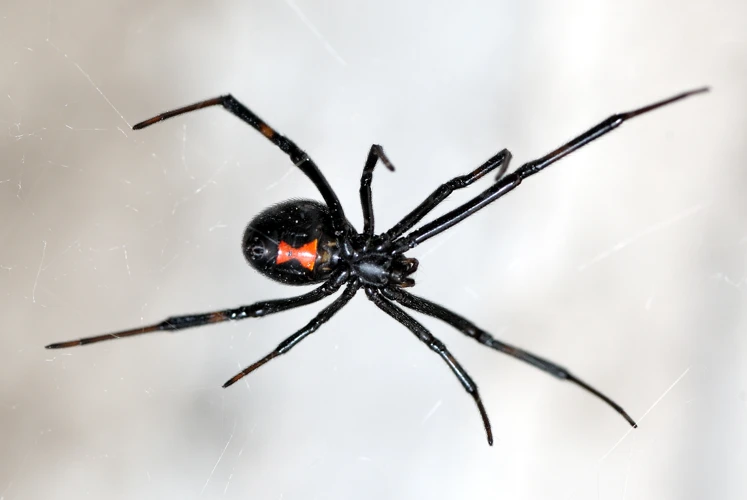
Introduction

The decline of the black widow spider population has become a growing concern for researchers and conservationists alike. Despite their notorious reputation, black widow spiders play an important role in the ecosystem, particularly in controlling pest populations and serving as prey for larger animals. The habitat destruction and range contractions that threaten their populations are a result of a combination of factors, including human activity and climate change. This article will explore the causes and effects of habitat destruction and range contractions on black widow spiders, as well as other threats they face and the conservation efforts being made to protect them.
What are Black Widow Spiders?
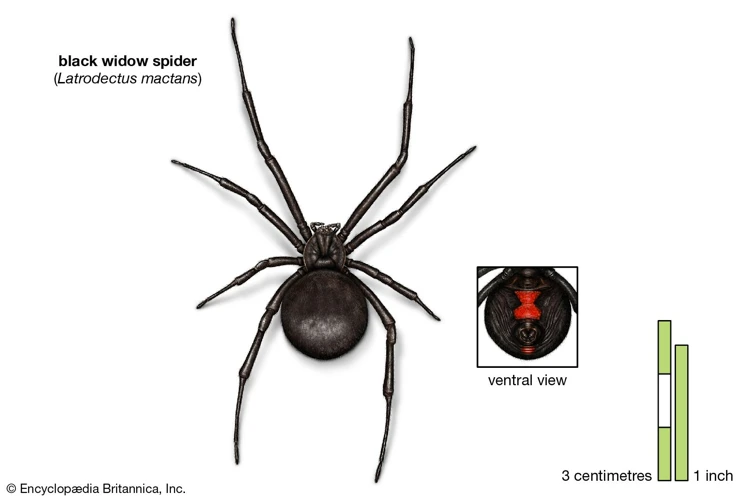
Black Widow Spiders are a type of venomous spider that are found in different parts of the world. They belong to the Latrodectus genus and are known for their distinctive black color and the red hourglass-shaped marking on their abdomen. These spiders are commonly found in warm and temperate regions, usually in areas with a dry and arid climate. Black Widow Spiders are most commonly found in North America, where they are known to thrive in a variety of habitats such as forests, fields, and even urban areas such as abandoned buildings.
The following are some important facts about Black Widow Spiders:
- Black Widow Spiders are highly venomous and can cause severe reactions in humans when they bite.
- These spiders are known for their unique web-spinning abilities, which allow them to catch prey like insects and other small animals.
- Female Black Widow Spiders are larger than males and are known to be more venomous.
If you want to find more information on the habitats and distribution of Black Widow Spiders, please follow this internal link: /habitats-black-widow-spiders/
The Importance of Studying Black Widow Spiders
One of the most important reasons to study Black Widow spiders is their potential danger to humans. These spiders are venomous, and their bites can result in serious health issues if not treated promptly and appropriately. However, despite their infamous reputation, Black Widows also play an essential ecological role in many ecosystems, making it crucial to understand their habits and behaviors.
