mapping can aid in preserving their populations and protecting them from potential threats. By implementing the strategies discussed above, conservationists can work towards maintaining healthy ecosystems and ensuring the continued role of black widows within them.
Global Distribution of Black Widow Spiders

It’s fascinating to explore the worldwide range of black widow spider populations. These venomous spiders have established themselves in many regions, adapting to diverse climates and habitats. Understanding their distribution can help us be aware of potential threats and provide insight into conservation efforts. From North America to South America, Africa to Asia, and Australia, black widow spiders have made their presence known. Identifying the factors affecting their distribution, such as climate and competition, can help us track their populations. Let’s dive deeper into the map of black widow spider populations around the globe. To learn more about identifying black widow spiders, check out our article on Identifying Black Widows.
North America
North America is home to several species of black widow spiders, including the Southern black widow, the Western black widow, and the Northern black widow. These spiders are found throughout much of the United States, as well as in parts of Canada and Mexico.
The Southern black widow, also known as Latrodectus mactans, is the most widespread species in North America. They are commonly found in the southeastern United States, but have been identified in other regions as well. They prefer warm and humid habitats, such as forests, fields, and gardens.
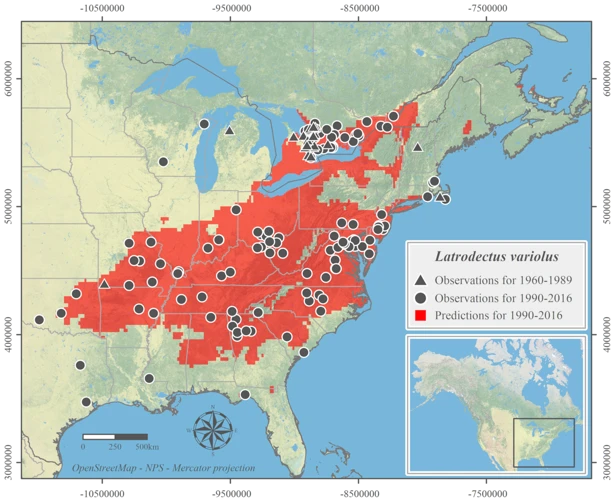
The Western black widow, or Latrodectus hesperus, is found in western parts of the United States, particularly in California. They prefer arid environments such as deserts, but can also be found in coastal regions and forests. The Northern black widow, or Latrodectus variolus, is found in the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. They prefer forested areas and are less commonly encountered than their southern and western counterparts.
According to a study conducted in 2020, the Southern black widow population has been increasing in urban areas due to the abundance of man-made structures that serve as suitable habitats. Additionally, the Northern black widow population has been expanding its range further north as a result of climate change.
It’s important for individuals to be able to identify black widow spiders in order to avoid potential bites. Black widow spiders are known to be venomous and their bites can cause severe symptoms. Human activity, such as urbanization and climate change, can affect black widow spider populations and their habitat fragmentation.
Researchers continue to monitor black widow spider populations and their range as part of conservation efforts. By better understanding the factors affecting their distribution, we can make informed decisions on how to help mitigate their potential impact on ecosystems and human health.
South America
South America is home to several species of black widow spiders, including the Latrodectus geometricus and Latrodectus curacaviensis. These spiders are found in a variety of habitats, including dry scrublands, forests, and even urban areas. In Brazil alone, there are at least five different species of black widow spiders.
In Argentina, the black widow spider population is most abundant in the Chaco province, where the climate is hot and humid. The spider species found in this region is the Latrodectus mirabilis, which is a smaller species than the commonly known Latrodectus mactans found in North America. Further south, in the colder and drier Patagonian region, the black widow spider populations are less dense.
In Colombia and Venezuela, the species of black widow spiders are different from those found in Argentina and Brazil. The Latrodectus hesperus and Latrodectus corallinus are the most common species, respectively.
It is important to note that despite the presence of black widow spiders in South America, these spiders are not responsible for the majority of spider bites in the region. The Brazilian wandering spider, also known as the banana spider, is actually the most venomous spider in the region, and its venom can cause paralysis and even death.
Understanding the distribution and habits of black widow spiders in South America can help scientists and health officials better prepare for and address venomous bites. It can also assist in educating the public on safety measures to take when encountering these spiders.
Africa
Africa is home to several species of venomous spiders, and the black widow spider is one of them. These spiders are found in various regions across the continent, including the southern, central, and eastern parts. One specific species, the Latrodectus indistinctus, is found in South Africa and known to be highly venomous.
In the northern regions of Africa, relatively little research has been conducted on black widow spider populations. However, studies have shown that they are present in Egypt and Tunisia. The limited research in these countries suggests that black widow spiders may be relatively uncommon in these areas.