Black Widow spiders are found in various locations and habitats worldwide, and understanding their distribution is essential. For example, mapping their presence in South America, Asia, and biomes where they thrive in North America can help understand their preferred habitats and how these habitats may be changing due to human activity. Additionally, understanding the reasons for their range contractions can help conservation efforts to mitigate habitat destruction and fragmentation caused by human activities such as urbanization and deforestation.
Further research is also needed to understand how climate change is affecting Black Widow spider populations and their habitats. This knowledge could lead to better management practices and conservation efforts that help reduce the impact of climate change on these species.
Studying Black Widow spiders is crucial for several reasons, including identifying their potential danger to humans, understanding their ecological role, and conserving these species. To learn more about black widow spiders, check out our articles on their distribution in Asia and their range expansion due to human activity. Additionally, explore the measures being taken to conserve Black Widow spiders, such as captive breeding and habitat restoration programs.
What is Habitat Destruction?
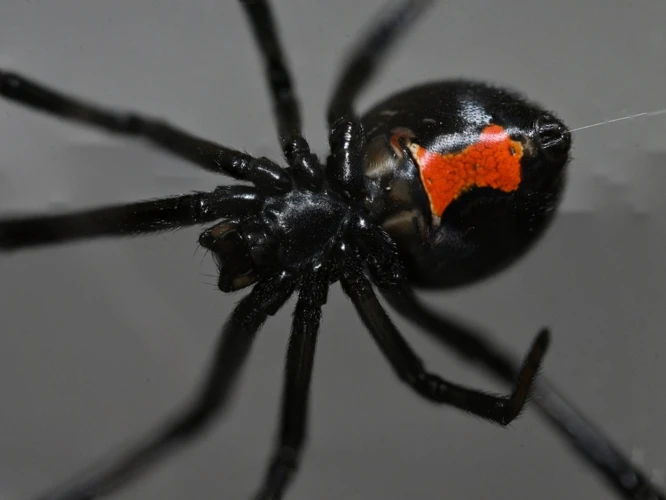

Habitat destruction is a term used to describe the process of damaging or altering the natural environment in which a plant or animal species lives. Black widow spiders, like many other species, are at risk of habitat destruction due to various human activities. This has resulted in negative impacts on their population size and distribution across the world. To understand the causes and effects of habitat destruction on black widow spiders, it is important to study their natural habitat, location, and range. For more information on the distribution of black widow spiders, check out the article on biomes where black widow spiders thrive.
Causes of Habitat Destruction for Black Widow Spiders
Habitat destruction is a major threat to black widow spiders. The following table summarizes the main causes of habitat destruction that are impacting black widow spiders.
| Cause of Habitat Destruction | Description |
|---|---|
| Urbanization | As human populations in urban areas continue to grow, land development destroys natural habitats where black widow spiders would normally be found. This also contributes to habitat fragmentation. |
| Deforestation | As forests are cleared for timber or agriculture, the natural habitats of black widow spiders are destroyed, and the spiders may not be able to adapt to the new environment. |
| Mining | Mining activities, such as surface mining and deep mining, can have a devastating impact on the environment. Mining can destroy habitats and pollute water systems, which can have indirect effects on black widow spiders. |
| Pollution | Polluted environments can result in reduced prey availability, habitat degradation, and can cause genetic changes. All of these can have negative impacts on black widow spider populations and their habitat. |
| Climate Change | The effects of climate change, such as extreme weather events, long-term changes in precipitation patterns, and warming temperatures, can change the distribution and abundance of black widow spider populations. |
According to recent studies, the population of black widow spiders is decreasing in many areas due to habitat destruction. However, black widow spiders have shown some degree of adaptability to human-dominated landscapes. Studies suggest that black widow spiders have successfully colonized urban areas and even persist in highly disturbed environments. To read more about the habitat of black widow spiders, check out this article.
How Habitat Destruction Affects Black Widow Spider Populations
Habitat destruction has had significant impacts on black widow spider populations. These spiders require specific habitats to survive and reproduce, and when those habitats are destroyed, their numbers decrease rapidly.
1. Disruption of food sources: Black widow spiders primarily feed on insects, and habitat destruction often leads to the destruction of these insects’ habitats as well. This makes it difficult for black widows to find food, and can ultimately lead to their death.
2. Loss of suitable nesting sites: Black widow spiders typically make their nests in undisturbed areas such as woodpiles, rock piles, and areas with thick vegetation. When these areas are destroyed, the spiders lose their homes, which can lead to a decline in their population.
3. Fragmentation of habitat: Habitat destruction also contributes to the fragmentation of the remaining habitat. This leads to smaller and isolated populations of black widow spiders that can’t interact and breed with each other, which leads to a reduced genetic diversity and viability.
4. Increased competition: As black widow spider populations decline due to habitat destruction, those that remain have to compete with each other for the remaining resources, which can lead to a further decline in their numbers.
These consequences highlight the importance of conserving the black widow spider populations. By understanding the effects of habitat destruction, we can take steps to conserve their habitats and ensure a healthy ecosystem. To learn more about conservation efforts for black widow spiders, check out our Conservation of Black Widow Spiders page.
Range Contractions for Black Widow Spiders
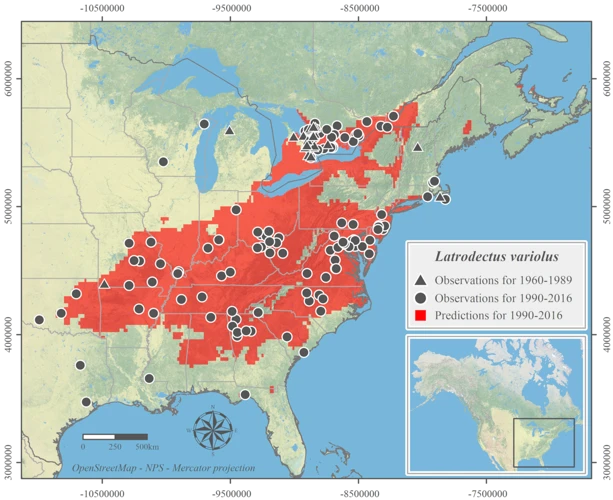
The range of black widow spiders has been contracting significantly in recent years, which is a cause for concern among researchers and conservationists. The reduction in their habitat and changes in environmental conditions are some of the reasons behind this phenomenon. These factors have led to a decrease in their population and a lack of genetic diversity, which could pose significant threats to the survival of these spiders. In this section, we will explore the reasons behind range contractions for black widow spiders and their effects on their populations.
Reasons for Range Contractions among Black Widow Spider Populations
Reasons for Range Contractions among Black Widow Spider Populations
Black Widow Spiders have been facing a range of threats that have contributed to their population decline. The following table summarizes the reasons for range contractions of Black Widow Spider populations.
| Threats | Description |
|---|---|
| Habitat fragmentation and destruction | Human encroachment and land-use changes have fragmented and destroyed natural habitats of Black Widow Spiders. |
| Climate change | Changes in temperature, humidity, and precipitation patterns have altered Black Widow Spider habitats, reducing their distribution and numbers. |
| Pesticides and pollution | The use of pesticides and other chemicals in agriculture, forestry, and urban areas have killed Black Widow Spiders, either directly or indirectly by damaging their prey base and habitats. |
| Competition and predation by invasive species | Non-native species like the Redback Spider (Latrodectus hasseltii) or Argentine Ant (Linepithema humile) have displaced or consumed Black Widow Spiders in their native range, reducing their range and numbers. |
Several of these threats also interact with each other, for example, habitat destruction can exacerbate the effects of climate change or the spread of invasive species. A holistic approach is needed to address the decline of Black Widow Spiders and their ecosystem functions. To learn more about the distribution and conservation status of Black Widow Spiders in different regions, read our articles on Asia, South America, and Australia.
Effects of Range Contractions on Black Widow Spiders
Range contractions, the process of a species’ habitat shrinking or becoming fragmented, can have severe consequences for the Black Widow Spider population. As these spiders’ habitats continue to disappear, so do their sources of food and shelter, which can lead to a decline in their population.
A decrease in genetic diversity: One of the effects of range contractions is the decrease in genetic diversity. This is because as the population sizes are reduced, the number of different genes carried by individuals also decreases. This can make the Black Widow Spider population more vulnerable to environmental changes and diseases.