The distribution of black widow spider populations in Africa is influenced by a range of factors, such as climate and habitat preferences. These spiders tend to thrive in areas with dry, warm climates, which may explain why they are more prominent in southern African countries. They can be found in habitats such as rocky areas, grasslands, and woodlands.
It’s important to note that black widow spiders in Africa pose a potential threat to humans. While bites are rare, those who are bitten may experience symptoms ranging from mild to severe. It’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately if bitten by a black widow spider.
There is still much to learn about black widow spider populations in Africa. Research efforts are ongoing, with a focus on understanding their distribution and potential threats they may pose to both humans and local ecosystems. Monitoring and tracking their populations will also help inform conservation efforts and improve understanding of their global distribution.
Source: Black Widow Bites Worldwide, Climate and Black Widow Distribution.
Asia
Black widow spiders are widely distributed in Asia and can be found in various countries, such as China, India, and Japan. Some species, like the Latrodectus tredecimguttatus, are found in the Middle East and central Asia. However, despite the fact that black widows are present in Asia, the region has not been extensively studied.
One of the challenges in mapping the distribution of black widow spiders in Asia is the lack of consistent data and the difficulty of accessing some regions. However, researchers have identified several species of black widow spiders that are commonly found in parts of Asia, such as the Latrodectus elegans in Japan, the Latrodectus dahli in China, and the Latrodectus hasseltii in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea.
Factors such as climate and habitat preferences also affect the distribution of black widow spiders in Asia. For instance, the Latrodectus hesperus can tolerate a wide range of temperatures and can be found in different habitats, while the Latrodectus bishopi prefers warmer climates and is commonly found in deserts.
In some regions of Asia, black widow spiders can pose a significant threat to humans and animals. In Japan, the Latrodectus hasseltii has been known to cause severe symptoms in humans, while in Malaysia and Singapore, the Latrodectus geometricus has been identified as a venomous species that can cause health problems.
The distribution of black widow spiders in Asia is complex and requires more investigative work. Researchers are continually working to identify new species and populations, as well as investigating the potential threats posed by these spiders.
Australia
Australia is home to several species of black widow spiders, including the Redback Spider (Latrodectus hasseltii) and the Katipo Spider (Latrodectus katipo). These spiders are found across the country, from coastal areas to the arid interior. The Redback Spider, which is closely related to the American black widow, is the most common and widespread black widow in Australia.
| Species | Physical Description | Habitat |
|---|---|---|
| Redback Spider | The female has a distinctive red stripe on its black body, while males have lighter markings. | Found in a variety of habitats, including urban areas, forests, and shrublands. |
| Katipo Spider | The female has a black body with a distinctive red stripe, while the male is smaller and lighter in color. | Found primarily in coastal dunes and forests. |
The distribution of black widow spiders in Australia is influenced by several factors. The Redback Spider, for example, is more common in urban areas, where it can often be found in sheds, garages, and outhouses. In contrast, the Katipo Spider is primarily found in natural habitats, such as sand dunes.
These spiders are known for their venomous bites, which can cause severe muscle pain, nausea, and sweating. However, fatalities are rare, thanks in part to the availability of antivenom. Despite the potential danger, black widow spiders are an important part of Australia’s ecosystem and are not typically considered pests.
Mapping the distribution of black widow spiders in Australia and understanding their habitat preferences is important for conservation efforts and for informing public safety measures. By monitoring populations of these spiders, researchers can gain valuable insights into the health of Australia’s ecosystems and the potential impacts of climate change on these important species.
Factors Affecting Distribution

When examining the distribution of black widow spider populations around the world, it is important to consider the various factors that can influence their range and habitat. Multiple variables such as climate, habitat preferences, and competition with other species all impact where these spiders can thrive and where their populations may be limited. In this section, we will dive deeper into these factors and explore how they impact the spatial distribution of black widow spiders.
Climate
The climate is one of the most important factors affecting the distribution of black widow spiders. These venomous spiders are found in a variety of habitats, ranging from deserts to forests and even in human-made structures, but they are most commonly found in warm, dry regions. Here are some key ways that climate affects black widow spider populations:
- Temperature: Black widow spider populations tend to be more abundant in warmer regions. In cold regions, populations may be limited to warmer microclimates, such as south-facing slopes or sheltered areas.
- Precipitation: While black widow spiders prefer drier habitats, they still require some moisture. Rainfall patterns can affect the availability of water, which in turn affects the availability of prey. In areas with low rainfall, populations may be limited by the availability of moisture and food.
- Seasonal variation: Black widow spider populations may fluctuate seasonally in response to changing environmental conditions. For example, in some regions, populations may be more abundant in the summer months when temperatures are higher and prey populations are higher.