Increase in competition: As the Black Widow Spider’s range becomes smaller, the population density increases, which can lead to an increase in competition for limited resources such as food and shelter. This competition can lead to stronger individuals dominating and excluding weaker ones, which can further reduce genetic diversity.
Inbreeding depression: Inbreeding depression is another negative effect of range contractions. This is where closely related individuals mate, which can lead to a decline in reproductive success and an increase in deformities and genetic diseases.
Long-term range contractions can put the Black Widow Spider in great danger of becoming endangered or even extinct. Conservationists are working to prevent this from happening by increasing public awareness of the importance of these spiders and their habitats, implementing habitat restoration projects, and studying the spiders’ movements and behaviors to better understand how they can be effectively protected.
If you want to learn more about the range of Black Widow Spiders, check out our mapping tool that tracks the location and distribution of these spiders. Alternatively, you can read about the impact of human activity on the Black Widow Spider’s range in our article on black widow range expansion and human activity. And don’t forget to read up on the risks and fatalities associated with Black Widow Spider bites in our article on black widow bite fatalities.
Other Threats to Black Widow Spiders
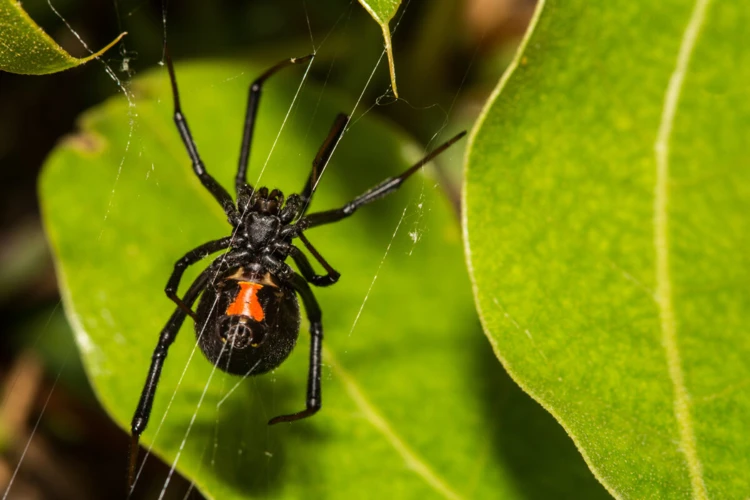

As if habitat destruction and range contractions weren’t enough, black widow spiders now face further threats in their already precarious state. These threats come in the form of a multitude of factors such as climate change, habitat fragmentation, and pesticides. Unfortunately, these threats aren’t just hypothetical – they’re already impacting black widow spider populations. In this section, we will explore these additional concerns and their potential impacts on the future of black widow spiders.
Climate Change and Black Widow Spiders
Climate change is an additional threat to Black Widow Spider populations, and it is important to understand its potential impact. The changes in climate patterns and temperature extremes associated with climate change can affect the prey availability and habitat suitability for the Black Widow Spider.
Here are some examples of how climate change can affect the Black Widow Spiders:
- Changing precipitation patterns can alter moisture levels in the soil, which can affect the prey populations that the Black Widow Spider depends upon.
- Rising temperatures can impact the hatching success rate of Black Widow Spider eggs as well as their survival rates, which can potentially reduce the population numbers.
- The increased frequency and intensity of natural disasters, such as hurricanes, can destroy the natural habitat of the Black Widow Spider.
There are other indirect impacts of climate change on the Black Widow Spider:
- Changes in precipitation patterns and temperature ranges can alter the vegetation cycles, which can lead to changes in prey migration patterns.
- The changes in the timing and length of the seasons can impact the feeding and breeding behavior of prey, which can affect the overall food availability for the Black Widow Spider.
- The increase in greenhouse gas emissions and resulting ocean acidification can significantly impact marine ecosystems, which can indirectly impact the Black Widow Spider by reducing the amount of prey available.
To mitigate these threats, there is a need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to implement measures that promote climate resilience. Conservation efforts should also be put in place to support populations that are vulnerable to the impact of climate change.
Habitat Fragmentation and Black Widow Spiders
Fragmentation of habitats is another major threat to the survival of black widow spiders. Habitat fragmentation occurs when a large, contiguous area of habitat is divided into smaller, isolated patches. This often happens due to human activities such as urbanization, deforestation, road building, mining, and agricultural expansion.
How Habitat Fragmentation Affects Black Widow Spider Populations
The fragmentation of habitats leads to smaller and isolated habitat fragments, which can be inhospitable to black widow spiders. Habitat fragmentation can lead to a decrease in the abundance of prey species, which can affect the growth, development, and reproduction of black widow spiders. Isolated populations of black widow spiders may also experience decreased genetic diversity, leading to decreased adaptability and increased susceptibility to diseases and other threats.
Causes of Habitat Fragmentation for Black Widow Spiders
Habitat fragmentation for black widow spiders is mainly caused by human activities such as urbanization and deforestation. Urbanization creates habitat fragmentation by replacing natural habitats with buildings, roads, and other human-made structures. Deforestation creates habitat fragmentation by removing forested areas, which are the natural habitats of black widow spiders.
Conservation Efforts for Mitigating Habitat Fragmentation
There are various conservation efforts in place to mitigate the effects of habitat fragmentation on black widow spiders. One of the most important efforts is the protection and restoration of the natural habitats of the black widow spiders. It involves planting native vegetation, removing invasive species, and creating natural corridors to connect fragmented habitats.
Another conservation effort is the creation of buffer zones around natural habitats, which helps to reduce human encroachment that leads to fragmentation. Education and awareness programs can also be conducted to educate people on the importance of preserving the habitats of the black widow spiders.
Habitat fragmentation is one of the major threats facing black widow spiders. The effects of fragmentation can be reduced through conservation efforts focused on habitat restoration, the creation of natural corridors, the creation of buffer zones around natural habitats, and public education programs.
Pesticides and Black Widow Spiders
The use of pesticides is a major threat to the survival of black widow spiders. Pesticides are substances that are designed to kill or control pests, but they can also harm non-target species. In the case of black widow spiders, pesticides can cause direct mortality, but they can also have sub-lethal effects such as reducing the spiders’ reproductive success.
Pesticides and Black Widow Spiders
| Pesticides | Effects on Black Widow Spiders |
| — | — |
| Insecticides | Can cause direct mortality or sub-lethal effects such as reduced reproductive success |
| Herbicides | Can destroy the vegetation that black widow spiders rely on for shelter and prey |
| Rodenticides | Can indirectly harm black widow spiders by reducing the populations of rodents, which are an important prey item |
In many parts of the world, pesticides are used extensively in agriculture, forestry, and urban areas. This widespread use of pesticides has led to contamination of ecosystems and water bodies, which can have far-reaching impacts on wildlife.
Black widow spiders are particularly vulnerable to pesticides because they occupy habitats with high pesticide use, such as farmlands and urban areas. Black widow spiders are predators that feed on insects and other arthropods, which can also be affected by pesticides.
To minimize the negative impact of pesticides on black widow spiders, it is important to adopt integrated pest management strategies that reduce the reliance on pesticides. These strategies include using natural enemies of pests, practicing crop rotation, and using pest-resistant crop varieties.
Public education is also essential in reducing the use of pesticides and protecting black widow spiders. By raising awareness about the harmful effects of pesticides on the environment and wildlife, individuals can make informed decisions about pesticide use and advocate for more sustainable pest management practices.
Conservation Efforts for Black Widow Spiders
Amid the growing concern about the threat to black widow spiders’ habitats and populations, conservation efforts have become increasingly vital. Many conservation organizations, researchers, and wildlife enthusiasts have embarked on various initiatives to aid the black widow spider’s survival. Here, we’ll explore some of the ongoing efforts to conserve black widow spiders, which range from captive breeding programs to public education and habitat restoration. These initiatives aim to raise awareness about black widow spiders and address the challenges that these arachnids face in the wild.