- Extreme weather events: Extreme weather events such as droughts and floods can have a significant impact on black widow spider populations. Droughts can reduce prey populations, while floods can displace spiders from their habitats and wash away egg sacs.
Understanding how climate affects black widow spider populations can help researchers predict how populations may change in the future as the climate continues to shift. It can also inform conservation efforts by identifying areas that may be particularly vulnerable to climate change and the potential loss of black widow spider populations.
Habitat Preferences
When it comes to the habitat preferences of black widow spiders, there are several factors that come into play. These spiders tend to live in dry, hot environments where they can easily find prey and shelter. Here are some of the key elements that affect their habitat preferences:
- Vegetation: Black widow spiders prefer habitats with dense vegetation. This can help them hunt more easily by providing cover for them and their prey.
- Rocky Areas: These spiders are also known to prefer rocky areas where they can burrow and hide from predators. This type of terrain also provides them with a source of shade and cooler temperatures during hot weather.
- Man-Made Structures: Black widows have also adapted to living near man-made structures such as buildings, sheds, and garages. This is because these structures provide shelter and protection from predators.
It’s important to note that black widow spiders are not picky when it comes to their habitat preferences. They can thrive in a variety of environments, but usually prefer areas with the previously mentioned elements.
Their habitat preferences can have an impact on their distribution and range, as they are often found in arid regions with little precipitation. This means that as climate changes occur and areas become drier, their range may shift to adapt to more favorable habitats. As a result, understanding their preferences is crucial in mapping their distribution and predicting population changes.
Competition with Other Species
In addition to climate and habitat preferences, competition with other species also plays a crucial role in determining the distribution of black widow spiders. These spiders face competition for food, shelter, and space with other species, including other spider species.
1. Other Spider Species: Some spider species may compete with black widow spiders for resources. For example, wolf spiders, which belong to the family Lycosidae, are known to prey on other spiders, including black widows. In some instances, they may even kill black widow spiders.
2. Prey: Black widow spiders primarily feed on insects, but they may also feed on other spiders. However, some other animals may also prey on black widows. For example, birds such as the roadrunner in North America are known to eat black widow spiders.
3. Habitat Loss: Habitat loss due to human activities such as deforestation and urbanization can also affect the distribution of black widow spiders. As their habitats shrink, black widow spiders may be forced to compete with other spider and animal species for the remaining resources.
The competition with other species is just one factor contributing to the distribution of black widow spiders. By understanding how these spiders interact with other species and the environment, researchers can better track changes in their populations and create effective conservation strategies.
Tracking Population Changes
As populations of black widow spiders shift and change, it’s important to keep track of their movements and habitat preferences in order to better understand these creatures. Keeping tabs on the distribution of black widow spiders is crucial for a number of reasons, including assessing potential threats to both human populations and other wildlife, informing conservation efforts, and even understanding wider ecological changes. In this section, we’ll explore some of the key ways in which researchers and everyday people are tracking black widow populations across the world. From citizen science platforms to cutting-edge technologies, there are a range of tools at our disposal that can help us better understand and protect these fascinating creatures.
Using Citizen Science
Citizen science has become an increasingly valuable tool for mapping the distribution of black widow spider populations across the world. These projects allow individuals from the general public to contribute their observations and data to ongoing research efforts. In many cases, citizen science programs provide the necessary data to help researchers understand the distribution of species over large geographic areas.
One example of a successful citizen science project is the Lost Ladybug Project, which began in 2000 as a way for individuals to report sightings of ladybugs in North America. Since then, the project has expanded to include other species, including black widow spiders. By harnessing the power of the internet and social media, the Lost Ladybug Project has created a database of over 50,000 ladybug sightings from all over North America.
The benefits of citizen science are numerous. Not only does it provide researchers with a large and diverse dataset, but it also engages the public in scientific research and education. Citizen science projects also allow individuals to gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and the species that inhabit it.
However, there are some challenges to using citizen science data. One of the primary concerns is ensuring the accuracy and consistency of the data collected. To address this, many citizen science projects have implemented quality control measures and provide training and resources for participants.
Overall, citizen science has proven to be a valuable tool in mapping the distribution of black widow spiders and other species. It allows researchers to gather data over large geographic areas that would not be possible through traditional data collection methods. By engaging the public in scientific research, citizen science projects provide a unique opportunity for individuals to contribute to our understanding of the natural world.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Large and diverse dataset | Accuracy and consistency of data |
| Engages the public in research and education | May require quality control measures |
| Allows for data collection over large geographic areas | |
| Provides a unique opportunity for individuals to contribute to research |
How Researchers Collect Data
One of the ways researchers collect data on black widow spider populations is through visual surveys. This involves physically observing and counting the spiders within a specified area. Depending on the scope of the survey, this could range from a small patch of land to a larger region.