Captive Breeding Programs for Black Widow Spiders
To combat the decline of black widow spider populations, some organizations have established captive breeding programs. These programs aim to breed black widow spiders in captivity and release them back into their natural habitats. Here are some details about these programs:
1. Purpose: Captive breeding programs for black widow spiders have the goal of increasing their population sizes and reducing the risks of extinction. These programs hope to establish self-sustaining populations that can continue to thrive even in the face of habitat destruction, predation, and other threats.
2. Method: The breeding process is usually conducted in a laboratory setting. Black widow spiders are captured from the wild and brought to the lab, where they are kept and monitored. The spiders are provided with all the necessary resources to reproduce and lay eggs. Once the eggs have hatched and the spiderlings have grown large enough, they are released into suitable habitats in the wild.
3. Effectiveness: The effectiveness of captive breeding programs for black widow spiders is still a topic of debate. While some programs have reported successful results, others have failed to sustain the released populations. Challenges include the difficulty of providing the spiders with the appropriate environmental conditions and the risk of inbreeding.
4. Limitations: Captive breeding programs for black widow spiders face several limitations. First, it can be difficult to capture enough wild individuals to establish a healthy captive population. Second, the cost and time required to run a breeding program can be prohibitive. Third, it is often challenging to find suitable release sites for the spiderlings once they have reached maturity.
5. Role in Conservation: Captive breeding programs are just one tool in the conservation toolbox. While they may not be the ultimate solution to saving black widow spider populations, they can play an important role in preserving genetic diversity and preventing extinctions. By working in conjunction with habitat restoration efforts and public education initiatives, captive breeding programs can contribute to the long-term sustainability of black widow spider populations.
Habitat Restoration for Black Widow Spiders
Habitat restoration is one of the key measures that can be taken to help protect and conserve Black Widow Spiders. Habitat restoration is a process that involves restoring degraded or destroyed habitats to their original state to provide a suitable environment for the species to thrive. This may include undertaking activities such as planting native vegetation, removing invasive species, and managing the landscape to restore natural habitats.
Benefits of Habitat Restoration for Black Widow Spiders
Habitat restoration can have numerous benefits for Black Widow Spiders. Firstly, it can help to mitigate the impacts of habitat destruction and fragmentation by creating new habitats that can support the species. Secondly, it can help to increase the range of the species by creating new habitats in areas where the spiders were previously absent or rare. Finally, it can also help to improve the overall health and resilience of Black Widow Spider populations, which can in turn improve their chances of survival in the long term.
Habitat Restoration Techniques for Black Widow Spiders
There are many techniques that can be used to restore habitats for Black Widow Spiders. Some common techniques include:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Vegetation Restoration | Planting native vegetation to improve the quality and diversity of the habitat. |
| Control of Invasive Species | Removing invasive plants or animals that are competing with Black Widow Spiders for resources or altering the habitat. |
| Wildlife Management | Managing the landscape to create suitable habitats for Black Widow Spiders and other wildlife that share their ecosystem. |
| Protection of Critical Habitat | Identifying and protecting areas of critical habitat from development or other destructive activities. |
The Role of Government in Habitat Restoration
Governments can play an essential role in habitat restoration efforts for Black Widow Spiders by providing funding, regulations, and guidelines for restoration activities. Many municipalities and government agencies have programs in place to support habitat restoration efforts, and some have even developed plans specifically for the conservation of Black Widow Spiders and their habitats. Many non-governmental organizations also participate in restoration efforts, often partnering with government agencies, local communities, and private landowners to achieve common restoration goals.
The Importance of Public Awareness
Another critical aspect of effective habitat restoration efforts for Black Widow Spiders is public awareness. Educating the public about the importance of the species and the value of habitat restoration can help to build support for conservation efforts and engage more people in habitat restoration activities. It can also help to raise awareness about the potential impacts of habitat destruction and other threats to the species, which in turn can help to increase support for conservation efforts.
Public Education about Black Widow Spiders
Public education about black widow spiders is crucial for their conservation. This is because many people are either unaware of the spiders or are otherwise misinformed about them. Providing accurate information about black widow spiders can help dispel many misconceptions and inspire people to take action to protect them.