Another method is through the use of sticky traps. These are adhesive surfaces placed in areas where black widow spiders are likely to travel. When spiders come into contact with the traps, they become stuck and can be collected for further study.
Researchers may use DNA analysis to identify and track black widow spider populations. This involves analyzing the genetic material of collected specimens to determine their relatedness and distribution.
Some researchers also use acoustic monitoring to detect black widow spider populations. By listening to the sounds produced by the spiders, researchers can identify the presence and behavior of the spiders in a given area.
There are multiple methods for collecting data on black widow spider populations, each with their own advantages and disadvantages. By utilizing a combination of techniques, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the distribution and habits of these fascinating arachnids.
Technologies for Monitoring Populations
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the way researchers monitor black widow spider populations around the world. Some of the most innovative technologies used for monitoring population changes include:
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Radio Telemetry | Radio telemetry involves attaching a small transmitter to the spider and tracking its movements using a special receiver. This technology is useful for studying the behavior and movement patterns of individual spiders. |
| Remote Sensing | Remote sensing involves using satellite imagery to analyze environmental conditions and habitat characteristics that affect the distribution and abundance of black widow spiders. This technology is especially useful for studying large-scale patterns and changes over time. |
| DNA Analysis | DNA analysis involves extracting DNA from spider specimens and analyzing it to identify different spider species and their genetic relationships. This technology is used to study the evolutionary history of black widow spiders and their relationships with other spider species. |
| Acoustic Monitoring | Acoustic monitoring involves using specialized equipment to record spider vocalizations. This technology is used to study the behavior and communication patterns of black widow spiders. |
| Automated Image Analysis | Automated image analysis involves using computer software to analyze photographs or videos of spiders. This technology is used to study spider behaviors, movement patterns, and interactions with other species. |
These technologies provide researchers with valuable information on the distribution, behavior, and habitat preferences of black widow spiders and inform conservation efforts to protect these important species. However, it is important to note that these technologies are not without limitations and must be used in combination with other monitoring methods to gain a thorough understanding of black widow spider populations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mapping the distribution of Black Widow spider populations across the world is an essential step towards understanding the habitat and range of these potentially dangerous creatures. By assessing their potential threats and informing conservation efforts, researchers can work towards protecting both humans and the Black Widow spiders themselves.
From our analysis, it is clear that Black Widow spiders are found across the globe, with the highest populations found in North and South America. However, factors such as climate, habitat preferences, and competition with other species can significantly impact their distribution.
To track changes in population trends, researchers rely on various data collection methods, including citizen science initiatives and advanced monitoring technologies. By employing these tools, researchers can gain insights into the factors driving changes in spider populations and use this data to inform conservation strategies.
Overall, mapping the distribution of Black Widow spider populations is crucial for understanding their behavior, conservation, and management. With this information, we can work towards mitigating potential human wildlife conflicts, protecting vulnerable ecosystems, and ensuring the persistence of these fascinating arachnids.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a black widow spider?
Black widow spiders are venomous spiders characterized by their shiny black color and red hourglass shape on their abdomen. They are known for their venom, which is dangerous to humans.
Do black widow spiders live all over the world?
No, black widow spiders are primarily found in warmer regions including North and South America, Africa, Asia, and Australia.
Are all types of black widow spiders dangerous to humans?
While all black widow spiders are venomous, not all of them pose a significant threat to humans. In North America, the southern black widow is the only species that is considered a danger to humans.
What types of habitats do black widow spiders prefer?
Black widow spiders typically prefer dry, dark habitats such as woodpiles, rubble piles, and abandoned buildings.
What are some potential threats to black widow spider populations?
While black widow spiders do not have many natural predators, habitat destruction and pesticide use can threaten their populations.
How do researchers track and monitor black widow spider populations?
Researchers use a variety of methods including visual surveys, bait traps, and citizen science initiatives to collect data on black widow spider populations.
Can any species of spider be mistaken for a black widow spider?
Yes, there are many other species of spiders that can be mistaken for black widow spiders. It is important to correctly identify the spider before attempting to handle it.
How does climate affect black widow spider populations?
Warmer temperatures allow black widow spiders to thrive and reproduce more quickly, potentially leading to an increase in their population size.
What can be done to conserve black widow spider populations?
Protecting their habitat, reducing pesticide use, and increasing public awareness about the importance of these spiders in their ecosystem can all contribute to the conservation of black widow spiders.
What should I do if I am bitten by a black widow spider?
Seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms of a black widow spider bite can include severe pain, muscle cramps, and difficulty breathing.