Effective public education programs can be created by partnering with local schools, community organizations, and nature centers. Some ideas for educating the public about black widow spiders include:
- Interactive displays: Creating interactive displays that showcase the behavior, habitat, and unique features of black widow spiders can help draw people’s attention and pique their curiosity. Touch screens, videos, and models of the spider can be used to provide more information.
- Public talks and workshops: Hosting talks and workshops about black widow spiders allows experts to share their knowledge and answer questions from the public. These sessions can be held at libraries, community centers, and schools.
- Brochures and fliers: Printed materials like brochures and fliers can be distributed to local businesses and community organizations, such as libraries and museums. These materials can help raise awareness and provide useful information about black widow spiders.
- Nature walks: Guided nature walks that focus on finding and identifying black widow spiders can be a fun and engaging way to learn about these fascinating creatures. Participants can be encouraged to take photos and share their experience on social media, helping to spread the word and raise awareness.
- Social media campaigns: Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram can be used to share information about black widow spiders through engaging posts, photos, and videos. Campaigns can be designed to appeal to different age groups and interests.
By providing accurate information about black widow spiders and engaging the public through interactive displays, talks and workshops, printed materials, nature walks, and social media campaigns, conservationists can help protect these important creatures and their ecosystems.
Conclusion
After analyzing the various threats to the Black Widow Spider, it is clear that its habitat destruction and range contractions are significant concerns that require attention. The Black Widow Spider is an important species to study because of its ecological role in controlling insect populations. However, its populations are declining due to habitat loss and other threats.
Conservation efforts are necessary to address the issue of habitat loss and fragmentation. Captive breeding programs can help to increase the population of Black Widow Spiders and protect them from further habitat destruction. Additionally, habitat restoration initiatives, such as planting native plant species and creating protected areas, can provide safe habitats for Black Widow Spiders.
Public education plays a crucial role in promoting conservation efforts for the Black Widow Spider and other threatened species. By increasing awareness and understanding of the ecological importance of the Black Widow Spider, more people can become involved in conservation efforts.
It is essential to recognize the interconnectedness of all species and their habitats. Habitat destruction and other threats to one species can have ripple effects on the entire ecosystem. Therefore, addressing the issue of habitat destruction and range contractions for the Black Widow Spider is not just vital for the survival of this species but also for the survival of other species that depend on it.
In conclusion, conservation efforts, public education, and increased awareness of the ecological importance of the Black Widow Spider are crucial in addressing the challenges posed by habitat destruction, range contractions, and other threats. We must take action to protect and preserve this species to ensure its survival and maintain the health of our ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do Black Widow Spiders look like?
Black Widow Spiders are typically black with a red or orange hourglass-shaped marking on their undersides. Females are typically larger than males and can reach up to 1.5 inches in length.
Are Black Widow Spiders dangerous?
Yes, Black Widow Spiders are venomous and their bites can be dangerous, especially for young children and the elderly. However, fatalities from Black Widow Spider bites are rare due to the availability of antivenom.
Where are Black Widow Spiders commonly found?
Black Widow Spiders are commonly found in warm, dry climates such as the southern United States, Mexico, and South America.
What is habitat destruction?
Habitat destruction is the process of natural habitats, such as forests or wetlands, being altered or destroyed by human activities such as urban development, logging, or agriculture.
How does habitat destruction affect Black Widow Spider populations?
Habitat destruction can cause Black Widow Spider populations to decline by removing the natural habitats they need in order to survive and reproduce.
What are range contractions?
Range contractions occur when a species’ geographic distribution becomes smaller over time, potentially leading to a decrease in population size.
What are the main reasons for range contractions in Black Widow Spider populations?
The main reasons for range contractions in Black Widow Spider populations include habitat destruction, climate change, and the use of pesticides.
What is habitat fragmentation?
Habitat fragmentation is the process of large, continuous habitats being broken up into smaller, isolated areas due to human activities such as land development.
What is the importance of public education about Black Widow Spiders?
Public education about Black Widow Spiders can help increase awareness of their importance as predators, the dangers of their venomous bites, and the importance of conserving their natural habitats.
What can be done to prevent further Black Widow Spider population declines?
To prevent further declines in Black Widow Spider populations, conservation efforts such as captive breeding programs, habitat restoration, and public education campaigns can be implemented.






